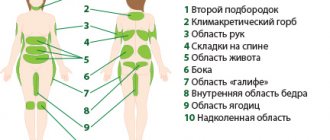
Metabolism plays an important role in the functioning of the body; it supports the functioning of all body systems and is responsible for vital energy. Failure of this process leads to serious problems that need to be recognized early and treated correctly. With metabolic disorders, the symptoms in women are different and may be similar to the signs of other diseases.
Causes of metabolic disorders
Failure in the metabolic process in the female body can occur under the influence of:
- systematic overeating;
- abuse of harmful products;
- stress;
- physical inactivity;
- lack of sleep;
- poisoning the body with toxins;
- bad habits;
- hypothyroidism;
- endocrine disorders accompanied by hormonal imbalance in the body;
- unfavorable heredity.
In men, metabolic disorders can be caused by testicular dysfunction. The appearance of excess weight is also affected by low secretion of testosterone and other hormones, which have a direct effect on metabolism.
In women, metabolic disorders can occur after an abortion, difficult childbirth, chronic or complicated pathologies of the reproductive organs.
Video
Other publications:
Vitamins for bodybuilding Pharmacies in the Moscow region where you can buy Vitrum antioxidant (Multivitamin Minerals), compare prices and make a pre-order OCTA: how to bring an unusual drink to the market and open your own production (in less than a year) LJ Magazine
Only with us: Enter promotional code bonus2020 in the coupon field when placing an order before March 31, 2020 and receive a 25% discount on everything!
Types of metabolic disorders
Metabolic disorders have their own classification. So, the following types are distinguished:
- Protein metabolism disorder. Protein is the basis for the production of hormones and enzymes. In the human body, it is not secreted by any glands, but enters it only with food. Insufficient consumption of foods enriched with proteins leads to the fact that the body begins to extract it from muscles, bones, and various internal organs. As a result, the normal functioning of the body is disrupted, which cannot but affect metabolism.
- Violation of fat metabolism. The main reasons are exhaustion or, conversely, excess weight. Fasting provokes hormonal imbalance, immune suppression, deterioration of skin, hair, etc. And in obese patients, the likelihood of developing diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular diseases associated with hypercholesterolemia increases.
- Disturbance of carbohydrate metabolism. The most common pathologies accompanied by this deviation are hyperglycemia (increased blood glucose levels) and hypoglycemia. If blood sugar levels are elevated, we can talk about constant overeating, diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, and pathologies of the adrenal glands. This deviation can be of either a primary or secondary nature. With hypoglycemia, we can talk about kidney and liver pathologies, a low-carbohydrate or no-carbohydrate diet, and disturbances in the digestive tract.
- Water metabolism disorder. In this situation, either fluid retention in the body or, conversely, dehydration (dehydration) may occur. Both conditions are equally dangerous. When fluid is retained, edema forms and the kidneys are subject to additional stress. When dehydrated, the risk of blood thickening increases, the activity of the urinary system is disrupted, hypertension develops, etc.
- Failure of vitamin metabolism. Avitaminosis, multivitaminosis, hypovitaminosis - all these deviations are the result of impaired absorption and distribution of vitamins. Each situation is fraught with serious consequences.
- Mineral metabolism disorder. An imbalance of minerals in the body provokes suppression of the functions of the immune system. As a result, many organs and tissues are affected, and various pathologies develop.
- Violation of acid-base balance. In a healthy person, acids and alkalis are in a harmonious state. When this balance is disturbed, the consequences can be different - from mood swings to death.
Protein metabolism
Proteins are an essential material for the body. The cause of their deficiency is starvation or diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Increased breakdown of proteins in the body occurs during cancer, tuberculosis, hyperthyroidism, fever, burns, stress, kidney disease and hypovitaminosis. Many of these factors often affect women specifically.
Manifestations of protein deficiency in the body in mild cases may be insignificant. With a moderate degree of protein deficiency in women, menstruation disappears, the skin becomes dry and cold, and diarrhea occurs. The nervous system suffers: patients become irritable, their memory suffers and their performance decreases. The immune system weakens, and pneumonia and urinary tract infections often occur.
Muscle and fat mass decreases. Hair falls out, nails become thinner. If the patient is immobile, she may develop bedsores that quickly become infected. This often occurs in older women suffering from a hip fracture or stroke.
Blood pressure gradually decreases and pulse becomes rarer. Swelling and anemia occur. In severe cases, multiple organ failure occurs.
Treatment of protein deficiency includes a balanced diet. In severe cases - intravenous administration of amino acids, liquid mixtures through a tube. Vitamins are a must. If necessary, treatment of concomitant diseases is carried out.
Symptoms
Metabolic disorders cause disorders of many functions in the body. As a result, the patient exhibits symptoms such as:
- destruction of the tooth structure;
- rapid weight gain;
- apnea;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- edema formation;
- changes in skin tone;
- layering of nails;
- hair loss and split ends.
Many women who have noticed symptoms of metabolic disorders, in particular rapid weight gain, try to get rid of the problem on their own. But self-medication in this case is dangerous, since it is unknown what exactly provoked such a failure. Therefore, any measures should be taken only after consulting a doctor.
The danger of self-medication is that weight gain is associated with impaired fat metabolism. The liver cannot cope with the processing of fat that enters the body in large quantities, so it settles on the walls of blood vessels in the form of LDL and cholesterol plaques. As a result, pathologies of the heart and blood vessels develop, which, with an unprofessional approach to therapy, can be extremely dangerous.
Therefore, having noticed the first alarming signs of a metabolic disorder in the body, a woman should immediately seek medical help.
Metabolism of fats (lipids)
Lipids represent a broad group of compounds, including fats themselves, as well as fat-like substances. These include:
- triglycerides,
- cholesterol,
- saturated and unsaturated fatty acids,
- phospholipids,
- lipoproteins,
- sterols,
- glycolipids, etc.
In our body, lipids have the following functions:
- Mechanical protection against damage. Adipose tissue protects vital organs from damage, softening possible blows.
- Energy. 1 g of broken down fat provides 9 kilocalories.
- Thermal insulation. Adipose tissue conducts heat rather poorly, so it protects internal organs from hypothermia.
- Warming. Brown fat, which is mostly found in infants, is capable of producing heat itself and preventing hypothermia to some extent.
- Promotes the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
- Adipose tissue is, in a sense, an endocrine organ that produces female hormones. For example, if a woman's body fat is less than 15% of her body weight, then her menstrual cycle or reproductive function may be disrupted.
- As compounds with proteins (for example, lipoproteins) they are part of the membranes of body cells.
- Cholesterol is important for the formation of steroid hormones, which are produced by the adrenal glands.
- Phospholipids and glycolipids prevent the development of atherosclerosis.
Symptoms of lipid metabolism disorders
Excess lipids may present with the following symptoms:
- hypercholesterolemia (excess cholesterol in the blood),
- hyperlipoproteinemia (increased levels of low-density lipoproteins in the blood, which contribute to the development of atherosclerosis),
- symptoms of atherosclerosis of the brain, abdominal arteries (“abdominal toad”), heart (angina pectoris, myocardial infarction), increased blood pressure,
- obesity and related complications.
Most often, excess lipids are associated with increased dietary intake, genetically determined diseases (for example, congenital hyperlipidoproteinemia), endocrine pathology (Cushing's disease, diabetes mellitus). Symptoms of lipid deficiency are as follows:
- exhaustion,
- development of deficiency of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, K with corresponding symptoms,
- dysregulation of the menstrual cycle and reproductive function,
- deficiency of essential unsaturated fatty acids, as a result of which the formation of biologically active substances is disrupted, which is accompanied by the following symptoms: hair loss, the occurrence of eczema, inflammatory skin diseases, kidney damage.
Most often, lipid deficiency occurs during fasting, unbalanced nutrition, as well as congenital genetic diseases and pathologies of the digestive system.
What tests need to be taken to check lipid metabolism?
When lipid metabolism in the body is disrupted, a person develops atherosclerosis.
Standard tests to determine the nature of lipid metabolism are:
- determining the level of total cholesterol in the blood,
- lipoproteinogram (HDL, LDL, DPONP, TSH).
Diagnostics
It is difficult to suspect a metabolic disorder on your own, but it is possible if you look closely at the symptoms. But this is not enough, because it is important to understand why the failure occurred. For this reason, with the previously described signs, you need to contact an endocrinologist, who will conduct an examination and interview, study the complaints in detail, calculate the body mass index, compare weight and height, and carry out many other diagnostic measures.
After the initial consultation, the patient is sent for a number of studies:
- Blood chemistry. The levels of triglycerides, thyroid hormones T3 and T4, lipoprotein, homocystine, creatinine, microalbumin, etc. are examined.
- Urine examination.
- CT scan.
- Doppler examination of the carotid arteries.
- Ultrasound of the gallbladder, pancreas, liver, kidneys.
- ECG.
A comprehensive examination is necessary to accurately determine the organ whose malfunction caused the metabolic disorder.
Carbohydrate metabolism
Disturbances in the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates in women may be associated with the following conditions:
- congenital enzyme deficiency, such as lactose;
- pancreatitis;
- intestinal diseases.
Manifestations of malabsorption: weight loss, apathy, fatigue, headache and others associated with a lack of energy supply to the body.
Glucose in the liver is converted into glycogen and stored there to prevent sudden fluctuations in blood sugar. This process is disrupted in the following diseases:
- hypoxia;
- liver diseases (hepatitis, including medicinal ones);
- hypovitaminosis C and B1;
- diabetes mellitus and hyperthyroidism.
The breakdown of glycogen is disrupted in glycogenosis - severe hereditary diseases.
The entry of glucose into tissues is regulated by various hormones:
- insulin;
- glucagon;
- adrenalin;
- somatotropic and adrenocorticotropic hormones;
- glucocorticoids;
- thyroxine.
In all diseases associated with disruption of the production of these hormones, carbohydrate metabolism is disrupted. In women, common causes of this are diabetes mellitus, pituitary adenoma, and thyroid disease.
Manifestations of impaired carbohydrate metabolism are hypoglycemia (decreased blood glucose levels) and hyperglycemia. Hypoglycemia occurs during heavy physical and mental stress, and in women, also during breastfeeding. Blood sugar levels in women can decrease with diabetes, kidney, liver and adrenal diseases, hypovitaminosis B1, and also with fasting. Symptoms of hypoglycemia: muscle tremors, weakness, sweating, dizziness, even loss of consciousness.
Hyperglycemia in women occurs after eating and during stress. It accompanies hyperthyroidism, diseases of the nervous system, adrenal glands, and diabetes. Severe hyperglycemia leads to impaired consciousness and coma. With a chronic increase in blood sugar levels, the retina, microvessels of the legs, kidneys are damaged, and infectious diseases are associated.
How to treat metabolic disorders?
Treatment of metabolic disorders requires an individual approach. To begin with, it is important to identify and eliminate the causes of the deviation, and then only deal with the normalization of metabolism.
Patients are usually helped by:
- diet correction;
- regulation of the daily routine;
- playing sports.
But such methods will be effective only if the metabolic failure is not associated with heredity or serious pathologies. If these measures are ineffective, the patient is given a course of pharmacotherapy.
Diet and nutrition
To normalize metabolic processes in the body, it is necessary to make adjustments to the diet. Experts recommend following these rules:
- Eat small meals throughout the day. Portions should be small, but they should be consumed often: at intervals of 2 to 3 hours. You should not allow yourself to feel hungry because it slows down your metabolism.
- Preference should be given to easily digestible foods: fruits, vegetables, berries, herbs, salads, fish.
- The last meal should be taken no later than 3 hours before going to bed.
- Include fish in the menu. It is enriched with Omega-3 fatty acids and other beneficial substances that help break down fats and prevent their deposition.
- Drink enough fluids.
At the same time, it is necessary to say goodbye for a long time to:
- baked goods;
- baking;
- flour products;
- milk soups;
- cereals;
- pasta;
- potato dishes;
- fatty meats;
- sausages;
- sausages;
- rolls;
- canned food;
- fermented milk products with a high percentage of fat content;
- mayonnaise and other similar sauces;
- sweets;
- sugar;
- sparkling water;
- packaged store-bought juices.
It is useful to regularly consume vegetable oils (preference is best given to olive oil) and walnuts.
Physical training
Under the influence of physical exercise you can achieve:
- increased energy costs;
- improving metabolism;
- improving the functioning of the central nervous system;
- restoration of the metabolic regulation process;
- increasing the activity of the glands.
A set of exercises should only be developed by a doctor. You need to start with minimal intensity loads - walking or massage.
Gradually the load increases. So, in a day the patient will need to walk about 10 km, run, swim, ski, etc. But a course of exercise therapy will be effective only if you are overweight. The average duration of classes is from 50 minutes to 1 hour per day.
How to speed up your metabolism?
Some people have a naturally fast metabolism, and all useful substances are well absorbed, and even with age, the metabolic rate does not decrease. But other people have very slow metabolic processes. It is necessary to combat very low metabolism using complex methods.
Fractional meals. You need to select foods with average calorie content and eat little by little, 5-6 times a day. Portions should be small and foods should be steamed or boiled without salt. Foods should be low in carbohydrates and very high in protein. Main meals should be in the morning, lunch and evening 4 hours before bedtime. You can have snacks. Small meals help activate digestive processes. An important condition is to consume food with moderate calorie content. If you suddenly switch to dietary products, then instead of losing weight, you can gain weight. Once a week you need to eat high-calorie foods so that the body does not retain nutrients, and instead of losing weight, it tries to gain calories. This scheme helps to restart the weight loss process. But you should not eat fatty and high-calorie foods more than once a week, because you can immediately gain weight and disrupt your metabolism.
It is also important to eat foods enriched with fiber.
Physical exercise. Sport is the basis of fast metabolism
People who play sports, even at 40 years old, are able to regulate their metabolism and control weight gain. Cardio training, aerobics, yoga and simply exercising on exercise machines help speed up metabolic processes and increase calorie consumption. Burning fat not only helps you burn calories properly, but also helps you lose weight. You can also consume fat-burning drugs to enhance the effectiveness of your workouts. You can also take supplements fortified with protein and vitamins for strength training, so high protein content helps not only increase muscle mass, but also speed up your metabolism.
Water balance. To speed up metabolic processes, you need to drink a lot of water, at least 2 liters per day. Water speeds up cell functioning and helps release excess energy. You should absolutely not drink alcohol. Alcohol retains water and disrupts metabolism. Alcohol reduces the body's performance. Alcohol also causes weight gain. It is not recommended to drink alcohol, but you can drink 50 ml once a week. red wine. It has a beneficial effect on the state of the circulatory system, but you should not abuse alcohol. You can drink alcohol no more than once a month.
Fresh air. Walking in the fresh air helps trigger fat burning processes. Walking in the evening is especially beneficial. They help enrich the body with oxygen and improve sleep, and healthy, full sleep is the key to good metabolism.
To increase energy consumption, it is necessary to adjust heat transfer. To do this, you can do a contrast shower and massage. It is also recommended to drink tea with ginger, eat citrus fruits and foods rich in vitamins. If there is a lack of microelements, you can take drugs to increase magnesium, iodine and iron. To adjust your metabolism, you need to consult with a nutritionist and trainer, since nutrition and sports are the most important aspects of losing weight.
Video on the topic:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=N4Y1nFJDuGY
Folk remedies
The following recipes will be effective for metabolic disorders.
Walnut infusion
Pour 2 tsp of boiling water over a glass. walnut leaves and leave for an hour. Strain the infusion and drink half a glass 4 times a day before meals.
Herbal collection
Take chamomile flowers, St. John's wort and immortelle herbs, and birch buds in equal proportions. Pour all ingredients into a glass container and store covered. Every day you need to brew a tablespoon of raw material with 2 cups of boiling water and leave for 20 minutes. After this, the infusion must be filtered and squeezed. Take before going to bed.
Garlic tincture
Grate 350 g of garlic on a fine grater or pass through a meat grinder. Pour the resulting slurry with 200 ml of high-quality vodka or alcohol and leave in a dark, cool place for a week or 10 days. After this, strain the tincture, discard the cake, and pour the medicine into a dark glass bottle. You need to start taking it with 2 drops, increasing it by 2 drops daily. The duration of therapy is 11 days.
Multicomponent infusion
Mix walnut leaves in equal proportions with:
- succession grass;
- black elderberry flowers;
- burdock leaves and roots;
- strawberry and birch leaves;
- hop cones;
- licorice roots;
- grass
1 tbsp. l. pour a glass of boiling water with a heap of dry raw materials and leave for an hour. Cool and filter. Take half a glass between meals.
Blooming Sally
Fireweed is very useful for weight loss. It can be purchased at a pharmacy and consumed instead of the usual tea or coffee. Pour 1 – 2 tea bags with a glass of boiling water and wait 15 minutes. Drink half an hour before meals. Take 2 – 3 times a day.
Prevention
To avoid metabolic disorders it is necessary:
- regularly hold fasting days;
- take vitamins 2 times a year;
- calculate the BZHU and strictly follow the obtained indicators;
- balance the diet;
- strengthen immunity;
- play sports to the best of your ability;
- avoid stress;
- follow the developed daily routine;
- give up bad habits;
- carefully monitor your weight;
- lead an active and healthy lifestyle.
Metabolic disorders are a dangerous deviation fraught with serious consequences. And therefore, one should not take it lightly - this deviation must be combated. And we’re not just talking about excess weight: in comparison with the consequences that metabolic disorders can lead to, excess body weight is one of the most easily solved problems.
(Visited 140 times, 1 visits today)