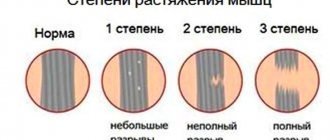
In this publication we will talk about the treatment of obesity in women of 1st and 2nd degrees. First, we will tell you the reasons why visceral or abdominal types of fat deposits arise, then we will show what male-type obesity in women looks like in the photo, and we will tell you how the psychosomatics of excess weight works. The article also contains a table that allows you to calculate and determine how many kg. A woman of a certain height and age should weigh.
Today, one of the most common problems of humanity is excess weight. It appears equally in both the male and female half of the population. Obesity refers to the deposition of excess fat in the body.
Often the cause of the pathology is an addiction to food or a sedentary lifestyle, although psychology also plays an important role in this matter. The risk group primarily includes people with a hereditary predisposition. Pathology belongs to the group that must be treated and everything should never be left to chance. To do this, you definitely need to contact a specialist, get tested and be patient.
Causes of obesity in women
- Genetic predisposition is the main cause of obesity. If at least one parent suffers from obesity, then the probability of developing pathology in the offspring is 50%;
- Disorders in the field of endocrinology. The most common diseases that affect weight gain are hypothyroidism (decreased thyroid function, that is, slow metabolism) and Cushing's syndrome (accumulation of fat in the abdomen and butt, a characteristic feature is increased blood pressure);
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Poor nutrition (addiction to fast food, eating at night, on the move and other habits that contribute to improper absorption of food and leading to consequences such as obesity);
- Unmet needs are often replaced by food. In addition, in some cases, eating is a necessary measure, at a meeting, with family on holidays, etc. As a result, the craving for food increases and a person does not eat to live, but lives to eat;
- Stressful situations and depression;
- Pathological fatigue and poor sleep;
- The impossibility of distinguishing between emotional and physical states. This includes eating emotional outbursts, when any feelings are interpreted as hunger;
- Sexual activity disorder. In this case, there may be a connection with hormones; female sexual energy depends on prolactin; in men, testosterone plays a role. The lower their level, the less attraction, and this problem requires treatment.
Morbid obesity:
- Occurs as a result of infections, diseases and injuries of the organs of endocrine regulation of metabolism - adrenal glands, pituitary gland (pituitary obesity), thyroid gland, gonads.
- It is not of a family nature.
- It is a consequence of diseases, not their cause.
- Extremely difficult to treat, hormonal obesity must be treated together with the root cause - diseases of the endocrine glands.
This division is arbitrary and in advanced stages it is no longer possible to separate one from the other; if you have severe obesity, your hormones will inevitably suffer.
In any case, to succeed in the fight against the disease, you will first have to take control of your appetite.
Types of obesity in women
By type, obesity in women varies as follows:
- abdominal, also known as android, central or male pattern obesity in women, is characterized by abundant fat deposits in the abdominal and chest area;
- gynoid, gluteal-femoral or female obesity, characterized by fat deposits in the lower part of the body: on the butt, hips and legs;
- mixed type, in which fat tissue is distributed relatively evenly.
Any deviation from the norm to a greater extent may indicate the development of obesity. There is a certain formula by which you can make the calculation.
Some people mistakenly believe that you need to use an excess weight calculator, which can be used to calculate it by subtracting it from your height, but this does not take into account other features of the body and body structure. Therefore, the system shown in the table below is more accurate, which can be used to calculate even at home.
| Height: | Age groups: | ||||
| 20-29 | 30-39 | 40-49 | 50-59 | 60-69 | |
| 150-160 | 48.9-59.8 | 53.9-65.8 | 58.5-69.9 | 55.7-65.8 | 54.8-64-6 |
| 162-170 | 61.6-69.2 | 68.5-75.8 | 72.2-79.8 | 68.7-76.8 | 66.5-75.0 |
| 172-180 | 72.8-80.9 | 77.0-83.9 | 81.7-88.1 | 77.7-84.1 | 76.3-81.6 |
| 182-190 | 83.3-92.3 | 87.7-95.8 | 89.3-97.4 | 86.5-95.6 | 82.9-92.9 |
But to find out more precisely, it is better to seek help from a specialist who will take into account other body parameters and body properties. Many people wonder how to determine the degree of obesity; this is quite simple to do.
Symptoms of obesity:
Signs of obesity are, of course, weight gain that is beyond what is normal for your height, gender, and age. Obese patients usually have other complaints, the severity of which depends on the degree of obesity.
As it progresses, shortness of breath, pain in the legs and back appear, the joints of the limbs and venous system suffer, and swelling appears. In severe cases, when the disease persists for a long time, atherosclerosis and hypertension are common, which become the killers of obese patients.
Obesity 1st degree in women (photo)
It should be noted that obesity is a disease that requires treatment.
Obesity of the 1st degree includes the following types:
- Alimentary constitutional genesis of the first degree refers to family diseases, develops due to overeating, lack of physical activity and poor diet. Often occurs in women after 40 years of age. In turn, there can be 2 types: progressive and stable;
- Exogenous obesity in women of the 1st degree is also associated with addiction to food and a sedentary lifestyle. The disease is not hereditary. At the initial stage it is easy to treat;
- Visceral obesity in women of the 1st degree is dangerous to health. The danger is associated with the location of the deposits - they form around the internal organs;
- Gynoid obesity in women of the 1st degree affects the lower part of the body. Treatment at this stage is not difficult.
At the first stage, obesity proceeds almost unnoticed. But, if the diet changes and evening snacks appear in the form of slices of cake and other things, then this is a sure sign that food has begun to occupy an important niche in life and, most likely, obesity is already beginning to develop. This can also be determined by the increase in the area of the ankles, hips, shoulders, abdomen and sides.
Treatment of stage 1 obesity in women involves the use of a proper nutrition system and increased physical activity. The main enemy on the way to achieving your goals is laziness.
To quickly lose weight, read the article: Mangosteen syrup: instructions for use... Another find in the field of weight loss is the drug Fire Fit, Fire Fit drops will save you from extra pounds. Next, read what are the signs of bronchitis in adults and children.
Diet for obesity
Diet for obesity is most important because it is much easier to lose weight through caloric restriction than through exercise. Just imagine, 100 ml of vegetable oil contains 800 calories, and an hour! jogging burns only 300 calories.
Nutrition for obesity primarily excludes foods rich in calories, but poor in substances beneficial to the body, such as sweets, white bread and other sources of quickly burning carbohydrates. That is, whether you want it or not, whether you like it or not, you will have to switch to vegetables and protein foods, and the menu for obesity is always meager, a slight feeling of hunger is constantly simply unavoidable.
Products for obesity must completely cover your daily protein needs, otherwise, instead of fat, muscles, minerals and vitamins will begin to be lost, otherwise there will be vitamin deficiency states and mineral metabolism disorders. You can achieve what you need using not only a limited set of products, but also methods of preparing dishes; recipes for obesity involve limiting fats, using cooking, stewing and baking, and steaming.
The higher the degree of obesity, the more limited the diet, since there is less opportunity to use exercise to burn fat due to a decrease in physical activity and exercise tolerance of patients. For example, a diet for grade 1 obesity may be lower than the daily calorie requirement by only 10-15% in order to begin to lose weight intensively, but a diet for grade 3 obesity will require a reduction in calories by 30% or more for the same result. The fatter you are, the more hungry you will have to be.
The diet for obese children should be prepared especially carefully, because it is dangerous to deprive them of many nutrients. A lack of calcium will lead to disruption of the formation of the musculoskeletal system, a deficiency of fatty acids will affect the development of the brain...
Treatment of obesity in a sanatorium becomes an excellent choice.
Under conditions of strict control over the fulfillment of prescriptions and a clearly drawn up menu, it is possible to boost your metabolism and begin to lose kilos. If you decide to go to a sanatorium, the treatment will provide you with the most important things: you will believe that you can cope and understand how to do it, and after completing the course of treatment, all that remains is to follow the diet and exercise regimen that you will be taught. Anti-obesity pills
Of course, anti-obesity pills, which are now so widely advertised as unrivaled means of weight loss, are in fact far from a panacea...
Anti-obesity drugs work in a variety of ways, from suppressing appetite to impairing the absorption of nutrients in the gastrointestinal tract. Now there are quite a lot of them, and some of them, in fact, are not a means to lose weight in the literal sense, but were created to treat hormonal disorders or to correct metabolism. Something used as a cure for obesity is actually intended for bodybuilders (building muscle mass), something in theory should have compensated for hypothyroidism or deficiency of sex hormones. Be that as it may, you must understand that medications for obesity act deeply, affecting the very foundations of metabolic regulation, and if used incorrectly, they can cause an endocrine disaster, simply destroying your metabolism forever. They are dangerous.
Obesity 2 degrees in women
If grade 1 was not identified in women and, accordingly, the necessary measures were not taken, then grade 2 occurs over time. At this stage, the body has 30-50% fat deposits of the total body weight.
Depending on the type, the disease develops differently:
- With alimentary obesity of the 2nd degree, the slightest physical activity causes shortness of breath. A massive fat fold may be observed in the abdominal area. At the same time, the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases increases. The pathology is most often observed in older women.
- Exogenous-constitutional obesity of the 2nd degree in women progresses depending on the increase in food cravings, that is, in order to lose excess weight, it is necessary to give up unhealthy foods and reduce portions.
- As for the visceral type of the 2nd degree, the situation here is seriously complicated, because fatty deposits spread to vital organs, thus, signs of fatty liver may be observed, the heart is affected and diabetes develops as a result. It is determined by the waist circumference; in women it should not exceed 80 centimeters, otherwise class 2 obesity is diagnosed.
The main signs of progression of stage 2 obesity in women and its transition to a more serious stage:
- increase in waist circumference;
- weight gain;
- increased shortness of breath with minimal physical exertion;
- increased heart rate;
- There is profuse sweating.
With obesity of the 2nd degree, problems appear not only in the body, but also in personal life, in the work process and other areas. Treatment of this stage requires a complete change in the usual lifestyle in terms of nutrition, bad habits and physical activity.
In addition, in some cases medications are required for treatment. If you do not get rid of obesity at this stage, then stage 3 may occur, when treatment is almost impossible.
Treatment
Diet
Traditional treatment of obesity involves following the rules of a balanced diet. Patients are recommended to consume foods high in coarse fiber, vitamins, minerals, and biological active components. The basis of the diet consists of vegetables, lean meats and fish, cereals, porridges, fruits (except grapes, bananas, mangoes), nuts, and herbs.
Nutritionists often recommend table 8 for obesity, which was created by the Soviet scientist Mikhail Pevzner. The goal of the diet is to speed up metabolic processes and “remove” excess fat. The daily calorie intake is 1700. The basis of nutrition is the above products. Prohibited:
- Hot sauces.
- Bakery products.
- Sweet waters, alcohol.
- Dessert.
- Fatty, fried foods.
To maintain muscle tone and improve the patient’s well-being, doctors recommend performing exercise therapy for obesity. Therapeutic exercises are carried out for 40-60 minutes every day. Morning exercises in combination with water procedures are welcome. To burn fat faster, it is recommended to perform strength exercises 2-3 times a week.
Psychotherapy
Overeating and obesity are often caused by mental instability. In stressful situations, a person does not know how to calm down and begins to “seize” the problem. Canadian scientists have proven that poor relationships between children and parents lead to an increase in the latter's body weight. Children who have good relationships with their fathers are less likely to be obese.
Cognitive behavioral therapy allows you to change your attitude towards nutrition, understand the reasons for overeating, and learn to cope with stress. After a course of psychotherapy, patients become more confident, accept failures more easily, do not relapse, and are less likely to return to their previous lifestyle.
Treatment of abdominal obesity in women
If abdominal obesity develops in women, complex treatment is required. First of all, preventive measures are carried out. Also, the nutritional principle is adjusted, a special individual diet is prescribed, and physical activity is required in order for excess weight loss to begin.
- Nutrition. The menu is designed to include low-calorie foods. Flour, chips, crackers, etc. are completely excluded. Salads and other dishes during a diet can only be seasoned with olive oil or lemon juice; mayonnaise and sour cream are fierce enemies. Carbonated drinks and sugary juices are also prohibited;
- “No” to bad habits. First of all, this applies to alcohol, because it often increases appetite. Even on holidays, it is better to give preference to mineral water or limit yourself to one glass of wine;
- Physical activity as a method of treatment. At the first stage, this may include walking and light jogging. It is difficult to immediately move on to more serious exercises. If you feel relief, it is better to add swimming and, if possible, cycling. In addition, over time it is necessary to add therapeutic aerobics. Physical activity must completely burn the calories consumed during the day and even more to get to the reserve.
The process of losing weight takes time, so all methods that offer to quickly get rid of extra pounds cannot be used. The doctor treats this problem, so before any measures are taken, it is necessary to take a hormone test. Next, the specialist will tell you what to do, prescribe medications for weight loss, special aerobics and create a diet.
Some are unable to complete it. But in order not to break down, experts do not recommend limiting yourself in everything. If you have a desire to eat something unhealthy, you can work it out in the gym. In addition, at the initial stage you need to determine how many kg you need to lose and note the results in a special diary.
Exercise for Obesity
Regular gymnastics (fitness is not indicated until weight loss), swimming under control of pulse and blood pressure - “without fanaticism”, but the most necessary thing at the first stage of the fight against excess weight is walking, once again avoid traveling in public transport or a car.
Whatever treatment method you would like to use, we recommend that you decide how to deal with obesity with your doctor. Many techniques have contraindications that are simply not taken into account when trying to self-medicate.
Visceral type of excess weight
Visceral fat is quite dangerous because it forms around the abdominal organs. Removing it causes a lot of trouble and requires serious work. Despite the danger posed by its excess, it is important for the body due to the fact that it performs the protective functions of organs. The volume of visceral fat should not exceed 15% of the total number of fat cells that are concentrated in the body.
Excess can cause a number of unpleasant diseases:
- Varicose veins of the legs;
- Myocardial infarction;
- a number of oncological diseases;
- gradual disruption of hormonal levels and metabolism.
The accumulation of visceral fat is often associated with genetics. But, regardless of this, there are other reasons. What’s most remarkable is that women with a so-called pear-shaped figure have a significantly lower risk of accumulating this type of fat. An increase in visceral adipose tissue occurs after 40 years, when the production of female hormones decreases.
Complications
Excess weight is the main cause of the most common diseases. If you ignore the situation and do not lose weight, this can lead to dangerous complications:
- Diabetes mellitus type 2.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (gastrointestinal diseases).
- Metabolic syndrome, which is characterized by tissue insensitivity to insulin.
- Myocardial infarction. Occurs due to impaired blood circulation in the heart muscle.
- Coronary heart disease. It develops against the background of narrowing of the lumen of the coronary arteries of the heart, which is why the heart does not receive enough nutrients.
- A brain stroke that suffers from poor blood circulation.
- Cholecystitis.
- Chronic venous insufficiency.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Arthritis.
- Spinal hernia.
- Osteoarthrosis.
- Cancer that develops when normal cells become cancerous.
- Erectile dysfunction in men.
- Fatty liver degeneration.
- Pancreatitis.
To avoid these consequences, it is important to adhere to a diet for obesity. The diet is prepared by a specialist, taking into account the patient’s age, BMI, food preferences, lifestyle, and the presence of concomitant chronic diseases.
How to recognize and how to calculate BMI
Obesity has several degrees with different symptoms. It is quite difficult to determine by eye how far your weight is from ideal, especially for hypersthenics (broad-shouldered women who have a genetic predisposition to be overweight).
In modern endocrinology and nutrition, a specific body mass index (BMI) is used. An important indicator allows you to assess whether there is obesity and what degree of pathology develops at one time or another in life.
How to calculate BMI? The formula is simple: weight (in kg) / height squared (m).
For example, a woman weighs 80 kg and is 1.65 m tall. BMI = 80: (1.65 x 1.65) or 29.38. Now you need to compare the value with the optimal values. If a woman is 165 cm tall and weighs 80 kg, then her BMI shows excess body fat. Another few kilograms and the category will change to 1st degree obesity.
Norm and deviations:
- body weight deficiency. BMI less than 18.5,
- optimal body weight. BMI from 18.9 to 24.9,
- excess body weight. BMI from 26.0 to 29.9,
- first degree obesity develops. BMI from 30 to 34.9,
- second degree of obesity develops. BMI from 35 to 39.9,
- third degree obesity develops. ITM more than 40.
Important! When assessing norms and deviations, it is important to take into account body type. Hypersthenics tend to be overweight and have broad shoulders. Normosthenics have developed muscles and an average build. With the asthenic type, women are thin, the fat layer is thin, and the muscles are underdeveloped. In the example considered, it is necessary to make an adjustment for the body type: for normosthenic women, the indicated weight will indicate the first degree of obesity; with a hypersthenic physique, the indicators only approach the critical level.
Obesity and exercise
These two concepts are closely related. The body's energy consumption in insufficient quantities can be observed in the following conditions:
- With physical inactivity, in other words, with a sedentary lifestyle, a person has almost no physical activity, therefore, energy is not consumed, but is stored in the form of fat cells;
- When the level of physical activity decreases, a similar condition is observed in athletes if they abruptly stop regular training, because they will receive more energy from food than they can expend;
- After fasting for a long time, when the body begins to recover from the stress caused by the diet and tries to store fat cells at the expense of consuming energy for other purposes;
- In the presence of endocrine diseases, for example, Itsenko-Cushing's disease, in which all nutrients are converted into fat deposits as a result of excess hormones. In this condition, abdominal obesity is observed.
According to the dynamics of pathology development
The formation of adipose tissue occurs at different rates for everyone.
Based on this criterion, 3 types of disease should be distinguished:
- Stable. The pathology is characterized by long-term preservation of body weight values at the same level.
- Progressive. From the name it becomes clear that the weight continues to increase.
- Residual. This refers to the presence of fat accumulations that are present after a persistent decrease in body weight as residual effects.
Unfortunately, women do not always turn to specialists in a timely manner, allowing obesity to increase. If treated at the initial stages of the pathology, the disorder can often be dealt with without any problems.
But if you seek help if you have an advanced disease, you should be prepared for long-term treatment.
Many people are not aware of which doctor to see if they are obese. For the initial examination, you need to see an endocrinologist. If the attending physician deems it necessary, he will refer you to other specialists, for example, a gynecologist or nutritionist.
Knowing now which doctor treats obesity, you should make an appointment with him at the first signs of deviation.
Types of obesity according to etiology
If we take into account the origin of the pathology, it can be primary (alimentary) and secondary (symptomatic). Each of the presented types of disease has its own causes.
Nutritional obesity develops due to:
- excessive consumption of food,
- low level of physical activity,
- influence of hereditary factors.
When the amount of calories consumed by food exceeds the body's energy expenditure, excess formation of adipose tissue occurs. Under the influence of poor nutrition and physical inactivity, a genetic predisposition may appear.
Many women use food as a way to deal with constant stress, which in turn can disrupt hormone production.
Female obesity of the secondary type is a disease that results from:
- traumatic, infectious or tumor lesion of the hypothalamus,
- hormonal imbalance,
- use of certain medications (glucocorticosteroids, antidepressants, contraceptives).
A common cause of obesity is hormonal imbalances that occur during puberty, pregnancy and menopause.