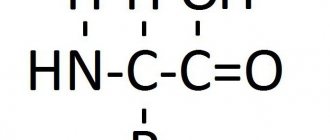Histidine? Healthy longevity is only possible with proper and balanced nutrition. In order for all systems and organs to function correctly, we must receive a large amount of useful substances per day. And in this list, the amino acid histidine is far from the last place. It is necessary for a number of biochemical processes to occur. Surely, many people do not know about the huge role of histidine in the life of the body. Therefore, we invite you to read about the beneficial properties of this substance. We will also tell you how this amino acid is used in sports and medicine.
Histidine in its optimal natural form and dosage is found in beekeeping products - such as pollen, royal jelly and drone brood, which are part of many natural vitamin and mineral complexes: “Leveton P”, “Elton P”, “Leveton Forte”, “ Elton Forte", "Apitonus P", "Osteomed", "Osteo-Vit", "Osteomed Forte", "Eromax", "Memo-Vit" and "Cardioton". That is why we pay so much attention to each natural substance, talking about its importance and benefits for a healthy body.
Conditionally essential amino acid histidine: for the liver and nerves
Histidine is an amino acid that is still controversial in the scientific world. Some scientists argue that it is not synthesized in the human body, and therefore must be regularly supplied with food. Others, on the contrary, cite research data according to which this substance can be produced in small quantities in the body. Therefore, increasingly, histidine, together with arginine, is classified in a special group - “ conditionally essential amino acids”
.
A little less common is the name “semi-essential amino acid”.
One way or another, the small amounts of histidine that the body produces on its own are not sufficient to maintain health. Moreover, in children under one year of age, the synthesis of this substance does not occur at all. Therefore, you need to monitor your diet, trying to diversify your diet.
What is histidine
Histidine is common in nature and is present in most living organisms. It is a component of protein and is also found in free form. This amino acid is also found in large quantities in the human body. This substance belongs to the group of proteinogenic substances, which means it is necessary for the production of protein. In its pure form, histidine is
colorless powder that melts at 287 degrees (L-isomer). This compound dissolves well in water, but poorly in ethanol. When decarboxylation occurs, histamine is formed in the body. To obtain drugs (Latin name - histidine) they are isolated from hemoglobin and blood, and also synthesized. By the way, today the world produces more than 200 tons of this substance per year.
Taurine
Taurine, which is a biologically active substance, was isolated from bovine bile (hence the name of the substance, because taurus means “bull” in Latin).
Important!
Taurine, which is classified as both amino acids and so-called vitamin-like substances, is synthesized by the human body, but is not completely excreted from it, remaining in the tissues in free form (all other amino acids are processed and fully used by the body as building material ). Thus, taurine is present in the heart muscle, leukocytes, skeletal muscles and the central nervous system.
Benefits of taurine
- Removal of toxins.
- Improving energy and lipid metabolism.
- Calming the nervous system.
- Normalization of metabolic processes in eye tissues.
- Transport of minerals.
- Regulating calcium levels in the body.
- Stabilization of insulin levels in the blood.
- Normalization of digestion.
- Strengthening the immune system.
- Removing “bad” cholesterol.
- Improving the functioning of the heart muscle.
- Decreased blood pressure.
- Promoting the digestion of fats.
- Increases mental and physical endurance.
- Stabilization of cell membranes.
Taking into account the fact that taurine, firstly, is present in many foods consumed daily, and secondly, it is synthesized in the body, its deficiency in healthy people is extremely rare (with the exception of vegetarians, whose levels of this substance are below normal ).
What foods contain taurine?
The main sources of taurine are:
- shrimps;
- crabs;
- shellfish;
- fish (especially liver);
- oysters;
- mussels;
- crayfish.
In addition, this amino acid is found in beef, pork, poultry, and dairy products.
Histidine: the story of an important scientific discovery
The story of an important scientific discovery
occurred at the end of the 19th century, at a time when chemistry was developing very actively in Europe.
The famous German physiologist and biochemist A. Kossel isolated sturine from sulfuric acid hydrolysates in 1896. In the same year, the Swiss chemist S. Hedin managed to obtain L
from other proteins, and he carried out the work independently of his colleague. W. Pauli also made a great contribution to the study of this substance.
A. Kossel is known for creating the classical method for the quantitative isolation of “hexon bases,” which also include such amino acids
like arginine and lysine. Thanks to his achievements, scientists later discovered that proteins are polypeptide in nature. This biochemist also conducted research in cell biology, studied the chemical composition of the cell nucleus, and was involved in the isolation and description of nucleic acids. For his work, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine on December 10, 1910.
The importance of histidine for the body. "Body Brick"
Despite the fact that this substance is little known to a wide range of people, the importance of histidine for the body
great.
It would not be an exaggeration to call this amino acid a “building block of the body.”
Firstly, it is involved in protein synthesis, and therefore helps build muscles. Secondly, histidine is part of many enzymes, such as gastrin, which is involved in the digestive system, improving the absorption of a number of vitamins.
This compound also improves nitrogen balance
in the body, helps the proper functioning of the liver. It plays a significant role in the functioning of the immune system - with its participation, the formation of leukocytes and red blood cells occurs. In addition, it is found in large quantities in hemoglobin. In addition, histidine is a component for the production of such an important substance as L-carnosine.
More histidine for the body
needed
for
the synthesis
of histamine,
a unique hormone that is involved in 23 basic physiological functions.
For example, the sexual health of both men and women depends on its content in the blood. Another great benefit of histamine is the fight against various infections. In recent years, scientists have noted that many people have high levels of histamine in their blood, which is caused by diseases such as heart attack, hypertension, obesity, tooth decay and various types of allergies. Histamine
is a mediator of allergic reactions, dilates small blood vessels and constricts large ones. Allergy mediators are substances that are released from cells or created as a result of biochemical processes in the body, necessary for the proper occurrence of an allergic reaction.
At the same time, do not forget about other useful properties
:
- helps young children grow;
- participates in the regulation of blood acidity;
- relieves allergies;
- helps to recover from a serious illness;
- helps normalize sleep;
- necessary for the formation of myelin sheaths of nerve cells;
- important for the normal functioning of the cardiovascular system.
It also has adaptogenic properties, reducing the impact of destructive factors on the body.
Functions of histidine
One of the most striking characteristics of histidine is the ability to transform into other substances, including histamine and hemoglobin. It also participates in a number of metabolic reactions and contributes to the supply of oxygen to organs and tissues. In addition, it helps remove heavy metals from the body, restore tissue and strengthen the immune system.
Other functions of histidine:
- regulation of blood acidity;
- acceleration of wound healing;
- coordinating growth mechanisms;
- natural restoration of the body.
Without histidine, all processes associated with growth will stop, and regeneration of damaged tissue will become impossible. Also, a consequence of the lack of histidine in the body is inflammation of the skin and mucous membranes of the body, and recovery after surgery will take a longer time. In addition, histidine has a therapeutic effect against inflammation, which means it is an effective medicine for arthritis.
In addition to the beneficial properties already mentioned, this amino acid has another equally significant ability - it helps to form the myelin sheaths of nerve cells (their damage causes Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases, as well as other degenerative diseases). Also, this semi-essential amino acid is involved in the synthesis of red and white blood cells (erythrocytes and leukocytes), which again helps strengthen the immune system. And finally, it is important to say that histidine protects the body from radiation.
What happens when there is a lack of histidine?
It has been established that with a lack of histidine
Children's growth and development slows down. For adults, this condition is dangerous because it can lead to rheumatoid arthritis. In addition, a deficiency of this amino acid impairs the recovery of injured areas of the body, and therefore recovery after surgery may be delayed. In addition, another effect appears - the condition of the skin and mucous membranes worsens.
Doctors are sure that the deficiency
in the body leads to stomach diseases and cataracts.
also weakens
, which is especially dangerous for infants.
Cases have been recorded of children suffering from dermatitis due to a lack of this amino acid in their food. It has been noticed that with a lack of histidine in the body, people complain of loss of strength. In addition, libido decreases, hearing deteriorates and fibromyalgia develops. Other symptoms of deficiency
:
- Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases;
- zinc deficiency;
- speech disorders;
- gait changes;
- decreased mental activity;
- irritability;
- absent-mindedness;
- delayed puberty;
- atypical allergic reactions.
Lack of amino acids in the body leads to a disorder called histinemia. This is a rare genetic disorder that causes the body to stop producing the enzyme that breaks down histidine. In these cases, mental development decreases, speech and motor functions are impaired.
What is histidine
It is well known: when we eat meat, we consume protein, and proteins contain amino acids. Histidine is one of the most important amino acids for maintaining life on Earth. This proteinogenic substance is involved in the formation of proteins and affects a number of metabolic reactions in the body.
All amino acids are the building blocks for proteins. After protein is digested, the body receives individual amino acids. Some of them are replaceable (the body is able to produce them) and essential (can only be obtained through diet). In this regard, histidine is a unique substance - an amino acid that is replaceable and irreplaceable at the same time. Or, as they usually call it, semi-replaceable.
Infants have the greatest need for this amino acid, since they need histidine as a growth agent. Babies get it through breast milk or baby food. This substance is also indispensable for adolescents and people after serious illnesses. An unbalanced diet and frequent stress lead to amino acid deficiency, which can manifest as slowing or complete cessation of growth in children and rheumatoid arthritis in adults.
Excess amino acid Side effects
It must be said that achieving an excess of amino acids
difficult because it is well absorbed by the body.
But exorbitant doses of the substance can lead to allergic reactions, asthmatic manifestations, and also reduce the time of sexual intercourse in men. Here it would be appropriate to say about the side effects
that drugs cause:
- weakness;
- headache;
- disturbance of consciousness;
- dyspepsia;
- nausea;
- decreased blood pressure;
- hand trembling;
- skin rashes.
In case of an overdose of this medicine, the following symptoms may occur: collapse, Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock. It is not recommended to use this amino acid for patients with bronchial asthma, arterial hypertension and organic diseases of the central nervous system.
Contraindications and harm of histidine
Contraindications to taking L-histidine are organic diseases of the central nervous system, individual intolerance, bronchial asthma, arterial hypotension. Also, overweight people should avoid drugs based on L-histidine.
Most often, harmful properties occur when L-histidine is consumed in large quantities. In case of an overdose, Quincke's edema, collapse, anaphylactic shock, an increase in stressful situations, even mental disorders can occur. In addition, manifestations of allergic reactions, dizziness, headache, impaired consciousness, and dyspepsia are possible. As well as a decrease in blood pressure, tremor, fever, skin hyperemia, paresthesia, blood thickening, nausea, vomiting and bronchospasm.
But, despite the contraindications and harm, every person needs to know what foods contain this vital amino acid, and, if possible, consume them as often as possible.
Histidine: substance in sports
It has been proven that histidine takes part in protein synthesis. Therefore, the muscles grow and become strong, which is important for athletes. In addition, it causes an increase in the secretion of somatotropin,
which stimulates the growth of cartilage, bones and muscles.
Also histidine as a substance in sports
valued because L-carnosine is synthesized from it in the body. It is known to be a strong antioxidant found in the brain and muscles. It increases endurance by preventing the accumulation of waste products. In particular, it neutralizes acid that is produced during intense muscle tension.
In addition, they are included in various sports nutritional supplements, which are used for muscle growth and recovery from injuries. It has been noted that it is especially effective when taken together with beta-alanine, which enhances the mutual effect of amino acids. If consumed in this form, you can improve results in both strength sports and athletics.
This substance is part of the Leveton Forte vitamin complex. This drug is based on herbs and bee products and helps increase stamina and performance.
Glycine
This nonessential amino acid got its name from the ancient Greek word “glycys”, which translates as “sweet” (the fact is that glycine has a sweetish taste).
The main purpose of glycine is to restore the nervous system, thereby normalizing mental activity in general. In addition, it is glycine that promotes the production of other amino acids and is part of the structure of hemoglobin.
Benefits of glycine
- Slows muscle tissue degeneration.
- Participation in the synthesis of DNA and RNA.
- Relieving nervous tension.
- Relieving attacks of aggression.
- Reducing the need for sweet foods.
- Improving overall well-being and lifting your mood.
- Increased mental performance.
- Stimulating the immune system.
- Binding and neutralization of toxic substances.
- Reduced alcohol dependence.
- Promoting the restoration of damaged tissues.
Important!
Glycine can be used for a long time, since this amino acid, even in large dosages, does not cause harm to health.
The human body synthesizes glycine itself, but some of this amino acid should still be replenished through food. Otherwise, the body will use up its own reserves of glycine, which will lead to weakness, exhaustion, sleep disturbances, and intestinal disorders (in severe cases, growth and development may be delayed).
What foods contain glycine?
The daily norm of glycine is about 3 – 6 g (depending on the intensity of physical and mental stress).
Products containing glycine:
- meat (beef and poultry);
- animal liver;
- gelatin and its by-products;
- fish (especially cod liver);
- chicken eggs;
- nuts (especially peanuts);
- cottage cheese;
- oats;
- seeds;
- buckwheat grain.
Histidine in medicine: great prospects
Due to its numerous properties, histidine in medicine
today it is used everywhere. Since it is part of many enzymes, it has a beneficial effect on the liver. It is also considered a good remedy for the treatment of hepatitis, helps with arthritis, urticaria. That is why this substance is a component of many drugs. In particular, histidine hydrochloride is prescribed as a remedy against gastric ulcers and hepatitis. The amino acid is often used as one of the components of complex treatment of atherosclerosis.
In 1976, Soviet scientists V.S. Yakushev and R.I. Livshits conducted a series of experiments on animals, during which they established what limits the formation of malondialdehyde in tissues during experimental myocardial infarction. All this makes it promising for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
It is worth saying that histidine has prospects in medicine
very significant.
In one recent study, scientists found that histidine combines well with. Doctors are confident that this combination is an excellent medicine against ARVI and other colds. After a series of experiments, it turned out that patients who took histidine with zinc
recovered much faster. It is worth noting that this microelement improves the absorption of amino acids. In turn, histidine transports zinc into cells, increasing their performance.
The substance is also used for radiation exposure and for the removal of heavy metals, and is used as a treatment for AIDS. In addition, histidine has proven itself as a cure for kidney diseases.
Histidine
Histidine is an amino acid obtained from proteins as a result of hydrolysis. It is found in the highest concentration (almost 8.5 percent of the total) in hemoglobin. It was first isolated from proteins in 1896.
What is histidine
It is well known: when we eat meat, we consume protein, and proteins contain amino acids. Histidine is one of the most important amino acids for maintaining life on Earth. This proteinogenic substance is involved in the formation of proteins and affects a number of metabolic reactions in the body.
All amino acids are the building blocks for proteins. After protein is digested, the body receives individual amino acids.
Some of them are replaceable (the body is able to produce them) and essential (can only be obtained through diet).
In this regard, histidine is a unique substance - an amino acid that is replaceable and irreplaceable at the same time. Or, as they usually call it, semi-replaceable.
Infants have the greatest need for this amino acid, since they need histidine as a growth agent. Babies get it through breast milk or baby food.
This substance is also indispensable for adolescents and people after serious illnesses.
An unbalanced diet and frequent stress lead to amino acid deficiency, which can manifest as slowing or complete cessation of growth in children and rheumatoid arthritis in adults.
Functions of histidine
One of the most striking characteristics of histidine is the ability to transform into other substances, including histamine and hemoglobin. It also participates in a number of metabolic reactions and contributes to the supply of oxygen to organs and tissues. In addition, it helps remove heavy metals from the body, restore tissue and strengthen the immune system.
Other functions of histidine:
- regulation of blood acidity;
- acceleration of wound healing;
- coordinating growth mechanisms;
- natural restoration of the body.
Without histidine, all processes associated with growth will stop, and regeneration of damaged tissue will become impossible.
Also, a consequence of the lack of histidine in the body is inflammation of the skin and mucous membranes of the body, and recovery after surgery will take a longer time.
In addition, histidine has a therapeutic effect against inflammation, which means it is an effective medicine for arthritis.
In addition to the beneficial properties already mentioned, this amino acid has another equally significant ability - it helps to form the myelin sheaths of nerve cells (their damage causes Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases, as well as other degenerative diseases). Also, this semi-essential amino acid is involved in the synthesis of red and white blood cells (erythrocytes and leukocytes), which again helps strengthen the immune system. And finally, it is important to say that histidine protects the body from radiation.
Histidine in medicine
Although the preventive and therapeutic potential of histidine has not yet been fully studied, a number of studies have already proven the effectiveness of the amino acid.
In particular, this beneficial substance is known to help lower blood pressure. By relaxing blood vessels, it prevents hypertension, atherosclerosis, heart attack and other cardiac diseases.
It has already been proven that daily consumption of this substance reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease by almost 61 percent.
Another area of application of histidine is nephrology. The amino acid has a positive effect on the condition of people with chronic renal failure (especially in old age).
In addition, this substance has shown its effectiveness in the treatment of hepatitis, stomach ulcers, urticaria, arthritis and AIDS.
Daily norms
Therapeutic doses of histidine range from 0.5 to 20 g per day.
But even consuming 30 g of amino acid per day does not cause side effects. So, in any case, the researchers convince us. But they immediately clarify: provided that taking the drug does not last long.
But still, the most adequate dosage is 1-8 g per day. More precisely, the individual minimum requirement for an amino acid can be estimated using the formula: 10-12 mg of the substance per 1 kg of body weight.
Histidine in the form of a dietary supplement is best taken on an empty stomach. So its action is more effective.
Combination with other substances
Recent studies have shown that the combination of histidine and zinc is an effective remedy against colds. In addition, zinc promotes easier absorption of the amino acid.
In addition, an experiment involving 40 people showed that a “cocktail” of zinc and histidine minimizes the duration of illnesses caused by viruses or bacteria.
A cold with amino acids lasts on average 3-4 days less.
Reception features
Histidine in the form of a dietary supplement is useful for people with arthritis, anemia or after surgery.
People with bipolar disorders, allergies, asthma and various types of inflammation should avoid this drug. Also, women during pregnancy and lactation, as well as people with folic acid deficiency, should be wary of supplements containing the amino acid.
Chronic diseases, injuries and stress increase the need for histidine. In this case, it is quite difficult to satisfy the body’s needs exclusively through products. But the problem can be solved with the help of bioactive additives. Indigestion and low acidity are also the reason for more intensive intake of the substance.
Impaired histidine metabolism is manifested by the rare genetic disease histidinemia. Such patients lack the enzyme that breaks down the amino acid. As a result, the level of amino acid in the urine and blood increases sharply.
The Dangers of Deficiency
Research shows that people with rheumatoid arthritis typically have low levels of histidine. Amino acid deficiency in infants often causes eczema. In addition, insufficient consumption of the substance leads to cataracts, and also provokes diseases of the stomach and duodenum.
It is known that histidine affects the immune system, for this reason a deficiency of the amino acid increases allergies and makes the body more prone to infections and inflammatory processes.
Insufficient consumption of the substance has an extremely negative impact on the health of children and adolescents during intensive growth and formation of the body.
Also, amino acid deficiency can “remind” itself of developmental delays, decreased libido, hearing impairment and fibromyalgia.
Is excess dangerous?
There is no information about the possible toxicity of histidine. But still, consumption of amino acids in particularly high doses can cause allergic or asthmatic reactions, provoke a deficiency of copper and zinc, and, on the contrary, increase the concentration of cholesterol in the blood. In men, an excess of histidine causes premature ejaculation.
Histidine in food
Properly selected products will help you meet your daily requirement for amino acids.
For example, just 100 grams of beans provides more than 1 gram of histidine (1097 mg), the same amount of chicken will provide an additional 791 mg of the substance, and the same serving of beef will provide approximately 680 mg of histidine.
As for fish products, approximately 550 mg of the amino acid is contained in a 100-gram piece of salmon. And among plant foods, wheat germ is the most nutritious. In 100 g of product – within 640 mg of amino acid.
However, it is important to note that these figures are approximate, since the saturation of food with nutrients depends on many factors. And the storage conditions of the product are of no small importance.
If we are talking about histidine, then to preserve its maximum amount in peas, walnuts or corn, products must be kept in sealed conditions, away from direct sunlight and oxygen.
Otherwise, histidine is quickly destroyed.
To maintain amino acid balance in an adult body, the substance that is synthesized in the liver from other amino acids is usually sufficient. But for children during periods of intensive growth and some other groups of people, it is important to supplement amino reserves from properly selected food.
Protein products contain, if not all, then at least the majority of amino acids necessary for humans. Products of animal origin contain so-called complete proteins, therefore they are more useful in terms of supplying amino substances.
Plant foods contain only some of the essential ones. Although it is not difficult to replenish histidine reserves, especially since the body is capable of producing it, there are still cases of deficiency of the substance.
Eating foods from different groups will help avoid a decrease in concentration.
A high concentration of histidine is found in meat, fish, dairy products, and some grains (rice, rye, wheat). Other sources of amino acids: seafood, beans, eggs, buckwheat, cauliflower, potatoes, mushrooms, bananas, citrus fruits, melon.
You can provide your daily requirement of amino acids from dishes prepared from beef, pork, lamb and poultry, various types of hard cheese, soy products, as well as fish (tuna, salmon, trout, mackerel, halibut, sea bass).
From the group of seeds and nuts, it is important to consume almonds, sesame seeds, peanuts, sunflower seeds, and pistachios. And from dairy products - natural yoghurts, milk and sour cream. In the cereal category, wild rice, millet and buckwheat contain a lot of histidine.
Histidine is an amino acid important for health. It is essential for tissue growth and repair, the production of blood cells and the neurotransmitter histamine. This substance can reliably protect tissue from damage by radiation or heavy metals.
Therefore, it is important to monitor your diet in order to provide the body with enough amino acids. Products rich in the substance are necessary for children and adolescents, as well as people after injuries or operations. This semi-essential amino acid has already proven its effectiveness in maintaining human health.
And you already know how to provide yourself with this useful substance.
What foods contain histidine?
Since this is , we need to receive it constantly. It is not difficult to replenish the supply of this amino acid in the body, but not everyone knows which foods contain histidine
. Let's name the sources of amino acids in food of animal origin:
- beef;
- chicken;
- fish (salmon, mackerel, halibut);
- dairy products (yogurt, sour cream);
Many plant products also contain this substance in significant quantities:
- peanut;
- lentils;
- soya beans;
- rye;
- wheat;
- buckwheat;
- cauliflower;
- potato;
- mushrooms;
- bananas;
- melon.
Preparations containing amino acids
Amino acids contained in food products have an unstable form. Therefore, they often enter into chemical reactions, forming more complex compounds. Special preparations belonging to the category of dietary supplements are designed to compensate for the lack of amino acids in food.
For example, you can't get all the amino acids you need from peanuts alone, but if you have peanut butter on your whole grain bread, you'll get it. Likewise, red beans won't give you everything you need, but red beans and rice will do the trick.
Why are amino acids needed: meaning, benefits, features of the use of amino acids
The good news is that you don't have to eat all the essential amino acids at every meal. As long as you have multiple sources of protein throughout the day, your body will capture what it needs from each meal. You can figure out how much protein you need if you know how much you weigh. Every day, children should eat about 5 grams of protein for every pound they weigh. That's a gram for every 2 pounds you weigh. Protein needs will increase as you grow, but will then level off as you reach adult size.
Conventionally, we can distinguish 3 categories of dietary supplements based on amino acids:
Amino acid complexes
. Multicomponent preparations with an extended profile. Typically contain 11-18 types of compounds. Provide comprehensive nutrition to the body.
Amino acids BCAA
. Nutritional supplements consisting of three types of amino acids: leucine, valine and isoleucine. Unlike conventional proteinogenic compounds, BCAAs are absorbed directly into the muscles. Therefore, they are part of many pre-workout complexes and anabolic drugs.
Adults, for example, need about 60 grams per day. To figure out your protein needs, multiply your weight in kilograms by 5 times, or you can simply take your weight and divide. For example, a 70-pound child should have about 35 grams of protein each day. If you only know your weight in kilograms, you need about 1 gram of protein every day for every kilogram of weight.
What foods contain lysine?
You can check the nutrition label to see how many protein grams are in a serving. But if you eat a balanced diet, you don't need to track it. It's quite easy to get enough protein. Here's an example of how a child can get about 35 grams of protein per day.
Isolated amines
. Preparations containing only one amino acid. For example, arginine, glutamine or L-carnitine. They are used to correct metabolism in accordance with set goals (weight loss, activation of nitric oxide production, etc.). The scope of application of the isolated amino acids is described in detail in the article creatine, more than 180 years have passed. And prejudices about him still live and flourish. How to take creatine correctly? What are its side effects? What is better to take: powder or capsules? About this in our article.
Of course, you can choose your favorite combination of protein-rich foods - now that you're "pro protein"! Whether the strategy is cutting carbs or cutting fat or cutting calories overall, almost everyone agrees that protein is good for you. And do sources make changes?
What is it about protein that makes it so important, and what do you need to include in your diet to reap the benefits? There are 4 main types of compounds in biochemistry. Carbohydrate nucleic acid proteins. . They differ in their chemical structures. Proteins are compounds that are made up of amino acids that contain an amino group and a carboxyl group. Proteins are formed when these amino acids are strung together and folded into complex shapes. They may be structural proteins, such as keratin in our nails or actin in our muscles, or they may be chemically functional, such as enzymes.
Daily amino acid requirement
To know how much food we should eat, we need to know about the daily requirement of amino acids
histidine So, a person needs 1.5-2 grams of this substance per day. To properly prepare your diet, you can use the following formula: 10 mg of amino acid per kilogram of weight. Athletes who experience significant stress and require a special diet may take more amino acids. It is believed that the amount of histidine consumed in food should not exceed 7-8 grams per day. At the same time, some sources contain information that the therapeutic dose of this compound can reach up to 20 grams.
To summarize our reasoning, we can say that the conditionally essential amino acid
histidine is very important for health.
In addition to participating in the formation of proteins, it is an important component of many enzymes. It also helps the liver, immune system and heart perform their functions. Without this “building block of the body”
our life would be impossible.
Histidine
(
L-α-amino-β-imidazolylpropionic acid
) is a heterocyclic alpha amino acid, one of 20 proteinogenic amino acids. It is one of two conditionally essential amino acids (along with arginine). Indispensable only for children.
| Are common | |
| Systematic name | L-2-amino-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanoic acid |
| Abbreviations | His, His, H CAU,CAC |
| Chem. formula | C₆H₉N₃O₂ |
| Rat. formula | C6H9N3O2 |
| Physical properties | |
| Molar mass | 155.16 g/mol |
| Thermal properties | |
| T. float. | 287 °C |
| Chemical properties | |
| pKa | 1,70 6,04 9,09 |
| Classification | |
| Reg. CAS number | 71-00-1 (L-histidine) 351-50-8 (D-histidine) 4998-57-6 (DL-histidine) |
| PubChem | |
| Reg. EINECS number | 200-745-3 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Data are based on standard conditions (25 °C, 100 kPa) unless otherwise stated. | |
Histidine is soluble in water, sparingly soluble in ethanol, and insoluble in ether.
Ingredients in cosmetics
Acrylates / C10-30 Alkyl acrylate crosspolymer
(Acrylate / C10-30 alkyl acrylate crosspolymer)
A water-soluble polymer, film-forming agent, gelling agent, stabilizer, thickener, suspending agent, often used in hair care products as well as skin care products, often moisturizers. Once applied, the substance forms a cohesive, soft, plastic layer on the hair or skin. The resulting film has water-binding properties and leaves the skin feeling like a smooth surface. As part of hair cleansers, acrylamide polymers reveal their amazing antistatic properties, serve as a binding component and stabilizer, and also maintain foaming at an optimal level. Acrylic copolymers and polymers form a fast-drying, durable, water-repellent film in hair fixatives and manicure varnishes. Skin care products created on the basis of acrylamide polymers prevent premature aging and fading of the skin, help normalize the hydro-lipid balance, heal small cracks and wounds, and therefore are a real salvation for thin and dry skin (especially when it comes to open areas of the skin legs and arms subject to loss of moisture, chapping and various mechanical damage).
Aqua
(Eau, Water, Water)
This is filtered water used in cosmetics. All water undergoes a filtration process to remove any substances that may affect the stability and performance of the product.
Apple Fruit Stem Cells
(PhytocellTech Malus Domestica, Apple Stem Cells)
Apple stem cells stimulate and protect hair and skin stem cells, support hair growth and prevent gray hair. Apple stem cells have a high restorative effect, slow down the aging process of the skin, protect against harmful ultraviolet exposure, stimulate the synthesis of collagen and elastic fibers, restore microcirculation, enhance metabolic processes and blood circulation, restore healthy color, dryness and flaking disappear.
Aesculus Hippocastanum Seed Extract
(Horse Chestnut Seed Extract)
anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effect
Since one of the causes of cellulite is swelling, which first compresses the veins, lymphatic vessels, and then the arteries, chestnut extract is used in anti-cellulite products, since it has a pronounced anti-cellulite and draining effect. Reduces congestion, promotes the removal of excess fluid from problem areas, and helps normalize blood and lymph circulation in the problem area.
tonic effect, improves microcirculation in the skin, promotes the removal of cell metabolism products, has antioxidant activity;
reduces blood flow to the surface layers of the skin, which is important for reactive skin;
reduces the feeling of “heaviness” in the legs, relieves “evening” leg fatigue;
strengthens the walls of blood vessels, is used to combat rosacea, prevents the formation of blood clots in the blood vessels of the legs, resolves subcutaneous hemorrhages;
since esculin has the ability to absorb harmful UV radiation, horse chestnut extract is used in sunscreens;
The main property of horse chestnut extract is the activation of those enzymes that stimulate the hair follicle. Therefore, horse chestnut extract is often an active component of hair loss and hair growth products.
Apigenin
(4',5,7-trihydroxyflavone or Apigenin)
Cosmetic effect: used in hair care products as a conditioning agent, is an antioxidant, and is also effective against various inflammations. Apigenin has anti-allergenic properties and helps relieve swelling and redness. Apigenin is extremely effective in treating irritated skin, burns, and stimulates skin cell renewal.
Apigenin protects the skin from oxidative stress and harmful ultraviolet radiation, tones, refreshes and brightens the skin, helps get rid of acne, and protects against wrinkles.
Representatives of traditional medicine use apigenin to cleanse and whiten the skin.
Allantoin
(Allantoin)
Allantoin is a powerful anti-irritant (relieves skin irritation) and is a by-product of uric acid extracted from urea (urea). Allantoin is a popular cosmetic ingredient due to its effectiveness and low cost.
Exfoliating effect: When in contact with the skin, allantoin has been shown to have a keratolytic (exfoliating) effect. It softens the stratum corneum, helping to remove dead cells. Thanks to this property, allantoin effectively prevents clogging of pores, the formation of comedones (blackheads) and inflammatory elements.
Healing effect: Allantoin has a pronounced effect on the regeneration of skin cells, stimulates the healing of the skin, wounds and scars. This effect of allantoin is indispensable when creating cosmetics for the care of chapped, chapped, burnt skin. Allantoin protects the skin from the effects of external adverse factors.
Antioxidant Action: More recently, it has been shown to have antioxidant activity, making it an effective ingredient in anti-aging products. In combination with biotin, ascorbic acid, calcium pantothenate, etc., it has additional vitaminizing and biological activity.
Conditioning effect: Allantoin has a softening and moisturizing effect on the skin and hair. It increases the water content in the intercellular matrix and also creates a feeling of smoothness of the skin.
Almond Seed Extract
(Sweet Almond/ Prunus Amygdalus Seed Extract, Sweet Almond Extract, Almond Oil)
Prunus Amygdalus (Sweet Almond) Seed Extract is a plant extract most often used as a light, nourishing oil pressed from almonds. Also used in the form of extract, protein substance, powder, etc.
Antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effect: Sweet almond extract - has antimicrobial activity, protects against adverse external influences, eliminates dryness and irritation.
Anti-aging effect: smoothes out fine wrinkles, evens out the microrelief of the skin, increases its elasticity, providing a long-term tightening effect by enhancing the synthesis of its own collagen (under the influence of the amino acid complex AK-12) and the formation of a three-dimensional high-molecular protein film on the surface of the skin, which evens out the microrelief of the skin, gives it elasticity. Contains vitamin A, which is a powerful antioxidant and restores skin elasticity, vitamin E has a healing effect, slows down cell aging and eliminates inflammatory processes on the skin. Vitamin F normalizes the function of the sebaceous glands and prevents pore enlargement.
Hair care: Almond extract stimulates hair growth, prevents drying of hair and scalp, prevents split ends, gives silky shine, makes hair manageable. Almond extract is good for dry and damaged hair. It coats the hair very well and makes it softer and silkier. Thanks to it, moisture loss is reduced and protects hair from external factors.
Alcohol Denat.
(Denatured Alcohol, Ethanol, Ethyl alcohol, Denatured alcohol, Ethyl alcohol, Denatured alcohol)
Denatured alcohol is ethyl alcohol mixed with other ingredients to form a substance that is not suitable for consumption.
Cosmetological effect: Alcohol Denat. - antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory substance, also used as an anti-foaming ingredient and solvent.
In the cosmetics and personal care products industry, alcohol is used in color cosmetics, lotions and toners, fragrances, shaving products, oral care products, skin care products and hair care products.
Harmful effects of alcohol on the skin: Denatured Alcohol can be extremely drying and irritating to the skin and can create free radicals. People with oily skin should avoid high concentrations of problematic types of alcohol. Unfortunately, it is the types of alcohol that are harmful to the skin that are often found in cosmetic products for oily or problematic acne-prone skin. The problem is that alcohol stimulates the nerve endings in the skin, causing irritation, which in turn leads to even more oil production in the skin pores.
In case the ingredient Alcohol Denat. (Denatured Alcohol) is at the top of the product's cosmetic ingredients list and can be problematic for all skin types. If Alcohol Denat. (Denatured Alcohol) is listed at the end of the ingredients list and is not in sufficient concentration to cause any problems for the skin.
Biotin
(Biotin, Vitamin H, Vitamin B7)
Biotin is known as vitamin H, and also as vitamin B7 or coenzyme R, biotin is part of the B vitamins. It is a water-soluble vitamin produced inside our body by the intestinal microflora (under the influence of intestinal bacteria), as well as from food (the liver is richest in biotin, kidneys, peas, beans). Empirical formula: C10H16O3N2S.
Biotin is a coenzyme involved in the transfer of CO2 to organic compounds, e.g. in the biosynthesis of fatty acids. Biotin is essential in the metabolism of carbohydrates (carbohydrates), fats and amino acids (the building blocks of proteins).
Internal uses of biotin: Biotin is an ideal vitamin for hair and skin. It supports healthy intestinal flora and stabilizes blood sugar. Thanks to this vitamin, hair becomes lush, skin smooth, and nails transparent. Biotin is recommended for use in seborrheic dermatitis, diabetes mellitus, and candidiasis. A contraindication to its use is hypersensitivity.
Signs of biotin deficiency are mainly skin lesions and deterioration of hair condition: too oily or dry skin, dandruff, hair loss.
A lack of biotin in the body can cause nervousness and depression, drowsiness, fatigue, gray color of the mucous membranes of the larynx and mouth, hypotension, muscle weakness and soreness, anemia, high blood sugar and cholesterol, nausea and loss of appetite, and slow growth.
Biotinoyl Tripeptide-1
(Biotinyl Tripeptide-1)
Biotinoyl tripeptide-1 is a product of the interaction of biotin and Tripeptide-1, a synthetically created ingredient, a protein derivative. The Biotinoyl Tripeptide-1 molecule contains 3 amino acids: glycerine, histidine and lysine.
Cosmetic effect: Biotinoyl tripeptide-1 is used as a hair nourishing substance. Often used in products for stimulating hair growth and preventing hair loss, conditioners, and masks. In cosmetic products, this complex of amino acids has a beneficial effect associated with the nutrition and strengthening of the hair follicle, and actively helps slow down the aging process of hair.
Butylene Glycol
(BG) (Butylene glycol)
Butylene Glycol (BG) is an ingredient often used in cosmetology, an alcohol, a petroleum product, an aliphatic diol. At the moment, Butylene Glycol is considered the safest solubilizer (fluidizing agent) on the cosmetic market.
The functions of butylene glycol in cosmetic products can vary and depend on the formula: butylene glycol is positioned as a humectant, acts as a surfactant, promotes gliding, is used as a solvent in cosmetics and food products, and a preservative. Butylene glycol regulates the water balance of the skin, forms a protective film on the skin, protects against dryness, and gives the skin special softness and elasticity. In cosmetic product formulations it is often used as a chemical enhancer, i.e. a component that enhances the effect of other ingredients, for example, preservatives, fragrances, moisturizing additives. Often used in hairsprays and hair styling products.
According to the CTFA, Butylene glycol is a better humectant and less toxic ingredient than propylene glycol and a much better alternative to propylene glycol and ethylene glycol.
C10-30 Alkyl acrylate crosspomer
(Acrylate/C10-30 alkyl acrylate crosspolymer)
Acrylates / C10-30 Alkyl (alkyl)acrylate crosspolymer is a water-soluble polymer also known as a carbomer. It is a film-forming agent, gelling agent, stabilizer, thickener, suspending agent, often used in hair care products as well as skin care products, often moisturizers. Once applied, the substance forms a cohesive, soft, plastic layer on the hair or skin. The resulting film has water-binding properties and leaves the skin feeling like a smooth surface.
An interesting fact: in food products (chips, French fries and crispbread), acrylamide poses a real danger to our body, being a harmful carcinogen. However, the use of acrylamide polymers in cosmetics is quite justified. As part of hair cleansers, acrylamide polymers reveal their amazing antistatic properties, serve as a binding component and stabilizer, and also maintain foaming at an optimal level. Acrylic copolymers and polymers form a fast-drying, durable, water-repellent film in hair fixatives and manicure varnishes.
Skin care products created on the basis of acrylamide polymers prevent premature aging and fading of the skin, help normalize the hydro-lipid balance, heal small cracks and wounds, and therefore are a real salvation for thin and dry skin (especially when it comes to open areas of the skin legs and arms subject to loss of moisture, chapping and various mechanical damage).
C12-15 Alkyl Benzoate
(C12-15 Alkyl benzoate)
C12-15 Alkyl Benzoate is an antimicrobial substance that has an increased ability to clean and disinfect the skin surface by dissolving and binding fats and silicones.
C12-15 Alkyl Benzoate is an emulsion thickener that gives the cream a certain consistency and texture, has binding functions, and increases the spreadability and distribution of the product over the surface of the skin.
C12-15 alkyl benzoate is also used as an emollient and skin moisturizing and nourishing agent. Leaves the skin feeling smooth and silky without the feeling of excessive oiliness, “heaviness” of the product used, and eliminates the feeling of stickiness and stickiness. C12-15 alkyl benzoate is classified as “oil free” ingredients that do not have a comedogenic effect (do not clog skin pores). This is why C12-15 alkyl benzoate is an important ingredient in the care of oily and acne-prone skin.
Calendula Officianalis Flower Extract
Calendula extract has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, and is potentially an antioxidant, although this has not been confirmed in practice.
Camellia Sinensis
White Tea Leaf Extract
The plant extract of white tea leaves, thanks to the polyphenols contained in the extract, is a powerful antioxidant, anti-inflammatory agent, anti-irritant (eliminates irritation), has anti-carcinogenic properties, and protects the skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet solar exposure.
According to modern research, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) in tea extract can prevent collagen breakdown and reduce the harmful effects of sun rays, which brings great potential for the use of various forms of tea in cosmetology.
Chlorphenesin
Chlorphenesin is an alcohol used as a preservative in cosmetics.
Associated with a number of side effects, phenoxyethanol and chlorphenesin were part of the reason Mommy's Bliss Nipple Cream was discontinued. These two ingredients, according to research, can depress the central nervous system and cause dermatitis on the face.
Cellulose Gum
Cellulose Gum is a film-forming/fixing agent of plant origin, also used as a thickener.
Citric Acid
Citrus extract is used mostly to stabilize the pH balance, shifting the balance towards alkaline.
Cyanocobalamin
(Vitamin B12)
Vitamin B12 is an antioxidant, part of the vitamin B complex. There are studies showing the positive effect of vitamin B12 on the treatment of psoriasis. However, the antioxidant effect when applied topically has been demonstrated to a very limited extent.
Cell-Communicating Ingredients
Cell-Communicating Ingredients - ingredients that support communication between cells. In theory, communication between cells has the ability to tell skin cells to look and function like normal, healthy skin cells, or to limit the ability of other substances to tell the cell to behave abnormally.
Cell-to-cell communication ingredients do this through direct communication with the skin cell, or by blocking damaging cellular metabolic pathways or other cellular communicative substances. Ingredients that support communication between cells complement the action of antioxidants to improve the functioning of skin cells.
Cinnamomum Zeylanicum
(Cinnamon) Bark Extract
Cinnamon extract is a plant extract with antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. Its antibacterial properties may help fight acne/pimples/pimples, but it may be a skin irritant.
Colloidal Silver
Colloidal Silver is a solution of crushed silver; due to its antibacterial properties, the substance can be used to combat acne/pimples/pimples, however, prolonged contact can give the skin a blue-gray tint. Silver can irritate and be toxic to the skin.
Pumpkin
(Cucurbita Pepo) Seed Extract
Pumpkin seed extract is an antioxidant, thickener, emulsifier, and skin-related ingredient. Pumpkin is a good source of antioxidant carotenoids, essential fatty acids, phytosterols, proteins, sugar, salicylic acid and a whole complex of micro- and macroelements (including calcium, potassium, chromium, copper, magnesium, manganese, selenium, silicon, zinc, etc.).
Also found in pumpkin are pectin, carotene, sugars, vitamins C, B1, B2, B6, PP. Pumpkin seed oil extract, with long-term use, can lighten age spots, moisturize and nourish the skin, improve skin elasticity, renew the surface layers of the skin, prevent the appearance of new stretch marks and reduce existing ones, an effective remedy for rashes, eczema and burns.
The extract is used in hair tightening products, anti-acne products, and hair products as a nourishing and strengthening component that improves hair structure. The high content of zinc and selenium normalizes the activity of the prostate gland, preventing the occurrence of prostatitis, improves spermatogenesis, restoring the normal sexual state of the body.
Copper Tripeptide 1
Copper tripeptide stimulates hair growth due to its beneficial effect on hair follicles and accelerates the eyelash growth cycle.
Copper peptides stimulate the formation of healthy skin cells and wound healing by breaking down damaged and scar tissue, as well as stimulating healthy collagen structures and slowing down the aging process.
Cyclopentasiloxane
(D5, Decamethylcyclopentasiloxane, Cyclomethicone, Cyclopentasiloxane, Cyclomethicone)
Synonyms: cyclomethicone, cyclopentasiloxane or D5, decamethylcyclopentasiloxane, cyclomethicone pentamer, volatile silicone. Silicones have been used in cosmetics for over 50 years. Their combination with natural oils makes it possible to make the product both useful (biologically active - due to natural oils), and pleasant to use (lighter, “dry”) and less comedogenic (due to silicones).
Used: in lotions and tonics, creams, lotions, gels for face and body, in makeup removers, in pre- and aftershave lotions, shower gels, chemical solvents, in deodorants and antiperspirants, in hair care products, in massage and bath oils, in sunscreens.
However, hair care products usually contain a mixture of dimethicone and cyclomethicone. Cyclomethicone reduces the viscosity of the composition, improves its distribution throughout the hair, and dimethicone forms a thin film on the hair, which gives silkiness and shine.
Cyclomethicone does not carry such a beneficial load for the skin as base oils, but it can improve the sensations when applying the product to the skin and alleviate the oily phase of the cosmetic product. From this position, cyclomethicone has the following properties: - reduces the stickiness and fat content of the care product, gives a “silky”, “dry” feeling on the skin, does not leave an oily trace, - is a solvent for oils and fats, increases their fluidity, - facilitates application and distribution products on the skin and hair due to better glide, - reduces oily shine and improves absorption of the product, - is non-occlusive (i.e. does not create an airtight film on the skin, does not interfere with skin breathing), - softens the skin at the time of application and until evaporation from it - when evaporating, it does not cool the skin, as water and alcohol do.
Disodium Phosphate
Disodium Phosphate is an inorganic salt used in cosmetics to prevent the rusting effect of metallic substances used in cosmetics. According to the FDA, this ingredient is considered safe for use.
Diazolidinyl Urea
Diazolidinyl Urea is a water-soluble preservative that is effective against a wide range of bacteria and has antifungal properties. Considered safe in dosages up to 0.5%, but is usually used in smaller quantities due to mixtures with other preservatives.
Perhaps the substance is a formaldehyde-releasing substance, although this sounds terrible, the amount of formaldehyde is much lower than the recommended norm. Moreover, other ingredients (such as proteins) help release formaldehyde and evaporate it before it can become active and cause harm to the skin.
Dipotassium Glycyrrhizate
(Licorice Extract)
Licorice extract (licorice, licorice) is a plant extract that contains: glycyrrhizic acid, glycyram (monoammonium salt), glycyrrhetinic acid, flavonoids, chalcones, saponins, tannins and others. Flavonoids (polyphenolic compounds) are analogues of vitamin P, improve blood circulation, and reduce capillary fragility.
Denatured Alcohol
(Alcohol Denat., Ethanol, Ethyl alcohol, Denatured alcohol, Ethyl alcohol, Denatured alcohol)
Alcohol Denat. - antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory substance, also used as an anti-foaming ingredient and solvent.
In the cosmetics and personal care products industry, alcohol is used in color cosmetics, lotions and toners, fragrances, shaving products, oral care products, skin care products and hair care products.
Denatured Alcohol can be extremely drying and irritating to the skin and can create free radicals. People with oily skin should avoid high concentrations of problematic types of alcohol. Unfortunately, it is the types of alcohol that are harmful to the skin that are often found in cosmetic products for oily or problematic acne-prone skin. The problem is that alcohol stimulates the nerve endings in the skin, causing irritation, which in turn leads to even more oil production in the skin pores.
In case the ingredient Alcohol Denat. (Denatured Alcohol) is at the top of the product's cosmetic ingredients list and can be problematic for all skin types. If Alcohol Denat. (Denatured Alcohol) is listed at the end of the ingredients list and is not in sufficient concentration to cause any problems for the skin.
E200
(Sorbic Acid)
Sorbic acid (Sorbic Acid/ E200) is a preservative and has an effective antimicrobial effect - it inhibits the growth of most microorganisms, especially yeast and mold. Contained in the juice of rowan trees of the genus Sorbus.
Sorbic acid exhibits antimicrobial effects only at a pH below 6.5. Sorbic acid does not have a bactericidal effect, it only slows down the development of microorganisms, so it makes sense to add it only to hygienically clean products.
Sorbic acid has low toxicity and is easily absorbed by the body. The substance is very rarely an irritant, but sometimes when using E200, skin irritation and rashes are possible, and according to some reports, the destruction of vitamin B12.
Glycerin
Glycerin is a humectant, a skin-identical ingredient (present in the skin naturally), present in all natural fats, attracts water from the lower layers of the skin (dermis), increasing the amount of water in the surface layers of the skin (epidermis) and thus maintaining the external barrier and preventing skin dryness.
In its pure form, glycerin is not used in cosmetics and even dries the skin, since water from the upper layer of the skin goes into the environment, but glycerin mixed with emollients is the basis of many moisturizing creams. When properly formulated, glycerin enhances the skin's natural defenses by filling the area of the so-called intercellular matrix and by attracting the necessary amount of water to maintain skin homeostasis.
There are also studies that suggest that the presence of glycerol in the intercellular layer helps other skin lipids do their job.
Glycine Soja
(Soybean) Oil
Soybean oil is an antioxidant, anti-irritant (relieves irritation), a skin-related ingredient that is a natural moisturizing factor (NMF). The actions of soybean oil are actively aimed at nourishing and moisturizing the skin, as well as increasing its moisture-holding capacity. In addition, regular use of soybean oil creates a protective barrier on the surface of the skin, protecting it from drying out and aggressive environmental influences. Thanks to its excellent emollient properties, soybean oil perfectly copes with the problems of dry, chapped and rough skin, and its tonic effect will return lost freshness, pleasant color and radiance to your face.
Hydrolysed Glycosaminoglycan
Hydrolysed Glycosaminoglycan is a fundamental skin-related component that nourishes the skin.
Also used in hair growth stimulating products. Inhibits 5-alpha-reductase, which converts the male sex hormone testosterone into the more potent androgen dihydrotestosterone, which could potentially be effective in the fight against male pattern baldness, but the effect of this substance on stimulating the growth of long eyelashes is questionable, since eyelash growth does not depend on the level of estrogen and testosterone.
Hydrogenated Castor Oil
Hydrogenated Castor Oil is an emollient ingredient obtained from cator oil under the influence of hydrogen, similar in consistency to wax, which is why the substance is also known as “castor wax”.
Hydroxyethylcellulose
Hydroxyethylcellulose - a plant extract, due to its ability to coat the surface with a film, is often used in hair styling products, also has a fixing / holding property, can be used as a thickener or emulsifier.
Isopropyl Cloprostenate
Isopropyl Cloprostenate is a synthetic ingredient created by the company whose product is RapidLash Eyelash Growth Conditioner. An ingredient similar in form and function to bimatoprost, an eye drop medication for the treatment of glaucoma and eye pressure, bimatoprost has been approved by the FDA as safe for cosmetic use under the brand name Latisse. Isopropyl cloprostenate is classified as a cosmetic ingredient whose function is described as a hair conditioning agent, but theoretically, as a related substance to bimatoprost, has the potential to affect the growth of eyelashes and eyebrows.
Jagulans Regia
Walnut Leaf Extract
Walnut Leaf Extract (Jagulans Regia/Walnut Leaf Extract) is a plant extract that has potential antioxidant properties, but this has not been proven by research. In dermatology and cosmetology, the extract is used as a wound-healing, bactericidal and anti-inflammatory agent; it is used for eczema, seborrhea, hair loss, acne, psoriasis, and dermatitis.
Krameria Triandra
(Rhatany, Krameriaceae) Root Extract
Krameria, ratania (Krameria Triandra, Rhatany, Krameriaceae) is a shrub from the moth family, the root of which is used to make medicines.
The plant extract of this plant has antioxidant and potentially protective properties against photoaging. The substance also has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, promotes natural skin repair, reduces oxidative stress and oxidative degradation of lipids under the influence of free radicals.
Linoleic Acid
Linoleic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-irritant, humectant, Cell-Communicating Ingredient, and used as a thickening agent. There are studies showing the effectiveness of linoleic acid in the mechanisms of cell regulation and restoration of the skin's protective barrier.
Lupinus Albus Seed Extract
Lupinus Albus Seed Extract is a plant extract that has antioxidant and moisturizing properties, but may be irritating to the skin. This leguminous plant produces isoflavones, a form of plant estrogen that has powerful antioxidant properties.
Licorice Extract
(Dipotassium Glycyrrhizate)
Licorice extract (licorice, licorice) is a plant extract that contains: glycyrrhizic acid, glycyram (monoammonium salt), glycyrrhetinic acid, flavonoids, chalcones, saponins, tannins and others. Flavonoids (polyphenolic compounds) are analogues of vitamin P, improve blood circulation, and reduce capillary fragility.
Licorice root extract contains glycyrrhizic acid, which is a unique natural surfactant with anti-inflammatory properties. Its content provides a gentle cleansing effect, non-irritating and soothing to the skin.
Licorice root also has reparative (restorative) and immunoactive effects. In anti-age creams, licorice extract is a natural phytoestrogen that stimulates the formation of collagen fibers; it actively prevents the deepening of existing wrinkles and the appearance of new ones.
Lecithin
Lecithin is a moisturizing substance related to the skin - natural moisturizing factor (NMF - natural moisturizing factor), has emulsifying, stabilizing and thickening properties.
Lecithin is a special substance (phospholipid) that is found in egg yolks; the cell membranes of animals and plants are largely formed from it; it has a pronounced effect on restoring the barrier functions of the skin, on the processes of nourishing the cell, and ridding it of toxins. Without lecithin, the process of formation of new cells and restoration of damaged ones is impossible. These and other properties of lecithin can significantly improve the condition of the skin with psoriasis, eczema, hyperkeratosis, ichthyosis, neurodermatitis and other diseases.
Its importance for cells, especially damaged and aging cells, cannot be overestimated. Lecithin has a direct membranotropic effect by directly integrating damaged cell membranes into the phospholipid structure, restoring the impaired barrier function of the lipid bilayer.
Essential fatty acids of plant phospholipids help increase the activity and fluidity of membranes, participate in the inhibition of lipid peroxidation, increase the activity of cellular enzymes, and are precursors of many biologically active compounds.
Methylparaben
Methylparaben is a preservative. It is believed that more than 70% of products contain some form of parabens.
Parabens are also believed to cause skin irritation much less frequently than other preservatives and have a broader spectrum of antifungal and antimicrobial protection. However, the reputation of parabens suffered after a version was put forward about the link between parabens and the development of cancer.
Myristoyl Pentapeptide-17
Myristoyl Pentapeptide-17 improves eyelash growth by stimulating the production of keratin, the proteins that form eyebrows and eyelashes. Sends signals to eyelash follicles to produce new cells and continue growth. In clinical trials, peptides improved eyelash length and thickness by 25% after 2 weeks and by 72% after 6 weeks.
Octapeptide-2
Octapeptide-2 may act as a hair growth stimulator, at least due to the counteraction of the substance BMP4, which inhibits hair growth in the development phase of hair follicles. This peptide is believed to combat hair loss of pigmentation.
Oleanic/oleic acid
Oleanic / oleic acid is a fatty acid used as a surfactant (surface active substance) - a cleansing detergent, as well as a thickener.
To be continued a little later.
Chemical properties
Histidine is an aromatic alpha amino acid with weak basic properties due to the presence of an imidazole residue in the molecule. Forms colored products in the biuret reaction and with diazotized sulfanilic acid (Pauli reaction), which is used for the quantitative determination of histidine. Together with lysine and arginine, histidine
forms a group of basic amino acids. Forms colorless crystals.
Foods rich in histidine include tuna, salmon, pork tenderloin, beef fillet, chicken breasts, soybeans, peanuts, and lentils. In addition, histidine is included in many vitamin complexes and some other medications.
Role in the body
The histidine residue is part of the active sites of many enzymes. Histidine is a precursor in histamine biosynthesis. One of the essential amino acids, promotes tissue growth and repair. Contains in large quantities in
The reaction of histidine decarboxylation is of great physiological importance, as it is the source of the formation of a biologically active substance - histamine, which plays an important role in the process of inflammation and the development of some allergic reactions.
Decarboxylation occurs mostly in mast cells of connective tissue in almost all organs. This reaction occurs with the participation of the enzyme histidine decarboxylase.
A hereditary disease, histidinemia, associated with a histidinase defect, is known, which is characterized by an increased content of histidine in tissues and delayed mental and physical development.
The amino acid histidine is semi-essential in adults and absolutely irreplaceable in children, because it performs many important functions in the body.
Beneficial properties of histidine
Histidine is important for every person and is simply irreplaceable during the growth period of the body; it is part of many enzymes. Histidine is part of hemoglobin and is involved in its synthesis. In addition, histamine is synthesized in the body from histidine, and it is also important for the synthesis of white and red blood cells and the powerful antioxidant carnosine. Histidine is a blood clotting regulator and a component of the myelin sheaths that protect nerve fibers. This amino acid strengthens the immune system, protects our body from all kinds of infections, radiation, absorbs ultraviolet rays and removes heavy metals. Histidine promotes tissue growth and repair, promotes healthy joints, and increases muscle endurance, allowing athletes to train longer and with greater intensity. Supports the function of the auditory nerve, reduces the severity of allergic reactions. The amino acid L-histidine plays an important role in protein metabolism, increases libido, fights stress, improves and normalizes the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, promotes a healthy nervous system, which has a beneficial effect on the functioning of all organs and systems of the body.
In medicine, L-histidine is successfully used in complex therapy for the treatment of stress, arthritis, atherosclerosis, allergies, ulcers, gastritis, anemia, hepatitis, and acquired immune deficiency syndrome. This amino acid is also used during the recovery period after illnesses and injuries.
Unfortunately, such a useful amino acid has contraindications and harm, which mainly concerns dietary supplements and medications.
Biological need
The minimum daily requirement for histidine for an adult is 12 mg per 1 kg. body weight, i.e. for a person weighing 60 kg. 0.7 g is needed per day. The optimal daily requirement for an adult is 1.5 - 2 g. The maximum permissible dosage of histidine is 5-6 g per day.
For infants, the requirement for histidine is 34 mg/kg. weight, i.e. 0.1 – 0.2 g.
The need for histidine increases during intense physical activity, during the recovery period after severe injuries, wounds, and operations.
The body's daily requirement for histidine
On average, the daily intake of histidine for an adult is 1.5-2 grams. The maximum permissible dosage of L-histidine is 5-6 g per day. But do not forget that for each person the exact dose is selected individually by a specialist and it will depend on many factors, for example, on the general state of health, weight, and age of the person. You need to know that a reasonable intake of amino acids, including L-histidine, will help avoid the consequences of its deficiency or excess in the body.
Histidine content in foods
Stewed meat has 15-20% more histidine than fried meat and 35-40% more than raw meat.
Cooked fish contains 25-30% more histidine than raw fish
The protein of plant products is, on average, 20% less digestible than that of animal origin, and the protein of chanterelle mushrooms is digestible only 30%, which is why additional coefficients were introduced.
To best preserve amino acids in cereals and nuts, they should be stored in hermetically sealed containers, protected from direct sunlight.
Cereals and legumes are consumed not in dry form, but in the form of porridges; usually the ratio of grain and water in the finished dish is 1:1 for legumes and 1:2 for grain porridges.
With a normal diet, a sufficient amount of histidine can be obtained from small portions of meat and fish - about 150 g of ready-made fish or meat dishes contain the daily requirement of the amino acid. You will need 200-300 grams of cheese or cottage cheese, this is a reasonable portion for daily consumption. Seeds and nuts will require 300 - 400 grams, so complete vegetarians should think about: either an amino acid deficiency or a serious excess of calories, because these products are very high in calories. Cereal porridges cannot be considered as the main source of histidine, because 1.5 - 2 kg. Only a Gargantua or a person with serious physical exertion can eat porridge. This is how peasants ate in the Middle Ages: a large volume of high-calorie grains was compensated by hard work on the land.
Foods containing amino acids: sources of essential compounds
Amino acids are the structural units of proteins, the “building blocks” that form any protein entity. Amino acids are found in the human body (muscle fibers, soft tissues, etc.), in plants (cereals, legumes), meat and dairy products. From the point of view of biological value, essential amines
- compounds that enter the human body from the outside: together with food and special additives. Unlike non-essential ones, they are not synthesized by living cells. This means they are in constant shortage.
Amino acids in sunflower protein
The following table compares different plant proteins.
Proteins contain 20 different amino acids as building blocks, which are linked together by peptide chains. These amino acids can be divided into essential and semi-independent amino acids. Essential amino acids are vital, but the human body cannot produce them on its own. Adequate supply through daily nutrition is important. The essential amino acids are isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan and valine. The most “deficient” compounds are tryptophan, methionine, lysine. According to WHO, they are the ones who most often “fall out” of the overall picture. The following foods are designed to compensate for the lack of essential amino acids:
Legumes
. Contains valine, tryptophan, phenylalanine. Rich in histidine, leucine, threonine, methionine and other components (you can get acquainted with the specifics of certain compounds by clicking on the link).
Amino acid profile
Half-family amino acids such as arginine and histidine cannot be created in the human body during certain developmental periods in life, for example.
newborns. You probably know you need to eat protein, but what is it? Many foods contain protein, but the best sources include beef, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy, nuts, seeds, and legumes such as black beans and lentils. Your body uses the protein you eat to make many specialized protein molecules that have specific jobs. For example, your body uses protein to make hemoglobin, the part of red blood cells that carries oxygen to every part of your body.
White meat (chicken breast)
. Contains BCAA (isoleucine, valine, leucine), lysine, tryptophan, phenylalanine, histidine.
Dairy products (cottage cheese, cheese, low-fat and UHT milk, etc.)
. Sources of essential amino acids: lysine, tryptophan, arginine, phenylalanine, valine.
Eggs
. Foods rich in BCAA amino acids, phenylalanine and methionine. They are perfectly absorbed by the body, providing comprehensive protein nutrition to the body.
Other proteins are used to create heart muscle. In fact, whether you're taking it or just hanging out, protein does important jobs like moving your legs, carrying oxygen into your body, and protecting you from disease. When you eat foods that contain protein, the digestive juices in your stomach and intestines go to work. They break down protein in food into basic units called amino acids. The amino acids can then be reused to make the proteins your body needs to maintain the muscles, bones, blood and organs of the body.
Squirrels are sometimes described as long necklaces with beads of various shapes. Each bead represents a small amino acid. These amino acids can combine to make thousands of different proteins. Scientists have found many different amino acids in protein, but 22 of them are very important for human health.
Fish
. Contains high concentrations of essential amino acids. In particular, isoleucine, lysine, phenylalanine and other compounds.
Cereals (rice, buckwheat porridge, etc.)
. Sources of valine, isoleucine, leucine, histidine.
Seeds and nuts
. Foods rich in threonine, histidine, isoleucine, arginine, lysine and other amino acids. Contains a full complex of protein compounds of plant origin.
Of these 22 amino acids, your body can make 13 of them if you never think about it. Your body cannot make the other nine amino acids, but you can get them by eating protein-rich foods. They are called essential amino acids because it is important that you get them from the foods you eat.
Protein from animal sources such as meat and milk is called complete protein because it contains all nine essential amino acids. Most plant proteins are considered incomplete because they lack one or more essential amino acids. This can be a problem for those who don't eat meat or dairy. But people who eat a vegetarian diet can get all their essential amino acids by eating plenty of protein-rich plant foods.
Histidine deficiency
Under normal conditions, with a normal diet, histidine deficiency is not observed in adults. Histidine deficiency is possible during extreme diets or fasting, when people are forced or of their own free will to refuse to consume protein foods. Lack of amino acids manifests itself in muscle pain and weakness. The bone marrow stops producing red blood cells (erythrocytes), which leads to anemia, but blood clotting increases, which leads to the risk of blood clots. Histidine deficiency is associated with deterioration of hearing until complete disappearance. Sexual desire decreases sharply, and men may develop erectile dysfunction.
Cataracts develop. Diseases of the stomach and duodenum are possible. Immunity decreases, which leads to bacterial and viral infections, the tendency to allergies increases, and children develop eczematous dermatitis: inflammation of the skin with itching, weeping, and crusting.
Children deprived of breast milk and with inadequate feeding are stunted in growth and development, even to the point of mental retardation.
The Dangers of Deficiency
Research shows that people with rheumatoid arthritis typically have low levels of histidine. Amino acid deficiency in infants often causes eczema. In addition, insufficient consumption of the substance leads to cataracts, and also provokes diseases of the stomach and duodenum. It is known that histidine affects the immune system, for this reason a deficiency of the amino acid increases allergies and makes the body more prone to infections and inflammatory processes. Insufficient consumption of the substance has an extremely negative impact on the health of children and adolescents during intensive growth and formation of the body.
Also, amino acid deficiency can “remind” itself of developmental delays, decreased libido, hearing impairment and fibromyalgia.
Excess histidine
With a normal diet, histidine does not accumulate in the body and no symptoms of excess are observed. However, when using pharmacological preparations of L-histidine, adverse reactions are possible,
Histidine removes copper and zinc from the body; excess histidine provokes allergic reactions and attacks of bronchial asthma; in men it can lead to premature ejaculation.
To avoid the development of complications, histidine preparations can be used only for clinical indications under medical supervision.
Application nuances
Histidine in the form of a dietary supplement is prescribed to patients in the postoperative period. And also for people suffering from anemia and arthritis. In the presence of bipolar disorders, asthma and allergies, amino acid preparations are contraindicated. Pregnant and lactating women should take supplements containing it with caution. And also in case of lack of folic acid in the body.
Histidine is indispensable for stress, injuries, chronic diseases and high physical activity. It is vital for athletes. In these cases, food sources will not cover the need. Dietary supplements are the solution to the problem. However, you should not exceed the recommended dosage. The body’s “response” can be digestive failures and decreased acidity.
Amino acid metabolism disorder is a rare hereditary pathology (histidinemia). It is characterized by the absence of a special digestive enzyme. The result is a sharp increase in the concentration of histidine in the patient’s body fluids and urine.
Side effects
In case of an overdose of L-histidine pharmacological preparations, the following side effects are possible:
- Immediate allergic reactions: Quincke's edema, a sharp drop in blood pressure with loss of consciousness (arterial collapse), anaphylactic shock.
- Mental disorders
Less serious side effects in which the dosage of the drug should be reduced:
- From the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia (impaired digestion in the stomach)
- From the central and peripheral nervous system: headache, dizziness, tremor (shaking limbs), disturbances of consciousness, paresthesia (feelings of “crawling goosebumps”, “tingling of needles”)
- From the autonomic nervous system: local increase in temperature (local hyperthermia), fever, decreased blood pressure, bronchospasm
- Allergic reactions: skin rash.