BCAAs
Sergey Sidoruk 01/07/2019 no comments
0
What are the benefits and harms of BCAA?
2 (40%) 1 vote
A healthy diet is an integral part of any sport, otherwise muscles will not increase, and endurance may decrease due to depletion of energy reserves. Even with high-quality nutrition, a moment arises in the life of a bodybuilder when microelements become insufficient, because the body consumes a lot of protein. If you continue on the established path without using supplements, the risk of overtraining increases and there will be little or no muscle growth. Let's take a closer look at BCAA amino acids - harm to the body or, conversely, a necessary supplement for achieving sports results.
The role of amino acids in sports
After such a long conversation, you can already decide what responsibilities are assigned to protein compounds in order to help achieve the desired results in sports.
The amino acids consumed provide:
- Fast delivery to the muscles of the building material they need. In this case, it is worth distinguishing the specified protein compounds from the protein supplements that bodybuilders use. The former enter the blood within 15 minutes, while the latter require long-term absorption (up to 2 hours from the moment of administration). Therefore, the additional benefit of their use is to prevent the “protein window” during training;
- Maximum provision of the athletes’ body with protein, which ensures the optimal flow of all necessary vital processes;
- Acceleration and support of recovery processes occurring in muscle tissue;
- Normalization of hormone production and optimization of all anabolic processes;
- Maintaining a positive nitrogen balance in the body;
- Optimization of ongoing energy processes in the muscles, strengthening of protective and immune functions;
- Burning excess fat, normalizing protein metabolism;
- Normal functioning of all departments and organs of the human body.
The effect of BCAAs on the body and muscles
A significant portion of muscle mass consists of leucine, isoleucine and valine. In addition, these amino acids provide a lot of additional energy, which is a great advantage for an athlete during training. During active sports, muscles lose contractile protein, so its renewal is very important. When taking BCAAs, the endurance of the body and muscles increases. Taking this supplement before a workout will help relieve fatigue, and after a workout it will prevent the loss of important amino acids or restore energy. Energy will appear due to the release of the hormone serotonin, which will appear due to the action of BCAAs. These amino acids have the same effect on a woman’s body as they do on a man’s body.
Taking sports supplements correctly
Today, amino acids can be purchased in a wide variety of forms. The most common are liquid concentrates and gelatin capsules.
There is a misconception regarding how to take these proteins. Many believe that only on an empty stomach, since such a step will contribute to their better absorption. This is an absolute fallacy!
It must be remembered that amino acids for athletes should not be taken on an empty stomach, as they can cause very severe irritation of the gastrointestinal tract.
Therefore, it is better that they enter the body along with the food consumed.
Time of receipt
Before you start taking amino acids, you should read the manufacturer's recommendations. In some cases, it will be more rational to do this after completing the workout. When consuming protein compounds, you need to take into account that tryptophan and threonine have a relaxing effect on the human body. Therefore, it is better not to consume them in large quantities before training.
What are BCAA's?
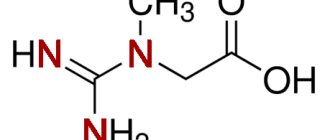
The abbreviation BCAA means the English name "Brained Chains Amino Acids" or branched chain amino acids. This, for many a meaningless abbreviation, hides 3 of the most important amino acids - leucine, isoleucine, valine.
essential for the human body . This means that the body cannot produce them on its own. Therefore, their reception from the outside is important.
Damage to amino acids and side effects
People have always had a lot of questions about taking these supplements. How safe are they? Is it possible or not to take them? What dominates in them: harm or benefit? Maybe it's better to change your diet? Unfortunately, the pharmacy will not be able to provide answers to all your questions, and this is not profitable for dealers.
If you want to assess the harm or benefit caused by these supplements, you need to know which amino acids for athletes to take and how they are obtained. Let's pay attention to the structural protein units - cottage cheese, eggs, meat, dairy products, legumes.
All of them contain protein or, in other words, amino acids in significant quantities. The question already arises of how such components can harm a person. These products are consumed by everyone, so what side effects were observed after consuming them? None! This means that the benefits from them are significant, but the harm is zero.
Overdose
The amino acids an athlete needs can be obtained from food, but it is better to take them in their pure form. The main thing is not to overdo it with the dosage. However, such a phenomenon as an overdose practically does not occur. After all, manufacturers always offer instructions for use, in which the recommended doses are somewhat underestimated.
An overdose from the use of amino acids is possible only when a person doubts the competence of sports pharmacists and arbitrarily exceeds the dosages specified in the instructions.
Even in this case, the harm caused to the body will be minimal, but the occurrence of side effects cannot be avoided, and this happens solely from careless handling of the drugs used.
In this conversation, it is inappropriate to point out which amino acids can cause harm. Side effects include:
- Kidney dysfunction
. Since it is the kidneys that remove urea, creatinine and other waste products, as well as waste proteins, in the case of chronic diseases they will not cope with their work. In the case of our preparations, we are talking about the supply of pure proteins per 50 grams. in a day; - Sleep disturbance
. If you take protein compounds in their pure form, this side effect may occur. In particular, glutamine (glutamic acid) can cause a psychostimulating or stimulating effect. Glycine has a sedative effect.
Once you start taking amino acids, you should not experiment with their daily dosages. Harm to the body is possible if the recommended norm is exceeded by more than five times.
In the photos posted online, you can see a huge number of different packaging jars of the same drug. You need to choose protein compounds not by stickers or packaging, but solely by the manufacturer. It’s better if it’s European.
Amino acids are the so-called building blocks that form proteins in the human body. Their most important distinguishing feature from carbohydrates and fats regarding their chemical characteristics is that amino acids consist of 16% nitrogen. The benefits of amino acids for our body
is directly related to the influence of proteins on the course of many vital processes in it and to the need to function normally when they are deficient. After all, in our body proteins form muscles, tendons, organs and glands, as well as nails and hair. Agree, you can’t go anywhere without them.
What can a lack of protein lead to?
Note that a lack of proteins can provoke improper functioning of the water-salt balance, followed by many problems. Proteins appear in our body through synthesis from amino acids. And they, in turn, are formed from proteins that come with the products that we eat. From this we can conclude that amino acids are the most valuable nutritional element necessary for the normal functioning of our body.
Foods High in BCAAs
Branched chain amino acids are three of the eight essential amino acids. They are found mainly in protein-rich foods. With a balanced and healthy diet, you should not have any problems meeting your body's daily minimum nutrient requirements. However, certain factors can radically increase these needs, so supplementation may be necessary.
Watch your diet
For example, the Flash Diet dramatically reduces the body's reserves of BCAAs, which must be replenished immediately to avoid muscle tissue breakdown. In this case, BCAAs will help with the support and restoration of muscle tissue.
Liver disease and high-intensity training also increase the need for leucine, valine and isoleucine, so athletes and patients should regularly take increased amounts of them.
What types of meat are rich in BCAAs?
Foods particularly rich in leucine are: beef (approx. 1690 mg/100 g), raw salmon (approx. 1615 mg/100 g), eggs (approx. 1090 mg/100 g) and wheat products (approx. 920 mg /100 g).
Valine and isoleucine are also found in significant quantities in meat and other animal products. Dried peas (approx. 1160 mg/100 g) and walnuts (approx. 750 mg/100 g) with their high BCAA content are especially good for vegetarians.
Meat eaters can get most of their minimum daily intake of BCAAs by eating chicken breast (approx. 1220 mg/100 g) and rice (approx. 330 mg/100 g). A healthy adult needs about 10 g of BCAAs per day, but this amount, of course, can vary depending on each individual case.
If you regularly exercise, then you should consider taking either BCAAs alone or in combination with whey protein.
The aminoacidstudies website has compiled the top 7 proteins to make it easier for you to choose the right product for you.
The benefits of amino acids and their types:
In general, there are 28 types of these very important acids. Many of them are synthesized in the liver, but not all are produced by our body. Therefore, it is important to pay due attention to nutrition to ensure that you get all the necessary amino acids. Next, we will tell you which foods it is highly not recommended to refuse, since in this case the chances of encountering an amino acid deficiency will increase significantly. Often people, in particular those who are professionally involved in sports, also take special supplements that contain them. But we strongly advise against prescribing them for yourself. It is better to do this by contacting a qualified specialist.
See what a lack of amino acids can lead to and how to prevent it:
The most important amino acids needed by the body:
Let us note the most important amino acids, without which the body cannot function normally and faces various problems. This:
- valine is involved in tissue synthesis in our body and reduces the pain threshold;
- Leucine significantly increases the body's defenses and reduces the risk of encountering numerous ailments. If you often get sick, then there is a high probability that the reason for this lies in a lack of leucine, due to which the body cannot properly protect itself, and the disease occurs;
- threonine is responsible for the gastrointestinal tract and;
- methionine “monitors” the level in the blood and helps it stay at a low level that does not threaten our health;
- isoleucine takes part in energy metabolic processes;
- lysine helps to better absorb calcium;
- Tryptophan controls appetite, preventing us from overeating or staying hungry.
The benefits of amino acids are enormous. In particular, these “building blocks” (at least most of them) are excellent: they help prolong that desired youth longer and are responsible for the prevention of cancer. Secondly, they “melt” subcutaneous fat. Food rich in protein is recommended in many diets, since the body requires significant energy expenditure to process it, and as a result, we lose weight and remain slim.
What foods contain amino acids:
To avoid amino acid starvation, it is best to start by normalizing and regulating your diet, doing everything possible to supply the body with their important representatives. So, in particular:
As you can see, the benefits of amino acids for our body are enormous. They truly are his assistants, providing improved well-being and assistance in the fight against health problems.
Today you can find a bunch of questions from athletes regarding the harm of amino acids
. Moreover, it is almost impossible to determine what is the source of negative reviews. But let's start from the very beginning.
Companies producing and selling sports nutrition highlight amino acids as having a very important role in pumping up huge muscles. This gives beginners the false impression that once they start taking amino acids, their muscles will literally burst from size. On the other hand, they are concerned about possible side effects that may occur in this regard. Do they really not do any harm? Let's figure it out.
- Amino acids sold as dietary supplements in sports nutrition stores are not drugs or medications.
- If all conceivable doses are exceeded, it is almost impossible to get food poisoning. So, for example, with an optimal dosage of 5 grams, consumption of amino acids in the amount of 30 g or even 50 grams will not bring any negative results.
- Amino acids are not capable of causing stomach ulcers, since they are contained in any protein product, be it meat or cottage cheese. Can meat or cottage cheese cause stomach ulcers? Probably a stupid question.
- Another myth about the harm of amino acids is possible... impotence. This statement does not fit not only with science, but also with common sense.
What are amino acids? These are the substances that make up ordinary protein. When it enters the body, it is broken down into amino acids, the same ones that are sold in sports nutrition stores. Amino acid complexes are obtained from whey protein, which is a protein and from natural cow's milk. It is then broken down into amino acids and sold as a supplement. At their core, these amino acids are pre-digested milk protein.
Now that we know where amino acids come from, we can ask a reasonable question: can, for example, eggs or milk cause stomach ulcers, impotence and other side effects? Probably not likely. It turns out that with the same degree of probability amino acids can cause all of the listed negative aspects.
However, if we get all these substances through food, then why do we need to consume them additionally? The thing is that specially prepared amino acids are absorbed much faster than if you ate regular protein foods. This means that your muscles will receive the necessary nutrition much faster and in the right volume for restoration of strength and new growth. In addition, most people do not consume enough protein foods, so when starting to work out in the gym, they often do not always have enough strength to complete the training program. And its effectiveness drops significantly, because the athlete’s first place is proper nutrition, without which there will be neither strength nor large volumes.
Thus, the side effects or harm of amino acids are nothing more than a myth that is absurd for perception by a person with at least a little understanding of biochemistry. Even if the maximum dosage is exceeded many times, the harm is so insignificant that it does not have any effect on the body. By the way, any doctor can confirm this to you. And all the questions related to the negative effects of consuming sports nutrition only speak of the illiteracy of a person who thinks in stereotypes instead of common sense.
Amino acids are viewed as tiny gold nuggets that can impart superhuman powers to those who develop the muscles of the body every day. Sports nutrition and nutritional supplements, cocktails and capsules contain amino acids and are popular among athletes.
What are amino acids and what are they needed for?
The human body is 20% protein. It is necessary for the normal functioning of the body and the coordinated functioning of all systems. The building block of protein is called an "amino acid" - an organic compound necessary to build the structure of the cell. Without amino acids, the process of transporting nutrients is impossible.
Why else do humans need amino acids?
- for the production of protein and enzymes;
- psychological background (mood);
- sleep quality;
- concentration;
- sexual activity;
- wound healing;
- restoration of muscle fibers;
- healthy bones;
- beautiful skin and hair.
Any disease is the result of an imbalance of essential substances in the body. Amino acids are responsible for the correct process of their intake and balance. When protein is consumed, it breaks down inside the gastrointestinal tract into individual amino acids, from which proteins, hormones and digestive enzymes that the body lacks are synthesized in the human body.
This complex biological process is called protein biosynthesis. The body must constantly obtain different amino acids through a varied diet, dietary supplements and its own production (biosynthesis).
Are BCAA amino acids harmful to health?
Sports nutrition preparations in the form of amino acid powders are actively recommended for use by athletes.
They claim that they are quickly absorbed and can be taken even during the training process. But alarming reviews about these supplements are regularly found online. How do you know if bcaa is dangerous for the body? Harm of BCAA amino acids to the body
BCAA consists of three main components: leucine, isoleucine and valine. Each of them is a so-called essential amino acid, the reserves of which in the body can only be replenished from protein foods of animal origin. Drugs can be made by processing natural raw materials (eggs, milk), or synthesized chemically. The market provides a choice of both options. Taking them does not cause obvious and sudden harm to a healthy body. But there are conditions (related to the athlete’s health characteristics) under which it would be wiser to refuse this supplement, or use it under the strict supervision of a doctor.
The effect of bcaa on the body as a whole
bcaa affects the body as a source of valuable nutrients, because every muscle organ needs amino acids as a basic component of protein molecules. But in general, these dietary supplements can be used for specific achievements, for example:
Lack of protein foods of animal origin in the diet
Intense workout aimed at gaining mass
Reducing body fat without losing muscle mass
Athletes describe the following subjective experience of the influence of BCAA on their body:
Increases endurance during anaerobic training.
The usual weights are easy, and the training process is less tiring.
Muscle mass is noticeably strengthened, but the lightning-fast effect of steroids is impossible.
The complex of these substances has an anti-catabolic effect, preventing the destruction of protein after exhausting exercise.
How do BCAAs affect the gastrointestinal tract?
Some reviews of BCAA's focus on stomach problems associated with their use. The effect of capsules and powder on the gastrointestinal tract is undeniable, because each dose triggers digestive processes, accompanied by the release of juices from the stomach, gall bladder and pancreas. Amino acids, unlike proteins, are absorbed into the blood within a few minutes, and digestion continues to work “idle”. This leads to the digestion of literally one’s own mucous membranes, which is fraught with gastritis, erosions, and ulcers.
For this reason, it is very important to take btsaa with some “real” dish: salad, chicken fillet. The most common training option - liquid amino acids - also protects the stomach from failures.
Effect of bcaa on the liver
BCAA amino acids are perceived by the liver as a natural and necessary component of the blood. Therefore, fears that a high-quality supplement from a trusted sports nutrition supplier can harm the liver are unfounded.
The data obtained by scientists prove that the liver does not decompose bcaa, and their effect is manifested at the muscle level - they nourish the fibers, replenishing energy even at the end of a four-hour strength training.
Side effects from taking bcaa
Considering that an active person needs an increased intake of essential amino acids, a side effect occurs only as an exception to the rule or a consequence of errors:
Long-term and repeated use on an empty stomach can lead to gastroduodenitis and gastritis.
Allergic intolerance to one or more components of dietary supplements is isolated and strictly individual in nature. It can manifest itself in completely different ways, like any allergy.
The importance of amino acids in the human body
The goal is for amino acids to enter the body and be in the correct combination. If one type is unavailable or not enough, protein production slows down, metabolic processes are disrupted, and the rate of elimination of breakdown products and toxins is reduced. Older people are not the only ones who suffer from this. Young people also feel a lack of nutrients; the following signs help determine their limited intake:
- body weight problems;
- deterioration in the appearance of hair, hair loss, fragility, dryness;
- poor skin condition;
- insomnia;
- mood swings;
- decreased potency/libido;
- arthritis;
- diabetes;
- hypertension, etc.
The function of amino acids extends far beyond the definition of “building blocks.”
Main functions of BCAAs
- Since BCAA is a broken down protein, presented in the form of three essential acids, which are the basis for building muscles, its main function is to obtain material for building muscle mass. The effect of BCAAs on the body is manifested mainly in this.
- Also, these three amino acids provoke other important substances that are very important for the body. For example, insulin is produced, which delivers energy to muscle cells.
- BCAAs can help prevent muscle loss. This property is very important for athletes following a low-calorie diet, since during this period their body receives very few calories, and BCAAs will compensate for this and block muscle loss.
Benefits and uses of amino acids
Depending on the possibility of protein synthesis in the body, amino acids are divided into groups. The first is essential, these are food proteins containing amino acids necessary for humans, which our body is unable to produce on its own. Their supply is provided by the diet and other exogenous sources.
Essential amino acids:
- 1. Phenylalanine. Has an analgesic and antidepressant effect. A precursor to the synthesis of norepinephrine and dopamine, two brain chemicals essential for well-being.
- 2. Valine, isoleucine and leucine are simultaneously classified as essential and branched chain amino acids (bcaa amino acids). Prevents the breakdown of proteins in muscle fibers during exercise. Additional supply of valine ensures rapid recovery of the body and reduces muscle damage.
- 3. Threonine. The source of the synthesis of glycine and serine, without which the normal construction of collagen and muscle fibers and elastin is impossible. Threonine strengthens the heart muscles and ligaments in the body. With its help, teeth and bones retain their strength for a long time.
- 4. Tryptophan. Precursor to serotonin, a brain neurotransmitter. Helps suppress pain, calms, improves sleep. The main reason for the presence of tryptophan in sports nutrition is its ability to increase pain tolerance and performance during rigorous training.
- 5. Methionine. Helps eliminate fat. It contains sulfur, which is essential for the production of the antioxidant glutathione. Methionine is needed by our body to make two other sulfur-containing amino acids, cysteine and taurine. Without them, the body is unable to effectively remove toxins, synthesize strong, healthy tissue and prevent cardiovascular disease.
Methionine is a lipotropic amino acid that helps the liver, prevents the accumulation of fat in the organ and ensures normal functioning to eliminate toxins from the body. Methionine supports liver function by regulating the supply of glutathione, which is necessary to neutralize toxins in the liver.
- 6. Lysine. Promotes healing of mucous tissues. Helps release growth hormone, increases the rate of muscle recovery.
- 7. Leucine is one of the main and largest amino acids, actively involved in the synthesis and restructuring of proteins. Necessary for normal functioning and maintenance/growth of muscle mass.
The body produces nonessential amino acids itself in the quantities required. There are few of them, only four types: serine, glycine, alanine, aspartic acid.
The third group includes amino acids that are necessary for humans, but which the body produces in small quantities. Their deficiency negatively affects the human condition, especially noticeable in people who lead an active life.
The supply quickly runs out and the shortage must be constantly replenished. Amino acids of this group are considered conditionally essential:
- 1. Arginine. Necessary for the synthesis of nitric oxide. Dilates blood vessels, increases blood flow and exercise tolerance. Arginine is involved in many metabolic processes, improves blood circulation, strengthens the immune system, and increases male libido. Arginine accelerates the process of burning fat and reduces cholesterol. Lack of arginine leads to the development of osteoporosis in older women.
- 2. Histidine. A histamine precursor, it has antioxidant properties and plays a key role in the synthesis of carnosine. Histamine helps fight cell damage caused by free radicals during exercise. Carnosine helps convert lactic acid into useful fuel for muscles to use during exercise.
- 3. Tyrosine. Precursor to dopamine. When the body's muscles are unable to bear further stress, tyrosine kicks in and increases the performance and speed of muscle recovery. Athletes are ready for long and hard loads without the danger of “overtraining.”
- 4. Glutamine. The most abundant amino acid found in muscles. Her share of responsibility is to maintain a person’s immunity at a high level, quickly restore muscles and stimulate protein anabolism. Production slows down with age, so an additional source of supply is needed.
Glutamine slows down the aging process. The supply of this amino acid is important for elastic skin. When there is a lack of available glutamine, the body takes the necessary protein from muscle mass and converts it into glutamine and energy. Muscle protein is destroyed, the fibers become thinner, and the skin sags.
Scientists call glutamine the “inner fountain of youth.”
- 5. Proline. Improves tissue properties, promotes wound healing and skin density.
- 6. Cysteine. Forms collagen in tissues, improves the elasticity of ligaments and tendons. Needed for building muscle and burning fat.
It is impossible, or almost impossible, to build muscle tissue, recover after physical activity and maintain muscles during the “drying” period, without receiving the required amount of amino acids into the body. An important role is played by bcaa amino acids, which are metabolized not in the liver, but in the muscles. They serve as a source of energy during training and prevent premature destruction of muscle fibers.
BCAA amino acids are essential for exercise performance and exercise tolerance. With additional intake into the body, tests show an increase in the number of red blood cells in the blood, hemoglobin, hematocrit and serum albumin.
It has been proven that muscle strength is quickly restored, the destruction of protein fibers slows down even during periods of intense exercise, lipid oxidation increases, which promotes weight loss.
When gaining muscle mass
Amino acids should be taken shortly before and after exercise. Sometimes there is an additional dose in the morning. The rest of the time it is more advisable to use protein.
When losing weight
To speed up the process of losing kilograms, provide frequent intakes of amino acids. The main goal is to reduce the desire to eat, suppress catabolism, but preserve muscle. It is necessary to take it in the morning, before and after exercise in the gym, between meals.
Amino acid dosage
A complete diet fully covers a person’s needs, but if we are talking about athletes and bodybuilders, an additional source of amino acids is needed; they are consumed faster.
There are several points to consider:
- When taking protein mixtures, there is no need for additional amino acids. Only the BCAA amino acids (valine, leucine and isoleucine), which restore the “gaps,” are excluded. It is enough to take them only on the day of training.
- The dose is calculated based on the athlete’s body weight. With a weight of 60 kg, the daily portion will be 14 grams; as the weight increases, the dose also increases. A heavyweight will need up to 30 grams per day. Important: we are not talking about the weight of the drug, but the mass of the amino acid. Information varies; information is obtained from the instructions on the package.
- The dose per day is divided into 2 doses. The first is taken in the morning after sleep, the second at the end of training.
Preparations containing amino acids may look different: tablets, capsules, gels, solutions, etc. There is no significant difference between them, only in the characteristics of administration.
Myths about harm
There are many myths surrounding these beneficial substances. At the same time, there are no clinical trials confirming their harm. I would like to go over the main “horror stories” in a few words. I hope this will finally dispel your doubts.
Myth No. 1: BCAAs in sports nutrition are chemicals . The statement is fundamentally incorrect. Amino acids can only be obtained from natural products. Meat, milk, cottage cheese, fish - they are all sources of proteins. I have already written in more detail about the content of amino acids in food products.
In sports nutrition, you simply get a concentrated set of BCAAs. Those. The daily intake of such amino acids in the diet corresponds to several scoops. Just because the product is concentrated, it does not become chemical. These are still natural ingredients.
Myth No. 2: BCAA amino acids cause ulcers and gastrointestinal upset . Studies show that even if you exceed the daily norm, you will not get poisoned. If you systematically abuse these substances, you can only harm your kidneys. In this case, for a long time it is necessary to exceed the daily intake by 10-15 times.
Myth #3: Proteins and BCAAs lead to impotence . It was always strange for me to read about this. Millions of men around the world use sports nutrition. However, none of them spoke about its harmful effects. Moreover, there are no clinical trials to confirm this.
ARTICLES ON THE TOPIC:
- Did you know that whey protein is not a steroid, but a natural...
- Why are amino acids needed during training for women?
- Tips for losing weight: when to drink protein to get maximum effect
When purchasing a dietary supplement, just pay attention to the ingredients. Various dyes, sweeteners, and preservatives found there cause gastrointestinal upset. They can also provoke allergies and negatively affect liver function. It is better to buy amino acids from well-known companies and with a minimum of additives.
Contraindications and side effects
It is difficult to exceed the dosage of amino acids, because the manufacturer includes detailed instructions with each package. In rare cases, undesirable effects from use are possible:
- impaired renal function (exceeding the daily dose of BCAA amino acids);
- increased intake of glutamine has a stimulating effect on the body;
- Excessive glycine content “puts the body to sleep.”
It is possible to experience the side effects of amino acids only if you exceed the daily dose multiple times (several times).
The role of amino acids is significant not only for athletic and active people. A balanced diet provides the necessary amount of dietary protein for normal life. Additional intake of nutritional supplements allows athletes and bodybuilders to restore their strength faster, train more productively, maintain tone, health and achieve high results.
If you take any product - no matter whether it is of plant or animal origin - and “decompose” it into its chemical components, then its fundamental components will be proteins, fats and carbohydrates. The latter are perceived by most people, especially women, as a potential danger, because lipids and sugars are the enemies of the figure. But people favor proteins, known from the school curriculum as “the building material of the body,” and include food products containing them in large quantities in the daily diet. These organic components, in turn, consist of amino acids, about which, by the way, we know little. The task of today's article is to reveal their many secrets.
Are there any benefits to taking BCAA?
The benefits of amino acids are manifested in the normal course of metabolism in the most difficult part of training - anaerobic. Accompanying them with every meal, a person recovers better between workouts.
There is also an additional positive effect of BCAA amino acids, which manifests itself in the functioning of the hormonal system:
They stimulate the natural production of growth hormone.
One of the components of bcaa is processed into a beneficial substance that suppresses cortisol, known as the “stress hormone” and a destroyer of muscle cells.
This added benefit will convince any athlete to supplement their diet with amino acids.
The essence and classification of amino acids
Amino acids... They form all living nature that surrounds us - flora and fauna. Combining in various, numerous combinations, the components of proteins form, by and large, the global part of the Universe - according to scientific research, the types and chemical structure of amino acids are absolutely the same throughout outer space. This fact allows a person to feel like a particle of the vast Universe, its small grain of sand...
Having been embodied in various combinations, amino acids give animal and plant proteins the right to exist. The former are more nutritious and better absorbed by the human body, which is direct evidence of the harm of vegetarianism to the physical health of the earth's inhabitants. The reason for this situation is the following: animal meat is rich in essential protein components - components that cannot be synthesized directly in the human body, and therefore must enter the latter from the outside. There are few of them, but they are all quite important for our life.
- Valine – participates in the growth and synthesis of tissues, reduces sensitivity to pain.
- Leucine – strengthens the immune system.
- Threonine - stabilizes the gastrointestinal tract and metabolic processes.
- Methionine – lowers blood cholesterol levels.
- Lysine – thanks to it, calcium is well absorbed and the activity of the herpes virus is significantly reduced.
- Phenylalanine – is involved in the synthesis of hormones, as well as the essential amino acid tyrosine.
- Tryptophan – regulates appetite, controls sleep and pain threshold.
- Isoleucine – participates in energy metabolism.
Arginine and histidine, although officially classified as essential components, in practice are partially replaceable, because their synthesis in the human body is very slow.
Essential amino acids have an effect on the body similar to that of vitamins. Of course, a lack or complete cessation of supplying the body’s organs with these elements is fraught with serious illness, and ultimately death.
There are several more non-essential amino acids that are produced in the internal environment of the human body. Their sources are organic raw materials, that is, food, and precursors.
- Glycine – provides body cells with oxygen and strengthens the immune system.
- Alanine – promotes the formation of antibodies and serves as a source of energy.
- Proline – strengthens the heart.
- Serine – “dresses” nerve fibers with a fatty sheath.
- Cysteine (cystine) – has antioxidant properties, replaces methionine.
- Asparagine – removes ammonia from the body.
- Glutamine – stabilizes blood sugar levels, fights fatigue and schizophrenia.
Non-essential amino acids also include tyrosine, glutamate, and aspartate, which are also very important in their functionality.
In total, there are about 300 protein components in nature, of which at least 50 are “housed” in the human body. But there are only 20 components directly involved in the synthesis of “building material” (according to other sources - 21 or 22).
What are BCAs?
BCAs are long-chain amino acids. They include only three essential amino acids for humans: isoleucine, leucine, and valine, which are allocated to a specialized class due to the unique structure.
In the human body, the share of these amino acids is forty-two percent of the total number of essential amino acids, which emphasizes their importance for stable life and activity.
Important! According to research, it has been proven that amino acids with a special branched chain ensure the preservation of muscle mass and strength during active exercise, as well as during periods of stress, and they also increase the degree of endurance.
Readers found these materials useful:
Harm and benefits of amino acids
The “atoms” of the body’s building material are present in our body in sufficient quantities. To begin with, muscles are essentially 100% protein, and 20% is made up of bone and cartilage tissue. Also composed of amino acids:
- many hormones involved in metabolic processes;
- antibodies that increase resistance;
- enzymes that trigger and maintain the normal course of biochemical reactions;
- hemoglobin, which transports oxygen molecules to body cells.
Of course, the importance of amino acids for health is enormous. Firstly, they are an excellent means of building muscle mass, which is successfully used by athletes, especially after intense training, as a result of which collagen is destroyed. Due to their anabiotic properties, protein components quickly penetrate into the blood and after 20 minutes begin to function in muscle tissue.
Secondly, amino acids destroy subcutaneous fat. dulls appetite, so food containing large amounts of protein, as well as special dietary supplements, helps to lose excess weight.
Third, protein building blocks—not all of them—are wonderful antioxidants. In other words, they are responsible for prolonging youth and preventing cancer. Taurine, sulfur, arginine, and tyrosine, in particular, have such properties.
Fourthly, amino acids support the functioning of the central nervous system and brain, heart muscle and blood vessels, kidneys, bones - that is, the whole organism as a whole, because each protein component has its own specialization.
Damage to the structural units of protein fibers also occurs. Thus, improper use of essential amino acids causes food poisoning and problems in cardiac function. Athletes who have reduced the amount of protein entering the body can instantly lose all the muscle mass they have built up with the help of “building blocks”.
Bcaa and its composition
High-quality sports nutrition bcaa is a complex of three natural amino acids: leucine, valine, isoleucine.
These components are isolated from whey protein, the raw materials for which can be fermented filtered cow's milk and eggs.
Wherein:
- Valine is necessary for men and women who engage in fairly high physical activity to maintain normal nitrogen levels so that their muscles can receive sufficient energy for growth, general metabolism, and restoration of tissue structure.
- Isoleucine is responsible in the body for men and women for the synthesis of hemoglobin, normalization of blood sugar levels, and energy supply to muscle tissue cells.
- Leucine is not only an active component of metabolism, but also a kind of catalyst that forces all components to work interconnectedly with full efficiency.
In normal life, these essential amino acids are not synthesized independently in the body of men or women, so they can receive them by eating:
- Meat;
- Cereals;
- Orekhov;
- Eggs;
- Brown rice;
- Fish;
- Legumes, especially soybeans;
- Gribov;
- Dairy products;
- Peanuts;
- Liver.
Advantages
If the correct dosage is observed, the complex of essential amino acids cannot cause harm. Moreover, it performs a number of important functions:
- firstly, the body receives high-quality nutrition for the formation of new muscle fibers and overall health promotion;
- secondly, bcaa amino acids trigger anabolic processes;
- thirdly, the advantage of amino acids is that they stop catabolism even after active training sessions. The body receives everything it needs to stop the breakdown of its own fibers due to protein deficiency;
- fourthly, sports training, proper nutrition and bcaa amino acids allow you to burn subcutaneous fat much faster and achieve your desired results;
- fifthly, sports nutrition is absorbed within 15-20 minutes after consumption, which allows us to talk about the maximum effectiveness of the training process;
- sixthly, when taken correctly and without any special contraindications, amino acids do not cause harm. Moreover, the body of any person (and especially an athlete) urgently needs them.
https://youtu.be/lLSj7QTQkXE
Sports nutrition amino acids – what are they?
In sports nutrition, it is customary to conditionally divide the types of product under consideration into several categories:
- Complex amino acids;
- BCAA;
- Individual amino acids.
Complex Supplements
contain all the amino acids (20 pieces) from which protein is formed. At its core, it is the same protein, but in a more convenient form for consumption. Another benefit is faster absorption.
BCAAs
– This is the most popular type of amino acids in sports nutrition. They can be taken both during the period of weight gain and during “drying”. It is recommended to take it before and after training. During “drying” they are used to preserve muscle volume and accelerate metabolism to speed up the fat burning process.
Individual amino acids
They are a sports supplement containing only one amino acid. Some of the most popular in this category are carnitine and glutamine. Carnitine is great for taking during “drying”, because this substance can accelerate the process of utilization of subcutaneous fat. There is an opinion that the more glutamine there is in the blood, the less likely it is that catabolic processes will occur, so this supplement is also worth paying attention to.
The choice is yours, but it is worth noting that the most common amino acids in sports nutrition are BCAA. Professional athletes prefer to enrich their diet with this supplement option. Individual amino acids can be taken if you have an acute deficiency in them. Instead of complex supplements, the option with ordinary protein will be more economical.
The best amino acids according to customers!
Simply a monumental amino acid product in its composition. A bold decision was implemented: to supplement the amino complex with vitamin and testosterone booster matrices. As well as stimulants and energy drinks for focus and concentration. This approach is completely justified: this product works both during and after training. Providing consistently high levels of energy, endurance and quality recovery.
Where are amino acids found?
The sources of these substances are foods high in protein:
- Poultry eggs: chickens, ducks, quails, geese. They contain all the necessary essential amino acids. Protein from one egg covers about 10% (6.3-6.5 g) of the daily requirement for an adult.
- Fish is a source of healthy fats and amino acids. Protein from fish is easily digestible and is recommended for dietary nutrition and for children's menus.
- Animal and poultry meat supplies the body with complete protein and contains cystine and methionine. Beef contains less saturated fat, which is a source of “bad” cholesterol, than pork.
- Vegetable protein from soybeans provides essential amino acids. Soy products contain little fat, but can affect hormonal levels and provoke the appearance of tumors in people with a special form of cancer that is sensitive to hormones.
- Dairy and fermented milk products are rich in tryptophan. Their use helps strengthen joints and bones.
Some amino acids can be obtained from buckwheat, oatmeal, broccoli, onions and garlic, peanuts, and almonds. The source of glycine is ready-made dishes with gelatin. A balanced diet that includes plant and animal proteins will help you get essential amino acids.
Recommended daily dose of BCAA
The standard dose of isoleucine is 48 to 72 mg per kilogram of body weight. The recommended dose of leucine is 2 to 10 grams. This equates to approximately 20g of combined BCAA amino acids with a balanced ratio of leucine and isoleucine per day. [39]
One dose of a BCAA dietary supplement should contain 5 to 10 grams , depending on the timing.
Ideally, BCAA's should be taken 30-60 minutes before exercise and then immediately after exercise. At the same time, it is recommended to mix BCAA with water and take it during exercise in order to have enough energy and suppress fatigue at the same time. [39] [40]
Conditionally essential amino acids
The most important of them are:
- glutamine; acetyl L-carnitine.
Glutamine regulates glucose levels during exercise, protects the body from infections by increasing immunity, and helps in wound healing.
The use of acetyl L-carnitine is effective during physical activity to increase aerobic performance. Also this amino acid:
- helps in the economical consumption of glycogen when performing strength exercises;
- is responsible for the transfer of fat to mitochondria, where its metabolism and utilization occurs;
- regulates the activity of antioxidants and the response to stressful situations;
- helps reduce the amount of lipofuscin, which is an aging pigment.
Amino acids are the constituent components of proteins. Therefore, they help restore muscle structure and are necessary for their growth in volume.
Is BCAA harmful?
Recently, among people associated with sports, there has been a lot of noise about BCAAs. Reviews say completely different things: sometimes these amino acids are necessary for the body, sometimes they cause harm.
If you consume a product of dubious quality and origin, then, of course, it can be hazardous to health. The demand for BCAAs is growing, and in connection with this, underground enterprises are not sitting idly by, producing dubious counterfeits.
Incorrect storage conditions can also have an adverse effect on the quality of the product. To avoid this, it is important to study the necessary operating rules and follow them to avoid spoilage of the food additive. Also, be sure to know your consumption guidelines and stick to them.
The effect of BCAAs on the liver is possible only if you have liver and kidney diseases. In this case, use may indeed cause some side effects and it is better to consult a doctor before use. But in general, in the absence of such diseases, there is no harm from BCAAs. Reviews mainly talk about the good help these amino acids provide to the athlete’s body.