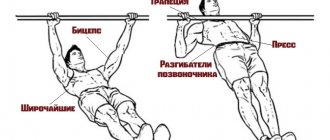
What muscles does cycling exercise work?
As mentioned earlier, the bicycle exercise is mainly used to develop the abdominal muscles. Due to the fact that when performing we bend and rotate the torso. The load is placed as if on a straight line,
and on
the oblique
abdominal muscles. In addition to them, they work:
- Gluteal muscles. They stabilize the pelvis and are responsible for hip extension.
- Muscles of the back of the thigh. Extend the leg at the knee and hip. And they are also responsible for stabilizing the pelvis.
- Muscles that extend the spine.
They are also torso stabilizers.
You can learn how to train the oblique abdominal muscles from the article “LATERAL PRESS EXERCISES“
Although the exercise is aimed at developing the abs. But with the wrong technique. The above muscles can take on a dominant role. And the effectiveness of your work will greatly decrease.
Increased tone
What muscles are pumped up when cycling and what is the best way to do it? If you are interested in these questions, there are some recommendations that you need to follow:
- When pedaling in a circular motion, if you imagine a clock, the muscles of the thigh or quadruple are activated maximum at the 9 o'clock position, in the pull-up phase. The cycle begins when the hip and knee press on the pedal. This action is aided by the gluteal and quadriceps muscles, followed by the hamstrings and calves.
- The gluteal fibers are responsible for initiating the downward phase of the bicycle pedal stroke, so they work every time you press. You can improve your tone by going to the mountains. Steep hills force your muscles to work harder. The ride will put a lot of stress on both your buttocks and thighs. This results in improved strength and muscle tone after recovery.
- Cycling targets the calf muscles through plantar flexion during the pedal stroke. Plantarflexion is actually the same action created when you stand on your tiptoes. The maximum tension occurs at the points of the pedal stroke that correspond to five and six o'clock on the clock face - the leg is bent and the toes are pointing down.
The calf muscles play a small role in cycling, but the benefits from them will be fully justified by the slimness and beautiful relief.
What will we get from doing this exercise?
- Comprehensive workout of all abdominal muscles. Due to this, we can not only achieve the desired cubes, but also reduce the volume of the waist. Thus giving the body a more athletic appearance.
- Accelerates metabolism, which promotes faster fat burning. In order for the effect to be more pronounced, it is worth adding a power load. And also reconsider your diet.
- Exercise bicycle will strengthen the muscles of the legs and pelvis. Of course they will not increase in volume. But their general appearance will change. Which is very important for girls.
- Performing this exercise is an excellent way to combat blood stagnation in the pelvis. This is especially true for people leading a sedentary lifestyle. Or office workers who spend many hours in a sitting position.
- Posture also improves due to the fact that a large number of stabilizer muscles are involved.
- During the exercise, the abdominal muscles are in constant tension. Therefore, they receive both dynamic load during twisting and turning. And static, at the moment of maintaining full muscle contraction. This load is somewhat reminiscent of the VACUUM EXERCISE.
It is worth considering the fact that the exercise bike is great for home workouts. This makes it public. And the correct inclusion of it in your training program. It will help you create a thin waist, sculpted abs and a toned body.
Anaerobic vs Aerobic
The brain sends a signal to the body, regardless of which muscles are trained when cycling. But what powers the fibers during the thousands of contractions that occur during a long ride? You've probably heard the terms aerobic and anaerobic. They describe two ways in which muscles receive energy.
During aerobic exercise, tissues use oxygen, glucose and fatty acids carried in the blood to produce adenosine triphosphate. ATP is the energy source that allows muscles to contract. The ability to ride a bike for long periods of time depends on the delivery of oxygen and fuel molecules (glucose and fatty acids) to the fibers. And this, in turn, depends on the blood circulation and respiration provided by the heart and lungs.
When performing anaerobic exercise, muscles draw on stored glycogen (which is formed from glucose) and convert it into ATP. During this type of high-intensity exercise, the fibers produce energy without oxygen. Anaerobic training comes at a cost because a waste product called lactic acid builds up. It causes a burning sensation and causes rapid fatigue.
Bicycle exercise technique
Option for beginners
Since the classic version with rotations can be very difficult for beginner athletes. There is an easier version of this exercise. Where only the legs are involved in the work. To better stabilize your torso, you can grab onto something with your hands. When performing the exercise, most of the load will shift to the lower sections of the rectus abdominis muscle. Also, the gluteal and hamstrings will take an active part. The oblique muscles are not involved in this version.
Performance:
- Place a special rug or something on the floor so that you can lie on it comfortably. Or sit on a bench.
- Place your hands behind your head or grab something.
- Press your lower back to the floor. To do this, we will need to round it up a little.
- Tighten your abs and bend your legs at the hip. Until they are perpendicular to the floor.
- Now we bend our legs at the knee joint until they form an angle of 90°.
- And from this position we begin to rotate our legs, as if we were pedaling a bicycle.
During movement, the lower back should not bend or lift off the floor. Movements should be smooth. We work not for speed, but for quality. While rotating the legs, we should feel the work of the main muscle groups. We focus special attention on the press.
Execution option for more professional athletes
Now we are adding rotational movements with the upper body to the previous version. Thus, we actively use the oblique and rectus abdominis muscles. In order for the exercise to be beneficial, your movements must be synchronized. You need to pull the elbow to the opposite knee, the left to the right and vice versa, the right to the left.
Performance:
- We lie down on the floor; for convenience, you can use a gymnastic mat.
- Bend your knees until they form a 90° angle. Then we lift them up.
- We place our hands with palms on the back of the head.
- Press your lower back to the floor. It should remain in this position throughout the entire execution.
- From this position, we begin movements with the left elbow to the right knee. At the end point of the twist, exhale. At the same time, we straighten the left leg and keep it suspended.
- Next, while inhaling, we change sides and now, the right elbow moves towards the left knee.
- We do this for a given number of times
Don't cross your arms at the back of your head. This will create additional stress on the cervical vertebrae. And on the last repetitions, you will involuntarily pull yourself by the head to do at least one more repetition. All your movements should be smooth. There is no need to turn the exercise into elbow swings. Work at full range. Trying to touch your elbow to your knee. The lower back should be pressed to the floor. To avoid excessive stress on the spinal column.
Training on a recumbent bike
If you're wondering what muscles cycling strengthens, the following information may be helpful: Recumbent models provide more back support than upright models. It may take some time to get used to traveling in such a vehicle, but sitting lower than the standard level on a bucket seat with a backrest will provide invaluable muscle benefits. What muscles are strengthened when riding this type of bicycle:
- Quadriceps (hips).
- Glutes (buttocks).
- Hamstrings.
- Tibialis anterior (lower leg muscles).
To get the most out of your cycling exercises, follow these guidelines:
- Make sure the seat height is comfortable. The knee should be slightly bent when the leg is at right angles to the floor;
- Try to maintain a rotation speed of 90-120 rpm, as this will cause minimal stress to the joints;
- If you don't feel comfortable being outside, use an exercise bike.
- Make sure you dress appropriately for the weather. There is no logic in cycling if you can't stay warm or feel uncomfortable;
- Take your muscles to the next level with clipless pedals. When the foot is not held in place by a clamp, the muscles control the pedal stroke, resulting in a better toning effect.
Fitness experts acknowledge that cycling is a low-impact sport, with various injuries often occurring during cycling or training. The most common are foot injuries, knee bursitis, tendon ruptures, lower back pain and muscle strain. Most injuries can be treated quickly, but you can avoid them entirely with specific flexibility exercises, strength training and precautions. Wearing a helmet, traveling at a safe, manageable speed, and following local driving laws greatly reduces the risk of tragedy.
We hope you have found the answers to the question of what muscles cycling trains and are ready to improve your fitness!
How can we make the exercise more difficult?
In addition to these two options, we can further complicate the exercise. This is done so that progress does not stop. Because our body gets used to the same type of movements too quickly. What can we do to avoid this?
- Take extra weight into your hands. For these purposes, barbell weights, a small kettlebell or dumbbells are perfect. It is very important not to overdo it with weight.
- Attach weights to your legs. There are special weights with sand that can be attached to the lower leg. They will also make the exercise more difficult.
- Rubber expander . The principle here is the same as working with weights. Only when working with an expander will we have to fight the force of resistance.
- Slower pace of execution.
If we perform the bicycle exercise at a slow pace, we can increase the time when the abs work statically. That is, the moment of its complete contraction.
You should start with these options only after you have completely mastered the basic technique. But you must understand. That lifting weights will affect the thickness of your muscles. Making them more voluminous. What can affect your waist width? So you should approach this step wisely with full awareness of what you are doing.
Basic errors during execution
Performing the exercise using the muscles of the legs and buttocks
Many athletes do not quite correctly understand the essence of performing the bicycle exercise. They focus on bringing their elbows together with their knees, completely forgetting to include the abs in the process. But our main task is to load the abdominal muscles as much as possible. To do this, we must exhale, pull in the stomach a little and try to bring the lower ribs to the pelvis. This moment will allow us to tighten our abs. This is why there is an option for beginners. So that we can learn to tense the muscle groups that we want to load.
Hand twisting
That is, at the moment when the athlete, performing an exercise, begins to put pressure on his head with his hands. Thus trying to bring the upper body closer to the pelvis. This approach can lead to injury to the cervical vertebrae. To avoid this, it is best to place your palms next to your ears. This way we will completely eliminate the possibility of helping ourselves with our hands. And we can only rely on the abdominal muscles.
Lifting the lower back off the floor
When we lift our lower back off the floor, we create additional stress on the spine. Also, transferring weight to the pelvis will affect balance. And instead of concentrating on the work of the press. We will put a lot of effort into stabilizing the body. Of course, we are not talking about the option where we raise the pelvis and hold the lower back with our hands in weight.
Tips for maximum efficiency
- Before you start doing the cycling exercise, you should warm up properly. Particular attention should be paid to the hip and knee joints, as well as the lower back.
- It is best to perform this exercise at the beginning of your workout. Because there are more chances that you will do it. At the end of the workout, you simply may not have enough strength and motivation to do it.
- If you cannot reach your elbow to your knee, then you should work on your flexibility.
- There is no need to throw your pelvis while moving. This will not help you in any way, but will only confuse you.
- If you find it difficult to keep your straight leg suspended. Then, at the initial stage of mastering the exercise, you can lower it to the floor.
- Try to work at the maximum possible amplitude. But do not forget that we do not lift the lower back off the floor.
- While performing, do not hold your breath. At the moment of twisting we exhale, and at the moment of relaxation we inhale.
- To perform the exercise, we use only a hard surface. Making a bike on the couch is not the best solution. Since it will create additional stress on the spine.
- Don't chase too many reps. Quality is more important to us. It is better to do 5 times in a set, with full awareness of the matter and concentration on the work of the press. Than make 10 just to have it.
In a word, we can say that the bicycle exercise is one of the best for working out the abdominal muscles. The main thing is to master its technique and learn to feel the tension of the press. For beginner athletes, it is best to master cycling with a simpler technique. For greater results, it is best to perform this exercise with others to develop the abdominal muscles. The articles “BEST EXERCISES FOR THE UPPER OR LOWER PRESS” can help you with this.
Good luck to everyone in your training!
Number of approaches and repetitions
The number of approaches and repetitions depends on the level of physical development of the person. With a small number of repetitions, a beginner will pump up the abs well without causing harm to the body.
Training table:
| Athlete level | Number of repetitions | Number of approaches | Rest between sets |
| Beginner (rotation of legs in the air) | 16 | 3 | 90 seconds |
| Advanced (with turns in one direction or the other) | 6 (per side) | 2 | 1 minute |
| Experienced (with turns in one direction or the other) | 10 (per side) | 5 | 1 minute |
We recommend reading: Food additive E104: dangerous or not, effects on the body