Duration of creatine course.
Based on the above studies, most say that creatine can be taken on an ongoing basis. But you have to be careful because there are studies that have found downregulation of cellular transporters. In theory, this could lead to a significant decrease in muscle sensitivity to this supplement. According to data, this occurs after approximately two months of daily creatine supplementation.
So, after a two-month course, it would be reasonable to take a break for 3-4 weeks; this period of time is quite enough to restore muscle sensitivity.
There is no effect from taking creatine, the reason?
Many athletes are concerned about the question: how to take creatine correctly? After reading articles, as well as sports literature, you decided to take creatine, already chose a method and purchased a supplement, completed the course, but there was still no result. There is no explosive power, no increase in muscle mass. So what's the problem?
According to statistics, the effect of creatine is not achieved in 30% of athletes who used it. This is due to the transport of creatine into the blood from the stomach. For the simple reason that creatine has the required effect only if, when it enters the blood, its natural structure is preserved.
Due to the personal characteristics of the body of some athletes and the general instability of the creatine solution, it can turn into useless waste in the stomach - creatinine. Therefore, more stable solutions of creatine are required, for example creatine with grape juice. Simple carbohydrates (glucose and dextrose) significantly accelerate the delivery of creatine into the blood before it turns into waste. In addition, gelatin capsules with creatine may be effective, as they partially prevent the conversion of creatine into waste.
Taking creatine is an individual matter, but general recommendations will be appropriate and useful for you.
Tags:
athlete's diet
1
okbody
To leave a review, log in or register:
https://youtu.be/L6Lrw6G-JjE
Creatine and water retention
The property of creatine to retain water will allow you to increase weight by an average of 2-4 kg per cycle. It doesn’t look like puffiness and swelling, the muscles are more likely to fill up and the relief will improve. But it won't last long. During the necessary creatinine pause, water is removed from the body naturally.
When mentioning how much weight you can gain with creatine, precisely due to dry mass, experts vary the coefficients on average from 0.5 to 1.6 kg per month. You can say for sure only by knowing the individual characteristics of the body and the athlete’s training program.
Thus, creatine for weight gain is just as important as protein gainers.
Time of administration, before or after training
Just like medications, sports nutrition for bodybuilding must be taken at a certain time. And if everything is clear about how to take creatine monohydrate, then the opinions of athletes and experts differed regarding when to take the supplement. Some believe that it should be consumed before training, while others believe that it should be consumed after. In addition, the administration time may vary depending on the form of the purchased drug - powder, liquid or capsule. The timing of intake is affected by the supplements included in sports nutrition.
The powder is most often taken before training. If you are loading with creatine, then the drug is divided into 4 parts, 5 g each, and taken throughout the day. During the maintenance phase, the drug is drunk 2 times a day - one part before training, and the second after.
According to experienced athletes, it is not so important when the supplement is taken. After all, performance mainly depends on the level of amino acid content in the muscles.
If it is high enough, then the result will be. Although there is creatine with a transport system, which is taken only before training.
By taking the powder before training, you can ensure its stable level for 1 - 1.5 hours. If training is not carried out during this period, the substance will simply leave the body naturally.
Thus, sports nutrition is best taken before training, approximately 1 hour before. This is how long it takes for the substance to be absorbed by the body. The training usually takes one and a half hours. After which, the remaining unused substance will be removed. For example, the lesson runs from 9 to 10-00 in the morning. In this case, the drug should be taken at 8-00. By the allotted time, the substance will have time to enter the muscles, and they will be ready to accept the load.
At 9-00, when training begins, amino acid reserves in the muscles will gradually begin to be used up and by 10-00 they will completely dry up. After that, the blood will supply creatine to the muscles, and its level will still be high. As you can see, it makes no sense to train longer. And the drug itself, taken before exercise, is active before, after and throughout the entire workout, which is very beneficial. It turns out that taking an amino acid after a workout is useless? This is not entirely true.
Many people are interested in how to take creatine monohydrate on days without training and is it necessary to do it? There is an opinion that the course should not be interrupted for a day and that the powder should be consumed daily. Otherwise, training the next day after rest, when the level of creatine in the body decreases, will be ineffective. There is no scientific basis for this, so everyone decides for themselves whether to take the supplement on rest days while taking a course or not. Some athletes reported faster muscle recovery after training if they also took the supplement on rest days at night.
Creatine with a transport system contains substances that improve its absorption. The components of this supplement promote rapid delivery of the substance to the muscles. You should take creatine with the transport system only on training days.
Thus, knowing how to take creatine correctly, you can avoid troubles in the form of side effects that usually result from the use of chemical drugs. Creatine-based sports nutrition will help significantly improve results, gain muscle mass and eliminate the feeling of fatigue during training. By learning to choose, prepare and consume creatine correctly, you can reach new heights in bodybuilding.
Why take creatine?
Many people confuse weight gain with mass gain. The main difference is that in the 2nd case, the priority is precisely the acquisition of lean muscles for subsequent work on the relief, and in the first, on the contrary, as a protection against dystrophy and deficiency of adipose tissue, it is important to increase the total body weight in any way.
To understand whether creatine is needed when gaining weight, you need to know its main functions.
The ability of creatine supplements to increase useful muscle volume is associated with water retention and does not partly affect actual muscle growth, since they are “deflated” during the natural removal of excess fluid.
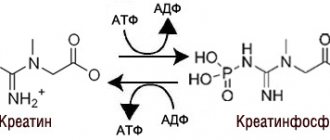
However, creatine in the body is important for its effect on phosphocreatine, which not only improves energy transport at the intercellular level, but also in turn is a stimulator of ATP resynthesis, increasing the productivity of intracellular energy exchange. Thus, the productive performance and endurance of muscle fibers increases, which, when interacting with intensive training and protein consumption, provokes their development, regeneration and, accordingly, growth.
In addition, the active substance in the supplement increases strength, endurance, suppresses lactic acid, and also reduces inflammation in injuries.
Thus, creatine helps to gain weight and quickly recover after exercise.
Creatine for gaining muscle mass also stabilizes the heart rate in athletes with disorders of the cardiovascular system, allowing ectomorphs with cores to train fully, provoking tissue growth without harm to health.
A special role in increasing muscle volume is played by the ability of creatine to stimulate the natural synthesis of proteinogenic amino acids, as well as their transport to the muscle depot.
There are about 16 effective supplement formulas, but if you choose which creatine is best for gaining muscle mass, it is undoubtedly monohydrate - the most fully absorbed mixture of creatine and water molecules. It is slightly inferior to hydrochloride, a relatively young formula that has already gained popularity among many eminent athletes due to the highest quality of absorption and power of action.
Side effects and harm to the body
Creatine is a fairly safe supplement, and dangerous, and especially irreversible, effects when taking it are almost impossible. Most of all cases of painful reactions are associated with additional substances characteristic of a particular manufacturer brand.
The most common side effect is fluid retention, which results in mild swelling. But fortunately, the amount of accumulated water is not so large as to have any harmful effects on health. Moreover, in no case should you fight this with the help of diuretics: it is extremely easy to get a dangerous form of dehydration, which, by the way, can also arise from insufficient water consumption while taking creatine.
In some cases, creatine causes digestive disorders, which are usually associated with the loading phase. Typically, this side effect can be resolved by reducing the dosage or using another form of creatine, such as citrate or malate. Also, it is not recommended to take creatine for people with kidney disease.
Otherwise, the supplement no longer gives any cause for concern. To avoid discomfort during the cycle, it will be enough not to consume excessive amounts of creatine and drink plenty of water in order to prevent dehydration.
Functions of creatine
The main functions of creatine are as follows:
- Helps the body produce protein
- Acceleration of metabolism
- Increased stamina
- Preventing muscle wasting
- Helps muscles recover after exercise and eliminates burning sensations
Some believe that sports nutrition with creatine can be used for weight loss. Motivating this is that the substance stimulates metabolism, which means that the weight loss effect is inevitable. However, many athletes received a bonus in the form of weight loss only after stopping the drug. To achieve weight loss while taking this amino acid, you need to drink more water. Then, in addition to losing weight, you can get a beautiful relief.
It must be remembered that taking creatine monohydrate is incompatible with drinking coffee and alcoholic drinks. On the contrary, better absorption of the substance is facilitated by carbohydrate nutrition and sweet drinks. This way the substance will quickly get into the muscles and perform its function.
How to take creatine monohydrate
Currently, there are two main ways to take the most effective formula of creatine - monohydrate. Option 1 - with loading, option 2 - without loading. By the way, both ways to drink creatine are effective. Also, each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages.
According to the first option, you will have to take 20 grams of powder per day for 5-6 days (4 doses of 5 grams each), with a glass of sweet juice or water with sugar/honey. This is called the loading phase. According to the theory, the muscles should be completely saturated with creatine during this time. Then, the maintenance phase begins, which involves taking creatine monohydrate in the amount of 2-3 grams once a day.
Scientific research shows that with this approach, the maximum level of creatine in muscles can be maintained for up to 10-12 weeks. It would seem that this is the ideal regimen for taking creatine. However, as new modern independent scientific research shows, you can completely do without the loading phase.
According to the second option, how to take creatine monohydrate, the loading phase is excluded from the dosage regimen. Just take 5-6 grams of creatine per day. Personally, I prefer this regimen for taking creatine. It copes no less effectively with the task of pumping up muscles and increasing endurance. In addition, taking creatine without loading minimizes the risk of side effects and reduces creatine consumption, unlike taking creatine with loading.
Another argument why you should choose a creatine supplementation regimen without a loading phase is that, according to scientists, the body is able to absorb no more than 5-7 grams of creatine per day. Everything else is simply excreted in the urine. That's it, friends. Draw conclusions.
When to take creatine?
As you understand, not only how correctly, but also when to take creatine matters a lot. Indeed, at different times of the day, the body can react differently to sports nutrition, including creatine, regardless of the form of its release. There are several options for when to drink creatine:
- you can take the supplement in the morning, immediately after sleep;
- can be taken an hour before training;
- You can drink creatine after completing your workout.
Which option can be considered the most optimal? According to scientific research, it is most advisable to take creatine about half an hour after training along with fast protein or with grape or other sweet juice. On rest days, it is most effective to take creatine monohydrate in the morning, immediately after sleep, with a glass of juice or water with sugar/honey.
These recommendations on how and when to take creatine apply to all forms of creatine, be it capsule or powder. The main thing is to follow the recommended dosages and regimens for taking creatine.
Choosing Creatine
There is no clear answer to the question of which creatine is best for gaining muscle mass. There are more than 15 effective formulas, each of which has its own benefits. However, according to research, monohydrate is the most effective for this purpose. It is available in 3 types:
- capsules;
- pills;
- powder.
Manufacturers claim that the rapid absorption of liquid creatine makes it the best among analogues. Indeed, this is one of the main benefits of the supplement in this form. However, due to this, the overall effectiveness of the substance decreases. Therefore, experienced athletes still choose creatine in powder form.
Hu from Creatine? For those who are not in the know
If you don’t quote Wikipedia, then this is a substance that is found in animal meat and fish. It ensures energy metabolism in muscles. A high concentration of this substance increases performance, improves well-being, and increases strength potential.
For the average person, a balanced diet is enough to get enough creatine. But when working with iron, the reserves of the substance are quickly consumed and in order to feel how it works, an additional intake is necessary.
It is unrealistic to obtain the required concentration of the substance through food. A person is unable to digest such an amount of meat in a day. Later, when we move on to dosages, you will understand why.
Creatine without sports
Many people with a lean body constitution think about the effectiveness of creatine without active sports. There is a simple rule here: almost any supplement works only with regular physical training. Moreover, due to the peculiarities of taking creatine, it will be most effective only after active warming up of the muscles.
For an ordinary person, the amount of this substance contained in food is enough. Animal meat and fish are richest in creatine. Taking the supplement would be justified for adherents of a vegetarian lifestyle. In this situation, there is often a deficiency of the substance in the body, so the daily need for it is met artificially.
Fish is rich in creatine
How to take creatine
There are two methods of reception: with and without loading. Loading involves a sharp increase in the concentration of the substance, and then maintaining the required level.
Without loading, it means a gradual increase in the amount of creatine in the muscles by taking small doses over a long period of time.
The reception scheme with the loading phase looks like this:
- First week. The supplement is taken 4 times a day, 5-10 g per serving. That is, 7 days, 20-40 grams of the supplement are consumed per day.
- From the second to the fourth week, the supplement is consumed twice a day, 3-5 g. Thus, the required concentration of the substance is maintained.
Taking this supplement without loading means that from the first to the fourth week you drink creatine twice a day, 5-10 grams.
If you take powdered creatine, then dilute it with cold boiled water with the addition of fast carbohydrates. They help it to be better absorbed. To kill two birds with one stone, dilute it with non-sour juice. Do not use orange or similar juices; acidity will ruin the properties of the supplement.
If there is no juice, or the toad is pressuring you to throw away so much money on a dubious drink, then add honey to the water.
How do I take creatine
To get all the bonuses as quickly as possible, I start the reception from the loading phase. The first week I take the supplement 4 times, 5 g each, then until the end of the month I maintain the concentration in small doses of 5 g twice a day. I dilute it with water and honey.
Bonuses of taking creatine
During the first 7 days of taking it, while the concentration of the substance was rising, I did not notice any serious changes. But already from the second week, performance increased noticeably.
The volume of training increased, by the end of it I did not feel exhausted, and I began to catch “comes” less and less. Strength indicators increased, failure began to occur later. In addition, due to water retention, which is typical for this supplement, body weight increased.
What kind of creatine do I use?
There are several types, but the recognized leader is monohydrate. This is what works for most people. Yes, unfortunately, there are those who do not feel the effect of taking this supplement.
If we talk about specific brands, I liked the monohydrate from MyProtein more. It works, tastes good, and the price tag doesn't make you want to sell your last pair of pants. To avoid being slipped in the “Chinese original”, buy creatine in a company store.
Speaking of taste. I took “Berry Explosion”, but if you plan to take creatine for a long time, then I advise you to use two flavor options. It's more expensive, but it doesn't get boring, especially during the loading phase.
What to combine creatine with
The classic combination of creatine monohydrate + BCAA works great. If you make a shake, then take both in powder with the same taste or options without flavoring fillers.
When to start taking creatine to gain muscle mass?
A guy comes to the gym, it’s immediately obvious that it’s his first time. And almost right out of the gate he gives me a list of what he wants to buy: protein, gainers, creatine. I don't argue with him, I suggest:
— Buy anabolic steroids immediately.
He doubts.
— Can you give yourself an IV? – I’m interested.
“No, why?” he’s already getting scared.
- Well, of course, today you can start giving yourself IV drips with nutrition!
I see that he is on the verge of running away, then I explain that in the first six months he may forget all the names he has learned, they will not be useful. Often, it is impossible to get through in any other way.
Returning to the nitrous oxide example, injection occurs when maximum speed is reached on conventional fuel. Then you need to take creatine, then the result stops in one place, and you have several workouts in a row and the weights in the exercises do not increase, and stagnation begins.
Actions of creatine - scientifically proven facts
Taking creatine in combination with strength training leads to a synergistic effect - mutually enhancing each other's effectiveness in relation to hypertrophy (growth) of muscle fibers and diameter (Research: Hespel P, Op't Eijnde B, Van Leemputte M, Urso B, Greenhaff PL, Labarque V, Dymarkowski S, Van Hecke P, Richter EA, Oral creatine supplementation facilitates the rehabilitation of disuse atrophy and alters the expression of muscle myogenic factors in humans, J Physiol 2001;536:625-633. doi: 10.1111/j.1469 -7793.2001.0625c.xd
).
Creatine promotes muscle mass gain, strength, muscle power, as well as muscle hydration (saturation with water). (Study: Branch JD. Effect of creatine supplementation on body composition and performance: a meta-analysis. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2003;13:198-226
).
When comparing training combined with creatine to training without it, there was a 25% increase in weight gain in the group of athletes who trained and took creatine. (Research: Kilduff LP, Pitsiladis YP, Tasker L, Attwood J, Hyslop P, Dailly A, Dickson I, Grant S. Effects of creatine on body composition and strength gains after 4 weeks of resistance training in previously nonresistance-trained humans. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 2003;13:504-520
).
12-week training with creatine supplementation provided greater gains in muscle mass and strength in athletes than training without the use of this supplement (Research: Huso ME, Hampl JS, Johnston CS, Swan PD. Creatine supplementation influences substrate utilization at rest. J Appl Physiol 2002;93:2018-2022
).
The mechanism of action of creatine and reasons for its effectiveness
To understand the reasons for the effectiveness of creatine, let’s consider the mechanism of its action on the body. Creatine has been found to act in several ways:
- If the concentration of creatine phosphate in skeletal muscle increases, it can be used by the body to provide short-term high-intensity work. This primarily applies to repeated intense exercise over short periods of time (for example, strength training). Research: Demant TW, Rhodes FC.
Effects of creatine supplementation on exercise performance. Sports Med. 1999;28:46-60 . - Increasing creatine phosphate helps maintain muscle tension more effectively. Research: Demant TW, Rhodes FC.
Effects of creatine supplementation on exercise performance. Sports Med. 1999;28:46-60 . - Creatine supplementation may improve cellular homeostasis by inhibiting pH changes.
- A decrease in the level of creatine phosphate in the cell leads to an increase in the amount of ADP, which is subject to rephosphorylation, which, in turn, increases the rate of glycolysis (glycogen synthesis). Research: Demant TW, Rhodes FC.
Effects of creatine supplementation on exercise performance. Sports Med. 1999;28:46-60 .
Thus, creatine has a direct effect not only on the growth of strength and mass of the athlete, it also increases the rate of recovery after strength loads (increases performance). However, informal research has found that as the rest time between sets decreases, the number of working repetitions decreases as well. At the same time, the growth in strength indicators and muscle mass was lower than in those athletes who rested for 2-3 minutes between each repetition. This fact shows that creatine, if it contributes to the growth of endurance, does so only indirectly, since in purely high-repetition training (from 15 repetitions) athletes who took creatine showed almost the same performance as those who trained without it.
Creatine and Muscle Growth: Two Main Theories
You probably know that the effects of creatine are not limited to stimulating muscle growth. It is also highly effective in terms of developing strength - and this may be part of the answer to our question. As you get stronger, you can lift heavier weights in the same rep range. By doing this, you create more mechanical tension in the target muscle, and this is the main catalyst for muscle hypertrophy. This is the first possible explanation.
Further enhancement of muscle growth may be due to the volume-forming effect of creatine. The fact is that creatine acts as an osmotically active substance and attracts water into muscle fibers. Water doesn't just physically increase muscle size; There is a theory that increased cellular hydration promotes muscle hypertrophy.
More specifically, in vitro studies have shown that cellular swelling increases muscle protein synthesis and slows down the breakdown of protein molecules—a three-pointer for hypertrophy! How this all happens in living cells is unclear, but the theory provides a promising and plausible explanation for creatine's effectiveness.
It should be noted that in this situation we do not have to choose only one of the possible options. Both cellular swelling and mechanical stress can play important roles in muscle growth, along with muscle microdamage. It is very possible that creatine has a positive effect on two, or even all three, of these mechanisms.
The best creatine and its most popular types
You will also be interested to know what types of protein exist and why you should use it.
Creatine monohydrate
Creatine monohydrate is the most sold and used form of creatine. This is the original type of creatine and has some disadvantages. For example, some people may experience bloating or other minor side effects.
Creatine hydrochloride
This form of creatine is said to eliminate the side effects found with creatine monohydrate. However, there is no research to prove that this is true. What has been proven is that creatine hydrochloride is more soluble in water and is taken in a lower dose.
Micronized Creatine
Micronized creatine is essentially the same product as creatine monohydrate. It is only produced in the form of crushed powder, which, according to manufacturers, improves solubility in water and absorption into the body. Read below about how to drink creatine monohydrate powder.
Creatine ethyl acetate
This supplement is a combination of creatine and an ester. Although it is not as well studied, many argue that it is not much different from creatine monohydrate.
Buffered Creatine
Buffered creatine is creatine fortified with magnesium, which improves the absorption of creatine by the body. According to the manufacturers, this supplement is capable of removing the byproduct of creatine, creatinine.
The consistency of creatine supplements varies, for example, it is available in the form of tablets, capsules, powder or liquid. Which form of supplement release you accept and take is, of course, up to you, because each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Liquid creatine most often has a good and pleasant taste, but, as many believe, is not very effective. The powdered supplement is the most popular and is easily soluble in any drink. Creatine tablets are slow to digest, but this may be a benefit for some people.
Creatine forms and effectiveness
Creatine, like any other nutritional supplement, comes in many forms. Some of them are better known and occupy leading positions in iron sports. This:
- Creatine monohydrate;
- Crealkaline;
- Anhydrous creatine;
- Creatine-glutamine-taurine;
- Creatine nitrate;
- Creatine tartrate (creatine with tartaric acid);
- Creatine titrate (helps absorb more creatine);
- Magnesium creatine;
- Long lasting creatine.
If we look separately at the most popular types of creatine and their effects, we can draw logical conclusions about which creatine is best for gaining muscle mass.
- Creatine monohydrate. Used in iron sports by weightlifters to increase strength endurance and muscle mass. The chemical composition successfully combines a microparticle of water and creatine. Available in pills, powder and tablets.
- CreAlkaline. Contains a creatine molecule, and alkali is used instead of water. It is believed that an alkaline microparticle can increase the biological effect of creatine by eliminating the acidic region of the stomach. It is considered a less effective supplement compared to its predecessor.
- Anhydrous creatine. Chemical composition – microparticle of creatine without the presence of water. Creatine content per serving is higher than monohydrate. The supplement is considered a worthy replacement for creatine monohydrate.
- Creatine-glutamine-taurine. Experimental combination of taurine with glutamine and creatine. It is believed that glutamine accelerates the synthesis and retention of creatine, and taurine increases strength.
- Creatine nitrate. Creatine is combined with a microparticle of organic nitrate (nitric oxide) in one chemical formula. The composition is used to increase strength characteristics and total body weight. Nitric oxide dilates blood vessels, creatine is better absorbed by the body.
Based on many years of experience of famous athletes, we can confidently select a “favorite”. This is definitely creatine monohydrate. Among all the “competitors”, this is the best creatine for gaining muscle mass.
How to use
In professional circles, you can often hear recommendations about taking creatine supplements in courses. This approach is characterized by the presence of a loading phase, when 20-30 grams are taken per day. creatine in 4-5 doses, and then the maintenance phase begins with a daily dose of creatine in the range of 5-10 grams. (depending on the intensity of the load and weight).
However, current research shows that this approach is unlikely to be effective. Our body needs creatine at every moment of time, and it simply cannot store this substance more than a certain individual norm. Accordingly, the recommended supplement regimen is 3-6 g. in one dose daily.
However, a more complex principle of taking creatine – cyclic – also demonstrates effectiveness. This is a purely individual dosage regimen, which involves manipulated doses within 1-2 grams. for more effective growth of strength indicators. This cycle is outlined by the trainer, but in general the scheme looks like this: for 6-9 days, creatine is taken at the rate of 0.3 g. per 1 kg of weight, and then for 2-3 weeks 0.03 g. per 1 kg of body weight.
What is creatine?
It is one of the three most popular sports supplements among gym goers. It is believed that it gives a noticeable increase in strength and is necessary when gaining muscle mass . This sports supplement is recommended for use if you have 1-2 years of training experience, this is due to achieving the greatest effectiveness from taking it. Let's take a closer look at the effect and mechanism of action. This is a natural substance that is broken down into phosphate in the human body, thereby taking part in the production of ATP (the main supplier of energy for muscle function). Creatine is a natural substance for the body, produced in it for normal energy metabolism. The mere fact that this substance is synthesized normally makes it clear that it does not pose a health hazard. For athletes, its effects on increasing explosive strength and gaining muscle mass are especially important. It may well provide an increase in one-repetition maximum in the bench press by 5-10 kilograms in the first week of use, and muscle mass gain can be about 5 kg per month. Its use is recommended for experienced athletes, as they are closest to the maximum results possible for their body.
Pharmacology of the drug
In order to understand the process of the substance’s action on the body, you need to know that ATP is a source of energy, without which contraction of muscle fibers is impossible. Therefore, a certain amount of this substance is always available in the body, but it is enough for a limited number of muscle contractions.
How does adenosine triphosphate manifest itself?
Large ATP stores help a person lift heavier weights and do more repetitions. At the same time, the necessary amount of energy enters the muscles, which is quickly converted, which contributes to the gain of muscle mass. This phenomenon is usually called explosive force.
Effects
Once we understand the mechanism of action of the drug, you can imagine the benefits of taking it. Positive effects from using the drug during constant strength loads:
- rapid growth of muscle strength;
- muscles are able to develop even greater energy;
- your performance will begin to increase (and you will be able to do more repetitions);
- gaining muscle mass;
- quick recovery after training.
The drug is relatively inexpensive.
Rules of use
The recommended daily amount is 3 to 5 grams. However, there is no consensus on the time of admission. Many people mix the powder with any supplements they have taken previously, for example, whey protein. The drug can be easily dissolved in tea, juices, water (it is best that it is warm). Do not forget that creatine should only be consumed fresh. Do not dissolve the powder in advance. It is advisable to take it in courses - for eight weeks with a break of four.
Side effects?
If the drug is used in recommended doses, it is safe. Remember that the following principle applies to creatine: more is not better . If there is an excess of adenosine triphosphate in your body, then all this will simply begin to be excreted. Creatine pumps water into your cells, so it is extremely important that you drink enough fluids while taking the product. Experts do not recommend using it before the age of eighteen. There is only one reason - no studies have been conducted on teenagers.
What effect does caffeine have on creatine?
According to the manufacturers of the monohydrate, too much caffeine can lead to a deterioration in the results that a person would achieve with creatine consumption. But caffeine in small doses will not affect weight gain in any way. Therefore, you can safely drink several cups of coffee a day (five milligrams per 1 kg of weight per day), without fear that this will in any way affect the effect of the drug.
Some myths about creatine
“Creatine harms the liver and kidneys.”
This myth comes about because creatine creates a byproduct called creatinine. Doctors check creatinine levels when looking at the health and function of your kidneys. Typically, when creatinine levels are elevated, the problem is not the supplement you are taking, but an underlying medical condition.
“Creatine does not make muscles bigger. It only promotes fluid accumulation.”
During the first two weeks, this statement will be considered true. During the loading phase, the body begins to retain fluid. After this stage, creatine begins to act at full capacity, increasing the size of muscle fibers, their specific gravity and density.
“Cretin causes dehydration.”
This statement appeared a long time ago. Many people are afraid to take the supplement due to fear of dehydration. Of course, this statement is just a myth. As mentioned above, creatine promotes fluid retention in the body. Read on to find out what you can take creatine with.
“Creatine causes stomach pain.”
A small caveat needs to be added to this statement. Yes, many people complain of stomach pain when taking the supplement, but the main reason for this is the wrong dosage or frequency of taking creatine. If you don't eat right and take large amounts of creatine, then you can't avoid stomach pain. Follow the recommendations and stomach pain will not become a problem for you.
Important conditions for taking creatine monohydrate
Creatine is not recommended for cutting. The reason is that it promotes the accumulation of water in the body. In addition, it requires simple carbohydrates for absorption. In such conditions it is impossible to “draw” the relief. At the same time, the ability to retain water makes creatine a necessary supplement during the off-season. It is taken to prevent injuries, since “filling with water” improves the biomechanical characteristics of muscles.
What is important to know when taking creatine
Creatine for muscle growth is more effective during anaerobic exercise. Its effect is most pronounced when performing exercises performed for no longer than 30 seconds. For this reason, taking creatine during endurance exercise is irrational. The reason is that due to fluid retention, aerobic training will make it difficult for the muscles to work and will lead to rapid fatigue.
Better absorption of creatine is observed in combination with insulin. It can be obtained from simple carbohydrates with a high glycemic index. This can be easily achieved by simply mixing creatine in juice. The highest concentration of sugar is typical for grape juice. It promotes insulin release better than other drinks. For the same purpose, you can use a high-carbohydrate gainer, and the more sugar it contains, the better.
Rating
Research by experts in the field of sports physiology and sports nutrition, as well as reviews and comments from athletes of different levels, have formed the following rating of creatine supplements:
- CellMass 2.0 from BSN. A powerful complex for use after training. In addition to the optimal dose of creatine, it contains glutamine and a full range of amino acids. Convenient serving dosage – only 9.5 g.
- Micronized Creatine Powder from Optimum Nutrition. It is considered the “purest” supplement – 100 grams of the product contains as much as 99.9% creatine.
- Micronized Creatine Monohydrate from AllMax Nutrition. An excellent option for budget creatine - almost 100% creatine content.
- CON-CRET from ProMera Sports. The choice of many professional athletes. Available in several different flavours, it contains no sweeteners or stimulants and does not require a loading phase.
- Creatine by Dymatize. “Working” budget supplement without any enrichments.
- Creatine from MusclePharm. A sensational product on the market is a mixture of five types of creatine, providing maximum replenishment of the substance pool.
- Performance Creatine from SAN An almost ideal supplement in terms of quality and cost per serving.
- Creature Powder from Beast Sports Nutrition. Another improved formula of 5 types of creatine.
- Lava from Universal Nutrition. One of the most powerful post-workout complexes with a high content of creatine and components that ensure its rapid absorption.
- SizeOn by Gaspari Nutrition. A complex for taking directly during training, loved by athletes precisely because of the optimal creatine content in an effective combination.
When choosing a supplement, remember:
- creatine is absolutely harmless;
- the supplement is necessary for every person, regardless of the type and intensity of exercise;
- the optimal daily dose is 5 g. in one go;
- intake time is not tied to the time of training - take protein when it is convenient (with the exception of when creatine is part of post-workout complexes);
- give preference to supplements from leading brands in your segment.
Author of the article: Shalukhin Alexander Alexandrovich
Personal trainer, pharmacologist, nutritionist Creates and conducts personal training programs for body correction. Specializes in sports traumatology and physiotherapy. Conducts classical medical and sports massage sessions.
How to Choose the Best Creatine
You can buy creatine either as regular monohydrate (a white powdery substance that is tasteless and insoluble in water) or as microcrystalline creatine in capsules. The advantage of the capsule form is that you do not have to mix the powder with water - monohydrate, as we mentioned, is extremely poorly soluble in liquid. In addition, when taking tablets, it is easier to control the dose of the supplement.
Speaking about “advanced” types of creatine, it is necessary to note Kre-Alkalyn in capsules. Although its effects on muscles are not fundamentally different from the effects of monohydrate, a noticeable benefit from taking it may be a decrease in abdominal swelling, bloating and stomach discomfort - an allergic reaction to taking regular monohydrate in some people.
Creatine monohydrate: disadvantages and harm
Today, monohydrate is one of the most researched sports supplements. Numerous experiments and scientific studies have not revealed any side effects for a healthy person (4). Regular consumption of doses up to 3 g of creatine per day is classified by doctors as “minimal risk of side effects for health” (5).
Despite the safety of the supplement, people suffering from chronic diseases (primarily asthma and various types of food allergies - including allergies to gluten and lactose), as well as pregnant women and people with any kidney disease, are advised to consult their doctor before starting to take creatine.
In addition, the effect on the body with regular and long-term use of creatine is not fully understood. There are studies showing that after 6-8 weeks of continuous use, monohydrate can provoke the formation of toxic compounds in the kidneys (6). In other words, it is safer to alternate a month of taking the supplement with a month of rest.
What is creatine: summary
- Creatine monohydrate is a sports supplement based on creatine found in meat that helps increase strength during exercise.
- Creatine should not be used for weight loss as it causes weight gain rather than weight loss.
- It is necessary to take monohydrate daily, in a dosage of 2-4 g; The time and form of administration are not important.
- To minimize possible risk, it is recommended to alternate 1 month of taking the supplement with 1 month of rest.
Scientific sources
- Creatine, An Article at Examine.com,
- Buford TW, et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: creatine supplementation and exercise, source
- Effect of creatine and beta-alanine supplementation on performance and endocrine responses in strength/power athletes, link
- Creatine Supplementation, link
Material rating:
Creatine - what is it? What is creatine monohydrate for and how to take it?
3.93 / 60
You need to enable JavaScript to vote
Hu from Creatine For those who are not in the know
If you don’t quote Wikipedia, then this is a substance that is found in animal meat and fish. It ensures energy metabolism in muscles. A high concentration of this substance increases performance, improves well-being, and increases strength potential.
For the average person, a balanced diet is enough to get enough creatine. But when working with iron, the reserves of the substance are quickly consumed and in order to feel how it works, an additional intake is necessary.
It is unrealistic to obtain the required concentration of the substance through food. A person is unable to digest such an amount of meat in a day. Later, when we move on to dosages, you will understand why.
How to take creatine
In general, there are a large number of different regimens for taking this supplement. But they all boil down to two basic principles:
1. The first scheme involves two reception phases: the loading phase and the support phase.2. The second scheme involves eliminating the loading phase.
Let's take a closer look at the first option. During the loading phase, the body is saturated with this drug and its reserves in muscle tissue are increased. This phase lasts on average 7 days. This week you need to take 5 grams. the drug 4-6 times a day. During this period, the maximum amount of creatine accumulates in muscle tissue, which remains at this level for a month, provided that a maintenance dose is taken.
This leads to the second phase – the support phase. During this phase, you need to take 5 grams of the drug once a day for 4 weeks. This is usually sufficient to maintain maximum concentration in muscle tissue. After the end of the maintenance phase, it is necessary to take a month's break from taking the drug to restore the body's own ability to synthesize creatine.
Now consider the second option, when the loading phase is excluded. Judging by the literature, the loading phase negatively affects the receptors, reducing their sensitivity, with decreasing dosages. To avoid this, the loading phase is eliminated, and the drug intake is evenly distributed over the month. Within a month you need to take 5 grams. creatine 2 times a day: in the morning immediately after sleep and an hour after training (these dates are not indicated by chance, the fact is that in order to achieve the maximum effect from creatine, it must be taken during periods when the level of insulin in the blood is maximum, and this is how once immediately after sleep and an hour after training). As a rule, during these 4 weeks the maximum concentration of the drug in the body is reached, and strength indicators increase.
Yes, I almost forgot, creatine is available in capsules and powder form. I use powder. I dilute one teaspoon (5 g) in grape juice. It's more comfortable for me. It cannot be combined with coffee and alcohol. Regarding training: during the period of taking creatine, it should be as heavy and intense as possible with an emphasis on basic exercises, otherwise the effect of taking it will be small.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=kXE-wXn6qZc
I hope I answered the question of how to take creatine. Do you want to know the whole truth about sports nutrition? Then don’t forget to subscribe to blog updates and receive the latest articles in your email.
PS. By the way, I advise you to familiarize yourself with the nuances of the technique of basic exercises in video format.
How does creatine work?
Thanks to its beneficial properties and unique composition, creatine helps an athlete increase body weight by increasing strength and increasing cell volume. Other amino acids are involved in its synthesis - arginine, glycine and methionine. How it works?
After the creatine cocktail enters the athlete’s body, active saturation of muscle tissue occurs. Once this natural process is complete, the elements in this dietary supplement begin to be converted into creatine phosphate. It is phosphatocreatine that provokes the appearance of the energy-storing amino acid adenosine triphosphate in the athlete’s body. ATP reserves last for a short period of time, and after it is depleted, creatine phosphate comes to the rescue. This is how the process of ATP resynthesis occurs, which allows the muscles to work for some more time, increasing power.
Thus, thanks to the constant maintenance of ATP activity, the athlete can train for a long time with heavy weights; whereas in the absence of the supplement it quickly fizzles out and weakens. This effect during strength training helps the athlete achieve the effect twice as quickly. “Iron professionals” additionally use creatine for weight loss, increasing muscle mass, and during mass gain.