Author: Timko Ilya - the ruler of the entire site and fitness trainer | more details >> Rod. 1984 Trained since 1999 Trained since 2007. Author and creator of the site tvoytrener.com. CCM in powerlifting. Champion of Russia and South Russia according to AWPC. Champion of the Krasnodar region according to IPF. 1st category in weightlifting. 2-time winner of the Krasnodar Territory championship in t/a. Author of more than 700 articles on fitness and amateur athletics. Author and co-author of 5 books.
Place in the author rating:
out of competition
(become an author)
Date:
2012-05-29
Views:
382,423
Rating:
4.2
| All articles by the author >> | Medals articles >> |
Articles are loading...
| Article medals: | more than 100 thousand views |
Why medals are given to articles:
| Bronze medal: | |
| 1. The article is in the TOP 100 2. The article has more than 3. The article has more than 100 | |
| Silver medal: | |
| 1. The article is in the TOP 50 2. The article has more than 3. The article has more than 500 | |
| Gold medal: | |
| 1. The article is in the TOP 10 2. The article has more than 1 3. The article has more than 1,000 | |
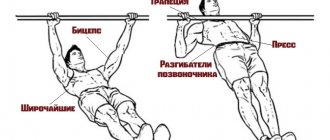
Main muscles - gluteus maximus Additional - back of the thigh Difficulty - medium
What muscles are used by leg extension in the machine?
This is a very large muscle group, containing 4 separate heads. Hence its name. From Latin “quadro” is translated as four. Its more scientific name is the quadriceps femoris muscle.
Each head of the quadriceps has its own name.
- Rectus muscle (head). Is the largest of the 4 heads. Located almost in the center of the thigh. It is superficial, therefore, with good development of this head, we can clearly see it. It is this that will give volume to the quadriceps, that is, its thickness. Its main functions include: extension of the lower leg (leg) and flexion of the hip (for example, when we sit down). Receives most of the load at the beginning of the movement.
- Vastus medialis muscle. It is a much smaller muscle. Located just above the knee, closer to the inside. Its shape resembles a drop of water. Responsible for leg extension.
- Vastus lateralis muscles. Located on the front surface of the thigh closer to the outer edge. Responsible for the extension and rotation of the legs outward. That is, feet apart.
- Vastus intermedius muscle. This head is located under the rectus muscle. Also responsible for leg extension and hip flexion. Its good development will begin to push the rectus muscle upward, thereby visually making your hips more massive.
All of these muscles attach to the femur and are one of the stabilizers of the legs and knee.
It is also possible to identify some assistant muscles that receive indirect load and serve more to stabilize the position of our body.
- Back muscles
- Hand
- Press
They work in static voltage.
Anterior thigh muscles
This group includes mainly flexor muscles.
Quadriceps
Many people know the synonymous name - quadriceps. From the name it is clear that it has 4 “heads”, each of which is considered as an independent link.
Lateral wide
The largest in its section, it covers a large anterolateral surface. It goes from the greater trochanter to the patella. Gives a beautiful roundness to the outer area. Promotes straightening. Most commonly used when we do squats.
Medial wide
Flattened, thick-fibered. Starts from the linea aspera, ending with the tendon. The beams are directed along an obliquely descending line from the inside to the front. Performs lunges, jumps, helps to squat, actively works when extending the knee.
Straight
The longest one presented. Consists of two heads. In the upper part it connects to the pelvic bone, downwards it goes to the knee joint. Takes part in the formation of the limb circumference. Works in jumps, pulling towards the body. Thanks to her, we can maintain balance.
The thinnest, weakest among the rest. Serves to separate the muscles of the thigh of the lateral group and the medial surface. It lies from the intertrochanteric line going downwards. Promotes straightening.
Tailoring
The narrowest, longest muscle. Originates from the ilium obliquely. Attaches to the surface of the shin. Bends the legs, abducts, turns and presses them to the stomach.
The anterior muscle group plays an extremely significant role. It is not so easy to set the complex bone apparatus in motion. This is a multi-level system that requires coordinated work.
It is considered the most problematic. The skin here is somewhat thinner, which affects the appearance, especially of the fair half of humanity. In addition, stretching and tearing often occur here.
Another name is adductors. Simply put, the main function is to bring the legs together. Strengthening them is very important; training programs are based precisely on this action. Let's look at each in more detail.
Comb
The structure is similar to a quadrangle. Attaches to the line of the same name in the femoral region. Located diagonally. Works while running, walking and squatting.
Thin
This is a long bundle located in the pubic area. Crosses the knee and attaches to the tibia. Extends and rotates the lower leg. Works in conjunction with other adductors (from the Latin adductor - leading).
Short adductor
Flat, small in size, stretches from the pubis downwards, to the rough line. Flexes and rotates the limb outward. Often injured during sports. It is necessary to warm up so as not to provoke tears and sprains. Healing takes quite a long time. The pain syndrome is localized in the groin area.
Adductor magnus
The fibers are located deep. They pass from the pubic symphysis. Fills the inner space of the femoral area. One of the most difficult to palpate. Its main task is to stabilize the pelvis and align it relative to the lower extremities. This is due to the characteristics of the fastening. Weakness and underdevelopment leads to hypertonicity and overstrain of neighboring areas.
Long adductor
Flattened, looks like a triangle. It is located on the anteromedial side and expands inferiorly. Most convenient for palpation.
Interestingly, the adductors are called “guardians of virginity” or “moral muscles.” Because their increased work and overexertion is associated with disturbances in the regulation of sexual activity. This “leg contraction” function leads to suppression of sexual arousal. It is especially developed in females, as this is a natural defense mechanism.
Spasms, pain, discomfort are far from uncommon for most of us. Many people face one problem or another. There may be one symptom, but there are many reasons. This condition occurs due to injuries, insufficient warm-up and overload. It is important to take sports seriously. Be sure to study the relevant literature or consult with trained trainers. The muscles of the anterior and posterior inner surface of the thigh, their anatomy and functions are very diverse, as are the problems with them.
A fairly common phenomenon among athletes. Unpleasant sensations arise due to increased physical activity. It usually appears after 8–12 hours. Disturbs at rest and when using overstrained muscles. Another striking sign is a decrease in endurance.
For a long time, the pathology was associated with the irritating effect of lactic acid. Anabolic loads promote the oxidation of glucose and the active release of metabolic products. In trained people, this process practically does not manifest itself.
However, recent research has put forward a new theory, which is considered the most reliable. According to her, the cause is a change in the structure of the muscles and the resulting inflammation. Muscle fibers are made up of myofibrils. These elements provide the strength and speed of contraction.
At the initial stage of playing sports, such a reaction is understandable and normal. In other cases, overexertion does not bring any benefit to the body. To prevent this, you need to warm up thoroughly and objectively evaluate your preparation. Regular anti-inflammatory drugs will help relieve symptoms.
It is important to differentiate this condition correctly
Myositis
This is inflammation of muscle tissue. The main symptom is severe pain and weakness; there may be the following accompanying manifestations: redness of the skin, swelling, increased temperature of the whole body. This happens due to: various injuries, hypothermia, vascular disorders or spinal defects.
If such symptoms are detected, you should consult a specialist. Only he will be able to make a correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment. As a possible surgical intervention.
Breaks
The thigh muscles are most susceptible to this effect. It is characterized by limited mobility, sharp pain immediately after a blow or excessive tension. An extremely dangerous condition. Some types of it require surgical intervention.
Sprains
Improper training or falls often cause deformity. Unpleasant sensations can be accompanied by hematomas or even a “click”, this indicates severe injury.
First of all, you need to apply a compress for 15–20 minutes. Ice or a cloth moistened with cold water will do this. Then make a fixing bandage, an elastic bandage or compression stockings will help. This will reduce swelling. Try to limit your movements. If it does not get better within 24 hours, contact the clinic.
Hypotrophy
This is a condition that occurs due to metabolic disorders. The muscles are literally “starving.” A rather dangerous disease that can lead to disability.
The main reason is insufficient supply of nutrients. This occurs due to: burns, hypothermia, intoxication, prolonged displacement, and can also be a congenital pathology. Symptoms are as follows: frequent pain, weakness, inability to perform usual actions, loss of body weight. Which leads to discomfort. To solve the problem, complex measures are used. Eliminate the primary factor, stimulate trophism, normalize metabolic processes.
At the “I Want to Walk” prosthetics center, we offer rehabilitation and adaptation to children with musculoskeletal disorders, give them the opportunity to join a full and vibrant life in society, demonstrate their abilities and talents, and master everyday and professional skills.
This is a neurological pathological manifestation characterized by a pulling action in the area of the buttocks and lower extremities. In this case, numbness, burning and increased tension in the knee area are also possible.
Occurs due to compression of the sciatic nerve. This can be provoked by: hypothermia, physical activity, an incorrectly placed injection, a defect in the spine or hip joint, or muscle strain.
It is extremely difficult to independently determine the correct diagnosis. It's best to leave this to a qualified professional. He will palpate and identify areas of pain and flattening. In the absence of serious pathology, a few days of rest will be sufficient; in some cases, medication, exercise therapy or massage are prescribed. Find out more about how to get rid of spasms here.
The disease is of a tonic nature, the cause is injury to the fiber or adjacent areas. However, this effect can affect innervation. Which leads to loss of sensitivity and motor function.
The clinical picture is very clear: involuntary contractions, weakness on the affected side, especially in the hip girdle. Active activity is impossible in this case.
The pain can be localized in various places. In the intestines, legs, lower back, it completely disappears when lying down.
It is treated with specially designed exercises that should be performed only as directed. They relieve tension, improve the patient’s general condition, promote relaxation, and restore tone and blood circulation. It is also possible to use drug therapy.
Advantages and disadvantages of this exercise
It may seem that since the exercise is popular and many people recommend it, then it should have only advantages. Yes, I agree they exist and this:
- The ability to detail the quadriceps and give them an expressive shape.
- An opportunity to finish off your quadriceps if you no longer have the strength to do heavy basic exercises.
- With the correct technique, extension can strengthen the knee ligaments.
- And of course, it provides isolated work on all 4 quadriceps muscles.
But in addition to all these advantages, you must take into account that this exercise is extremely dangerous for your knees! Cruciate ligaments are especially at risk
.
They prevent the knee joint from moving forward and backward, as well as in and out. That is, during strong extension of the knee with a fixed pelvis (which is what happens in this exercise), these ligaments are very stretched. Or rather, one of them is the front one. This may lead to its rupture. Yes, it can be treated, but for me it’s not worth it. And after such an operation, you are unlikely to be able to continue your training with the same intensity. Especially for beginners, doing this exercise does not make any sense. After all, you can’t build muscle mass with extensions! Why am I telling you all this? Because it is very important to me that you have an understanding and are aware of all the risks before you start doing leg extensions in the machine. And knowing this, you will already decide whether it is worth exposing your knees to such danger.
But still, exercise can bring not only injuries, but also benefits. The main thing is to know when to do it and avoid making serious mistakes. The most important thing is to do everything with the right technique.
How to pump up your thighs from the inside
Tips and tricks to help improve your exercise performance
Remember that even if you work out hard in the gym, but without paying attention to nutrition, you will not achieve results.
What should you consider if you decide to pump up your inner thigh? Fat leaves the body evenly, and therefore it is very important to understand that if you are overweight, you will not achieve quick results. This is explained by the fact that, as a rule, fat deposits are the last to go from the inner thighs - this area is usually not very involved in everyday life, is difficult to train, but accumulates fat faster
So, pay attention not only to physical activity, but also to nutrition. This will help speed up the process of CORRECT weight loss
This is explained by the fact that, as a rule, fat deposits are the last to go from the inner thighs - this area is usually not very involved in everyday life, is difficult to train, but accumulates fat faster. So, pay attention not only to physical activity, but also to nutrition. This will help speed up the process of PROPER weight loss.
For inner thigh exercises, men will need to eat more protein foods so that the healthy protein promotes muscle growth while burning fat.
But you shouldn’t completely exclude fats and complex carbohydrates from your diet - it’s important for you to maintain hormone levels at the same level, as well as receive energy, which will later be spent during training. You can look up the intake rates for proteins, fats and carbohydrates on the Internet on specialized websites where there are calculators that can help you easily calculate how much you need to eat.
If a man does not get enough protein, you can use protein shakes, which are sold in sports nutrition stores. They should not replace a meal if you have the opportunity to eat, for example, an omelet or chicken breast, but protein shakes can and should be used as a supplement to your diet.
Technique for performing exercises for the inner thigh
Now let's talk about how to pump up the inner thighs and what exercises are suitable for this. Firstly, you can train at home or in the gym - the place practically does not matter. The main thing is your desire. Secondly, to increase the effectiveness of training, you will need to use weights. They can be dumbbells or a barbell. Beginners can perform exercises with a barbell and then gradually increase the load.
- Barbell squats are one of the most effective exercises for pumping up your inner thighs. To do this, place the barbell on your shoulders and place your feet shoulder-width apart. We begin to squat slowly and smoothly, reaching the point when your legs are at an angle of 90 degrees. You can't bend your back. We also do not recommend that you squat more than the specified value, since in this case the load on the knee joints increases to the maximum - you put pressure on them not only with your own weight, but also with the weight of the barbell. Men should not perform the exercise with strain - work the muscles of the inner thigh smoothly.
- Lunge exercises are another way to quickly tone up your inner thighs. Take 1 dumbbell in each hand. We place one leg forward so that it is approximately in line with the back leg. Then we bend it slightly at the knee, squatting a little. We return to the starting position. These are lunges that will help you train your inner thighs. You can also bend your back leg slightly, bringing it to the floor, but not touching it.
- The following exercise for the thigh muscles can be performed even at home. We lie down on one side and put our lower hand behind our head. We bend the lower leg and place our free hand where it is convenient. Next, we raise the upper leg to a height of about 45 degrees and return it to its original position. Remember that when you lower your leg back down, you should do it slowly and smoothly - this will allow the muscles in the hip area to be used as much as possible. Perform the exercise until you feel a slight numbness in the muscles of the inner thigh. Then work the other side in the same way.
Remember that regular training will definitely bring results!
Do you want to quickly remove fat from the outer thigh at home? Looking for effective exercises to tone your outer thighs? Here! In this article we will tell you about a set of exercises with which you can pump up the necessary muscle group. Remember: regular training, adherence to exercise technique and proper nutrition will help achieve maximum results.
| Exercises | Sets | Repetitions/Time |
| Taking the leg to the side | 3 | 25 |
| Reverse hyperextension | 3 | 15 |
| Wide stance squats (plie squats) | 3 | 15-20 |
| Lunges forward | 3 | 15 |
Execution technique
From the outside it may seem that the exercise is very easy to perform. I sat down on the exercise machine and began to straighten and bend my legs. But unfortunately, it only seems so. There are technical issues and subtleties that must be taken into account. And before you start the exercise. We will need to customize the simulator for ourselves.
Initial position:
The leg extension machine resembles a chair. It has an adjustable backrest that moves forward and backward. Special soft cushion for feet. It is also adjustable, thereby rising higher or lower. To ensure that the pelvis does not come off the seat, there are handles on the sides. Which you have to hold on to with your hands. The system for installing weights varies. From barbells to special blocks.
- Go to the leg extension machine. Set the weight you need by hanging weights or setting the limiter to the desired number of blocks.
- Adjust the backrest so that your thigh rests completely on the seat. And the knee went slightly beyond the edge of the seat.
- Place your feet under the bolster. It must be adjusted so that it is located in the lower part of the lower leg, in the area of the ankle joint. In this case, your legs should be bent at an angle of 90° or a little stronger.
- Next, straighten your back and bring your shoulder blades together. We rest against the back and grab the handles with our hands.
Important!
The knee should not have an acute angle when bending. This will only increase the load on the joints. And there will be a risk of injury!
Performance:
- After taking the starting position, while exhaling, straighten your legs at the knee joint.
- Do not pause at the top point. As you inhale, bend your legs to the starting position.
Why I don’t recommend staying in the top position. It all comes back to keeping your knees healthy. Yes, if we take a short pause at the top, our quadriceps will receive a greater load. But it will also affect the joints. Therefore, you should choose health or efficiency.
Load by muscle group
- Sartorial muscle, m. sartorius has the appearance of a narrow ribbon and is the longest muscle in the human body. Located on the anterior surface of the thigh, the muscle spirals downwards, moving to its inner surface, and then, rounding the epicondylus medialis from behind, passes to the anteromedial surface of the leg.
The muscle starts from the spina iliaca anterior superior and, heading obliquely downwards, passes into a flat tendon, which attaches to the tuberositas tibiae, and a number of fascicles are woven into the fascia of the upper leg.
Action: the muscle flexes the thigh and shin, rotating the thigh outward and the shin inward, thereby taking part in throwing the leg behind the leg.
- Quadriceps femoris muscle, m. quadriceps femoris; is located on the anterolateral surface of the thigh, and in the lower parts it passes to the lateral side of it.
Each of the four heads has its own origin, but, approaching the knee area, they all enter the common tendon, which passes along the anterior surface of the patella and attaches to the tuberositas tibiae.
a) Rectum femoris, m. rectus femoris, the longest of the four heads. Occupies the anterior surface of the thigh. The muscle originates as a thin tendon from the spina iliaca anterior inferior and the upper edge of the acetabulum.
Moving down, the muscle passes into a narrow tendon, which fuses with the base and anterior surface of the patella. Having reached the tibia, the tendon of the muscle attaches to the tuberositas tibiae. Below the patella, this tendon is usually called lig. patellae
b) Vastus medialis muscle, m. vastus medialis, occupies the anteromedial surface of the lower half of the thigh. The muscle bundles that form it are directed obliquely from top to bottom and from the inside to the front. In front it is slightly covered by the rectus muscle.
The muscle originates from the labium mediale lineae asperae femoris and, moving downwards, passes into a wide tendon, which is partially woven into the common tendon together with the rectus muscle, and partially attached to the medial edge of the patella, forming the retinaculum patellae mediale.
c) Vastus lateralis muscle, m. vastus lateralis, occupies almost the entire anterolateral surface of the thigh. From above it is somewhat covered by m.tensor fasciae latae, and in front by m.rectus femoris. The muscle bundles that make up the muscle are directed from top to bottom and from the outside to the front.
The muscle originates from the trochanter major, linea intertrochanterica and labium laterale lineaasperae. Moving down, the muscle passes into the broad tendon, which partially connects with the rectus tendon into the common tendon, and partially attaches to the lateral edge of the patella, forming the retinaculum patellae laterale.
d) Vastus intermedius muscle, m. vastus intermedius, located on the anterior surface of the thigh between mm. vasti medialis et lateralis, directly under m. rectus femoris. This muscle is the weakest among the other heads.
It originates from the anterior surface of the femur, starting from the linea intertrochanterica, and, going down, passes (almost half its length) into the broad tendon, which in its distal section joins the tendon of the m.rectus femoris, passing into the common tendon of the quadriceps muscle.
located under the quadriceps tendon, above the patella; c) subcutaneous subpatellar bursa, bursa subcutanea infrapatellaris; lies anterior to the patellar ligament; d) deep subpatellar bursa, bursa infrapatellaris profunda: lies at the attachment of the patellar ligament to the tibial tuberosity and a number of other bursa. Some of these bursa may communicate with the cavity of the knee joint.
Action: the quadriceps muscle, by contracting all its heads, extends the tibia, due to m. The rectus femoris is involved in hip flexion.
- Articular muscle of the knee, m. articularis genus, a flat plate consisting of several well-defined muscle bundles, lies on the anterior surface of the thigh under m. vastus intermedius. The muscle originates from the anterior surface of the lower third of the femur and, moving downward, is attached to the anterior and lateral surfaces of the knee joint capsule.
Action: tightens the capsule of the knee joint.
- Adductor magnus
- Long adductor
- Short adductor
- Thin
- Comb
When performing squats parallel to the floor, in addition to pumping our legs, we also work the gluteal muscles. The position of the feet determines which part of the leg the load will be placed on. When the feet are set wider than the shoulders, the main load will be directed to the inner part of the thigh; with a narrow position, the muscles of the outer thigh are pumped.
Along with doing squats, your buttocks will also increase in size.
Don't be afraid of this, the development of these muscles is also important, as is the development of the back, hips and other parts of the body. Against the background of well-developed general muscles, undeveloped buttocks will create an absurd picture
Your buttocks may also appear significantly larger than they actually are if you have underdeveloped, flat hamstrings. In this case, it is important to include work on the hamstrings in your training in order to maintain the necessary proportion between the buttocks and legs. The hamstrings can be well developed by performing straight-legged deadlifts and squats with approximately the same weights.
It must be said that squats use almost all muscle groups in the body. Do not forget that the development of the muscles of the legs, back and pelvis is the basis for muscle growth throughout the body. By devoting a lot of time and effort to squats, you start the process of pumping up all the muscles of the body. More squats equals more potential. Strong lower body muscles are the first step in creating toned arms and shoulders.
Training your legs with calf raises helps build your calves. When performing an exercise on one leg, the body weight acts as a weight; for additional load, you can also take a dumbbell in the hand opposite the leg on which the load is being applied. The position is changed when the maximum pain in the calf is reached.
The jump rope is a wonderful example of how to pump up your legs without using complex exercise equipment. You can start with 20-30 jumps, increasing the number of repetitions every day, and then the tempo of the exercise. Jumping rope also helps increase endurance in the lower extremities. Another great example of how to pump up your legs at home is lunges.
When performing this, it is important to monitor the position of the knee: it should not go forward of the feet. Do not discount squats with dumbbells - they are a good alternative for those who want to exercise at home
This exercise is isolating, performed in a special simulator and is aimed at pumping one muscle, namely the biceps femoris (femoral biceps).
In addition to the hamstrings, the auxiliary load falls on the following muscles:
- Calf muscles, sartorius, gracilis muscles;
- Gluteal muscles - as stabilizer muscles;
- The quadriceps femoris (quadriceps) acts as an antagonist muscle.
Standing leg curl machine;
Performing standing leg curls in a machine has a number of beneficial properties:
- Formation of strength and endurance of the hamstring muscles;
- The exercise gives flexibility and stretch to the thigh muscles;
- Isolating (targeted) pumping of the back of the thighs;
- Standing leg curls maintain a toned appearance of the back of the thighs and prevent the formation of cellulite;
- Creates a clear separation between the gluteal muscle area and the hip area;
- When working for a large number of repetitions, it improves the relief of the muscles of the back of the thigh;
- There is no load on the spine, which makes it possible for people with back problems to do it.
- Adjust the lever of the machine to suit your height, rest your torso on the back of the machine, leaning forward about 30-45 degrees (as this leaning position is more natural for the hamstrings), place the lever roller on the back of your right leg (total a few inches under the shin), the left leg is on the platform (or on the floor, depending on the type of machine) and motionless.
- Keeping your torso leaning forward, make sure your leg is fully extended and grab the side handles of the machine. Place your toes straight. This is your starting position.
- As you exhale, bend your right leg up as far as possible without lifting your left leg off the floor. Once you have fully bent your leg, hold it in this position for a second, feeling the tension in the hamstring muscle.
- As you inhale, straighten your leg back to the starting position. Repeat these movements for the recommended number of repetitions (typically 12-15 repetitions per set are recommended).
- Do the same now for the left leg.
Recommendations for implementation
There are several simple techniques that will help you load the quadruple major thigh muscles in a new way. It's about:
- Full and partial amplitude. If we fully extend the leg, then the load falls more on the broad medial head. But if we work with a little more weight in a partial amplitude. That is, extend your leg halfway. Then the direct and intermediate heads will be involved in the work. When using partial amplitude, you will need to tilt the back slightly back. This will stretch these heads more.
- Turning the feet. The position of our legs also determines which head will receive the most load. If you turn your feet inward towards each other. This will stretch the lateral head more, and it will be used more than the others. Turning your toes to the sides will shift the emphasis to the medial head.
- One leg extension. This is a more professional technique; beginners do not need it. Performing an extension with one leg, it is easier to focus on the work of the hip. Also, using this exercise, you can reduce the imbalance in the development of the quadriceps of each leg.
You can try each of these techniques. The main criterion should be the correct execution technique. So work on it before making these kinds of changes to the exercise.
Preparing for the exercise
Some athletes really like to write about preparing for this exercise; they include hamstring stretching, some “warm-up” exercises, etc. in the program. In practice, all this is not necessary. Isolation movements are performed after basic exercises. Usually the muscles are already sufficiently filled with blood and elastic to allow the movement to be performed efficiently.
In fact, if this is the first exercise in the plan for some reason, it is worth including a stepper during your cardio warm-up, and starting with light weights during work. Most curling machines have an adjustable pad that we rest our feet on. It should be adjusted carefully enough so that the calf muscles do not become clogged during movement. This problem is the main reason why most athletes fail to benefit from movement.
- It is not allowed to bend the legs at the knee by lifting the pelvis. This option will be quite harmful, as it can lead to lower back injury if the angle in the joint is disturbed. Usually, if there is a strong lift of the pelvis, it is recommended to reduce the load and remove excess weight;
- You should not sharply push the exercise pad up and lift the weight due to inertia. Untrained knee ligaments can be injured if you work unevenly, and many machines are designed to transfer the load from an unevenly moving cable to the knee;
- You should slowly bend your legs, hold in the peak contraction, and just as smoothly straighten your legs in order to get a load and not get injured;
- If you cannot work smoothly, concentrating flexion on exhalation, it is recommended to remove the load and work with less resistance from the machine;
- It is better not to rest the kneecap on the exercise machine bench, if there is such a constructive possibility;
- The feet must be kept parallel to each other and not rotated with the toes during the exercise. It is ideal if the athlete does not maintain the distance between the knees while performing the exercise.
Errors
- You cannot rest your knees on the bench;
- It is not allowed to push the weight in jerks;
- If the training plan does not provide for this, movement at a reduced amplitude is not recommended;
- It is better to avoid actively involving your hands in the work, do not “cling” with them to the handles of the simulator;
- Do not lift your pelvis when working
Basic mistakes
Too much weight
I will not tire of repeating that this mistake applies to any exercise. But it is the isolated who bear the greatest risk. And if we take on weight that we can't handle. Then the resulting injury is all that shines for us. And I already said that straightening the legs can cause rupture of the knee tendons. This will lead to complete refusal of training. But this is not the worst thing. You may remain crippled for life, confined to a wheelchair. I don’t see the point of doing this exercise with heavy weights, since it has no effect on muscle growth. Therefore, you can safely work in multi-repetitive mode. And use light weight.
Jerking movements
I think everything is clear here. Jerking movements occur when you are unable to cope with weight. And I have already written about the consequences above. Your main task is to ensure control over your weight and your movements. Feel the thigh muscles contract and stretch.
Safety
Hip extensions are completely safe exercises. All athletes are advised to perform them, since the spine does not receive too much stress during such leg work. However, this exercise should be performed with caution by those people who have injuries to the knee or elbow joints.
The fact is that the knee joint takes an active part in the extension of the leg, so it is important that it is healthy. As for the elbow joints, the athlete's body weight is partially transferred to them, so this part of the body must be strong.
In this exercise an accelerated pace is important , but do not overdo it, as jerking can negatively affect the condition of the joints. This is especially true for those athletes who prefer to work with leg weights or an expander.
Inclusion in the training program
This exercise is mainly used in several cases:
- As a supplement at the end of a leg workout to get the most out of your quadriceps.
- As a warm-up before leg training. In this case, a small weight is used, purely to warm up the quadriceps.
- And before performing a basic exercise, in order to tire the muscle and then push it with more weight.
In each of these options, preference is given to a large number of repetitions from 15 to 20. Mostly 3-4 approaches are used.
My personal recommendation is not to use this exercise on an ongoing basis. If you can do without it, then feel free to replace it with something more effective and less dangerous. And most importantly, don’t forget about technology. Take care of your knees!
Good luck to everyone in your training!
Functions
The main functions of the hip joint are hip extension and external rotation. In addition, the upper portions of the muscle can abduct the thigh, while the lower portions can adduct it.
As a strong hip extensor, the gluteus muscle is suited for powerful lower extremity movements such as stepping, climbing, or running. At the same time, during normal walking the muscle is used little.
The ROM and hamstrings work together to extend the torso, tilting the pelvis backward, as happens, for example, when we straighten up from a forward bend. The gluteus maximus also provides eccentric control when bending the torso. The fibers of the superior portion of the muscle can extend the knee due to their connection with the iliotibial tract.
BNM also plays the role of a stabilizer. The muscle balances the pelvis on the heads of the femurs, thus maintaining the vertical position of the body. The insertion through the iliotibial tract allows the muscle to support the lateral aspect of the knee and provides external rotation of the hip joint in a standing position, and also helps to elevate the medial longitudinal arch of the foot.
Friends, this and other questions will be discussed in detail at the seminar “Diagnostics and treatment of problems in the joints of the lower extremities.” Find out more...
The connection of the BMU with the sacroiliac joint and its ligaments explains the contribution of the muscle to the self-stabilization of this joint.
The BJM relieves stress on the ischial tuberosities as it supports the body in a sitting position through dynamic contraction.
If the BJM is paralyzed, climbing stairs and running may be difficult. However, other muscles that can extend the hip joint can come to the rescue here. The muscle can also be trained to functionally extend the knee if the quadriceps femoris muscle is weak or paralyzed.
Research has found that contracting the deep abdominal muscles helps contract the gluteus maximus, which helps control the anterior pelvic tilt. Weakness of the MJ is believed to underlie many low back injuries.
Gluteus maximus inhibition
As noted by physiotherapist Vladimir Yanda, the gluteus maximus muscle is a phasic muscle, and its work can be suppressed for various reasons:
- Arthrogenic inhibition of the hip joint.
- Stiffness of the iliopsoas muscle, which transmits reciprocal inhibition to the PMU (as in inferior crossed syndrome).
- Reflex pain suppression due to pain in the hip joint or lower back.
- Weakness due to muscle strain.
- A sedentary lifestyle and lack of physical activity leads to the fact that hamstrings begin to do all the work for the BYM. This is explained by the mechanism of energy conservation, when the body tries to save BNM for such complex activities as running, climbing stairs, etc. Thus, without exercising, you will not be able to engage the gluteus maximus muscles, but will only increase their inhibition and force the hamstrings to take on the entire load, turning them into dominant synergists.
All of these factors not only affect the time it takes for the gluteus maximus to activate, but also the level of activation.
Activation of the gluteus maximus muscle
There are many different exercises to work your gluteus maximus muscle. Below are the main ones (in order of increasing activation of the BNM).
MVIC = maximum voluntary isometric contraction (maximum voluntary muscle contraction).
NB The plank stands apart among low-intensity exercises due to its static nature and the need to maintain a neutral position of the hips and back while performing it. In general, exercises from the low-intensity group mainly use the MJ as a stabilizer for the hip and spine.
Anatomical features of the femoral biceps
To figure out how to pump up your thigh muscles, you need to study the structure of this muscle group, as well as the functions they perform.
Anatomy of the muscles of the legs and buttocks
The posterior muscles of the femoral leg include:
- biceps;
- semimembranous;
- semitendinosus.
The biceps muscle consists of two bundles that run along the thigh and are attached to the head of the fibula. The semitendinosus muscle runs along the inside of the thigh. The semimembranosus is attached to the ischial tuberosity from above and reaches the tibia.
The main functions of the biceps femoris are:
- bending the leg at the knee joint;
- stabilize the knee;
- in combination with the gluteus maximus muscle, it participates in the extension of the torso;
- shin rotation.
We previously wrote about a lying knee bending machine and recommended bookmarking this article.
Usually in fitness and bodybuilding they use a set of traditional basic and isolated exercises that involve all the muscles of the back of the thighs.
Pumping up your legs at home is not that difficult. All you need is the desire to achieve your goals at all costs and firm confidence in your abilities. Before you start training, you should consult with a trainer who, in accordance with your physical fitness, will select a set of exercises and determine the training regimen.
Readers found these materials useful:
Anatomy of the thigh muscles
Conventionally, the muscle mass of the thigh is divided into three parts:
- The front part is the quadriceps.
- Back – biceps femoris.
- Internal – adductor muscles.
Particular attention should be paid to the quadriceps - the quadriceps muscle of the thigh. It consists of four bundles: intermediate, direct, medial and lateral. They form most of the volume of the thigh muscles.
A set of exercises for the rear thigh
Among the many exercises, there are the best ones that are effective for the muscles of the back of the thigh and they are in front of you:
No. 1. Incline with lift
The exercise is similar to the yoga warrior pose. It tones your muscles, challenging your coordination and balance.
- Stand up straight and tighten your abs.
- Bend your torso forward while lifting your leg up.
- Stretch your arms out in front of you for balance with your torso and thigh parallel to the floor.
- Hold this position for several seconds.
- 15 times for each leg.
No. 2. Deadlift with dumbbells
An effective technique for the rear end. If you do the exercise at home, you can use bottles of water or sand as weights.
- Take a weight, place your arms along your body, bend your legs slightly at the knees.
- Slowly bend at the hip joint (not at the waist) and lower the dumbbells as far as possible.
- Please note that your back should be straight, do not round it.
- 3 sets of 12 repetitions.
No. 3. One leg bridge
This exercise works great on the hamstring area:
- Lie on your back with your hands on the floor for stability.
- When you bend one leg, straighten the other and lift it off the mat.
- Pressing the heel of your supporting leg, lift your pelvis up, keeping your body in a “bridge” position.
- Slowly lower your pelvis down, your leg still up.
- 3 sets of 15 times.
No. 4. Touching the floor
Thanks to the wide range of motion, the exercise effectively works the back thigh and buttocks. The technique combines all the benefits of deadlifts and deep single-leg squats, but without the pressure on the knee joints.
- Take the dumbbell in your right hand and lift your leg of the same name.
- Keeping your back straight and your left knee slightly bent, lean forward to touch the dumbbell to the floor.
- In this case, the right knee is bent, and the thigh is located close to the left. No need to lift it up.
- When you straighten your back, try not to place the foot of your bent leg on the floor.
- If you are a beginner, try doing the exercise without weights.
- 12 repetitions for each leg in 2-3 sets.
No. 5. Side and diagonal lunge
Effectively target your outer, inner, and back thighs with this exercise:
- Lunge to the side to the left, bringing your right hand and dumbbell to your left shin.
- Lower your buttocks as low as possible. In this case, the left knee is bent 90°.
- Curtsy carefully.
- Once you complete 12-15 reps, do it the other way. Only 3 sets.
No. 6. Body lifts
- A challenging variation of simple lifts.
- Lie on your stomach, place the fitball between your legs.
- Engage your abs and extend your arms in front of you.
- As you inhale, squeeze the ball, lifting your hips and arms off the floor.
- Hold this position for 10 counts, then slowly lower down.
- Only 10 times.
No. 7. Bent-overs with a kettlebell
This exercise not only works your hamstrings, but also your hamstrings and glutes.
- Take the weight in your right hand and lift your left leg off the floor.
- Keeping your back neutral, lean your torso forward, lifting your left hip. The leg will rise up and the weight will fall towards the floor.
- 3 sets of 12 times for each leg.
No. 8. Hip extension with expander
Effectively pump up your hamstrings and buttocks in just one minute:
- Get into the “on all fours” position.
- Grab the handles of the expander with both hands.
- Place your foot in the center of the rubber.
- Bring your working thigh to your chest without touching the floor and move it back, fully straightening it.
- 3 sets of 15-20 repetitions for each leg.
No. 9. Diagonal Lunge
Additional weights increase the effectiveness of the exercise.
- Stand straight, place your feet slightly wider than your shoulders. Dumbbell - in front of you.
- Take a large step back diagonally, like a curtsy.
- Lower into the lunge deeply until your hips form a right angle.
- Return to the start and repeat on the other side.
- 2 sets of 15-20 repetitions.
No. 10. Dumbbell rows to the chest while standing on one leg
The exercise works not only the back of the thigh, but also the upper back.
- From a standing position, take a warrior pose (as in exercise No. 1).
- Find balance.
- While holding this position, perform dumbbell rows to your chest 10 times.
- Repeat with the other leg.
No. 11. Platform lifts
The exercise imitates climbing stairs , but with a higher height, which makes the exercise even more effective.
- Stand in front of the platform (step), place one foot on top.
- Perform the lift while simultaneously lifting the knee of the other leg up.
- Return to the start.
- Only 20 times.
No. 12. Leg straightening
The exercise works the deep muscles of the thighs and buttocks.
- Get on all fours, hands strictly under the shoulder joints.
- Move your hip to the side, bending your knee 90°.
- Slowly straighten your leg completely until it is parallel to the floor.
- Stay in this position for several seconds.
- Return to the start.
- 2 sets of 20 repetitions in each direction.
No. 13. Deep reverse lunge
The step back should be deep so that the tension and stretch in the back of the thigh is felt. 3 sets of 12-15 times.
No. 14. "Iron" in the plank
The plank perfectly works the muscles of the whole body. To increase the load on your hips and buttocks, you just need to raise your leg with the knee bent. When you stand in the plank, do not lower your pelvis down, but do not lift it up either. 10 lifts with each leg. Only 2 sets.
No. 15. Hip abduction
- Move your hip back as far as possible without leaning too far back.
- Tighten your abdominal muscles to maintain balance.
- When you put your foot down, don't put it on the floor.
- Repeat the movement 20 times at an average pace. Then perform diagonal hip abduction 20 more times.
- Do similar movements for the other leg.
How often should you exercise at home or in the gym?
You need to train your hamstrings once a week, provided that the training is intense. The main rule: the heavier the weight, the fewer repetitions per week you need to do. Otherwise, there is a risk of overstraining the muscles. This applies to core exercises such as barbell deadlifts or deep squats.
Exercises for the back of the thigh are performed both separately and in complex training. This means that when training the front surface, a small part of the load is distributed to the biceps.
Video about exercises for the back of the thigh
5 best exercises for the hamstrings:
The back of the thigh in women is one of the indicators of the attractiveness of legs. She is more susceptible to the appearance of fat deposits and cellulite, since she does not receive the proper load (especially during sedentary work). To get your back thigh in shape, you need to pay attention to regular physical activity, watch your diet and do massage. You should definitely include exercises for the back of your thighs in your workouts.