Accessible and detailed information about what carbohydrates are, their types, the glycemic index, digestion, fiber, glucose, and the relationship between body fat storage and physical activity.
Carbohydrates are a key source of energy in the human body; just 1 gram provides 4 calories of energy. When carbohydrates are broken down in the body, glucose is formed; it is extremely important for the preservation of tissue protein, fat metabolism and nutrition of the central nervous system.
The main purpose for which carbohydrates are needed in the human body is to supply the body with energy to maintain all its functions and full functioning.
There are the following types of carbohydrates: simple and complex; In order to understand this issue more deeply, it is necessary to look at it from a scientific point of view.
What are carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the main ingredient in most foods and serve as a source of energy for the human body. Depending on the number of structural units, carbohydrates are simple and complex.
The first category is also called fast carbohydrates. They are easily digestible and lead to a rapid increase in blood sugar. This means that the substances have a high glycemic index.
Such elements provoke metabolic disorders and cause weight gain. Systematic consumption of foods containing simple carbohydrates not only leads to obesity, but also causes many other diseases.
Complex carbohydrates, which include starch and fiber, contain many linked saccharides. They contain a large number of structural elements. Food with such carbohydrates is considered very healthy. During the digestion process, it gradually saturates the body with energy. This gives a long-lasting feeling of fullness.
Your carbohydrate needs
To function fully, our bodies need carbohydrates, especially glucose, which the body prefers to use to fuel tissues and internal organs - and is the only source of energy for red blood cells. When the body does not have enough carbohydrates, the body begins to use protein from the muscles and organs to create glucose.
The recommended daily allowance of carbohydrates is 130 g. This is the minimum necessary for the health of the brain, red blood cells and central nervous system. Without getting enough energy, you risk losing muscle mass, which your body will spend on creating glucose. 130 g is the minimum for adults. Most people need more. According to American experts, 45-65 percent of the energy from your daily calorie intake should come from carbohydrates. This percentage difference is due to the fact that each organism is individual and there is no single approach that is ideal for everyone.
The approximate daily intake of carbohydrates should be 50% of the number of calories in your daily diet, but this is an average figure that we advise you to change depending on your goals.
How to determine your daily requirement?
- Decide what percentage of protein you need and convert it to a decimal (for example, 50% - 0.5)
- Multiply your daily calorie intake by that number to get the number of calories you need from carbohydrates.
- Divide this number by 4 to get your desired amount of carbohydrates in grams.
Calculator
Functions of carbohydrates in the body
The key function of carbohydrates in the body lies in their transformation into energy. ATP, which is a universal source of energy, contains the monosaccharide ribose. ATP is formed due to glycolysis. This process involves the oxidation and breakdown of glucose into pyruvic acid.
Glycolysis occurs in several stages. Carbohydrates are oxidized to water and carbon dioxide. This process is accompanied by the release of energy.
The main functions of carbohydrates include the following:
- Structural.
Polysaccharides are the material for supporting elements. Cellulose, which is part of the structure of cell walls, gives plants rigidity. Fungal cells contain chitin. - Energy.
Carbohydrates represent the main source of energy. The breakdown of 1 g of carbohydrates releases 17.6 kJ of energy. - Protective.
The thorns and thorns of plants are made up of these elements. - Storage.
Carbohydrates are stored in the form of starch in the structure of plants and glycogen in animals. When there is a lack of energy, these substances are broken down into glucose. - Osmotic.
Substances help regulate osmotic pressure. - Receptor.
The elements are present in the composition of cellular receptors.
Individual carbohydrates form complex structures with protein elements and lipids. As a result, glycoproteins and glycolipids are formed. These elements are present in the composition of cell membranes.
Cellulose
The practical benefits of carbohydrates have always been no less important than their biological role. The use of carbohydrates can be found in completely different areas of human activity. Cellulose (fiber) has been used by humans since ancient times. First, man began to use wood as a fuel and building material. Then they learned to make thread from cotton, flax and other fibrous plants. Later, technologies appeared that made it possible to obtain paper from wood. Paper, at its core, is a thin layer of fiber fibers that are compressed and glued. The result is a durable, smooth surface on which ink does not bleed.
Initially, only plant materials (cotton and rice stalks) were used to make paper. Fibers were extracted from it purely mechanically. But as society developed, the listed sources became insufficient to cover the need for paper. The bulk of it goes to newspapers. Considering that the quality of the paper does not play a special role here, they began to add up to 50 percent of ground wood to it. Subsequently, technologies emerged that made it possible to get rid of wood-related substances such as resins, lignin, etc. This is how diverse the practical uses of carbohydrates can be.
Today, the most common method for isolating cellulose is sulfite. It is used in various areas where carbohydrates are used. The chemistry of the process is very simple. According to this method, the wood is crushed and boiled in a mixture with calcium hydrogen sulfate. Then the cellulose, freed from all impurities, is separated on filters. The resulting lye contains monosaccharides, so it is used as a raw material for the production of alcohol. Cellulose is also used in the production of viscose, acetate and copper-ammonium fibers.
Sometimes carbohydrates are confused with hydrocarbons. Despite the fact that these two classes of substances have similar names, they have nothing to do with each other. The use of saturated hydrocarbons in everyday life and in production is a completely different story.
Classification of carbohydrates
Carbohydrates come in many varieties. This should definitely be taken into account when planning your diet. The classification of carbohydrates is divided into simple and complex or fast and slow.
Simple or fast carbohydrates include the following:
- Monosaccharides.
This category includes galactose, fructose, and glucose. These components are present in berries, fruits, and honey. Such substances are quickly absorbed and sharply increase blood sugar levels. As a result, glycogen is formed in the tissues, which is required for energy. When it is in excess, the substances form fatty deposits. To avoid negative consequences, the amount of monosaccharides should be no more than 25-35% of the total carbohydrates eaten during the day. - Disaccharides.
These mainly include sucrose, which includes regular sugar, and maltose. This component is present in malt, molasses, and honey. It is also found in milk sugar.
Complex or slow carbohydrates include polysaccharides. These substances include a large number of monosaccharides. They take a long time to digest and have a less sweet taste than simple carbohydrates. The main polysaccharides include the following:
- Starch and glycogen. These substances are present in cereals, legumes, potatoes, and corn.
- Cellulose. The element is found in cereals, seeds, vegetables, fruits, and bran.
- Cellulose. Ingredients include lettuce leaves, apples, pears, and carrots.
- Pectin. The substance is present in carrots, cabbage, citrus fruits, and strawberries.
- Inulin. The element is found in chicory, onions, barley, and garlic.
The main advantage of complex carbohydrates is that they slowly saturate the body. Thanks to this, the feeling of hunger does not occur prematurely.
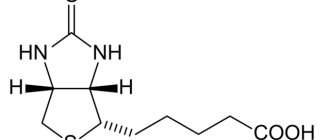
1.1. The concept and essence of carbohydrates
Carbohydrates, as essential components of the diet, not only determine the main energy homeostat of the body, but are also essential for the biosynthesis of many carbon-containing polymers. Over the course of a lifetime, an average person consumes about 14 tons of carbohydrates, including more than 2.5 tons of simple carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are the main component of the human diet, as they are consumed approximately 4 times more than proteins and fats. With a typical mixed diet, carbohydrates provide about 60% of the daily energy value, while proteins and fats combined provide only 40%. Carbohydrates in the body are used primarily as a source of energy for muscle work. The more intense the physical activity, the more carbohydrates are required. With a sedentary lifestyle, on the contrary, the need for carbohydrates decreases.
About 52-66% of carbohydrates are consumed with grain products, 14-26% with sugar and sugar products, about 8-10 with tubers and root vegetables, 5-7% with vegetables and fruits.
Carbohydrates are a fairly strong irritant of the exocrine pancreas, including the most active stimulator of insulin synthesis, which plays an important role in regulating carbohydrate metabolism and maintaining optimal glucose homeostasis for the body. Long-term nutritional overload with easily digestible carbohydrates initially causes β-cell hyperplasia, then can lead to weakening of the insular apparatus due to overstrain and the creation of preconditions for the development of diabetes mellitus
1.2. The role of carbohydrates
Carbohydrates serve as the main source of energy. The body receives over 56% of energy from carbohydrates, the rest from proteins and fats.
Depending on the complexity of their structure, solubility, and speed of absorption, carbohydrates in food products are divided into simple carbohydrates: monosaccharides (glucose, fructose, galactose), disaccharides (sucrose, lactose) and complex carbohydrates or polysaccharides (starch, glycogen, fiber).
Simple carbohydrates easily dissolve in water and are quickly absorbed. They have a pronounced sweet taste and are classified as sugars.
The most common monosaccharide, glucose, is found in many fruits and berries, and is also formed in the body as a result of the breakdown of disaccharides and starch in food. Glucose is most quickly and easily used in the body to form glycogen, to nourish brain tissue, working muscles (including the heart muscle), to maintain the required blood sugar level and create liver glycogen reserves. In all cases, with great physical stress, glucose can be used as a source of energy.
Fructose has the same properties as glucose and can be considered a valuable, easily digestible sugar. However, it is absorbed more slowly in the intestines and, entering the blood, quickly leaves the bloodstream. Fructose in a significant amount (up to 70 - 80%) is retained in the liver and does not cause oversaturation of the blood with sugar. In the liver, fructose is more easily converted into glycogen compared to glucose. Fructose is absorbed better than sucrose and is more sweet. The high sweetness of fructose allows you to use smaller amounts to achieve the required level of sweetness in products and thus reduce the overall consumption of sugars, which is important when building calorie-restricted diets.
Excess sucrose affects fat metabolism, increasing fat formation. It has been established that with an excess intake of sugar, the conversion of all nutrients (starch, fat, food, and partly protein) into fat increases. Thus, the amount of incoming sugar can serve to a certain extent as a factor regulating fat metabolism. Excessive sugar consumption leads to disruption of cholesterol metabolism and an increase in its level in the blood serum. Excess sugar negatively affects the function of intestinal microflora. At the same time, the specific gravity of putrefactive microorganisms increases, the intensity of putrefactive processes in the intestines increases, and flatulence develops. It has been established that these deficiencies manifest themselves to the least extent when consuming fructose. The main sources of fructose are fruits and berries. Glucose and fructose are widely represented in honey: the glucose content reaches 36.2%, fructose - 37.1%. In watermelons, all sugar is represented by fructose, the amount of which is 8%. The third monosaccharide, galactose, is not found in free form in foods. Galactose is a breakdown product of the main carbohydrate in milk, lactose.
Of the disaccharides in human nutrition, sucrose is of primary importance, which, upon hydrolysis, breaks down into glucose and fructose. Sources of sucrose in human nutrition are mainly cane and beet sugar. The sucrose content in granulated sugar is 99.75%. Natural sources of sucrose are melons, some vegetables and fruits.
Carbohydrate content per 100 g of food
| Vegetables and fruits | |||||
| White cabbage | potato | beet | apples | grape | |
| Glucose | 2.6 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 2.0 | 7.8 |
| Fructose | 1.6 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 5.5 | 7.7 |
| Sucrose | 0.4 | 0.6 | 8.6 | 1.5 | 0.5 |
| Hemicellulose | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.6 |
| Cellulose | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.6 | — |
| Starch | 0.1 | 16.0 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.6 |
| Pectin | 0.6 | 0.4 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 0.6 |
Complex carbohydrates, or polysaccharides, are characterized by a complex molecular structure and poor solubility in water. Complex carbohydrates include starch, glycogen, pectin and fiber.
Starch has basic nutritional value. Its high content largely determines the nutritional value of grain products. In human diets, starch accounts for about 80% of the total amount of carbohydrates consumed. The conversion of starch in the body is mainly aimed at satisfying the need for sugar.
Glycogen in the body is used as energy material to power working muscles, organs and systems. Glycogen restoration occurs through its resynthesis at the expense of glucose.
Pectins are soluble substances that are absorbed in the body. Modern research has shown the undoubted importance of pectin substances in the diet of a healthy person, as well as the possibility of using them for therapeutic purposes in some diseases, mainly of the gastrointestinal tract.
Fiber is very close in chemical structure to polysaccharides. Cereal products are characterized by a high fiber content. However, in addition to the total amount of fiber, its quality is important. Less coarse, delicate fiber is easily broken down in the intestines and is better absorbed. Fiber from potatoes and vegetables has these properties. Fiber helps remove cholesterol from the body.
The need for carbohydrates is determined by the amount of energy expenditure. The average need for carbohydrates for those who are not engaged in heavy physical labor is 400 - 500 g per day.
Simple carbohydrates
These carbohydrates are characterized by a simple structure. Thanks to this, they are quickly absorbed in the body. With a lack of physical activity, substances increase blood sugar. After this, it quickly falls, which provokes a feeling of hunger. Unspent carbohydrates are transformed into fat deposits. At the same time, their deficiency causes fatigue and increased drowsiness.
Simple carbohydrates are divided into 2 categories - monosaccharides and disaccharides.
Monosaccharides include:
- glucose - it is found in most fruits and berries. The component is also present in honey and green plant fragments;
- fructose - this substance is present in honey, berries, and fruits. It is also found in the seeds of certain plants;
- galactose is the only monosaccharide that is of animal origin. It is part of lactose, or milk sugar.
Disaccharides are considered the most important for human nutrition. The molecule contains glucose. The second sugar can be fructose, galactose or glucose.
There are these types of disaccharides:
- sucrose - it includes glucose and fructose. This category includes sugar from cane or beets;
- maltose - the substance contains 2 glucose residues. It is present in licorice sugar;
- Lactose is an element that includes glucose and galactose and is found in the milk of mammals.
List of healthy foods that contain fast carbohydrates:
- potato;
- pumpkin;
- corn;
- a pineapple;
- banana;
- melon;
- watermelon;
- White rice;
- nuts;
- dried fruits.
However, there are harmful foods that should be completely avoided.
These include:
- baked goods made from premium flour;
- candies;
- sweet carbonated drinks;
- snacks;
- alcohol;
- cakes, waffles, cookies.
Quality carbohydrate sources
Carbohydrates are an integral part of any diet. The body receives most of its energy and many vitamins and nutrients from them. Foods where carbohydrates are found in abundance include many plant foods such as rice, pasta, beans, potatoes and many other grains and vegetables.
When choosing grain products, we highly recommend choosing whole grain options such as whole grain bread, brown rice, whole grain pasta, quinoa, oats, and bulgur.
Sources of complex carbohydrates
What carbohydrates contain that are slowly digested:
- vegetables;
- legumes;
- cereals*;
- fruits;
- beet;
- carrot;
- corn;
- peas;
- potato;
- turnip;
- beans;
- lentils;
- lima beans;
- pinto beans;
- split peas;
- barley;
- oats;
- rice;
- rye;
- wheat;
- edible seeds.
*as well as grain products - whole grain wheat bread, crackers or pasta.
Sources of simple carbohydrates (Natural)
- Fructose (fruit sugar)
- Lactose (milk sugar)
- Fruits and juices such as apples, oranges, pineapples.
- Dairy products such as milk and yogurt.
Complex carbohydrates
These products are based on polysaccharides - starch and cellulose. Such substances ensure normal digestion and satiate a person for a long time.
The list of foods that contain a lot of complex carbohydrates includes the following:
- all vegetables - with the exception of potatoes and pumpkin;
- citrus fruit;
- berries;
- apples and pears;
- apricots;
- millet, pearl barley, buckwheat, oatmeal;
- legumes
Beverages in this category include unsweetened tea and coffee. There are also some complex carbohydrates in meat and fish. They are found in eggs, kefir, and cottage cheese.
Diet of complex carbohydrates
To lose weight, it is important to maintain food intake and water balance. It is advisable that breakfast, lunch and dinner take place at the same time every day. If you feel hungry between main meals, you cannot ignore it. Snacks are added, but no more than 2 times a day.
Without carbohydrates, human existence is impossible.
In the morning, metabolic processes in the body proceed faster, so in the first half of the day carbohydrates are a must on the menu. Minor consumption of cereals and fermented milk products for dinner is allowed, provided that you have had an energetic day. The main thing is that the total amount of carbohydrates does not exceed the daily norm. Regardless of your goal: gaining, maintaining or losing weight, it is best to eat at regular intervals.
Fast carbohydrates
Fast carbohydrates are considered simple and include only 1-2 molecules:
- 1 molecule contains monosaccharides;
- 2 molecules are present in disaccharides.
All fast carbohydrates have a high glycemic index. It exceeds 70. Such substances have a sweet taste and are perfectly soluble in water.
The breakdown of simple carbohydrates begins in the oral cavity. They penetrate the blood very quickly. Within a few minutes after consumption, glucose levels increase significantly. At the same time, it stays at a high level for no more than 30-40 minutes. Then just as suddenly it decreases.
Fast carbohydrates are required to restore energy after difficult physical activity or stress. They help bring a person out of a hypoglycemic coma.
However, you should not constantly use such substances. This provokes depletion of the pancreas and causes it to function under stress. It is an excess of simple carbohydrates that provokes the development of type 2 diabetes. When you eat simple carbohydrates at night, they transform into fats.
Foods with a high glycemic index include the following:
- sugar, honey;
- baked potatoes, mashed potatoes;
- boiled carrots and pumpkin;
- bananas, melons, watermelons, pineapples;
- confectionery;
- dates;
- bakery products.
Carbohydrates and weight loss
Many people associate carbohydrates exclusively with sweets, and, consequently, with excess weight. However, there is an easy way to channel your energy into losing weight. We are not talking about so-called carbohydrate diets; however, restriction in protein and healthy fats can negatively affect the health of the body. Therefore, such radical diets are possible only after an individual consultation with a doctor.
You can and should adjust your diet on your own. However, this must be done correctly and, first of all, you should give up fast carbohydrates. Those involved in sports are allowed to eat some foods with a high GI (their daily dosage should not exceed 1 g per kilogram of weight). Products with a low and/or medium glycemic index should be consumed at the rate of 2 g of carbohydrates per 1 kg of weight.
You can’t deny yourself any food group. Carbohydrates must come from cereals, vegetables, fruits, and bread.
Carbohydrates should be an essential part of any person's diet, especially if they engage in physical activity. After all, they are the main source of energy! Plan your diet correctly. Be energetic and beautiful!
Sources: C. A. Rosenbloom, E. J. Coleman (Eds.) Sports Nutrition A Practice Manual for Professionals. 5th edition. Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, Chicago, IL; 2012.
Slow carbohydrates
Slow carbohydrates are also called complex carbohydrates. They include 3 or more molecules. Therefore, these substances are characterized by slow breakdown. They are usually absorbed in the intestines. Complex carbohydrates include dextrin, starch, cellulose, glycogen, and glucomannan.
Eating slow carbohydrates promotes a smooth flow of glucose into the human body. In this case, no peaks or jumps are observed. It is complex carbohydrates that satiate a person for a long time, maintain a stable mood and make him more balanced.
The glycemic index of such products ranges from 0-40.
These include the following:
- durum wheat pasta;
- brown rice, barley, pearl barley, buckwheat, millet;
- legumes;
- fruits - peaches, oranges, cherries, apples, pears;
- vegetables and herbs - onions, spinach, zucchini, peppers, tomatoes, cabbage;
- mushrooms.
2.1. Use of carbohydrates in parenteral nutrition
Carbohydrates are used for parenteral nutrition due to the fact that they are the most accessible sources of energy for the patient's body. Their energy value is 4 kcal/g. Considering that the daily energy requirement is about 1,500–2,000 kcal, the problem of isolated use of carbohydrates to cover it becomes clear. If we transfer the calculation to an isotonic glucose solution, then this will require transfusing at least 7–10 liters of liquid, which can lead to complications such as overhydration, pulmonary edema, and cardiovascular disorders.
Structure of carbohydrates
The structure of carbohydrates includes several carbonyl and hydroxyl groups.
Depending on their structure, substances are divided into 3 categories:
- monosaccharides;
- oligosaccharides;
- polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are the simplest sugars that contain only 1 molecule. They have several groups that differ in the number of carbon atoms in the molecule. Monosaccharides containing 3 carbon atoms are called trioses. If the composition contains 5 atoms, they are called pentoses, if 6 - hexoses.
Pentoses, which are present in nucleic acids, are considered the most valuable for living organisms. Hexoses, which make up polysaccharides, are also of great importance.
Oligosaccharides contain 2-10 structural elements.
Depending on the quantity there are:
- diosis;
- trioses;
- tetraose;
- pentasaccharides;
- hexasaccharides.
The most significant are disaccharides, which include sucrose, maltose and lactose, as well as trisaccharides. This category includes melicitose, raffinose, and maltotriose.
Olisaccharides can contain homogeneous and heterogeneous structures.
Depending on this, the following types are distinguished:
- homooligosaccharides - all molecules have the same structure;
- heterooligosaccharides - molecules differ in structure.
Polysaccharides are considered the most complex carbohydrates. They include many monosaccharides - from 10 to several thousand.
Such substances include the following:
- starch;
- chitin;
- glycogen;
- cellulose.
Polysaccharides have a more rigid structure than oligosaccharides and monosaccharides. They do not dissolve in water and do not have a sweet taste.
Classification
Depending on the number of carbon atoms included in the molecule, the following groups are distinguished:
- Monosaccharides or simple sugars. They are also called “fast” carbohydrates or “easily digestible”. These include glucose, rabinose, galactose, fructose.
- Disaccharides or complex sugars (sucrose, maltose, lactose) break down into two molecules of monosaccharides when broken down.
- Polysaccharides – starch, fiber, pectins, glycogen (animal starch). These are “slow” carbohydrates - they are broken down within a few hours.
Simple
Simple carbohydrates are often referred to simply as “sugar.” They consist of two sugar blocks connected together. These blocks can be glucose, fructose and galactose. Because the chains are short, they are easy to break, which is why they taste sweet as soon as they touch your tongue. They are also quickly digested and absorbed into the blood.
Read more about the health benefits and harms of sugar.
Foods rich in simple carbohydrates include sweeteners (sugar, syrup, honey), sweets, jellies, jams and refined flour. Fruits, vegetables, beans and milk also contain fast sugars, but they also contain important vitamins and minerals, fiber and protein, so you shouldn't limit them.
Complex
Complex carbohydrates are different in that they simply contain fiber, which slows down their absorption. They consist of three or more sugars linked in a chain and are typically found in foods that are also rich in protein, healthy fats, vitamins and minerals. They contain the same sugars as simple sugars, but their chains are longer and harder to break down. It is because of this that their taste does not seem so sweet. Longer chains also slow down digestion, leading to a smoother insulin response and a longer feeling of fullness. Foods rich in complex carbohydrates include bread, rice, pasta, beans, whole grains and vegetables.
Fiber is a type of dietary fiber that is not absorbed by the body. The uniqueness of fiber lies in its ability to increase in size and not be digested by food enzymes produced in the stomach and small intestine. The swollen plant mass, passing throughout the gastrointestinal tract, cleanses its walls of undigested food debris and stimulates intestinal motility.
Composition of carbohydrates
The composition of carbohydrates is divided into the following categories:
- Monosaccharides
- contain 1 monomer unit and are not hydrolyzed to form simpler carbohydrates. Monomers are varied. This is due to the difference in structure. Typically, monosaccharides in living organisms are ring carbon chains that contain 5 or 6 carbon atoms. The most important monosaccharides are ribose and deoxyribose, which are present in nucleic acids. They also include glucose as a source of energy and fructose. - Disaccharides
- include 2 monomer units. We can say that they consist of 2 monosaccharides. Substances combine through hydroxyl groups. In this case, water is separated. The most famous disaccharide is sucrose. Its molecule includes glucose and fructose residues. 2 glucose residues are part of maltose. - Polysaccharides
- include more than 10 monomer units. This category includes starch, chitin, cellulose, etc. Starch and glycogen accumulate in organisms as reserve nutrients. Starch has a less branched structure than glycogen. Cellulose forms the walls of plant cells. Due to this, it realizes structural and protective functions. Chitin solves similar problems in fungi and animals.
Diet food
There are many diets that are based on the complete or partial exclusion of carbohydrates from the diet, as well as increasing the consumption of proteins and fats. The US Department of Agriculture conducted a survey, according to which it was found that people who eat foods rich in carbohydrates are predominantly of normal weight. Foods that are high in carbohydrates are more nutritious but lower in calories.
As you know, in America more than half of the population suffers from the problem of excess weight. Moreover, the number of such people is steadily growing. A long-term survey of the population on the foods they eat showed that people whose diet is dominated by carbohydrates receive fewer calories than those who eat proteins and fats, with the same amount of food eaten. This group of people of all those surveyed, and there were more than 10,000 people, had the lowest body weight. The reason is that per 1000 calories of carbohydrate-containing foods, there is a lot of fiber and water. This group of people received more nutrients from food, namely: vitamins A and C, carotene, calcium, iron and magnesium. Fats, cholesterol, zinc, sodium and vitamin B12 were contained in small amounts in their diet.
The use of carbohydrates and fats in foods is closely related. However, so does the use of carbohydrates with proteins. The high effectiveness of carbohydrates as energy sources lies in their ability to store protein. When a large amount of carbohydrates is consumed in food, the body uses fewer amino acids as energy material. In general, these substances are not essential components of nutrition, since they can be synthesized from amino acids and glycerol; however, their role cannot be underestimated. The intake of carbohydrates in food should be at least 50 grams per day. Otherwise, metabolic processes may be disrupted.
However, excess consumption of carbohydrates leads to the formation of subcutaneous fat. When building a diet, it is important not only to satisfy a person’s need for these substances, but also to balance the consumption of their different types. It is important to monitor the ratio of simple and complex carbohydrates. When a lot of sugars enter the body, they cannot be fully synthesized into glycogen and turn into triglycerides, which contribute to the formation of fatty tissue. When insulin levels in the blood are elevated, this process accelerates.
Complex carbohydrates, unlike simple ones, are broken down slowly, so their content in the blood increases gradually. In this regard, it is advisable that the main carbohydrate part in food products consists of difficult-to-digest substances. Their share should be between 80 and 90 percent. The lack of complex carbohydrates is especially noticeable for those who suffer from diabetes, obesity, atherosclerosis and diseases of the cardiovascular system.
As you already understand, carbohydrates are most often used in nutrition and medicine. But the scope of carbohydrates does not end there. Where else are they used?
Properties of carbohydrates
The main properties of carbohydrates include the following:
- Molecular mass.
Among carbohydrates you can find very simple elements, the molecular weight of which is approximately 200, and giant polymers. Their molecular weight reaches several million. - Solubility in water.
Monosaccharides easily dissolve in water and form syrups. - Oxidation.
This process leads to the production of the corresponding acids. For example, the oxidation of glucose with an ammonia solution of silver oxide hydrate leads to the formation of gluconic acid. - Recovery.
When reducing sugars, it is possible to obtain polyhydric alcohols. Hydrogen in nickel, lithium aluminum hydride, etc. act as a reducing agent. - Alkylation.
This term refers to the formation of ethers. - Acylation.
This concept includes the formation of esters.
Glucose
This carbohydrate is well absorbed by the body and can be used in some medications. In addition, glucose is widely used in the confectionery industry. It is used to make marmalade, caramel, gingerbread and other products. In the textile industry it plays the role of a reducing agent. And in the production of glyconic and ascorbic acids, glucose is the starting product. It is also used to synthesize some industrial sugars.
Fermentation of glucose is of considerable importance. It occurs during pickling of cabbage, cucumbers, milk and other products, as well as during ensiling of feed. In the production of beer, alcoholic fermentation of glucose is used.
Digestion of carbohydrates
Among carbohydrates, the human body primarily digests polysaccharides - starch from plant products and glycogen, which is present in animal foods.
Polysaccharides are broken down by digestive enzymes into building blocks - free D-glucose. This process occurs under the influence of salivary amylase and is accompanied by the formation of a mixture of maltose, glucose and oligosaccharides.
Digestion of carbohydrates continues and ends in the small intestine. This process is influenced by pancreatic amylase, which enters the duodenum.
The hydrolysis of disaccharides is triggered by enzymes that are present in the outer layer of epithelial cells lining the small intestine. In the epithelial cells of the small intestine, partial transformation of D-fructose, D-galactose, D-mannose into D-glucose occurs. A mixture of simple hexoses is absorbed by epithelial cells and enters the liver through the bloodstream.
Starch
Starch is a valuable nutrient. To make it easier for the body to absorb, products are subjected to heat treatment. At high temperatures, partial hydrolysis of starch occurs, as well as the formation of water-soluble dextrins. Dextrins, once in the digestive tract, are hydrolyzed to glucose, which is well absorbed by the body. If we talk about the use of carbohydrates in industry, we cannot ignore starch. The main products that are obtained from it are glucose and molasses. This further expands the area in which carbohydrates can be used. The process of producing glucose and molasses from starch can be briefly described as follows.
Starch is heated in a mixture with dilute sulfuric acid. Excess acid is neutralized with chalk. The calcium sulfate precipitate that forms during neutralization is filtered off. Then the solution is evaporated and glucose is isolated from it. If you do not complete the hydrolysis process, you will end up with a mixture of glucose and dextrins, which is called molasses. It is used in the confectionery industry. In addition, dextrins derived from starch are widely used as an adhesive and paint thickener. Starch proves how versatile carbohydrates can be used. The chemistry of the processes is not at all complicated.
Previously, starching of linen was used, which allows you to breathe a second life into the fabric and extend its service life. Starch and products derived from it are also used in the textile, pharmaceutical and foundry industries.
Metabolism of carbohydrates in the body
The metabolism of carbohydrates in the human body is based on the processes described below:
- The brain does not have a glycogen reserve, so it constantly requires glucose. Carbohydrates are the only source that helps cover the energy costs of the brain. It is the brain tissue that absorbs 70% of the glucose that is released by the liver.
- During active work, muscle tissue receives large amounts of glucose from the blood. In them, this substance is transformed into glycogen. When glycogen breaks down, enough energy is available for muscle contraction.
- The level of glucose in the blood is regulated by hormones - glucagon, somatotropin, cortisol, insulin, adrenaline. Insulin helps reduce blood glucose when it rises, facilitates its entry into cells and ensures the deposition of the substance in tissues in the form of glycogen. When blood glucose parameters decrease, somatotropin, cortisol, adrenaline and glucagon inhibit the uptake of glucose by cells. Due to this, glycogen is transformed into glucose.
Storage of glucose in the form of glycogen
The metabolism of carbohydrates in the body occurs as follows. After we eat something, the level of glucose in the blood rises and the pancreas is the first to react to this. It releases the hormone insulin, which signals the body's tissues to absorb excess glucose. Some of this glucose is used by muscle and liver cells to build the polysaccharide glycogen.
Muscles store 2/3 of the total amount of glycogen in the body and use it to provide their own nutrition during exercise. The remaining 1/3 is accumulated by the liver and is more generous in its distribution; When energy is depleted, it shares glycogen in the form of glucose in the blood with the brain and other organs.
When blood glucose concentrations drop and cells need energy, the bloodstream is flooded with pancreatic hormones, glucagons. Thousands of enzymes in liver cells release glucose into the blood to feed the rest of the body's cells. Another hormone, adrenaline, has a similar effect and is part of the body's defense mechanism during times of danger (the "fight or flight" response).
Although glucose can be converted to fat, body fat can never be converted back to glucose and provide normal nutrition to the brain. This is one reason why fasting or low-carb diets can be dangerous.
With a serious carbohydrate deficiency, the body faces two problems at once. First of all, due to a lack of glucose, it is forced to obtain it from proteins, thereby distracting them from such vital work as maintaining immune defense. The functions of proteins in the body are so irreplaceable that, just to avoid their use for energy, it is already worth maintaining the level of carbohydrates; this is called the "protein-sparing" effect of carbohydrates.
Also, without enough carbohydrates, the body cannot properly manage its fat reserves. (Fat fragments must combine with carbohydrates before they can be used to produce energy.) The minimum amount of carbohydrates required to fully protect protein and prevent ketosis for an average-sized person is about 100 g/day. And it’s better if these are easily digestible carbohydrates in an amount 3-4 times higher than this minimum.
Carbohydrate-rich foods
The following are foods rich in carbohydrates in large quantities:
- Bread.
Wheat flour is considered an important source of such substances. It is worth considering that bread should be consumed in moderation. In addition to starch, a whole grain product contains proteins, minerals, vitamins, and fats. These substances are very useful. - Rice.
Rice contains a lot of carbohydrates and B vitamins. However, nutritionists advise giving preference to unpolished varieties. - Legumes.
Such products have high nutritional value. They are characterized by a hard cellulose membrane, so it is important to pay attention to the correct cooking method. - Potato.
This product contains slightly less carbohydrates - about 20%. The remaining part is taken up by water. In addition, the composition contains vitamins and minerals. - Green vegetables.
In addition to complex carbohydrates, such foods include many vitamins. It is especially useful to eat fresh vegetables. Preference should be given to lettuce, peppers, green beans, young peas, and cabbage. You should definitely eat spinach because it contains a lot of iron.
Choose the right carbohydrates
When it comes to food and drinks, choose options filled with beneficial micronutrients and vitamins. The three rules below will help you with this. But, let us finally note that if you are a very active person who wants to increase your productivity, then not all of these rules will suit you.
- Eat more complex carbohydrates from natural foods
Vegetables, legumes, nuts and seeds, 100% whole grain bread, pasta, brown rice - these foods are a good source of fiber, vitamins, minerals and protein.
- Eat less processed food
Foods like white rice, white bread and regular pasta are more processed and therefore lack fiber.
- Eat simple carbohydrates in moderation
Most sources of simple (fast) carbohydrates are considered “empty calories” because they contain virtually no micronutrients but are high in calories. They are also the most common cause of blood sugar spikes. Fruits and milk are exceptions because they are high in vitamins and minerals.
Norm of carbohydrates per day for the body
The need for carbohydrates depends on the intensity of intellectual and physical activity. On average, the norm of carbohydrates per day for the body is 300-500 g. About 20% can be carbohydrates that are easily digested.
Older people should consume a maximum of 300 g of carbohydrates per day. In this case, the number of simple elements should not be more than 15-20%.
If you are overweight or have other pathologies, the amount of carbohydrates should be limited. However, this should be done gradually. Thanks to this, the body will be able to adapt to changes in metabolic processes. The restriction should start with 200-250 g per day. After a week, it is permissible to reduce the amount of carbohydrates to 100 g.
If you sharply reduce the amount of carbohydrates over a long period of time, there is a risk of developing various disorders.
These include the following:
- decreased blood sugar levels;
- general weakness;
- severe decrease in intellectual and physical activity;
- weight loss;
- metabolic disorder;
- increased drowsiness;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- hand tremors;
- feeling of hunger;
- colon cancer;
- constipation
Unpleasant symptoms can be eliminated after eating sugar or other sweet foods. However, they should be eaten in moderation. This will help avoid weight gain.
Excess carbohydrates, especially simple ones, are also harmful to the body. It leads to an increase in blood sugar levels. As a result, some substances are not used and lead to the accumulation of fatty deposits. This provokes diabetes mellitus, caries, and atherosclerosis. There is also a risk of flatulence, obesity, heart and vascular disease.
Carbohydrate requirement calculator
Age Gender Height Weight Goal Activity
If you're not sure what percentage of carbs is right for you, just follow the rule of thumb:
For weight loss, start with 45-50% and reduce the percentage. If you are actively training for more than an hour every day or preparing for an event that will require remarkable endurance from you (for example, a marathon), then you are better off increasing the percentage to 55-65%.
| Type of activity | Recommended rate |
| Very light weight exercises | 3-5 g/kg |
| Moderate intensity exercise, 60 min/d | 5-7 g/kg |
| Moderate/high intensity endurance exercise, 1-3 hours/day | 6-10 g/kg |
| Moderate to high intensity exercise, 4-5 hours/day | 8-12 g/kg |