Biotin - what kind of vitamin?
The beneficial properties of the compound were described by Wilderson at the beginning of the 20th century. Translated from Latin, “bios” means life. The component is soluble in water, alcohols, and is not prone to destruction under the influence of radiation.
Vitamin H has the following names:
- biotin;
- coenzyme R;
- AT 7.
Biotin takes part in many vital processes occurring in the body.
The compound is considered a water-soluble substance.
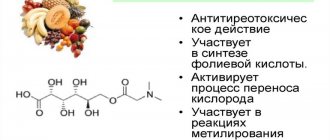
It is known that coenzyme enhances the activity of metabolism of fatty acids and leucine. Biotin takes part in gluconeogenesis. The component is included in hair cosmetics. Its use is advisable in the treatment of diabetes mellitus.
Daily requirement
| Daily intake of vitamin Biotin | ||
| Age | mcg/day | |
| 0—8 months | 5 | |
| 7-12 months | 6 | |
| 1—3 | 8 | |
| 4—8 | 12 | |
| 9—13 | 20 | |
| 14—20 | 25 | |
| 21 and > | 30 | |
For athletes , people doing heavy physical work and people suffering from alcoholism, the dose is increased.
The need for biotin is partially met by synthesis by intestinal microflora, but the main amount must be supplied to the body with food.
Why does the body need vitamin biotin?
Vitamin H is a vital compound. Coenzyme regulates:
- metabolic processes;
- glucose level;
- division of cellular elements;
- functioning of the nervous system;
- functioning of the digestive tract;
- adequate condition of blood vessels and heart.
Important! Biotin protects the brain from adverse effects, supports the functioning of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland, and controls the number of enzymes.
Biotin is synthesized by intestinal microflora in small quantities that do not satisfy the body's needs. This is why it is necessary to eat a balanced diet. It is also recommended to take the compound in supplement form.
The coenzyme helps maintain the beauty and health of hair, skin and nails. Biotin is a component of cosmetics. Its entry into the body improves metabolic processes in the epidermis, prevents splitting of nails and dry, brittle hair.
Important! External use of vitamin H is less effective than internal use. The substance is prescribed as an oral medication for alopecia.
Including biotin in your daily diet
There are two ways to provide the body with the necessary amount of vitamins B7: through a nutritious, varied diet or using synthetic vitamin supplements.
Vitamin complexes with biotin
Biotin is produced both as a monovitamin and as part of multivitamin complexes. The most common inclusion of biotin is in multivitamin B complexes, to which it belongs. Vitamins of this group in a complex dosage promote a high level of metabolism, maintain cognitive functions of the brain, and have a calming effect on the nervous system. They also interact in symbiosis with each other, so the complex use of B vitamins is optimal.
To get the most benefits, purchase a biotin supplement made from natural food sources without chemical fillers. These complexes are made by combining different nutrients so that the body recognizes the vitamins and minerals as normal food and uses them in the digestive process.
Food Sources of Vitamin B7
There are eight different forms of biotin, one of which, D-biotin, can only be obtained from food. This is further proof of why it is so important to eat nutritiously and correctly: it is always better to get vitamins and minerals from natural food sources.
According to research, a group of products has been identified where the biotin content is the highest:
- beef liver - 30 mcg per 85 g of product;
- egg yolk - 10 mcg;
- brewer's or nutritional yeast - 1.4-14 mcg per 7 grams of product (about 1 level tablespoon);
- red fish (salmon, pink salmon, chum salmon) - 5 mcg per 85 g of product;
- nuts (almonds, peanuts, sunflower seeds, walnuts) - 1.5-3 mcg per 100 g;
- avocado - 2-6 mg per 1 piece;
- cheese, dairy products (milk, yogurt, cottage cheese) - 0.2-1.5 mcg per 100 g;
- cauliflower - 0.2-2 mg per 100 g;
- whole grain bread - 0.2-1 mcg per 100 g.
To enrich your daily diet with vitamin H, it is recommended to include recipes for the following dishes in your menu:
- For breakfast: egg dishes, yogurt, cottage cheese casseroles, whole grain bread sandwiches with cottage cheese and red fish;
- For lunch: stewed beef liver, meat or chicken;
- For snacks: nuts, berries, fruits, avocados;
- For dinner: cauliflower cooked in batter, legumes (lentils, chickpeas), baked fish or meat, green salads (especially spinach).
Reference! Vitamin B7 is found only in egg yolk. Often in various diets it is recommended to eat only proteins, limiting the consumption of yolks as they are higher in calories. This leads to the dieter depriving himself of an additional source of biotin.
Names of vitamins with biotin for hair
Dietary supplements including coenzyme can be:
- monocomponent;
- polycomponents.
Experts call the following effective vitamins for hair loss containing biotin:
- Biotin Life Extension (600 mcg). The package contains 100 capsules. Daily dosage – 1 capsule, taken after meals.
- California Gold Nutrition Biotin (10,000 mcg). Each package contains 90 vegetable soft gels. The supplement helps increase energy, improve the functioning of the immune system, and maintain healthy skin, hair, and nails. The dietary supplement does not contain GMOs and gluten. It is recommended to take 1 capsule per day.
- Biotin Now Foods (5000 mcg). Each package contains 120 vegetable capsules. The dietary supplement has a quality certificate and is suitable for vegans and vegetarians. According to the instructions, take 1 capsule per day after meals.
- Doppelgerz Beauty Biotin (150 mcg). Vitamin B7 or biotin is designed to improve the condition of skin, nails and hair. The product is used for the treatment and prevention of alopecia. The package includes 30 capsules. The dosage is to take 1 capsule after meals.
- Blagomin vitamin H. The supplement contains vitamin B12 and biotin. The package contains 90 capsules. The course of treatment is 30 days. You should take 1 capsule per day after meals.
Biotin dosage. What is the norm for biotin?
It is important to understand that it will take time for visible effects, especially in hair treatments.
The minimum course of biotin is about three months. In case of treatment, it is advisable to agree on the duration of the course and dosage with the attending physician.
The dosage of biotin depends on the tasks.
• If there are no obvious problems with your hair, but you just need to support it, for example, in winter or after coloring your hair, then you can get by with dosages not exceeding 1000 mcg of biotin. • For signs of deterioration, dryness, brittleness and to stimulate hair growth, trichologists prescribe 5000 mg of biotin per day. • At the first signs of baldness and skin diseases, it is recommended to take biotin at a dose of at least 10,000 microns per day.
Biotin, like all B vitamins, does not accumulate in our body and is quickly eliminated from the body through urine and feces.
Therefore, taking biotin in doses significantly higher than the daily requirement for a long time is considered safe.
Indications for use of vitamin H (biotin)
The purpose of the compound is advisable for various pathologies. Vitamins with biotin for people are recommended in the following cases:
- alopecia;
- psoriasis;
- eczema;
- dysfunction of the nervous system;
- rapid weight loss;
- diabetes;
- depression;
- disorders associated with enzyme production;
- prolonged use of antibacterial drugs;
- oily, dry hair and skin;
- thinning of the nail plate;
- loss of appetite;
- difficulty falling asleep;
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Vitamin H deficiency, which has a special biological role, may be associated with the following factors:
- use of antibacterial drugs;
- use of COCs;
- drinking alcoholic beverages in significant quantities;
- disturbance of intestinal microflora;
- rapid weight loss.
Important! Taking vitamins containing biotin primarily affects the skin, hair and nails due to their rapid renewal.
Hypovitaminosis can be suspected by the following manifestations:
- chronic fatigue;
- pathological changes in complexion;
- dermatitis of various etiologies;
- depression and mood swings;
- digestive disorders;
- muscle tingling and cramps;
- memory loss;
- anemia;
- fragility and hair loss;
- increased glucose levels;
- splitting of nails;
- early gray hair.
Vitamin deficiency causes the following symptoms:
- alopecia;
- depression;
- early gray hair;
- chronic dermatitis and eczema;
- muscle wasting;
- developmental delay in children;
- high glucose concentration;
- decreased cognitive function.
Attention! The risk group for hypovitaminosis includes pregnant and lactating women, people who drink alcohol in significant quantities.
Hypovitaminosis
Causes
| This section is missing references to information sources. Information must be verifiable, otherwise it may be questioned and deleted. You may edit this article to include links to authoritative sources. This mark was set on December 6, 2020 . |
- genetic diseases ( Biotinidase deficiency
- no more than 5 cases per 100 thousand people[6][7]); - the use of antibiotics and sulfa drugs inhibits the healthy intestinal microflora that synthesizes biotin;
- abuse of diets that limit normal nutrition;
- digestive disorders caused by atrophy of the mucous membrane of the stomach and small intestine (malabsorption syndrome after resection of the small intestine);
- regular consumption of saccharin, which negatively affects the absorption and metabolism of biotin, and also inhibits the intestinal microflora that synthesizes biotin;
- consumption of raw eggs, the protein of which contains the glycoprotein avidin, which interacts with biotin;
- consumption of products containing sulfur compounds as preservatives (E221-E228) (sulfur dioxide, formed when such products are heated, as well as when they come into contact with air, destroys biotin);
- alcohol abuse (alcoholic drinks interfere with the normal absorption of biotin).
Manifestations
| This section is missing references to information sources. Information must be verifiable, otherwise it may be questioned and deleted. You may edit this article to include links to authoritative sources. This mark was set on December 6, 2020 . |
With a lack of biotin, the following are observed:
- skin lesions on the hands and feet
- dry and unhealthy skin tone
- pale smooth tongue
- drowsiness, depression
- muscle soreness and weakness
- hypotension
- high cholesterol and blood sugar levels, leading to the development of hyperglycemia
- anemia
- loss of appetite and nausea
- deterioration of hair condition
- growth slows down.
Absorption, exchange and excretion[edit | edit code]
Biotin is easily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and appears in the urine mainly unchanged, as well as in the form of metabolites: bis-norbiotin and biotin sulfoxides. The ring system in the biotin molecule is not destroyed in the mammalian body. Application. Large doses of biotin (5-10 mg/day) are used for seborrheic dermatitis in newborns, as well as for genetic defects of biotin-dependent enzymes. During long-term parenteral nutrition, vitamin preparations containing biotin should be added to nutrient solutions.