How does the disease develop? ↑
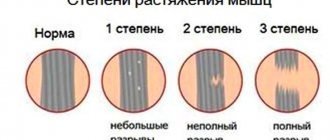
This term means that due to overload, a violation of the condition of one of the striated muscles has occurred.
The concept of "trigger"
A trigger point is a lump within the affected muscle, pressure on which causes pain.
The diameter of one such point is about 1-3 mm, but they can merge, forming a trigger zone up to 10 mm in diameter.
There are 2 types of trigger points - active and latent.
Active trigger
This is a very sensitive area of the muscle, identified by touch as a painful lump, being painful even at rest.
This trigger:
- prevents complete stretching of the affected muscle;
- weakens its strength;
- when pressed, it causes such sharp pain in a person that he literally jumps (“jumping symptom”).
Pain occurs not only locally, but also spreads over some distance.
Referred pain has one or more of the following characteristics:
- dull;
- aching;
- may be accompanied by numbness, tingling, or goosebumps.
As a rule, the location of this point coincides with the traditional acupuncture zone.
Latent trigger
Such points are found much more often; in rest they do not make themselves felt.
When certain situations arise, a latent point can transform into an active trigger.
These conditions include:
- hypothermia of this area;
- prolonged uncomfortable position with “use” of this muscle;
- increasing the load on the sore muscle.
One of the common causes of back pain is osteophytes. From our article you can find out why spinal osteophytes appear.
What is a paramedian disc herniation? Find out here.
There are three stages of the pathology:
- Stage 1 – acute. There is constant pain in the area of trigger points.
- Phase 2 – subacute: pain only when moving.
- Stage 3 – chronic: discomfort and slight pain in the area of the sore muscle; there are only latent trigger points.
There is such a point of view on the occurrence of pain: a trigger active point occurs in the place where microtrauma to the fibers that make up the muscle occurred.
A large number of calcium ions are released from damaged myofibrils, and other cell structures (for example, mitochondria) are also destroyed, from which ATP and its precursors are released.
Due to the constantly existing compaction, blood flow in the muscle is disrupted, it is damaged, and it becomes difficult for it to contract. As a result of such a vicious circle, the blood supply to the local muscle is increasingly disrupted, and the pain syndrome progresses.
Warm-up
Before loading your neck, you need to warm up your neck muscles and joints.
- To do this, stand up straight with your feet shoulder-width apart. Leave your hands on your belt. Some people may feel dizzy during exercise. Therefore, be careful.
- Tilt your head all the way to the right, then to the left. Slowly.
- Rotate your head clockwise and back. Again, do everything slowly. When you rotate your head, try to draw a circle with the maximum radius.
- Another great exercise is to draw a huge figure eight with your nose in the air. The movement is difficult, so it warms up the neck perfectly.
Spend at least 2-3 minutes warming up. And never start working with cold muscles.
Types of pathology ↑
Based on the frequency of involvement in the pathological process, the following muscle groups can be named:
- cervical muscles;
- back extensors;
- muscles of the shoulder girdle;
- pectoralis minor muscle;
- piriformis muscles.
Myofascial syndrome can be caused by any other muscle.
There are 2 types of syndrome:
- Primary: pain develops in muscles not affected by the pathological process.
- Secondary: muscle pain due to an underlying disease of the musculoskeletal system (intervertebral hernia, rheumatoid polyarthritis, spondylolisthesis, vertebral fractures).
Fig.: spondylolisthesis
Useful tips
The subclavian muscle is pumped more effectively if the athlete stands in a wide position. Additionally, this activates the clavicular heads and provides a good stretch. With a narrow emphasis, it is more difficult to perform training exercises, since most of the weight falls on the elbows. This position also provides a good load on the chest bone and the muscles close to it.
The quality of pumping of the subclavian muscle depends on the position of the legs during training. By placing the lower limbs on a hill, the athlete activates all the pectoral muscles in a comprehensive manner. To avoid injury, you should first warm up properly, and only then start doing push-ups.
The key advantage of the described exercises is that they are undemanding in the places where they can be practiced. By going on vacation, being at home, or finding 10-15 free minutes at work during your lunch break, a person can gradually pump up the subclavian muscle, thereby eliminating the possibility of its inflammation, as well as providing himself with a good, beautiful figure.
Sternocleidomastoid muscle: functions
- People who perform monotonous movements with certain muscle groups or hold their head or limbs for a long time in a certain position;
- Middle-aged women and men;
- Faces with rounded and skewed shoulders.
Thus, myofascial syndrome refers to any regional symptoms emanating from soft tissues and having the following basic characteristics:
- painful lumps are detected in the muscle;
- pain is not only local, but also reflected;
- There are active triggers in skeletal muscle ligaments that have the above characteristics.
Contracting independently, it ensures that the head is tilted towards the working fibers while simultaneously turning the head in the opposite direction. If the muscles on both sides tense, the neck and head straighten, it is possible to tilt the head back and move it forward, bend the neck and control it back to its original position.
And also, together with the trapezius muscle, it helps to hold the head (just imagine how difficult this is, because the average weight of an adult’s head is more than three and a half kilograms!) in a fixed, stable position while simultaneously working the lower jaw. For example, when chewing or talking.
How to pump up a man's sternum muscles at home?
Regarding the gym, everything is clear. We hope we were able to answer this question. But what about those people who cannot afford a membership to a fitness center? Should they really forget about training forever? No, no, no and no again! Even without barbells and expensive exercise equipment at home, you can properly increase the volume of your pectoral muscles. Don't believe me? But in vain!
How to pump up a man’s sternum muscles at home without iron? The best way to do this is to do push-ups. There are several variations of this exercise that allow you to adjust the load. The most effective are:
- Classic push-ups with wide arms.
- Push-ups with emphasis on the knees (suitable for beginner athletes with a low level of physical fitness).
- Elevated push-ups (fitball, bench). Like the angled barbell press, it shifts the load to the upper pectoral muscles.
- Plyometric (explosive) push-ups. When performing them, you need to quickly go down from the starting position, and then rise up with a sharp explosive movement, lifting your palms off the floor.
- Dips. In order for the pectoral muscles to receive the main load, you need to lean forward while performing.
View gallery
Pain syndrome and sternocleidomastoid muscle
Inflammation and overstrain in it are not uncommon phenomena. As a result of injury, excessive static loads or physical stress, so-called stress points arise in the muscle. A distinctive feature of such pathological processes is the reflection of the pain syndrome. This means that tension points and pain do not arise directly in the muscle fibers, but, for example, in the cheek, forehead, ear, temple, around the eyes, or manifest as headaches and toothaches.
The affected sternocleidomastoid muscle of the neck can cause other, at first glance, not quite typical symptoms of muscle pain: dizziness, lacrimation, pain in the eyes and their redness, even to the point of decreased visual acuity, cough, rhinorrhea (runny nose).
To palpate the muscle and identify possible painful points or inflamed areas, stand in front of a mirror, turn your head slightly to the side, for example to the right, then stretch your left ear towards your left shoulder. This way you will force the muscle to tense and you will be able to visualize it easily. It is this muscle shaft that is the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
If you are examining a muscle not in yourself, but in another person, then it is better to do this with the patient in a horizontal position. Place him on a flat surface, move his head slightly to the side and begin palpating from the mastoid process. Use three fingers of your working hand (index, middle and ring) to inspect with light sliding movements.
Using light massaging movements, feel it lengthwise from top to bottom and identify possible painful areas. If you find them, perform a lung massage, as if warming up and slightly rubbing the selected areas. Do not overdo it and if pain increases, stop, give the muscle a rest and continue the massage.
The sternocleidomastoid muscle must be stretched at the end of the therapeutic manipulations. This will consolidate the achieved effect and prevent the occurrence of pathological conditions and the progression of the inflammatory process.
How to quickly pump up the sternum muscles for a man?
This is perhaps one of the most popular sports-related queries on the Internet. Since the article is devoted to training the pectoral muscles, it cannot be ignored. So, how can a man build up his sternum muscles in a month at home or in the gym? There is no clear answer to this question. If you decide to take the path of a healthy lifestyle, then you must understand that gaining muscle mass is far from the fastest process, which requires endurance and patience. In addition, it all depends on genetics: in some athletes, the pectoral muscles can grow by leaps and bounds, while in others, on the contrary, they can be a lagging muscle group. Age, injuries, and general fitness also play an important role. You will be able to see the results of breast pumping only if you train competently and regularly, eat right and recover sufficiently.
View gallery
History of views on the problem ↑
- The first to describe such muscle compactions was the surgeon Frohrip from Germany back in 1834. He called them “muscle calluses.”
- A. Steindler, based on numerous studies, concluded that “calluses” do not exist in the muscle.
- Shtokman decided that such compactions were connective tissue hyperplasia, so in 1915 the syndrome was called “fibrositis.”
- In 1920, Virchow concluded that the cause of such lumps and pain was rheumatism. His conclusions were confirmed by the scientist Port.
The fundamental work that doctors now rely on is the two-volume book “Myofascial pain” by Travell and Simons.
The following scientists contributed to the formation of ideas about myofascial syndrome in Russia: F.A. Khabirov, E.S. Zaslavsky, R.A. Zulkarneev, Ya.Yu. Popelyansky, G.A. Ivanichev.
Petrov K.B. distinguishes three types of syndrome depending on its cause:
- vertebrogenic (provoked by pathology of the spine);
- arthrogenic (caused by joint disease);
- viscerogenic (arising from diseases of the internal organs).
Does it hurt under the left shoulder blade? Find out why there is pain under the left shoulder blade from our article.
How to treat pain in the shoulder joint? Read in this material.
What does prevention of osteochondrosis include? The answer is here.
Barbell for pumping shoulders
It wouldn’t hurt to also learn how to pump up your shoulders with a barbell. The barbell is a good alternative to dumbbells. It can replace them in almost all shoulder training exercises. Its only advantage is that it allows the arms to always be parallel to each other, which has a beneficial effect on the technique of performing some complex exercises.
Warm-up is also necessary. Examples of exercises you can do include angled presses, chin raises, and chest rows. An empty bar for 15-20 reps is fine for a beginner.
Perform the exercises very carefully, following the technique, otherwise you may get injured.
Stretching and training exercises for the sternocleidomastoid muscle
Stretch #1
Tilt your head back, turn your face to the side - this way the muscle on the opposite side of the tilt stretches. Repeat several times on both sides.
Stretch #2
Turn your head to the right and touch your chin to your shoulder (the muscle on the left is stretched). Repeat the stretch on the opposite side.
It is very important to breathe correctly when performing loads and stretches on the neck muscles, especially the sternocleidomastoid. Since it is also involved in the breathing process, to reduce its tension, when doing exercises, breathe deeply, but with your stomach.
Exercises aimed at strengthening muscle fibers consist of static tension of individual muscle groups by working them and counteracting muscle force. To do this, place your palm on your forehead and, resting it, try to move your hand with your head. Do the opposite, forcing the posterior fibers to tense, placing emphasis with clasped hands on the back of the head.
Upper, middle and lower chest workout
When performing push-ups, as well as various presses and fly-ups while lying in a horizontal position, all three sections of the pectoral muscles work, but the middle and lower bundles receive the greatest load. To focus on working out the upper section, you need to perform exercises on a bench lying down with an upward tilt. How to pump up the lower sternum muscles for a man? If you have poor development in this area, you should add dips or crossover flyes to your training program.
How to pump up the sternum muscles for a man in the gym? Let's look at the most popular exercises.
View gallery
Symptoms and signs ↑
With this syndrome, a painful lump is detected in the muscle - a trigger point.
The strength of the affected muscle and its tone decreases, pain also appears, spreading towards the joint, and autonomic disorders.
On the face
Manifested by the following symptoms:
- dull pain in the depths of the face (impossible to precisely localize);
- it is difficult to open the mouth (at a normal opening of 4.5-5.5 cm, it opens only to 1.5-2.5 cm);
- clicking in the temporomandibular joint;
- heaviness and discomfort develop in the chewing muscles;
- when chewing, the muscles get tired very quickly;
- the pain radiates to the teeth, ear, throat, palate;
- palpation of the facial or chewing muscles is painful in some areas;
- difficult to chew and swallow.
Variable symptoms:
- increased sensitivity of teeth to changes in food/drink temperature;
- tics in the facial muscles;
- increased blinking;
- stuffy ears;
- noise and ringing in the ears.
Pain occurs in the maxillofacial area; it is usually preceded by either malocclusion or cervical osteochondrosis.
The pain can spread to the neck and can cause chronic headaches.
Trigger points in this case are located in the area:
- masticatory muscles,
- pterygoid bone,
- upper part of the trapezius muscle,
- the upper part of the sternocleidomastoid muscle (in the area of the temporomandibular joint).
On the neck
A person experiences pain in the area:
- neck and shoulder girdle,
- scalene muscles,
- middle part of the sternocleidomastoid muscles,
- trapezius muscles,
- levator scapula muscle
- subclavian muscles.
Latent trigger points are found in all of the above muscles, especially those located on the back of the neck and back.
Active trigger points are usually located at the top of the trapezius muscle, in the levator scapulae muscle.
From the trapezius muscle, referred pain spreads to the back of the neck and to the angle of the lower jaw.
If the triggers are located in the neck muscles, the pain will radiate to the back of the head and eye area.
Figure: Trigger points of the head and neck
The more time the disease exists without treatment, the more the vessels that run through the neck and supply the brain begin to suffer.
This can happen:
- visual impairment;
- dizziness;
- unsteadiness when walking or standing;
- noise in ears;
- Pain in the eyes.
If the sternocleidomastoid muscle is spasmed for a long time, then vegetative symptoms appear in one half of the face: drooling, runny nose, lacrimation, pain in one side of the face.
On the pelvic muscles
This diagnosis is made if, based on the results of an examination by a proctologist, urologist or gynecologist, the pathology of the “subordinate” organs has been excluded.
This is due to the fact that the symptoms of this disease are very similar to the organic pathology of this area:
- sensation of a foreign body in the rectum;
- pain in the perineum;
- discomfort or pain in the vagina;
- pelvic pain;
- frequent urination;
- pain when walking;
- painful sitting;
- painful act of defecation;
- lower abdominal pain.
Fig.: myofascial pain syndrome of the pelvic muscles
On the shoulder
Latent triggers are usually located in the muscles of the back of the neck and back.
Referred pain goes from the trapezius muscle to the angle of the lower jaw and the back of the neck.
Trigger points are located in the muscles of the thigh and lower leg; when they are felt, pain occurs on both sides of either the knee or thigh.
If the trigger is in the tibialis or peroneus longus muscles, the pain will be on the front of the leg or the lateral (outer) ankle, respectively.
Piriformis syndrome may also occur with the following symptoms:
- pain in the buttocks and back of the thigh;
- pain in the perineum;
- painful bowel movements;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- pain when walking;
- Rectal pain or discomfort suddenly occurs.
The muscles with trigger points are located in the lower parts of the scapula, and referred pain occurs in the arm and hand.
Due to the similarity of symptoms, the syndrome has been treated for a long time as cervical radiculitis, humeroscapular periarteitis, and anterior chest syndrome.
Constantly existing pain in a certain muscle group causes sleep disturbance, depression and the formation of a stereotypical posture in which a person feels less pain.
This is how a vicious circle of “pain – spasm – pain – spasm” is formed. The longer such a circle exists, the more difficult it is to break it.
Anatomy
How to pump up a man's sternum muscles at home or in the gym? To get a complete and detailed answer to this question, you need to understand the anatomy. This knowledge will help you choose the right exercises to create an effective training program.
The pectoral muscles are divided into deep and superficial. The deep ones include the internal and external intercostal muscles, which take part in the movement of the ribs during breathing.
Superficial chest muscles:
- Pectoralis major muscle. It is one of the largest and strongest muscles in the human body, has a fan-shaped triangular shape and occupies most of the chest in front. It is responsible for rotating the shoulder joint, raising and lowering the arm;
- Pectoralis minor muscle. It is located under the pectoralis major muscle and works together with it. The shape is triangular. The main functions are lowering the scapula, raising the arm;
- Subclavius muscle. Responsible for raising the rib, lowering the collarbone down and moving it forward;
- Serratus anterior muscle. This muscle is located on the lateral surface of the chest. Main functions: rotation and abduction of the scapula forward, elevation of the rib (while fixing the scapula).
Topographically, the chest muscles can be divided into three bundles:
- Upper.
- Average.
- Lower.
Causes ↑
The risk group includes the following people:
- Hard physical work and sports. In this case, micro-tears constantly form in the muscle, which do not have time to heal.
- Sharp weight loss, which reduces the percentage of not only fat, but also muscle tissue. If against this background the body is given an inadequate load, myofascial syndrome will occur.
- Weakening of muscle tone: in the elderly, with prolonged immobilization, in weakened patients.
- Staying in an uncomfortable position for a long time (even while sleeping).
Myofascial syndrome is also caused by congenital or acquired skeletal abnormalities:
- lordosis;
- kyphosis;
- scoliosis;
- flat feet;
- combined types of spinal curvatures;
- Scheuermann-Mau disease;
- rickets;
- short first and long second metatarsal;
- different leg lengths;
- short shoulders with a long body.
- violation of posture and gait.
Diagnostics ↑
The diagnosis is mainly based on data obtained during examination of the patient.
Ultrasound examination of the affected muscle makes it possible to clearly identify its spasmodic areas and distinguish them from inflamed ones.
X-ray examination (and computed tomography) are also important in making a diagnosis: if they do not reveal pinched roots or destruction of the structure of the intervertebral disc, the nerves from which go to the sore muscle, the diagnosis is myofascial syndrome.
Diagnosis criteria for MFPS:
- muscle pain is associated with physical overload, hypothermia or being in an uncomfortable position;
- the presence of trigger points in the absence of muscle atrophy or wasting;
- typical referred pain when the trigger point is squeezed or punctured;
- blockade of the affected muscle eliminates all existing symptoms.
Why do vertebral dislocations occur in the neck? You can learn more about dislocation of the cervical vertebra on our website.
What are the dangers of spine and spinal cord injury? Read here.
Preparing to start classes
While pumping up your muscles, do not forget about the health of your cervical spine.
Read more: Exercises for gaining muscle mass - forgotten techniques
Please note - if you notice the following things in time, you will prevent a disaster:
- Your vision began to darken. After the first darkening, analyze why it happened. This may be a sudden change in body position. If your eyes become dark while at rest, you should think about it and stop exercising.
- No pumped-up muscle corset is worth your health problems. If a headache, insomnia and, most unpleasantly, sharp pain when turning the head appear, we stop exercising and go to a neurologist.
Muscle pain after exercise is normal. The main thing is to distinguish it from joint pain.
To pump up your neck muscles and avoid health problems, you should start and end your training with warming up and stretching. In addition, it is necessary to select an adequate load, since excessive weight or resistance can cause serious injury to the body.
In order to sufficiently warm up and prepare the muscles before training, you need to carry out several basic warm-up elements:
- rotations and tilts of the head in all directions;
- tilting the head diagonally;
- stretching back and forth and to the sides using your arms.
It is necessary to finish the training with the same stretching as in the video below, since the fibers tend to shorten. Shortening of muscles is an extremely undesirable phenomenon due to dangerous consequences for the body. Short-term shortening after exercise in the absence of stretching becomes long-term and even permanent, which leads to blockages, spasms, hypertension and severe headaches.
Treatment ↑
A complex effect is applied to the affected muscles:
- manual therapy;
- physiotherapy: magnetotherapy, acupuncture, acupressure, electrophoresis, phonophoresis;
- Exercise therapy, corrective gymnastics;
- swimming, underwater traction;
- medicinal influence.
The task of primary importance is to eliminate the cause of the development of MFBS:
- in case of poor posture – orthopedic correction, formation of the correct movement pattern, strengthening of the muscle corset;
- if the “short pelvis” syndrome is detected, the person should sit only on a specially selected cushion designed to balance the different heights of the sides of the pelvis;
- if the syndrome has developed in the ankle, as a response to the different lengths of the first and second metatarsal bones, special insoles are worn.
The second point of treatment is the elimination of pain, for this the following are used:
- Medications: Nimesil, Nurofen, Diclofenac and other similar drugs, used both in the form of systemic medications (tablets, injections) and in the form of ointments.
- Additionally, muscle relaxants (Mydocalm, Sirdolud), GABA-ergic drugs (Picamilon, Adaptol, Noofen) and B vitamins (Neurorubin, Neurobex) are also prescribed.
- Injection of lidocaine or novocaine into the trigger point.
- Acupressure: pressing on a trigger point with a gradual increase in the force of pressure on it as the pain decreases.
- Acupuncture and pharmacopuncture.
- Massage: its cup version is especially effective.
- Osteopathy.
- Hirudotherapy.
- Acupuncture.
When it comes to facial myofascial syndrome, the following treatment methods are additionally used:
- injection of botulinum toxin into the spasmed muscle;
- electrical stimulation;
- cryoanalgesia;
- thermomagnetic therapy;
- psychological methods (biofeedback).
The most effective at the moment are:
- manual therapy;
- Dr. Trofimenko's method (as a combination of several methods).
Manual therapy for myofascial pain syndromes is based on the technique of post-isometric relaxation: each muscle uses its own stroking, stretching and wrinkling technique, which will depend on the direction of the muscle fibers.
Trofimenko's technique is called by the author a method of acupuncture muscle relaxation; it allows you to achieve very good results in treatment.
Then the same needle makes a series of rotational or translational movements at high frequency.