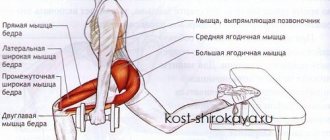
Quadratus lumborum [edit | edit code]
Quadratus lumborum muscle
Quadratus lumborum muscle
(
m. quadratus lumborum
) exhibits a strong contraction when walking on the side of the carried leg - this muscle helps the gluteus minimus muscles of the supporting leg stabilize the pelvis and prevent it from lowering towards the side of the carried leg. With unilateral contraction, it tilts the thoracic and lumbar spine on the same side. When contracted bilaterally, it, together with the serratus posterior inferior muscle, stabilizes the inferior thoracic outlet, providing a rigid frame for the diaphragm. Thus, it participates in the act of inhalation, which, however, is not considered one of its functions. The quadratus lumborum muscle does not flex the lumbar lordosis (as the long muscles of the head and neck act on the cervical lordosis), since its abdomen is located somewhat dorsal to the spinal column.
Home[edit | edit code]
- Iliac crest
- Iliopsoas ligament
Attachment[edit | edit code]
- Lower edge of the XII rib
- Vertebral processes of vertebrae L1-L4
Innervation[edit | edit code]
- Intercostal nerves, T5-T11
- Subcostal nerve, T12
- Iliohypogastric nerve, T12-L1
- Ilioinguinal nerve, L1
Functions[edit | edit code]
| Synergists | Antagonists |
| Intervertebral joints and discs (mainly lumbar region) | |
| Tilt in the same direction | |
| m. obliquus internus abdominis m. obliquus externus abdominis mm. rotatores lumborum mm. levatores costarum All deep back muscles of this area (except spinous and interspinous muscles) | m. obliquus externus abdominis on the opposite side m. obliquus internus abdominis on the opposite side m. quadratus lumborum on the opposite side All contralateral deep back muscles of this area (except spinous and interspinous muscles) |
Torso tilt. Functional muscle tests[edit | edit code]
Issues and comments
- The quadratus lumborum muscle cannot be palpated.
- The action of the quadratus lumborum muscle cannot be distinguished from the action of other muscles of the back and abdomen.
The described position is not very stable; it is better to bend the lower leg and straighten the upper leg and hold it.
Pelvic floor muscle training
Kegel exercises
Slow Compressions:
- Tighten your muscles as you did to stop urination.
- Slowly count to three.
- Relax.
- It will be a little more difficult if, holding the muscles, hold them in this position for 5-20 seconds, then gradually relax.
“Elevator” - we begin a smooth ascent on the “elevator” - squeeze the muscles a little (1st floor), hold for 3-5 seconds, continue the rise - squeeze a little harder (2nd floor), hold, etc. to your limit - 4-7 “floors”. We go down in the same stages, pausing for a couple of seconds on each floor.
Abbreviations:
- Tighten and relax your muscles as quickly as possible.
Ejections:
- Push down moderately, as if you were in a chair.
Start your training with ten slow compressions, ten contractions and ten push-ups five times a day.
After a week, add five exercises to each, continuing to perform them five times a day.
Add five to each exercise every other week until there are thirty. Then continue to do at least five sets a day to maintain tone. You should do 150 Kegel exercises every day.
Based on materials from applied-kinesiology.narod.ru
Whole spine Gluteal warm-up Hip
Wide grip pull-ups
What muscles work: developing technique, concentrated work on the lats.
Technique:
- Grasp the bar 25–35 centimeters wider than shoulder level.
- Inhale, arch your back and pull yourself up to your chest.
- As you exhale, gradually lower yourself down until your arms are completely straightened.
Note: the amplitude may not be full. It's OK. Work within the available amplitude, trying to pull yourself as close to your chest as possible.
Wide-grip pull-ups are a great way to develop technique. It is very important to learn how to turn off your biceps and deltoids when doing pull-ups. Of course, the biceps and deltoids will work regardless of your desire, but their work should be minimized to the limit so that the main load goes to our lats. But wide-grip pull-ups are the best exercise for training the latissimus dorsi muscles.
Seated Lateral Stretch
- get down on all fours;
- place your hands exactly under your shoulders;
- The knees and inner thighs should touch and be aligned under the pelvic bone;
- move your hips to the left side, rolling onto the outside of your left leg (your right leg should be on your left);
- look over your right shoulder;
- inhale as you stretch your left lower back and left hip;
- exhale to return to the center position;
- repeat on the other side.
Trapezius workout
https://youtu.be/R_R1zlywv_k
- Vertical lifts
Vertical raises work the trapezius, mainly the upper part, as well as the deltoids and levator scapulae muscles.
- Shrugs with a barbell
Shrugs are the basis for training the upper trapezius , mainly including its occipito-clavicular fascicles, as well as the scapular.
- Shrugs with dumbbells
The dumbbell shrug is designed to work the upper or clavicular trapezius, levator scapulae, mid rhomboids, and trapezius when complemented by shoulder lift by scapula closure.
- Shrugs on the simulator
This exercise, when used consistently, is excellent for developing the upper trapezius and levator scapulae muscles.
A set of exercises for stretching and relaxation
There are a number of effective movements that allow you to relax and stretch the iliopsoas muscle. They are able to relieve pain in the lower back, various “lumbago” in the leg and other areas, and also significantly increase the mobility of the hip joint.
Standing forward bend
This is a simple iliopsoas stretch that can be done in any setting.
Technique:
- Stand straight with your feet shoulder-width apart. Move your center of gravity closer to your toes.
- The back is straight, the stomach is tense, the hands are on the lower back.
- Begin to move your pelvis forward, while trying to push your chest forward and up. The body should look like a bow.
- To increase the deflection, it is better to lift your heels off the floor if this does not lead to loss of balance.
- Hold in this position for 7-10 seconds, then take a short break and repeat the approach.
As your training progresses, you can rotate your pelvis laterally, adding stretching.
Alternating stretch
The movement is similar to the previous exercise, but allows you to pull each leg separately, which increases its effectiveness.
Technique:
- Stand straight, feet shoulder-width apart.
- Take one leg back and place your toes on the floor.
- Place your hands on your tailbone and move it as far forward as possible. Straighten your chest, squeeze your shoulder blades together, try to “pull” your upper body up and back.
- Hold the position for 7-10 seconds, then repeat the same for the other leg.
Standing leg curl
A popular exercise to stretch the iliopsoas muscle. It is used in many sports as a general warm-up.
Technique:
- Stand straight with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Bend your right leg at the knee and take it back, grab it with your toes with your hand.
- Pull your toe behind your back with your hand so that your thigh is perpendicular to the floor. At the peak point, the knee should be directed exactly towards the floor.
- For additional strength, try to move your pelvis forward, this will lead to an even greater stretch.
Lying stretch
This is a good option for those who experience muscle spasms or severe pain. Performed in a lying position on any bench or couch.
Technique:
- Lie down on the bed so that your right leg is over the edge.
- Step your leg out to the side and press your heel firmly into the side of the bed for 5 seconds.
- After this, lower your foot to the floor to maximize the stretch in the target area. Hold the position for up to 20 seconds.
- The other leg should be bent at the knee, with your foot resting on the surface of the bed to ensure balance.
Repeat the same movement for the other leg.
Yoga
View gallery
Regular yoga classes have the potential to loosen the quadratus muscle and significantly reduce pain levels. The basis of classes should be stretching exercises for the lower back. Exercises have a positive effect on the emotional state of a person who has to constantly suffer from severe discomfort.
Gentle twisting while lying down
- lie on your side;
- apply a roller to your left thigh;
- turn your torso in the direction of the roller;
- hands lie on the sides of the roller (as shown above);
- turn your head in any direction (whichever is more convenient for you);
- You will have to look for the most successful position yourself, adjusting the bend of your hips and knees, pulling your thigh away from the lower ribs;
- hold in the chosen position for a couple of minutes;
- exhaling slowly, return to the starting position;
- repeat on the other side.
Development of the teres major muscle of the back
Most exercises with dumbbells and pulleys target the lats. This area responds well to load, so progress is noticeable quite quickly. Pumped up lats provide beautiful relief and power to the back. The teres major muscle is located under the latissimus, and it is this muscle that forms the correct position of the spine. Exercises for this area will help:
- make your back wider;
- draw the relief of the “small wing”;
- increase shoulder volume;
- strengthen your hands.
In fact, the teres major muscle is the framework of the latissimus, so without its development it will not be possible to form a truly powerful and sculpted back. This area is responsible for pulling the arm down and back and bringing it toward the body, so developing it will definitely have a positive effect on arm strength. Another important role is to support the spine, so it is recommended to perform such exercises for the back with osteochondrosis.
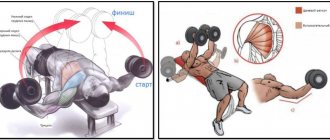
Bent-over barbell row
What muscles are worked: training the large round muscles of the back, working out the trapezius, biceps and rear deltoids.
Technique:
- Grasp the barbell with a medium grip.
- Bend your torso about 45 degrees, then inhale.
- Without rounding your back, make a pulling movement, pulling the barbell towards your waist.
- As you exhale, without jerking, lower the barbell to your outstretched arms.
- Repeat the movement.
If before we were talking about how to widen the back by making it a little thicker, now we are talking about how to increase the “density” of the back by widening it a little. Bent-over barbell rows are an ideal exercise for training your back width.
Exercises at home
It's not easy to train your back at home. This is due to the anatomy of movements. It is not possible to repeat them without weighting or a special load. And those exercises that allow you to load your back using your own body without special equipment are ineffective when it comes to serious loads. Let's look at some basic back exercises at home.
- Pull-ups. A serious complex exercise that can be performed even without a horizontal bar. It is enough to have a strong door that can support your weight. You can also use any other similar devices.
- Boat. A good exercise that develops the rhomboid and latissimus dorsi muscles. The technique is extremely simple: lie on the floor, slightly raise your outstretched arms and legs.
- Bridge. A static exercise with your own weight that perfectly develops back extensors without injury. Suitable for recovery or maintenance training. It is recommended for anyone who wants to develop not only strength, but also flexibility of the back muscles.
- Farmer's Walk. This exercise is in the home category because it can be performed with any home weight. All you need to do is take 2 thick bags, fill them evenly with books and get started. Develops all muscle groups with an emphasis on the trapezius muscles. There are options in the form of lunges, which additionally load the leg muscles.
Diagnostics
View gallery
How can you tell if your quadratus dorsi muscle is damaged? Diagnosis involves performing a series of examinations. There is a whole set of diseases whose symptoms are similar to quadratus muscle syndrome. Among these are:
- osteochondrosis;
- scoliosis;
- arthrosis;
- uterine fibroids;
- bladder infections;
- inflammation of the pelvic organs.
Therefore, the first priority is to conduct ultrasound and radiography. The results of such tests make it possible to exclude the development of the above diseases. Based on the results of the diagnosis, doctors have the opportunity to find out whether it is possible to talk about the development of quadratus muscle syndrome.
The presence of the disease can also be confirmed by palpation of the area in which discomfort occurs. Palpation of the quadratus muscle will cause a significant increase in pain. Especially if there is pressure on points in the area of the twelfth ribs.
Why you need to train the iliopsoas muscle
Given the basic functions of the muscle, it plays a huge role in many sports. For example, it is extremely important in all running sports, diving or long jumping, basketball, figure skating, football and other disciplines. The length and rhythm of the step also depends on it. Given that it is a very thick muscle with the largest cross-sectional area of its group, training the iliopsoas muscle with exercises is especially important in those sports that require explosive loading in the form of jumping, pushing off the surface, or transmitting momentum, such as in the javelin throw.
It is also important to remember that when running, jumping, especially long-term aerobic exercise, this muscle may begin to lose flexibility and contract. In this case, you need to pay attention to stretching the iliopsoas muscle. For people who do not exercise, stretching is recommended for those who often sit in a sitting position. This allows you to keep the pelvis in its natural position and prevent its gradual rotation (lumbar hyperlordosis and protrusion of the pelvis outward).