Weakening of the abdominal and side muscles, typical for women, is due to the fact that there are a lot of fatty deposits in this area, which protect and insulate the female reproductive system. The second reason is the intestines. When consuming large amounts of carbonated drinks and gas-forming foods (including healthy fiber), gas accumulates in it, and the abdominal cavity essentially bulges out.
One of the common mistakes is the idea that the abdomen consists of one separate muscle. This is wrong. Therefore, to strengthen the abdomen and sides, a load on all muscle groups is required.
Briefly about the structure of the abdominal muscles
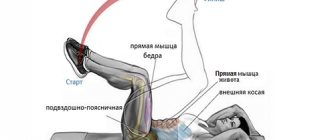
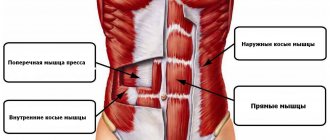
What muscles work when pumping the press? In the course of applying loads to the presented area, the so-called core muscles are involved. These structures form the abdominal corset, holding the internal organs and stabilizing the position of the body. Regardless of a person’s gender, the abdominal muscles include the rectus abdominis, oblique and transverse abdominis muscles. It is the rectus abdominis muscle that forms those same cubes and is most noticeably pumped during active training. However, without training the oblique and transverse muscles, posture may suffer and problems with maintaining balance may arise.
https://youtu.be/GliExN2tqVA
What are the benefits of a strong press for supporting the spine?
Once again, we note that the abdominal muscles are of great importance in supporting the spine. The more pumped the abdominal muscles are, the more stability they provide to the spinal column.
Let's look at exactly how a strong press can play a role in supporting the back:
- Thanks to the pumped up abdominal muscles, strong intra-abdominal pressure is created in front of the lower spine. This allows the intra-abdominal organs to be fixed in the correct position. The pressure also provides support to the lumbar spine. Further promoting spinal stability helps prevent vertebral slip (herniation) in the lumbar region.
- The more the abdominal muscles contract, the more the lower spinal column rounds. This prevents the development of excessive lordosis. Lordosis is an unhealthy arch in the lower lumbar region. Preventing lordosis ensures that excess stress on the lower back itself is relieved.
- Contraction of the abdominal muscle tissue also allows you to raise the spine into a vertical position. This lifts the chest and aligns the cervical spine.
In order to feel the importance of a toned abs for the spine, you can conduct a very simple experiment. Just try to tighten your abdominal muscles (pull your stomach in). When performing this exercise, you can feel how the lumbar deflection decreases, the spine in the neck takes on a more correct position, and the chest also takes on an elevated position.
Read also…. Bandage - application, choice, characteristics and varieties
This test allows you to very clearly feel the difference for the back with strengthened and unstrengthened muscle tissue on the abdomen.
Where and how often to exercise to strengthen weak abs?
The most comfortable place to pump up your abdominal muscles is your own apartment. The main thing is to have a gymnastic mat available. It is better to train in the middle of a spacious room, so that surrounding objects do not interfere with active body movements. It will be beneficial to use a large mirror, which will allow you to monitor the correct execution of the exercises and note inaccuracies.
Now let's talk about the frequency of classes. If weak abdominal muscles do not support your stomach, it is recommended to train at least 4-5 times a week. First, various bends of the body are performed to stretch and warm up the abdominal muscles. Then more serious loads are placed on the weakly inflated press. During each repetition you need to do 10 repetitions of movements. If you lack the strength to perform the exercises correctly, you should start with fewer repetitions.
How weak abdominal muscles affect your back
Orthopedists note that an underdeveloped abdominal muscular system can have negative consequences for both the spine and the back as a whole.
Many patients may find it quite difficult to strengthen their abdominal muscles. The reasons for the reluctance to overcome difficulties may be:
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Pregnancy
- Excess weight
- Various diseases.
Even in these cases, it is necessary and possible to perform physical exercises to strengthen the muscle tissue in the abdomen. In order to choose a set of exercises that does not harm the body, you need to contact an orthopedic specialist.
We list the main possible negative manifestations for back health with undeveloped abdominal muscles:
- The spine does not receive the necessary support from the abdominal muscles. This increases the pressure on its base. The spinal ridge strongly cuts into the sacrum, and increases the load on the lower discs. The formation of hernias and protrusions is possible.
- Due to insufficient intramuscular pressure in the abdominal cavity, overstrain of the lower back muscles occurs. A spasm of muscle tissue may develop, which will develop into osteochondrosis.
- Chronic back pain can occur due to the fact that under increased pressure on the muscle tissue of the back, an increase in the curve in the lower back (lordosis) occurs. The external manifestation of lordosis is a sagging belly and a clearly visible lumbar deflection.
In addition, it is worth understanding that with weak muscles, ligaments and joints have to work for them. And they, unlike muscle tissue, are less supplied with blood. Due to the fact that they take on excess load, they wear out quickly. And this can also lead to various serious diseases.
Strengthening the muscle corset will reduce the load on the spine, joints and ligaments. This will ensure the prevention of chronic back pain.
Seated crunches
People who have truly weak abdominal muscles should start moving towards progress with the simplest exercise. We are talking about twisting the body in a sitting position. You can train on the floor or on a chair.
So what should you do? In a sitting position, hands are placed behind the head. Take a deep breath into full lungs. As you exhale, the body smoothly turns to the side with tension in the abdominal muscles. The starting position is accepted. A turn is made in the other direction.
Despite the low complexity of the exercise, a noticeable effect can be obtained already after the first month. The muscles of the abdominal area will become toned, which will allow you to move on to more fruitful workouts.
For experienced
This exercise is more suitable for trained people.
- Find something solid to hold on to (the bottom of a closet or bed, the legs of a table).
- Lie with your head against the support, raise your arms above your head, grab hold.
- Stretch your legs on the floor.
- Inhale and slowly lift your outstretched limbs to the ceiling (your pelvis remains on the floor).
- When your legs and body form a right angle, inhale, then slowly move them back to the floor.
Important! Never raise your hips. If you can't keep them on the floor, don't do the exercise.
Plank
The plank exercise allows you to perfectly pump up weak abs and start the process of active fat burning. Despite its static nature, training requires significant effort and the ability to maintain balance. The exercise is performed according to the following scheme:
- The emphasis is placed on the elbows face down.
- The legs straighten and hold the body on the balls of the feet.
- The back is in a level position.
- The abdominal muscles are tensed as much as possible and maintained in this state for 30 seconds.
- During one workout, 3-4 approaches are performed.
Mill
A good solution for training weak abs is the mill exercise. In the starting position, the body is in a straightened position on the back. The legs bend at the knees and rest the feet on the floor. Hands are placed behind the back of the head. The left knee is raised. At the same time, the head rises from the floor. The right elbow reaches towards the knee. The starting position is accepted. Then the body movements are repeated with a change of arms and legs. To strengthen weak abdominal muscles, it is enough to perform 4 sets of 10 repetitions with training intervals every other day.
Why pump up your abs?
- Core stabilizer muscles include the lower back and abs. An inflated abdominal area, like the lumbar region, makes adjustments to your posture, making it beautiful, and allows you to maintain a healthy spine.
- A well-developed abdominal muscle corset supports and protects the internal organs.
- The degree of development of the abs directly determines the strength indicators of all key exercises in which the muscles of the middle of the body are involved.
- If performance in squats or bench presses does not increase or even begins to decline, it makes sense to pay attention to the abdominal muscles. The force is transferred through the arms and legs to the weight when the core muscles work stably.
- A toned, sculpted belly is beautiful, graceful and sexy.
- By pumping the abs, the internal organs are supplied with oxygen and blood, which increases their functioning. People with good, strong abs and a healthy diet have virtually no problems with the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, colitis, stomach ulcers or liver problems do not occur) - physical endurance prevents illness.
Bike
Weak abs can be thoroughly worked out by doing an exercise that simulates pedaling a bicycle. In this case, the leg muscles are also involved.
First, assume a position lying on your back. The legs are slightly raised and the knees are bent at a right angle. Hands are located on the sides of the body. Rotations are performed with the lower limbs. Tension is concentrated in the abdominal area. About 20 repetitions are performed. After several approaches, rotation should be done in the opposite direction.
A set of exercises to strengthen the abdominal muscles
Testing the abdominal muscles
Testing must be carried out on a flat, hard surface, preferably on the floor, laying down a gymnastic or developmental mat.
IMPORTANT!
The child must be undressed; panties can be left on.
The starting position of the child is lying on the floor, you sit facing the baby, next to his legs. It is recommended to place a small cushion made from a diaper or towel under the knee joints to bend the baby’s legs at the knee and hip joints.
Holding (fixing) the legs at the ankle joints, ask the child to sit down; the child can be interested in a toy.
When performing the exercise, you pay attention to three main points:
1 How easily your child sat up.
The muscles are well developed - the child sat up on his own, without the help of his hands, but only due to the tension of the abdominal press.
The muscles are well developed - the child sat down without your help, but in the process he helped himself with his hands, leaning on them.
The muscles are poorly developed - the child could not sit up on his own, but only with a little help from you.
The muscles are very poorly developed - the child, even with your help, had difficulty sitting down and cannot maintain himself in a bent position.
2 Abdominal muscles at the moment of performing the movement.
Normal - the abdominal muscles contract evenly, the tummy is even when moving, there are no protrusions.
Weak muscles - when performing movements in the middle of the carinatum, just above the navel towards the sternum, a protrusion is noted. Or a protrusion in the area of the white line of the abdomen. This indicates weakness of the linea alba.
3 The position of the ribs of the chest, since it is to them that part of the abdominal muscles is attached.
The muscles are well developed, the ribs are strong - no deformations or changes are observed during movement.
There may be indirect or additional evidence of rickets - at the time of movement, when their active contraction occurs, the ribs may turn outward, which leads to a change in the shape of the chest.
One of the important points in assessing the condition of the abdominal press is the condition of the umbilical ring. The presence of protrusions in this area is noted, which may indicate weakness of the muscles that form it. In most cases, this manifests itself as an umbilical hernia (for more details, see the article).
CONCLUSION:
if, after passing the test, you came to the conclusion that your child’s abdominal muscles are weak, namely, during the test, he was unable to sit up on his own without the help of his hands / there was a bulging of the abdominal line with a bulla / a change in the area of the lower ribs of the chest / the presence of an umbilical hernia / in a standing position, the child slouches and sticks his tummy forward (for those who stand), it is recommended to start strengthening these muscles.
But these exercises can also be done for general health, if everything is fine with your baby, because the health and happiness of children is the most valuable thing!
A set of exercises to strengthen the abdominal muscles
IMPORTANT! After each exercise, do not forget to give the child time to rest (2-4 seconds).
The lifting time and number of repetitions increase gradually. The lifting height increases starting from 5-6 months, we move to the half squat and full squat position!
1 If the abdominal muscles are weak and there is an umbilical hernia, it is recommended to place the child on his stomach as often as possible. If the child does not hold his head well and there is no support in his hands, then a cushion should be placed under the chest and shoulders.
2 “Hovering without leg support” You take the child by the chest facing you and lift him up. Alternately tilt the child's face towards you and lower the legs.
3 Work with the upper press!
IP - the child lies on his back, on the table. You move your hands under his shoulders, while also fixing the child’s head with the pads of your fingers.
3.1 Lift the child up, lifting the child’s head, shoulders and back from the table, approximately 45º from the table surface and lower it. Perform 8-10 times.
3.2 Raise the child and fix it at the top, counting to 6-8, lower it. Perform 4-6 times.
3.3 We alternately lift the child to the right - lower it, then to the left - lower it. Perform 2-4 times in each direction.
3.4 We perform similarly to 3.3, but the child does not touch the table surface. The exercise is performed like a light pendulum. Perform 2-4 arcs.
4 If this exercise does not cause discomfort to the child, then we perform its complicated form.
IP - the child lies on his back, you place one of your hands under the child’s back, fixing the head with your fingertips. With your other hand you take his hands into the lock.
4.1 Lift the child up, lifting the child’s head, shoulders and back from the table, approximately 45º from the table surface and lowering it. Perform 8-10 times.
4.2 Raise the child and fix it at the top, counting to 6-8, lower it. Perform 4-6 times.
5If the child holds his head well, then you can perform this exercise without fixing his head.
IP - the child lies on his back, you place one of your hands under the child’s back.
With your other hand you take his hands into the lock.
5.1 Lift the child up, lifting the child’s head, shoulders and back from the table, approximately 45º from the table surface and lower it. Perform 8-10 times.
5.2 Raise the child and fix it at the top, counting to 6-8, lower it. Perform 4-6 times.
6 Work with the lower press!
IP - the child lies on his back. You take the child’s legs by the calf muscles, by the wide part of them, in order to perform the movement under control and correctly! But without closing the knee joints! Also, do not grab the ankle joints, as they are mobile and fragile, and when performing the movement, the knees can move apart! If the child has small feet, then try to work with the thumb, index and middle fingers, without using the rest.
6.1 Alternately bring the child’s knee to the tummy (flexion) followed by straightening. Perform 5-6 times with each leg.
6.2 Perform simultaneous flexion and extension of the legs at the knee joints. Perform 5-6 times.
7 Work with the upper press!
If the child holds his head well, then you can perform this exercise without fixing the head. This exercise also helps train the muscles of the collar area and the child’s arms.
IP - the child lies on his back, you take each child’s hand so that your thumb is in his fist. The child’s thumb is opposed to the rest - we form the correct grip!
7.1 Lift the child up, lifting the child’s head, shoulders and back from the table, approximately 45º from the table surface and lowering it. Perform 8-10 times.
7.2 Raise the child and fix it at the top, counting to 6-8, lower it. Perform 4-6 times.
8 Work with the lower press!
IP - the child lies on his back. Your four fingers are placed on the knee joints, and your thumbs are placed on the back of the child's calf muscles, straightening the legs.
8.1 Simultaneously lift your legs up to an angle of 90º. Perform 5-6 times with each leg.
8.2 Perform a simultaneous lift of the legs and smoothly try to bring the legs closer to the baby’s chest. The exercise is performed smoothly, without jerking, so as not to injure the child. If you don’t succeed the first time, then do it gradually.
8.3 Raising your legs to 90º, spread them apart according to the child’s characteristics. The movement is performed smoothly, without causing pain to the child. Perform 5-6 times.
IMPORTANT! Exercises 6 and 8 are also effective in preventing colic and constipation in children!
9 Laying on weight. IP - the child lies on his back.
9.1 “Holding the body in weight.” Place the child on the edge of the table so that the head and shoulder girdle are suspended. With one hand you secure the child under the head, and with the other you “run” with your fingertips along the white surface. Stimulate the contraction of the child's abdominal wall.
9.2 “Keeping your legs suspended.” Place your baby on the edge of the table with his legs hanging over the edge. It is necessary for the child to raise his legs up. With one hand you secure the child by the tummy, and with the other you raise the legs, trying to get the child to start holding them up on his own.
If the child performs all the exercises with ease and pleasure, then you can proceed to more complex exercises that will better prepare your child.
10 IP - the child is lying on his back, a pillow is placed under the child’s shoulders and head. The exercise is performed for each hand separately. You take the child by one hand, placing your thumb in his fist. With your other hand, fix the hip area. You can place a small cushion or diaper or towel under the baby's knees.
10.1 Lift the child on one side, directing the movement of your hand towards the child’s free hand, in order to support him on his free hand. Do it to the best of your child's ability. 2-3 times with each hand. A child's desire to get up can be caused by some toy!
10.2 If the child copes with this exercise well, then take a smaller pillow, or in fact remove it altogether.
8 If you are ready, then this exercise can be performed on a fitball.
IP - the child lies on his back on a fitball. With one hand you take it by the hand, and with the other you fix your legs and knee joints, pressing them against the ball, while keeping the ball in a stationary position. You can also kneel in front of the ball and fix it with your knees.
8.1 Carefully lift the child up. Perform to the best of your child’s ability, gradually increasing to 5-7 times with each hand.
Backward rolls
The body position is taken while sitting on the floor. The back is kept straight. The stomach is slightly retracted. The legs are straightened and slightly apart to the sides. With your hands held in front of you, you grab any available crossbar. Alternatively, you can use a tightly rolled towel. The body is tilted back without touching the floor with your back. In a tense position, the body lingers for several seconds. A deep breath is taken and the bar is pulled up to the chest with your hands. As you exhale, a push is made in the opposite direction, after which the body returns to its original position. The exercise is repeated about 10 times for 3-4 approaches.
Weighted leg raises
To organize a workout, you will need a horizontal bar. The crossbar is grabbed with your hands. The body can freely straighten in a hanging position. The abdominal muscles tense, after which the lower limbs slowly rise to a position parallel to the floor. The position is held for a few moments. Then the legs smoothly lower down.
Beginners are advised to try to perform up to 10 repetitions over 2-3 sets. Subsequently, the number of leg pull-ups in a hanging position on the horizontal bar should be increased to 20 times. During training, you should try to control the accuracy of your movements and not swing your body. If the exercise is too difficult, you can raise your legs with your knees bent.
Pulling your knees to your chest
The knee tuck exercise helps strengthen the abdominal muscles. The lower back and gluteal muscles are also involved here. The training involves the following:
- The body is placed in a supine position on the floor, and the arms and legs are stretched out.
- The knees are bent and pressed towards the chest.
- At the same time, take a deep breath.
- The abdominal muscles are tensed to the maximum, the legs are straightened without touching the floor.
During one workout, 4 sets of 12-15 repetitions are performed. Regular exercise for 2-3 months allows you to achieve noticeable results.
Harmful exercises
Straight Leg Raise
An example of a harmful abdominal exercise is straight leg lifting with a fixed body. Moreover, whether you raise straight legs from a lying position, or do it from a vertical position with emphasis on the lower back, this harms your spine.
Studies have shown that straight leg raises cause significant compressive stress on the intervertebral discs of the lumbar spine. In this case, the maximum force occurs at the moment the heel lifts off the surface of the plane.
In general, it is the rectus muscle, which we call the abs, that works in this exercise when the pelvis is twisted. Until this moment, the iliopsoas bears the main load.
Contraction of the iliopsoas muscle creates increased pressure on the vertebrae in the lumbar spine, and this can gradually create conditions for the appearance or intensification of disc herniation, protrusion, scoliosis, hypertonicity around the vertebral muscles of the lumbar spine and the muscles of the pelvic day.
Especially if such a load is carried out regularly, the accumulation of microdamages begins in healthy discs, and even more so in those previously damaged by injury or simply having degenerative changes for any reason, damage and hernias occur.
Moreover, think about the fact that loading the lower back muscles in general is a bad idea, especially in dynamic movements with weights. The fact is that these are stabilizer muscles, the so-called. corsetry. Unlike any other skeletal muscles, they do not move bones.
Their job is to help maintain a safe and stable position of the pelvis, spine and hips. Strengthening your core does allow you to maintain beautiful posture and a healthy spine, but not such a load.
Jackknife
Why is it better not to do this exercise? Because again, the main load is borne by the iliopsoas muscle, which is located deep and is attached at one end to the lumbar spine and at the other to the femur.
The function of the iliopsoas muscle is to flex the thigh at the hip joint. That is, it pulls the leg (thigh) to the belt. The rectus abdominis muscle is involved indirectly here.
The following situation arises: excessive tone of this muscle makes it shorter, i.e. it pinches and changes the position of the spine, the angle of the pelvis and can cause pain and back injuries in the future. In people with a sedentary lifestyle, this muscle is already shortened, and many people additionally load it in the gym, instead of stretching it.
Torso bending on a bench
This exercise, although still the most popular, is unfortunately not effective, plus it is harmful to the back. The amplitude of movement, when the abs are involved in the work, is extremely short, so half of the exercise is aimed at the muscles of the lower back.
When performing trunk bending on a bench, a compression load occurs on the lower back, which exceeds the recommended threshold approved by the American National Institute for Occupational Health and Safety.
Their report states that prolonged stress while bending the torso on a bench over time can lead to various disorders in the back, an increased risk of spinal hernia, and the accumulation of a negative background that can result in various injuries.
Leg Throws
The essence of the exercise is that you raise your legs, and your counterpart throws them down. Of course, such a workout looks incredibly cool: you are so athletic, you sweat thoroughly and practically fight with your trainer. The pulse is high, sweat flows like a river, it’s incredibly hard for you, but alas, it’s all in vain.
Again, the whole problem is in the back and the excessive load on the lumbar spine. If you have had problems with your lower back or lower back, this exercise may cause pain. And even if the exercise doesn't cause immediate pain, it can cause chronic back pain over time.
Side crunches
Not only the rectus abdominis muscle needs strengthening, but also the oblique muscles. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to pumping the lateral press. To do this, you need to resort to the following training:
- Lying on your side, straightened legs pressed to the floor.
- The top hand is held behind the head.
- The body body rises up and lingers for a moment.
- A rollover is performed to the other side and the exercise is repeated.
The number of approaches in this case should be at least 3. It is advisable to do 10-15 body lifts on each side.