The presence of excess weight can be easily recognized by blurry shapes and an increased number on the scale. This allows you to detect the problem in time and begin to eliminate it. However, often fatty tissues attack a specific internal organ, which is not always manifested by external signs.
Fatty liver is a pathology of a secondary or primary nature, which is accompanied by the accumulation of lipid compounds in parenchymal tissues. The disease is diagnosed in children and adults, even those with a fragile physique.
Fatty iron dysfunction develops due to the consumption of alcoholic beverages, a number of diseases - diabetes mellitus, endocrine disorders, and also due to the use of medications.
So, fatty liver, what it is and how to treat it, etiological factors and clinical manifestations - let's look at it in detail.
What is fatty liver
Fatty liver is a disease of the hepatobiliary system, which is accompanied by the replacement of liver cells with fatty deposits. This disease occurs in men and women, less often in children. If the pathology is not treated in time, the liver will cease to perform its functions, which will ultimately lead to serious consequences. The disease is a chronic condition because it develops over a long period of time. Due to the appearance of deposits on the organ, it increases in size, its functioning is disrupted, which leads to the appearance of the first symptoms.
Stages of development
In the process of its development, fatty hepatosis (fatty liver) goes through three stages of development, each of which is accompanied by certain changes in the organ:
- The initial stage is accompanied by the appearance of small patches of fat on individual liver cells.
- The first stage - large fatty deposits accumulate in some areas of the organ.
- Second degree - all liver cells are affected.
- The third degree is the most severe stage, in which diffuse obesity is present on the organ and cysts form.
Fatty infiltration in liver cells is not accompanied by an inflammatory process, which explains the absence of symptoms in the early stages. However, as the disease develops and extensive damage to the parenchyma of the organ becomes noticeable, there is a high risk of developing liver failure, fibrosis or cirrhosis of the liver.
Causes of fatty liver
Fatty liver can develop for a variety of reasons. Be associated with a person’s lifestyle or manifest as a complication of other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The following reasons and factors increase the risk of developing pathology:
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
- Starvation diets for quick weight loss.
- Abuse of fatty, spicy and unhealthy foods.
- Long-term use of potent drugs.
- Obesity.
- Violation of metabolic processes.
- Deficiency of protein and vitamins in the diet.
- Hypovitaminosis.
- Severe forms of pancreatitis.
- Diabetes.
- Passive lifestyle.
If the disease manifests itself against the background of excessive alcohol consumption, the patient will be diagnosed with “alcoholic fatty hepatosis.” At the moment, the etiology of the disease is still being studied, so in the near future the list of causes may increase significantly.
In order for treatment to bring maximum benefit and complications not to develop, it is important to diagnose the disease in time, determine the root cause and only then carry out therapy. Otherwise, the prognosis may be unfavorable.
Causes of fat deposition in hepatocytes
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has many synonyms: lipomatosis, adiposis, steatohepatosis, liposis. All of these medical terms have the word “fat” at their root. Pathology develops against the background of such diseases:
- Acute and chronic hepatitis caused by viruses, autoimmune factors or intoxications. Inflammation of liver cells ultimately leads to their death and the accumulation of connective tissue in the organ.
- Predominance of fatty foods in the diet. Excess fats are deposited in hepatocytes. The organ saturated with them is called “white liver”.
- Metabolic syndrome. It includes increased blood uric acid levels, diabetes mellitus, sudden weight gain and hypertension. These factors together provoke the appearance of fatty liver.
- Dysfunction of the endocrine glands of the brain (epiphysis and pituitary gland).
Symptoms of the disease
In the initial stages of fatty liver, symptoms are absent or manifested by minor signs to which a person does not pay special attention, this may be discomfort in the right hypochondrium, increased weakness, fatigue. As the disease progresses, the symptoms become more pronounced and noticeable:
- Feeling of fullness in the abdomen.
- Pain of varying intensity and discomfort under the right rib.
- Nausea and vomiting of bile are not associated with food intake.
- Yellowness of the skin of the sclera of the eyes.
- Itchy skin, small rashes on the skin.
- Lack of appetite.
- Sharp weight loss.
- Abnormal stool: diarrhea, constipation, flatulence, rumbling.
The third stage of the disease is especially difficult, when multiple cysts form on the organ. The patient suffers from acute and severe pain under the ribs, nausea, vomiting, and there are constant problems with bowel movements.
All of the above symptoms may be present in other diseases of the liver or biliary system, so to make an accurate diagnosis and determine the extent of organ damage, you need to undergo a comprehensive examination.
Pain in the right side of the abdomen
Visceral fat - the one that forms around the internal organs - is not only the most difficult to remove, but also the most dangerous. People with a pronounced belly and a waist circumference greater than 85 centimeters have a higher risk of cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and fatty liver disease. If this is your case, be sure to check the condition of these organs at least once a year, and also discuss weight loss options with your doctor.
This symptom appears quite late and usually indicates an already developing complication of the disease - for example, cirrhosis. In any case, even if pain in the right side of the abdomen appears from time to time and irregularly, you should still consult a doctor.
By the way: Lose weight without destroying your liver. 2 healthy diets and one very harmful one
Diagnosis of fatty liver
Fatty replacement of the liver occurs over a long period of time. In the early stages, pathological changes in the structure of the organ can only be determined by testing for liver transaminases. Often the pathology is diagnosed completely by accident during a scheduled or unscheduled ultrasound examination.
Diagnosis of liver diseases is carried out by a gastroenterologist or hepatologist. To make a diagnosis, a specialist collects anamnesis, conducts an examination, and prescribes a number of laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods:
- General and biochemical blood test.
- Analysis of urine.
- Biochemical blood test for the concentration of bilirubin fractions and cholesterol.
- Ultrasound diagnostics (ultrasound).
- MRI examination.
- Liver biopsy.
- Breath test.
The most informative diagnostic method is a biopsy, which consists of taking tissue from a damaged organ, which is then examined in the laboratory. Biopsy results can identify adipose tissue, determine the stage, exclude or confirm the development of fibrosis, cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Based on all the examination results obtained, the doctor has the opportunity to obtain a complete clinical picture of the disease, make the correct diagnosis, and prescribe the necessary treatment. Thanks to the capabilities of a modern diagnostic base, it is possible not only to identify the disease, but also its cause, which significantly increases the chances of recovery.
You can read more about everything in the articles on the website: Ultrasound of the gallbladder and liver MRI of the liver. What you need to know about the liver CT procedure: indications, contraindications, preparation for the study
Treatment of fatty liver
If a diagnosis of fatty liver is made, treatment should be comprehensive. The patient must completely reconsider his lifestyle, give up bad habits, and strictly follow all medical prescriptions and recommendations. In the early stages of the disease, with proper therapy, the prognosis is favorable, but if the pathology is diagnosed too late, treatment can only alleviate the general condition of the patient, but cannot cure the disease.
The main methods of treating fatty liver include:
- Taking medications from different pharmacological groups to eliminate the cause and reduce symptoms.
- Dieting.
- Lifestyle adjustments.
- The use of folk remedies as adjuvant therapy.
Only an integrated approach to treating the disease will help stop or slow down its progression, thereby improving the patient’s quality of life and reducing the risks of severe complications.
Treatment is medicinal and effective
Taking medications is considered important in the treatment of fatty liver. In the initial stages, therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis, but in severe cases, inpatient treatment under the supervision of a physician is indicated. In a hospital setting, all drugs are administered intramuscularly or intravenously, which makes it possible to quickly eliminate the manifestations of the disease and increase the effect of treatment.
Any medicine can only be prescribed by a doctor, who will individually select the dose and duration of use. In practice, the following medications are most often used:
- Hepatoprotectors: Essentiale Forte, Heptral, Berlition, Essliver - improve liver function, protect it from the negative effects of toxins, and promote cell restoration.
- Sulfamino acids: Taurine, Methionine - help in the processing of fat in liver tissue.
- Anticholesterol drugs: Atoris, Vasilip, Nicotinic acid - reduce the level of lipids in the blood.
- Choleretic drugs - accelerate the flow of bile, eliminate its stagnation: Ursofalk, Ursosan, Ursoliv, Urdoxa.
- Detoxification drugs - cleanse liver cells from toxic effects: Enterosgel, Holosas, Ovesol, Polysorb and others.
- Antioxidant vitamins: tocopherol (Vitamin E), retinol (Vitamin A).
- B vitamins - B2 - riboflavin, B9 - folic acid.
If necessary, the doctor can prescribe other medications that will help restore liver function, improve metabolic processes, and eliminate disturbances in the functioning of other organs and systems.
We invite you to watch the video “Treatment of fatty liver.”
Prevention
The development of fatty liver can be avoided only by permanently eliminating from life the factors that increase the likelihood of its development and adhering to a healthy lifestyle. Preventive measures against fatty hepatosis include:
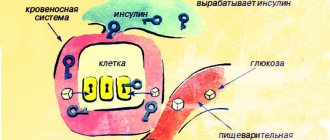
- Physical activity and sports activities (after training, insulin levels decrease for two days and the liver stops accumulating fats).
- Quitting bad habits (drinking alcohol, nicotine addiction).
- Regular monitoring of blood glucose and cholesterol levels (applies to patients with disorders of the endocrine and cardiovascular systems and overweight patients).
- Proper, healthy and regular nutrition (limiting sweet and flour products, animal fats, including low-fat protein foods, vegetables and fruits in the diet).
You can minimize the harmful effects of external factors by consuming foods high in special antioxidant substances, which you can read about in the article “Antioxidants: what are they useful for and where to get them.”
Fatty liver is a common and very dangerous disease, which gradually leads to disruption of not only the important cleansing organ, but also the body as a whole. Protecting yourself from illness is possible only by changing your lifestyle in favor of a healthy and active one.
Traditional methods of treatment
At home, you can treat the liver using traditional medicine. Medicinal herbs that you can buy at a pharmacy or collect and prepare yourself are considered especially effective. Various herbs and decoctions are prepared from them, the effectiveness of which has been proven by official medicine. The following herbs are recommended for the treatment or prevention of fatty liver:
- corn silk;
- rose hip;
- horsetail;
- chamomile flowers;
- birch leaves;
- juniper fruits;
- oats;
- milk thistle;
- Dill seeds;
- calendula inflorescences.
Decoctions or infusions of medicinal plants can be taken separately or in the form of collections. The method of preparation for all herbs is almost the same: dry raw materials are poured with boiling water, left for 1-2 hours, filtered and taken orally. Dosages may vary depending on the plant used.
Despite the safety and effectiveness of alternative treatment, it should be used after prior consultation with your doctor and only in combination with other methods of therapy.
To help you, our section on the website Traditional methods of treatment.
Diet for fatty liver
Any liver disease, including fatty liver disease, requires a strict diet, since poor nutrition is often the trigger for the development of the disease. For fatty liver, treatment table No. 5 is prescribed.
Basic nutritional recommendations
In addition to the fact that unhealthy foods need to be excluded from the diet, the patient should follow some recommendations:
- Small meals, 5 – 6 times a day.
- The number of calories per day should not exceed 1,200 kcal.
- Small portions.
- Do not eat food 3 hours before bedtime.
- Avoid overeating.
- Food should be steamed or served boiled or baked.
- Avoid fried, spicy and fatty foods.
- Avoid any alcohol and smoking.
- It is better to replace sugar with xylitol.
It is important to understand that without following a diet and following certain rules, it is impossible to cure fatty liver, even when the patient takes the most expensive and effective medications.
What can you eat
Table No. 5 includes the following food products:
- various porridges on water;
- lean chicken, rabbit or beef;
- low-fat fish;
- low-fat dairy and fermented milk products;
- marmalade, honey;
- non-acidic fruits and berries;
- vegetables;
- dried bread, crackers;
- vegetable oil;
- still table water, vegetable juices, weak tea, rosehip infusion.
You can prepare various soups, porridges, casseroles or main courses from permitted products.
What is prohibited
The category of prohibited products includes:
- any type of alcohol;
- fatty meat or fish;
- heavy cream, milk;
- canned food, pickles;
- cooking fats, lard;
- sour cabbage;
- fresh bread;
- offal: liver, kidneys, brains;
- hot and sour sauces;
- black coffee, cocoa;
- chocolate, cakes;
- sorrel, spinach, radish, radish;
- fried and hard-boiled chicken eggs.
You need to follow a diet for a long time, and sometimes for your whole life.
Treatment of fatty hepatosis
This difficult, dangerous disease is associated with a disorder in almost all metabolic processes of the body. Therefore, therapy is very important; it may involve a large number of methods, means, and medications. All of them will be directly intended to restore all links previously involved and destroyed in morbid obesity.
Diet for fatty liver
Food should be as low-calorie as possible. It is necessary to eliminate all red meat, fatty foods filled with “bad” cholesterol from the diet, and, if possible, give up sugar or its substitutes (fructose, etc.).
It is optimal to switch to a Mediterranean style of eating. It consists of consuming more fish, seafood, and algae. You need to include as many vegetables and fruits as possible in your diet, not forgetting the specific calorie content of each product individually. It also doesn’t hurt to eat more foods with vitamin E, C, and polyunsaturated acids.
Sample menu for the day
Morning
- Hard-boiled eggs – 2 pieces.
- Cottage cheese (fat content no more than 5%) – 200 grams.
Dinner
- Boiled chicken without skin – 300 grams.
- Kefir (fat content no more than 2.5%) – 250 grams.
Afternoon snack
- Low-fat yogurt – 240 grams.
- Grapefruit – 0.5 pieces.
Dinner
- Cottage cheese – 200 grams.
- Grated carrots (no sugar) – 150 grams.
Dish recipes
You don’t need any special recipes, so don’t be afraid of this diet, it’s very simple and accessible. It is advisable to steam or boil everything, but fried or smoked foods should be completely avoided, as should overly salted, sweet and baked goods. However, let's look at what else can be prepared.
Rice with vegetables
Place the washed rice in a frying pan with high sides and add water in a ratio of one to three. Lightly salt, pour in a tablespoon of vegetable oil, preferably extra virgin olive oil or Ghee.
After fifteen minutes (the rice is half cooked), add frozen vegetables to the container. You can use sets from the store: corn, broccoli, peas, celery, cauliflower, carrots, asparagus. Cover with a lid and simmer over low heat for another fifteen minutes.
Baked poultry (turkey, chicken)
Boiled chicken gets boring very quickly, just like steamed chicken. Therefore, it makes sense to diversify the menu by baking the bird in the oven. To do this, rinse the fillet thoroughly and then dry it with a paper towel. Grating meat with your favorite herbs is not difficult.
Wrap the prepared fillet in foil, place on a baking sheet, and bake for an hour. You can wrap it with vegetables - zucchini, eggplant, carrots or even potatoes. Then at the same time you will also get a side dish.
Steamed fish
Fish and seaweed are perfect for this diet, especially if you steam them. You should choose low-fat varieties, immediately excluding flounder and similar species. The fish needs to be cleaned and washed well, salt to taste.
Place the pieces in a single layer in a steamer, sprinkle with fresh lemon juice. Cook for fifteen minutes. You can add seaweed, which will then be delicious to eat as a side dish.
Medications
It would be superfluous to say that any medications for the treatment of hepatosis of this type should be prescribed by the attending physician. They can be natural (plant, animal), as well as synthetic.
- Animal-based drugs are usually produced from the liver of livestock (cows, pigs). They have many contraindications; allergic reactions and even infections with infectious diseases cannot be ruled out. These include "Progepar", "Hepatosan" or "Sirepar".
- People know many ways to support and treat liver problems using herbal materials. Traditional medicine also adopted this experience. They have few contraindications, and cause allergies extremely rarely, while improving digestion and speeding up metabolism: extracts of milk thistle, artichoke, pumpkin seeds, “Gepabene”, “Galstena”, “Peponen”, “Karsil”, “Liv 52”.
- Preparations based on essential phospholipids are most often made from soybeans. These medications include the famous “Essentiale Forte”.
- Doctors often prescribe inhibitors of lipid (fat) peroxidation. Most often they contain a substance - thioctic acid. These include “Berlition”, “Octolipen”, “Tiogamma” and others.
- There are also medications containing ursodeoxycholic acid (Livodexa, Ursofalk), as well as combined ones (Essel Forte, Rezalut Pro, Fosfontiale).
To support the liver, it does not hurt to organize the correct intake of vitamins and minerals. First of all, these are substances belonging to group B (thiamine, riboflavin, pyridoxine, cyanocobalamin) and tocopherol (vitamin E). However, they cannot serve as an independent means for organ restoration.
Fatty liver: treatment with folk remedies
Please note that you can take any medicine from people's experience only after consulting your doctor. Without understanding the causes, mechanisms, processes occurring in the body, you can significantly aggravate the problem.
Pumpkin + honey
A medium-sized ripe pumpkin should be washed well and the top should be cut off so that something like a lid comes out. You need to pour natural honey inside. The quality of the product used is very important; it must be free of sugar and other impurities. Pour honey into the pumpkin, cover with a lid, and take it to a dark, warm place for fourteen days. After two weeks, the vessel is taken out and the honey is drained. You should take one tablespoon three times a day. It is recommended to store aged honey in the refrigerator.
Rosehip, nettle, meadowsweet, etc.
To prepare the herbal mixture you will have to try. First you need to collect raw materials in the required quantity. It is best to do this yourself in environmentally friendly regions, but you can simply buy it at the pharmacy.
- Birch leaves – 4 parts.
- Dried rosehips – 4 parts.
- Meadowsweet flowers - 3 parts.
- Nettle leaves – 3 parts.
- Immortelle herb – 2 parts.
- Tansy – 2 parts.
- Mint – 2 parts.
- Corn silks – 2 parts.
- Calendula – 2 parts.
- Valerian root, dandelion, licorice – 2 parts.
The ingredients must be thoroughly crushed and then mixed together. For steaming you will need one and a half liters of purified water. Two tablespoons of the herbal mixture are poured into a thermos and poured boiling water, sealing the container tightly. You will have to insist exactly one night, and drink all the tea in a day. The course of treatment can start from one month and reach six months.
Miracle carrots and milk
For this recipe, it is better to use lactose-free milk, but if this is not available, then regular milk will do.
- Carrots (large) – 2–3 pieces.
- Milk – 150–200 grams.
Carrots must be washed, grated on a fine grater or chopped in a blender. Squeeze the juice from the resulting pulp. Heat the milk to 65–75 degrees, pour it into the carrot juice, there should be approximately twice as much of it. You cannot store the medicine, so you will have to redo it every day. Take half an hour before breakfast. If deterioration is observed, exclude milk from the recipe and stick to pure, slightly warmed juice.
Physical activity and prevention of fatty liver
With fatty hepatosis, it is important to get rid of extra pounds of fat, no matter where it is located. But various exercises, gymnastics and other sports activities are useful not only because of this. Building muscle mass will help restore lost insulin sensitivity, which is very important. Diabetes is the first step to organ obesity, so you need to be careful. Sports will help reduce “bad” cholesterol, which is also good.
Special studies were conducted that showed interesting things. In some patients who did not devote time to physical exercise, liver scars appeared much more often than in those who were actively involved. Sport will be an excellent preventive measure to prevent such an unpleasant, and most importantly dangerous, disease as fatty hepatosis. It won’t hurt to organize proper nutrition for yourself, not to gain excess weight, and to walk a lot in the fresh air. All this will help you worry less about liver problems.
Possible complications
If the disease is advanced, diagnosed too late, or the patient does not comply with medical prescriptions, the consequences of fatty liver are quite severe and irreversible. Against the background of this pathology, the following develops:
- hepatitis;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- liver failure;
- abdominal dropsy;
- fibrosis;
- coma.
Any of these diseases is quite dangerous to human health and life. To prevent their development, it is important to diagnose the disease in time, monitor your diet and lifestyle, and control your weight.
The key to successful recovery is the early diagnosis of fatty liver, so at the first signs of the disease there is no need to postpone a visit to the doctor.
You may be interested in articles on the site: How and why the liver hurts Diet and nutrition for fatty liver hepatosis Fatty liver degeneration Harmful foods for the liver