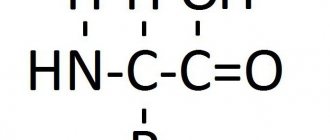Daily norm: 1800 - 5000 mg
Valine (2-amino-3-methylbutanoic acid L-Valine) is an essential aliphatic amino acid that has a stimulating effect.
This is one of the 20 proteinogenic amino acids. It is present in the body as part of proteins and in free form. It got its name in honor of the valerian plant. For the first time, during a study in 1901, the German chemist G. E. Fischer isolated the aminoisovaleric acid valine from casein.
Valine is a starting substance in the biosynthesis of pantothenic acid - Vitamin B5 and penicillin. Valine is a branched amino acid, which means it can be used by muscles as a powerful source of energy.
The human body is not capable of producing this amino acid itself, so it must be supplied to it through food and special dietary supplements (dietary supplements). In addition, you need to know how much the body’s daily need for valine is.
Valine: structural formula
An aliphatic radical is a hydrocarbon chain attached to the same carbon as the amine head and carboxyl tail. The carbon skeleton of valine is one carbon larger than alanine, but not one carbon sequence, but two, is attached to the second carbon atom (in the β-position), i.e. The amino acid appears to be bifurcated at one end, which is why it is called a branched-chain amino acid.
Being a proteinogenic amino acid, valine is part of the body's proteins.
Like other amino acids (except glycine), valine exists in two optical stereoisomers: left-handed (L) and right-handed (D). Only L-valine is found in natural proteins; D-valine is formed as a result of chemical synthesis and is a ballast amino acid that loads the liver.
What sports nutrition can it be combined with?
Valine in BCAAs can and should be combined with full-cycle amino acids during heavy loads, the only thing is that valine at the same time as tryptophan and tyrosine is undesirable - it inhibits their penetration into brain cells. Therefore, BCAAs and full-cycle amino acids should be separated. And so their even distribution throughout the day is quite appropriate. It can also be used with protein shakes and gainers, but with a break between doses, creatine or L-carnitine together before exercise.
Metabolism of valine
Valine is an essential amino acid. The body does not synthesize this compound, and it must come from outside through food.
Branched chain amino acids (valine, leucine, isoleucine) account for about 45% of the content of all essential amino acids in tissues. Branched amino acids prevent the breakdown of proteins to the same extent as the introduction of a full set of amino acids.
Once in the gastrointestinal tract, valine enters the liver. The liver lacks enzymes to metabolize branched chain amino acids. It delays other amino acids for biochemical transformations, and branched ones, incl. Valine gives the green light to enter the general bloodstream. As a result, the amino acids of food protein are separated, and predominantly a mixture of branched chain amino acids is sent to the muscles, the same three friends - valine, leucine, isoleucine. It is there that they enter into amino group transfer reactions, providing muscles with energy.
The formation of a pool of free branched chain amino acids in the liver depends on the content of taurine, which regulates the conversion of amino acids into glucose.
In muscles, branched-chain amino acids are included in muscle protein synthesis, forming a reserve from which they can be mobilized during exercise. During work, muscle protein breaks down, and branched amino acids enter a chain of biochemical transformations, the end product of which is glucose, which provides energy for work. It must be said that the intramuscular fund of free amino acids remains constant throughout the work, but after the load it increases, i.e. there is a certain inertia of the biochemical conveyor.
The need for valine is 3 - 4 g per day.
Minimum daily requirement for an adult: 14 mg. per 1 kg. body weight, for children - 110 mg. per 1 kg. body weight. You should not focus on the minimum daily requirement; it is not physiological, ensuring survival, but not a full life.
Methionine
This essential amino acid promotes the processing of fats. In addition, methionine prevents the deposition of fat in the liver, as well as in the walls of the arteries.
Benefits of methionine
- Promotes digestion.
- Neutralization of the effects of toxic metals and radiation.
- Reducing muscle weakness.
- Normalization of liver functions.
- Promoting the synthesis of nucleic acids, collagen and other proteins.
- Providing a moderate antidepressant effect.
- Strengthening the immune system.
- Normalization of the functioning of the nervous system.
- Reducing the level of “bad” cholesterol in the blood.
- Increased overall tone.
- Prevention of nail and skin diseases.
- Alleviation of toxicosis during pregnancy.
What foods contain methionine?
You can compensate for methionine deficiency by consuming the foods listed below that are enriched with this amino acid.
Products with methionine:
- meat;
- eggs;
- seeds;
- legumes;
- garlic;
- onion;
- yogurt;
- milk and dairy products;
- Cod liver;
- salmon fillets;
- seeds;
- cereals;
- nuts;
- corn and wheat flour;
- wheat sprouts;
- pasta;
- kefir;
- banana;
- soy;
- cottage cheese;
- tuna.
Structural function of valine
Valine is part of almost all proteins, giving them hydrophobic properties, i.e. The protein repels water from itself, hanging in the aquatic environment as an autonomous globule droplet. This amino acid is especially abundant in albumin, casein, and connective tissue proteins; it also accumulates in muscles. The valine content in protein ranges from 4.1% (horse muscle tissue) to 7-8% (human serum albumin, milk casein) and up to 13-14% (connective tissue elastin).
Valine is one of the main components in the synthesis of muscle proteins and tissues of the human body. It is necessary for the growth and development of all tissues, repairing damage to tissue proteins, and maintaining normal levels of nitrogen metabolism in the body. Valine in a mixture with other branched amino acids is used to correct severe amino acid deficiencies resulting from addiction to drugs, as well as as parenteral nutrition when caring for seriously ill patients.
Valine is a precursor to vitamin B3 (pantothenic acid).
It protects the myelin sheath, an insulator of nerve fibers in the brain and spinal cord, the destruction of which causes neurological diseases, the most dangerous of which is multiple sclerosis.
Main functions and benefits
Valine is a truly essential amino acid: without it, the human body has a very hard time.
Important! Absorption occurs in interaction with L-leucine and L-isoleucine. These three substances must be taken together in the following ratio: 2 parts valine, 2 parts leucine, 1 part isoleucine.
For children
In the first years of life, a child becomes vulnerable to disease, especially when the mother's antibodies no longer protect him. This is where proper valine intake becomes extremely important. After all, it is he who forms and supports the baby’s immune system.
A growing body requires this amino acid to build and strengthen muscles.
Its role also increases during active mental stress, which children experience during school. Also used to support mental health.
For adults
But valine is needed not only for the development of children. Adults should also monitor their intake of this substance. After all, it has the following properties:
- increasing endurance and resistance to extreme situations;
- helps with muscle growth and development;
- does not allow the level of serotonin (the hormone of joy) to decrease;
- removes excess nitrogen from the body;
- helps with liver and kidney diseases. Used in the treatment of addictions (alcohol, drugs);
- increases the feeling of fullness and is used during diets and in the treatment of obesity.
- strengthens the immune system.
You will probably be interested in learning about how to boost your immunity with vitamins.
Energy function of valine
Valine is a glucogenic amino acid that is metabolized into succinyl CoA and then included in the Krebs cycle, releasing energy for muscle function. The conversion involves dehydrogenase enzymes, NAD, vitamins B7 (biotin) and B12.
Together with its branched brothers - leucine and isoleucine - it provides energy for muscle function, which is why bodybuilders love it. During exercise, branched chain amino acids, and valine in particular, are the main source of amine nitrogen in skeletal muscle. A significant part of them is released during the breakdown of muscle proteins, which requires an increase in the consumption of these amino acids with food. Taking commercial preparations of branched chain amino acids in these conditions is justified because it compensates for the stress breakdown of muscle proteins.
general characteristics
In 1901, the German chemist Emil Fischer first isolated valine from casein by hydrolysis of proteins. This amino acid gets its name from valerian. Today this substance is known as an essential amino acid, which stimulates the activity of the body, contributes to the formation and maintenance of its structural and functional integrity.
Valine is an aliphatic amino acid with a non-polar character. It is closely related to leucine and isoleucine, with which it has a number of common properties. These hydrophobic substances rarely take part in biochemical reactions, but play a critical role in determining the three-dimensional structure of proteins. In addition, valine promotes the absorption of other amino acids.
Valine (L and D isomers) is also known as a glucogenic amino acid. That is, if necessary, the liver is able to transform this substance into glucose, which the muscles then use as an additional source of energy. In addition, it serves as the starting material for the synthesis of vitamin B3 and penicillin.
Regulatory function of valine
Valine is involved in regulating the functioning of the pituitary gland: a gland in the brain that tunes the body’s hormonal orchestra. It stimulates the production of growth hormone, which supports protein synthesis as opposed to protein breakdown.
In alcoholism and drug addiction, characteristic imbalances of amino acids have been identified, incl. with a branched chain, among which valine plays an important role. In emotional disorders associated with addiction, brain cells require more energy, which they obtain by utilizing branched chain amino acids, particularly valine. The breakdown of proteins in areas of the brain that respond to the regulation of emotions and the general tone of the body is activated, which leads to disruption of the functional activity of these areas and an increase in feelings of depression and irritability.
Valine affects the production of the hormone of joy - serotonin. Valine deficiency provokes depression, and, conversely, when amino acids are in balance, mood improves, a person experiences a surge of vigor and an increase in overall vitality, which is why valine is used to treat depression. Valine and tryptophan are competitors for transport when crossing the blood-brain barrier. Excess valine inhibits the accumulation of tryptophan in the brain and, in case of overdose, can lead to impaired brain function, including hallucinations.
In alcoholic encephalopathy (impaired brain function), due to poor liver function poisoned by alcohol, the concentration of aromatic amino acids (tryptophan, phenylalanine) in the blood increases and the number of branched chain amino acids (valine, leucine, isoleucine) decreases. As a result of competition for transport that carries amino acids across the blood-brain barrier, the concentration of valine in the brain decreases and tryptophan increases. This does not lead to anything good, because the absence of branched amino acids deprives the brain of energy to produce neurotransmitters. An energy-deficient brain plunges into depression and begins to work through the roof, which is externally expressed in a weakening of mental parameters.
The amino acid valine is used to treat drug and alcohol addiction, because alcoholism and drug addiction lead to severe amino acid deficiency. Additional consumption of valine helps prevent relapses and prolongs remission.
Valine improves muscle coordination and reduces sensitivity to pain. It improves adaptability to heat and cold. Being a glucogenic amino acid, it suppresses appetite and reduces sugar cravings through regulating blood sugar levels.
Drugs containing (Analogs)
Level 4 ATC code matches: Infezol
Dextrose
Medicines containing the amino acid Valine: Aminoven , L-Valine , Aminoplasmal B. Brown E 10 , Aminoven Infant , Kabiven , Aminosol-Neo , Aminoplasmal E , Aminosteril , Infezol , Moriamin , Nephrotect , Nutriflex , Cerebrolysate , Hymix .
Sources of valine
The largest amount of valine is found in eggs, cheese and other dairy products, meat, fish, especially salmon, and squid. From plant products, valine can be obtained in decent concentrations from nuts, especially walnuts, pistachios, red beans, pumpkin and sunflower seeds, and seaweed.
During the cooking process, the content of valine in products changes: in meat, chicken, fish it becomes more when stewing or boiling than in a raw product or after frying. In eggs, on the contrary, when frying, the amount of valine increases compared to the raw or cooked product.
For good absorption of valine, the presence of other branched-chain amino acids is necessary - leucine and isoleucine in the ratio valine : leucine : isoleucine = 1 : 1 : 2. In commercial preparations this balance is maintained.
The absence of valine in food makes it incomplete and leads to a negative nitrogen balance, i.e. the body will break down its own proteins and remove nitrogen. This state cannot last long, because it leads to exhaustion and death.
Valine goes well with slow carbohydrates (cereals, wholemeal bread) and polyunsaturated fatty acids (fish oil, flaxseed oil).
Tryptophan
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid used to synthesize serotonin directly in the brain. With a lack of serotonin, which regulates the biological clock, a person is susceptible to depression, neuroses, insomnia, attention disorders and headaches. Thus, tryptophan, like serotonin, is rightfully considered a powerful antidepressant.
Benefits of tryptophan
- Mood stabilization.
- Reducing the manifestation of hyperactivity syndrome in children.
- Regulating appetite, which is especially important for people suffering from bulimia, anorexia and obesity.
- Increased release of growth hormone into the blood.
- Reducing the harmful effects of nicotine and alcohol.
- Normalization of sleep.
- Reducing anxiety.
- Relieving tension.
- Relaxation of the nervous system.
- Increased performance.
- Reducing the manifestations of PMS (premenstrual syndrome).
- Reduced pain sensitivity.
- Promoting the production of vitamin B3.
Tryptophan deficiency can cause the following disorders:
- weight loss;
- diarrhea;
- dermatitis;
- growth disturbance in children.
Important!
The reserves of tryptophan in the body are replenished from the outside with food, while the high content of this amino acid in the diet does not lead to its excess in the body (but excessive consumption of synthetic tryptophan-based supplements can lead to the listed disorders).
What foods contain tryptophan?
To replenish tryptophan protein consumed during metabolism, a healthy adult should consume about 3.5 mg of this amino acid per kilogram of weight.
Food sources rich in tryptophan:
- Brown rice;
- homemade cheese;
- meat (pork, duck, game);
- peanuts and peanut butter;
- mushrooms;
- oats;
- bananas;
- soya beans;
- dried dates;
- sesame;
- Pine nuts;
- milk and dairy products;
- yogurt;
- fish (especially tuna);
- corn;
- seeds;
- shellfish
Valine in food
Using the table, you can calculate how much food you need to eat per day to get the amino acid necessary for life.
So, only 100 g of Parmesan is enough, you will have to eat 2 eggs, and drink almost 1.5 liters of milk. However, you can get by with 150 g of beef, 140 g of turkey or pork tenderloin. If you are a vegetarian, then you will have to eat a glass of peeled pumpkin seeds or eat 400 g of boiled soybeans (which is unlikely) or more than half a kilo of pea porridge (which is absolutely incredible), you will need half a kilo of walnuts, you can not count the rest of the products, because you will need to eat the required amount not within human power. I’m not calling for anything, I’m just showing by example what the dangers of a vegetarian diet are.
Valine deficiency
The lack of valine in the body can be either absolute, when there is insufficient supply of the amino acid from food, or relative, when the need for this amino acid increases due to physiological or pathological processes in the body.
With a vegetarian diet, it is very difficult to maintain protein balance: if you mindlessly lean on just vegetables and fruits, it is very easy to get problems associated with a lack of amino acids, primarily essential ones. Valine deficiency can also occur when it is insufficiently absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract due to diseases of the digestive system.
The need for valine increases due to the following conditions:
- Sports training, especially those related to strength and endurance
- Stress, both psychological and physiological: injuries, burns, previous surgeries, blood loss, etc.
- Pathological addictions: addiction to alcohol, drugs, incl. nicotine, and just a craving for sweets and a desire to eat everything indiscriminately.
- Diseases of the central nervous system: multiple sclerosis, depression
- Acute infectious diseases: ARVI, pneumonia, etc.
A lack of valine has a depressing effect on the nervous system. People suffering from a deficiency of this amino acid may experience fatigue, irritability, and depression. People struggling with alcohol or drug addiction may return to addiction if they are deficient in valine.
Amino acid deficiency
Although valine is easily replenished from food, there are known cases of amino acid deficiency. The lack of this substance affects the quality of myelin (the sheath of nerve cells), and also causes degenerative neurological diseases. Lack of amino acids manifests itself in the form of the so-called “maple syrup” disease (occurs in people whose bodies are unable to absorb leucine, isoleucine and valine). The unusual name of the disease is explained very simply: in such patients, the urine takes on the smell of maple syrup.
In addition, an experiment on rats showed that with a lack of valine, lipid formations appear in the liver tissue. Also, amino acid deficiency may be indicated by hair loss, weight loss, growth retardation, leukopenia or hypoalbuminemia (the level of albumin in the blood sharply decreases). Damage to the mucous membranes, arthritis, memory problems, depression, muscle atrophy, sleep disturbances, and weakened immunity are also possible.
People whose diet does not contain enough protein foods, as well as people who are professionally involved in sports, should take extra care in the form of dietary supplements to avoid valine deficiency.
Applications of valine
Valine is used as a dietary supplement in BCAA (branched chain amino acids). This is a mixture of the amino acids valine, leucine and isoleucine in a physiological proportion of 1: 1: 2. BCAAs release energy directly into muscle fibers, performing the function of muscle fuel. They apply:
- To improve training performance, especially in bodybuilding and weightlifting.
- Treatment of depression, insomnia, migraine, restoration of a positive emotional background, in the complex treatment of multiple sclerosis
- Treatment of pathological addictions: smoking, alcoholism, drug addiction
- Control appetite, eliminate sugar cravings, control weight, increase metabolism to burn fat and build muscle mass
- In the complex treatment of shock, burns, injuries, operations, excessive blood loss
- Stimulation of immunity during the seasonal rise of colds
Valine is recommended for use in muscle building programs. Taking dietary supplements containing valine has a strengthening effect on the muscles and is indicated for the restoration of muscle fibers after intense training. Intense muscle activity during powerlifting, bodybuilding and other strength and speed-strength sports entails the destruction of part of the contractile muscle proteins (actin and myosin). During the recovery process, valine replenishes muscle structures, and in these conditions it is important to have enough valine in the body. Therefore, for effective training and muscle building, you should regularly take BCAAs in your sports diet. This helps to make the most of the potential of the increased hormonal levels that arise during training and accelerate the growth of muscle mass and strength.
The absorption of free BCAA amino acids does not require additional energy and does not inhibit the restoration of energy reserves in muscle cells.
What is it needed for?
Valine is essential: to maintain the health and beauty of the body, as it accelerates metabolism and muscle growth, and also controls the level of nitrogen in the body. For this reason, it is also ideal for influencing the nervous system, combating stress, improving the immune system, and treating gallbladder and liver complications. For those who regularly engage in intense physical activity, valine can help repair muscle fibers that are injured during exercise, providing energy to cells by releasing glucose, which is converted into insulin in the blood. In this way, you can not only obtain greater energy value, but also avoid muscle catabolism.
Excess valine
Consumption of valine in too high doses is not indifferent to the body, so you should not exceed the recommended daily dosage - more than 4 g. At best, an overdose manifests itself in paresthesia: a feeling of numbness in the limbs, crawling sensations, allergic reactions, dermatitis, indigestion, and increased anxiety are possible. Regular overdoses can lead to thickening of the blood, cause liver and kidney dysfunction, and increase ammonia levels in the body, which manifests itself in nausea and vomiting. With a strong excess of valine, chills, rapid heartbeat, fears, and even hallucinations occur.
Contraindications and harm of valine
Valine supplementation should be done under medical supervision. Independent actions in this direction can end in a sad outcome. It is contraindicated for people with severe liver, kidney and heart failure, children under adulthood, pregnant women, as well as during lactation, hepatitis, diabetes, amino acid metabolism disorders, individual intolerance.
Valine may cause harm due to symptoms such as nausea (vomiting), rapid heartbeat, hallucinations, and chills.
In order not to expose our body to danger, to be more beautiful, calmer and more resistant to stressful situations, you should know which foods contain valine.