Why is vitamin A vital for humans?
Retinol, like genuine vitamin A, as well as its forms - retinoids and carotenoids, is involved in most metabolic, protective, regenerative functions of the human body. A lot of biological processes cannot do without it. It is a fat-soluble antioxidant, accumulated by the liver and muscle fibers, released as needed.
A persistent shortage of retinol, according to the World Health Organization, is involved in the annual mortality of 670 thousand children under 5 years of age. A third of the world's population is susceptible to vitamin A deficiency.
Why is vitamin A so important for human health? Let's get acquainted with its biological role, varieties, food sources, aspects of use, and specific benefits.
When to take
A systematic approach and constant consumption of food or preparations with microelements is required. The constant absence of the necessary food or capsules in the diet first causes deficiency and deficiency, and later develops serious diseases and weakens the immune system.
Where is vitamin A, in what foods - in meat and fish, liver and dairy foods. Most of the most common vegetables are rich in it. But only proper consumption with fats helps it to be absorbed.
It is recommended to drink it to ensure healthy skin and hair, slow down the appearance and deepening of wrinkles. It is important to monitor your body to prevent disruption of the immune system.
Look at our Clients' Acknowledgments and Success Stories – View
To properly organize your diet, you need to turn to specialists. Nutritionists and nutrition consultants at Elena Morozova's clinic will tell you where and what Vit contains. And what products are best included in the menu so as not to lack the necessary elements and maintain health.
Biological role of vitamin A
The value of retinol and its provitamins can hardly be overestimated - vitamin A affects the lion's share of the chemical and biological processes of animals, including humans.
- Activates enzymes that produce elements for the construction of connective tissue, collagen, hyaluronic acid components, cartilage, bones, teeth, hair, epithelium.
- Participates in the synthesis of the sulfur-containing amino acid - taurine, which is responsible for adequate transmission of nerve impulses.
- Affects the production of proteins for muscle tissue, DNA, RNA, cell membranes.
- Supports hematopoiesis.
- Provides the ability to see at dusk, protects the organ of vision, and moisturizes the cornea.
- Regulates the balance of sex hormones and spermatogenesis.
- Strengthens the immune system through the synthesis of lysozyme, immunoglobulin, interferon, and anticancer complex.
- Gives skin elasticity, prevents early aging and keratinization.
The fundamental role of vitamin A is to prevent oxidation, bind and neutralize free radicals.
Different Forms of Vitamin A
Natural forms of vitamin A are divided into animal vitamin elements - retinoids, as well as plant provitamins (precursors) - carotenoids. Animal products are endowed with retinoids; they are characterized by 100% activity and digestibility, since they come to us already dissolved in fat.
Carotenoids are coloring enzymes that give green, orange or red color to fruits, vegetables, herbs, berries, and beans. Which part will be broken down and absorbed depends on the type of carotene:
- beta-carotene dissolved in fat - 50%;
- food beta-carotene - 8.3%;
- alpha-carotene, gamma-carotene, beta-cryptoxanthin from food - 4.16%.
Synthetic pharmaceutical preparations of vitamin A have the formula of retinol acetate or palmitate and are available in oral and injectable forms. For the treatment of severe hypovitaminosis that causes skin ailments, special medications are used that are more active than retinol - retinoic acid (isotretinoin) and etretinate.
Vitamin A intake rate
Active retinol in excess is toxic; oversaturation of the body with it has negative consequences. Therefore, the retinol consumption rate developed by WHO indicates both the optimal dose and the maximum permissible limit (mcg per day):
- up to six months - 400 (max. 600);
- six months - a year - 500 (600);
- year - 3 years - 300 (600);
- 4 years - 8 years - 400 (900);
- 9 - 13 years old - 600 (1700);
- woman over 14 years old - 700 (2800);
- during pregnancy - 800 (3000);
- nursing mother - 1300 (3000);
- man over 14 years old - 900 (3000).
It is enough for an adult man to receive 900 mcg of pure retinol per day, for a woman - 700 mcg in order to feel satisfactory. The limit is 3000 mcg.
Vitamin A overdose
If you consume too much of the vitamin, the following symptoms are observed:
- drying of the skin;
- headache;
- nausea;
- disturbance of emotional state;
- bleeding gums;
- diarrhea;
- defects in the development of the embryo in the womb;
- miscarriage.
In medical practice, there have been cases where a person died from a severe overdose of retinol. Overdose is especially dangerous for pregnant women. It can cause osteoporosis and other serious pathologies in the mother, and severe developmental defects in the developing fetus. Therefore, expectant mothers need to take exactly as much vitamin A per day as prescribed by the doctor.
What foods contain vitamin A?
Sources of retinol are divided into plant and animal products, since these are initially different substances. Only once they enter the body, they are converted into retinol through a chemical chain.
Animal foods rich in vitamin A:
- fish oil, caviar;
- liver (fish, beef, veal);
- milk, its derivatives, butter;
- chicken yolk.
Green, red, orange fruits, salad greens and beans are rich in carotene. Cereals, contrary to misconception, are poor in vitamin A.
Excess: symptoms and consequences
An overdose will also not lead to good results. Constant consumption of foods high in vitamin A or medications can cause excess levels in the body. As a result, such uncontrolled use leads to negative consequences:
- cracks and jams will appear on the lips;
- frequent nausea and headaches that cannot be relieved with medications;
- various areas of the skin suffer from itching;
- frequent and irritation, increased excitability;
- painful and severe swelling appears.
Symptoms of Vitamin A Deficiency
Medicine distinguishes between primary and secondary deficiency of retinol (vitamin A). If the diet is poor in food sources of vitamins, or the baby is deprived of mother's milk early, this is a primary deficiency. Secondary deficiency occurs when the absorption and absorption of retinol is impaired. Reasons: smoking, alcohol consumption, diet low in fat, lack of zinc, vitamins E, C, B12.
Picture of symptoms of increasing vitamin A deficiency:
- decreased immunity;
- frequent infections - skin, genital, bronchial, somatic;
- night blindness;
- dry cornea;
- ulceration of the mucous membranes;
- brittleness of hair and nails;
- early skin aging, roughening, peeling.
Advanced vitamin deficiency of retinol (vitamin A) provokes infertility, blindness, skin ailments, and impaired intrauterine development. Promotes the growth of benign or malignant cells.
Interaction of vitamin A with other drugs
Retinol interacts most effectively with tocopherol (vitamin E). This is a necessary duet for the normal mechanism of biological function of valuable substances.
- The second significant element for adequate absorption of vitamin A is zinc; its molecules are involved in the breakdown and transport of retinol.
- Ascorbic acid enhances the role of an antioxidant and stimulates the immune system.
- Vitamin D in combination with retinol ensures normal growth, formation, and functioning of the musculoskeletal system.
Coenzymes B2 (riboflavin), B12 (cyanocobalamin) and folic acid are used in pairs in the treatment of a number of ailments caused by vitamin deficiency.
Indications for use of retinol
Taking a medicinal vitamin preparation eliminates the deficiency. The dose is selected by the doctor individually based on the results of laboratory data showing the level of retinol in the blood. It is important to avoid overdose, but to cover the real need.
Indications for the use of pharmacological retinol are:
- corneal opacities, twilight blindness (with riboflavin, folic acid);
- frequent colds, bronchitis, ARVI (in combination with ascorbic acid);
- lesions of the skin and mucous membranes;
- premature aging of the skin (paired with tocopherol);
- sexual infections;
- rickets (with vitamin D);
- brittle hair, nails (plus taking biotin);
- immunodeficiency states (plus zinc);
- infertility.
As a preventive measure, taking retinol is indicated for pregnant women, starting from the 2nd trimester, as well as during breastfeeding, along with folic acid.
Vitamin supplements that include retinol are useful for smokers, vegetarians, and people who limit fatty foods. Consumption of an antioxidant can stop external fading, therefore helping women during menopause maintain a youthful, attractive appearance.
When is the need for vitamin A increased?
Doctors recommend consuming increased amounts of retinol for people:
- those engaged in heavy physical labor;
- constantly facing stress;
- having chronic diseases;
- frequently undergoing x-rays;
- taking medications to lower blood cholesterol;
- often working at a computer, which strains the eyes;
- alcohol abusers.
The need for vitamin A is increased in athletes following a high-protein diet, as retinol accelerates the absorption of proteins. The vitamin in increased doses is important for actively growing and developing children from 3 to 12 years old, as well as for schoolchildren experiencing high intellectual stress.
Table of recommendations for taking Vitamin A
- Anemia (anemia) 10000-25000 IU/day Vitamin A deficiency can contribute to the development of symptoms of anemia.
- Children's diseases As prescribed by a doctor, Vitamin A plays an important role in the functioning of the immune system, therefore high doses of vitamin A (as recommended and under the supervision of a doctor) are successfully used for the prevention and treatment of measles and chickenpox in children.
- Cystic fibrosis (cystic fibrosis) 5000-10000 IU/day Cystic fibrosis leads to impaired absorption of fats, which in turn leads to a deficiency in the body of fat-soluble vitamins, such as vitamin A. Therefore, if you have cystic fibrosis, you need to take additional vitamin A.
- Infections As recommended by a doctor, Vitamin A is important for the proper functioning of the immune system and helps the mucous membranes resist invasion by microorganisms.
- Leukoplakia 28,500 IU/day under medical supervision Studies have shown significant effectiveness in the treatment of Leukoplakia with vitamin A supplements.
- Measles 200,000 IU/day for 2 days under medical supervision In countries where there is a general deficiency of vitamin A, adding vitamin A to the diet in the form of dietary supplements leads to a reduction in child mortality from measles.
- Night blindness 10,000-25,000 IU/day It has been noted that night blindness may be an early sign of vitamin A deficiency.
- Celiac disease As recommended by a doctor, Celiac disease can lead to a deficiency of vitamin A, and therefore this disease may require additional supplementation of this vitamin in the form of dietary supplements or injections.
- Immunity As recommended by a doctor, Vitamin A plays an important role in the normal functioning of the body's immune function. In some cases, supplemental Vitamin A may improve immunity.
- Iron deficiency As recommended by a doctor According to some studies, taking vitamin A along with iron helped combat iron deficiency more effectively.
- Hypermenorrhea (menorrhagia) 50,000 IU/day under medical supervision One study found that supplemental vitamin A in women suffering from hypermenorrhea led to significant improvements or complete normalization of menstrual blood loss.
- Stomach ulcer 150,000 IU/day under medical supervision Vitamin A can help scarring of stomach ulcers.
- Measles with complications On the recommendation of a doctor It is known that Vitamin A helps fight childhood diseases such as measles and chickenpox. Two studies of children with complicated measles found that high-dose vitamin A speeded recovery and reduced complications.
- Wound Healing 25,000 IU/day under medical supervision Vitamin A plays a central role in wound healing and can help when taken as a dietary supplement or in creams and ointments.
- Changes in PAP smear As recommended by your doctor Women with vitamin A deficiency are at risk of cervical dysplasia.
- Acne As recommended by a doctor Taking vitamin A in large doses (under the supervision of a doctor) can help treat acne. However, acne usually returns after stopping treatment.
- Alcohol addiction On the recommendation of a doctor Chronic alcoholics develop liver damage, which, in turn, leads to vitamin deficiency, including a lack of vitamin A, which requires correction.
- Conjunctevitis and blepharitis As recommended by a doctor It is not known whether vitamin A can help people suffering from chronic conjunctivitis, but studies show that these patients have vitamin A deficiency syndrome.
- Crohn's Disease According to the doctor's recommendation, Vitamin A is necessary for the growth and repair of cells in the small and large intestines and thus taking Vitamin A may improve symptoms in patients with Crohn's disease.
- Diarrhea As recommended by a doctor Only in cases of malabsorption, vitamin A should be used to treat diarrhea, otherwise it does not bring results and may even increase the risk of diarrhea in children with normal nutrition.
- Gastritis According to the recommendation of a doctor, Vitamin A helps in the treatment of peptic ulcers and can also be useful in the treatment of gastritis.
- Goiter As recommended by a doctor, taking a complex of vitamins A, C, E and beta-carotene can prevent the formation of goiter in conditions of iodine deficiency.
- AIDS (HIV) As recommended by a doctor People with HIV infection have a deficiency of vitamin A, probably associated with the high severity of the disease. To prescribe adequate vitamin therapy, you must consult your doctor.
- Hypothyroidism As recommended by your doctor People with hypothyroidism may have an impaired ability to convert beta-carotene into vitamin A. For this reason, some doctors recommend taking vitamin A supplements.
- Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) As recommended by a doctor Some studies suggest that taking vitamin A may alleviate PMS syndromes.
- Urinary Tract Infections As recommended by a physician Due to the high importance of vitamin A in immune function, a deficiency may increase the risk of many infections, including UTIs.
- Vaginitis According to the recommendation of a doctor Some doctors recommend vaginal application of vitamin A to improve the integrity of vaginal tissue and improve the function of local immune cells.
Background: green - scientifically proven, orange - insufficient evidence, White - no research done
Role in the body
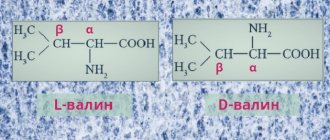
The concept of “vitamin A” includes retinol (vitamin A1), as well as retinoids similar in their biological activity: retinal, retinoic acid and dehydroretinol (vitamin A2). The precursors of retinoids are carotenoids, which are converted into vitamin A in the body in the presence of fats.
Vitamin A is named the first letter of the alphabet because it was discovered first. Its discovery was preceded by centuries-old observations indicating that with poor nutrition, people developed eye pathologies - corneal necrosis, dry conjunctiva, hemeralopia (night blindness). Gradually, it became clear that these problems are associated with a deficiency of a certain substance in the body. In 1913, simultaneously, two autonomous groups of scientists managed to isolate this substance and describe its structure.
The benefits of vitamin A are determined by the important role it plays in the body. It is involved in many biochemical processes on which the functioning and condition of almost all body systems depend.
Leather
Retinol is not called the beauty vitamin for nothing. Without it, collagen synthesis and epithelial cell regeneration are impossible, which is why it is included in most cosmetic creams. It is successfully used in the treatment of many skin diseases and injuries - acne, acne, psoriasis, burns, wounds, etc. With a lack of vitamin A in the body, collagen synthesis slows down, the skin becomes dry, wrinkled, and cracks form on it.
Mucous membranes
Retinol is also involved in the regeneration of mucous membrane tissue. The organs of the respiratory, genitourinary, digestive systems, the inner surfaces of the eyelids and organs of hearing have mucous membranes, so their condition largely depends on the content of retinoids in the body.
The immune system
Vitamin A is an active participant in the biochemical processes of the immune system. By increasing the activity of immune blood cells and increasing the barrier function of mucous membranes, it protects the body from bacterial and viral infections. With its deficiency, the body becomes more vulnerable to infection and suffers infectious diseases much more difficult.
Vision
Retinoids are necessary for the normal functioning of the visual organs. With their deficiency, dry cornea develops and the ability to see in low light is lost. Vitamin A deficiency has been proven to trigger the development of cataracts and macular degeneration.
Endocrine system
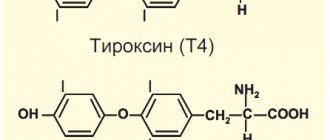
Retinoids are involved in spermatogenesis, the production of sex hormones, and prevent an increase in the concentration of thyroxine secretion from the thyroid gland.
Bones
Retinoids take an active part in the development of bone tissue - osteogenesis. With their deficiency, bone pathologies occur - due to an increase in the volume of spongy substance, the bones thicken.
A sufficient level of retinol in the body is also a necessary condition for healthy teeth, nails and hair.
Antioxidant action
Vitamin A and beta-carotene are powerful antioxidants. They protect brain cells from destruction by free radicals, prevent atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease. Maintaining sufficient levels of retinol in the body slows down aging and is considered a means of preventing malignant tumors.
Application in sports and bodybuilding
Vitamin A is directly involved in the process of muscle tissue growth, and also accelerates the formation of glycogen in the body, which is the main source of energy for stressed muscles. This makes it indispensable in sports and bodybuilding. In intensely training athletes, the consumption of retinoids occurs at an accelerated pace, so the daily need for them increases.