Maintaining the normal functioning of a healthy body is ensured by timely replenishment of vitamin and mineral compounds.
Fatty and polyunsaturated acids, absorbed by humans thanks to vitamin B6, provide not only excellent health, but also support natural beauty.
Vitamin B6 is useful for children and adults, because it is rightfully considered a storehouse of useful enzymes and takes an active part in many metabolic processes.
Without this element, a number of chemical reactions are not carried out, which leads to premature aging of cells and tissues that lose elasticity and flexibility.
General properties and description of the useful element
The modern pharmaceutical industry produces vitamin B6 in tablets and ampoules, and is part of biologically active and food supplements.
The need to take it is due to the fact that this element actively takes part in protein metabolism and the synthesis of necessary amino acids by the human body.
The absorption of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, and the amount of hemoglobin in the blood depends on the timely replenishment of pyridoxine reserves.
Participation in energy metabolism ensures the maintenance of activity when maintaining a healthy lifestyle and intense training or playing energy-intensive sports.
The property of regulating the functioning of the central nervous system (CNS) helps improve mood and get rid of stressful conditions.
By getting rid of pyridoxine deficiency, you can guarantee excellent health, normalize general metabolic processes and strengthen the level of immune defense of all organs and systems.
Indications for pathologies and diseases
What kind of vitamin is pyridoxine, B6 or B12? The correct answer is the first one, B6. It is prescribed for the following pathologies, diseases and conditions of the body:
- Toxicosis in pregnant women.
- Premenstrual syndrome.
- Various types of parkinsonism.
- Chorea.
- Pathologies of the peripheral nervous system. For example, neuritis, radiculitis.
- Pellagra.
- Acute and chronic gastritis (the vitamin is able to normalize the acid function of the stomach), peptic ulcers of both the stomach and duodenum.
- Chronic cholecystitis (the vitamin is directly involved in the processes of bile secretion).
- Anemia.
- Radiation sickness.
- Dermatitis, herpes zoster, psoriasis, neurodermatitis.
- Exudative diathesis.
- Prevention or reduction of negative side effects when taking certain medications.
Note that acute B6 deficiency will be observed in alcoholism, which aggravates alcoholic psychosis. Also, a lack of pyridoxine can occur during anti-tuberculosis therapy or taking oral contraceptives.
Physical and chemical properties of the substance
Being pyridine derivatives, vitamin B6 in ampoules is highly soluble in liquid, water and alcohol compounds.
Due to its unique chemical structure, the substance entering the body is integrated into the enzymes of soft and connective tissues, playing an important role in the processes of protein metabolism and hormone production.
In its free form, the substance is white crystals that are insoluble in fats and are destroyed during heat treatment.
The effectiveness of a compound that enters the human body is reduced by long-term storage before consumption, combination with alcohol and with an increased estrogen content.
Pyridoxine hydrochloride – instructions for use, price, reviews and analogues
Ampoules with pyridoxine solution and tablets with vitamin B6 can be purchased at stationary pharmacies, where a large selection of drugs from various manufacturers is available. It is better to buy high-quality dietary supplements with B6 on the iHerb website, where a huge range of supplements from premium pharmacological companies from all over the world is presented.
For Pyridoxine tablets, the price varies between 40-60 rubles.
The price of Pyridoxine in ampoules is 20-35 rubles.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
ZdravCity
- Pyridoxine (Vit B6) tab. 10mg n50Ozone LLC
- Pyridoxine (Vit B6) solution d/in. 5% 1ml No. 10 Borisovsky plantBorisovsky plant
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine h/x) (amp. 5% 1ml No. 10)
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine h/x) (tab. 10 mg No. 50)
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine h/x) (tab. 10 mg No. 50)
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine h/x) (amp. 5% 1ml No. 10)
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine h/x) (amp. 5% 1ml No. 10)
Europharm* 4% discount using promo code medside11
- Pyridoxine hydrochloride 10 mg n50 tabOzon LLC
- Pyridoxine hydrochloride injection solution 5% 1 ml n10 amp JSC “Yerevan HFF”
show more
Pharmacy24
- Pyridoxine-Darnitsa 5% 1 ml No. 10 solution for injection
- Pyridoxine hydrochloride (Vitamin B6) 50 mg/ml 1 ml N10 injection solution AT “Lekhim-Kharkiv”, Ukraine
PaniPharmacy
- Pyridoxine hydrochloric solution d/in. 5% amp. 1ml No. 10
- Pyridoxine solution d/in 50 mg/ml amp. 1ml No. 10 Ukraine, Lekhim-Kharkov CJSC
- Pyridoxine hydrochloric solution d/in. 5% amp. 1ml No. 10 Ukraine, Health LLC
- Pyridoxine hydrochloric solution d/in. 5% amp. 1ml No. 10 Ukraine, Darnitsa ChAO
show more
Foods to replenish vitamins
Knowing which foods contain vitamin B6, you can independently replenish your body’s reserves of useful substances without resorting to the use of dosage forms.
Consumption of elements with food is necessarily associated with minimal temperature processing of food products to increase efficiency:
- products of plant origin. This group includes brewer's yeast, ovaries and wheat bran; healthy vegetables include melon and broccoli, carrots and cabbage (cauliflower, Brussels sprouts and cabbage), garlic and asparagus;
- meat products and offal. To saturate the body with vitamin components high in B6, it is necessary to replenish the diet with pork or beef liver and kidneys, heart and beef, and lean pork.
A sufficiently high content that can replenish pyridoxine reserves is observed in fresh eggs and milk, and black molasses.
Cod and tuna remain invaluable stores of vitamin B6, which are important to eat regularly, which helps restore and normalize protein and energy metabolism.
Vitamin B6 overdose
An excess of vitamin B6 occurs only with uncontrolled use of pyridoxine-based medications, and its daily intake usually exceeds 100 mg.
This usually occurs:
- allergic reaction like urticaria (bright itchy rashes appear on the skin)
- there is a decrease in the acidity of gastric juice, which leads to indigestion
With a massive overdose of pyridoxine, the following occurs:
- feeling of numbness in fingers
- hands and feet
- impaired skin sensitivity in these areas
Daily intake of pyridoxine
Carefully compiled instructions for vitamin B6 give an idea of the need for the dosage of the taken component necessary for beauty and health.
These recommendations indicate that the daily dose of pyridoxine is significantly different for children and adults, and it is important to consult a doctor before taking the drugs.
a lack of
Pyridoxine deficiency due to lack of nutritional intake into the body is possible during total starvation .
The main reasons for the lack of the substance are pathological processes that interfere with the processing of the vitamin or lead to increased consumption of adermin.
In adults who eat normally and do not abuse bad habits, the development of pyridoxine deficiency is almost impossible. Vitamin deficiency can be caused by taking dietary supplements and medications containing substances incompatible with pyridoxine.
Symptoms of Vitamin B6 Deficiency
The clinical picture of pyridoxine deficiency manifests itself in newborns who are on unbalanced artificial feeding:
- Inappropriate convulsive reaction of fear to sharp sounds, unexpected touches;
- Excessive sleepiness;
- Tearfulness;
- Inflammatory changes in the skin - dermatitis.
In adolescents , active acne vulgaris (acne) skin rash may be a symptom of vitamin deficiency.
In adults, signs of pyridoxine deficiency appear during the action of significantly advanced pathological processes:
- The lips crack and peel, their edges turn bright red;
- The conjunctiva of the eyes becomes inflamed;
- The tongue takes on a purple tint and swells due to glossitis;
- Areas of skin around the nose, lips, ears, and genitals become oily, red, and covered with scales of horny epidermis - manifestations of dry seborrheic dermatitis;
- Pervasive nausea contributes to loss of appetite;
- Decreased mood, even to the point of depression;
- Dizziness;
- Increased fatigue;
- Paresthesia occurs, reminiscent of electric shocks, turning into numbness of the skin areas;
- In the blood, an increase in low-density cholesterol and cholesterol is determined against the background of a decrease in high-density cholesterol;
- Calcium stones may form in the kidneys.
A severe clinical picture in patients suffering from endogenous primary hypovitaminosis, which is based on the pathology of vitamin B6 metabolism at the molecular level:
- Anemia,
- Cramps,
- Thrombosis,
- limb deformity,
- mental retardation,
- pallor of the skin, blond hair and iris of the eyes, due to a congenital deficiency of pigments;
- ectopia or “subluxation” of the lens.
Reasons for shortage
Pyridoxine deficiency can have endogenous and exogenous causes.
Internal (endogenous) primary causes are congenital mutations at the molecular level:
- Homocystinuria. Lack of an enzyme dependent on vitamin B6 - cystatonine synthase. It is responsible for the processing of homocysteine and serine, an important intermediate process in the biosynthesis and metabolism of major proteins. As a result of point mutations in the DNA encoding cystathionine. Homocysteine products accumulate in the blood and urine.
- Cystatinuria. The disease is caused by a gene mutation in the enzyme cystathionase, which is responsible for the breakdown of cystathionine. Manifests itself as mental retardation.
- Knapp syndrome. Congenital disorder of the mechanism for converting niacin from tryptophan due to the lack of a B6-dependent enzyme.
- Pyridoxine-dependent convulsive syndrome. Develops in newborns when consuming canned milk due to a lack of vitamin.
- Anemia resulting from low activity of a special amino acid responsible for heme synthesis. It should be triggered by vitamin B6. Secondary endogenous causes:
- Stress;
- Feverish conditions;
- Metabolic situations associated with accelerated protein consumption - hyperthyroidism, diabetes, HIV;
- Liver diseases;
- Long-term intestinal infections with symptoms of malabsorption;
- Taking medications that are pyridoxine antagonists - sulfonamides, anti-tuberculosis drugs, contraceptive estrogens, penicillamines;
- Smoking;
- Alcohol.
Important! Through scientific tests it has been established that a lack of pyridoxine can provoke myocardial infarction.
Vitamin B6 and alcohol
Ethyl alcohol destroys the liver, where pyridoxine is activated. Nicotine and ethanol reduce the body's absorption of riboflavin (Vitamin B2), one of the main functions of which is to convert pyridoxine into a working form.
Ethyl alcohol destroys the component of pyridoxine - phosphopyridoxal. This is an important coenzyme of nitrogen-containing compounds (amino acids, porphyrins, nucleotides).
A complex of effective and beneficial properties of the substance
Understanding why the body needs vitamin B6, it is important to maintain its reserves by ensuring daily consumption of vitamin-containing preparations.
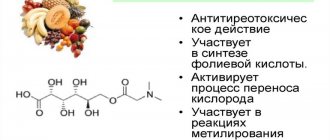
Due to this, there is overall improvement and preservation of youth; the beneficial properties of the element include the following effects:
- normal level of absorption of protein foods and healthy fatty compounds;
- active production of the essential amino acid niacin from tryptophan;
- suppression of irritation of the nervous system and skin manifestations of various diseases;
- relieving symptoms associated with stomach upsets and vomiting;
- normalization of the synthesis of nucleic acids, which slow down the aging process of tissues;
- reduction of muscle spasms, convulsive manifestations, numbness of the limbs;
- normalization of the urination process and acceleration of general metabolic processes.
Prescribed by specialized specialists for various diagnosed diseases, such as leukopenia and air or sea sickness.
The use of vitamin-containing preparations is useful for those who suffer from anemia and hepatitis, toxicosis during pregnancy and nervous disorders of varying complexity.
Indications for use
Pyridoxine is prescribed for its deficiency (chronic or temporary). But there are other situations when taking an additional course is required. When should you take vitamin B6? What can it be useful for? The indications are as follows:
- alcoholism;
- CNS disorders expressed by various neuritis, chorea minor, paranoia, depression;
- toxicosis during pregnancy;
- leukopenia;
- hepatitis of different stages and types;
- atherosclerosis, pressure surges;
- AIDS;
- dermatitis;
- seasickness;
- herpes zoster and others.
In all the described cases, it is recommended to take pyridoxine in a higher dosage (as prescribed by a doctor). B6 is often included in a complex of medications for the treatment of enuresis, epilepsy and childhood autism. In addition, it is prescribed to smokers due to its ability to regulate lung function.
Level of absorption and harm of vitamin consumption
The low price of vitamin B6 in pharmacy chains ensures the necessary replenishment of the body's reserves with useful components.
Excess vitamin preparations are actively eliminated during urination, thanks to the universal diuretic property of the element, 8 hours after taking it.
Pyridoxine that enters the body is well absorbed and is characterized by a minimal level of toxicity for all tissues.
You can avoid harm to the body by strictly controlling the dosage of medications taken and conducting medical studies to determine if there is an individual intolerance to the active substance.
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)
General characteristics of vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)
In the first half of the last century, scientific research related to vitamin B6 began, which is continued by many scientists to this day.
In 1934, researcher Paul Györgyi first discovered this vitamin. He was the first to give the now generally accepted names to the discovered substance in 1939 - vitamin B6, pyridoxine. In 1938, an American researcher was the first to isolate pure crystalline water-soluble pyridoxine. Vitamin B6 is actually a group of vitamins: pyridoxine, pyridoxinal and pyridoxamine, which are closely related and act together (calorizer). B6 is required for the formation of antibodies and red blood cells.
Physico-chemical properties of vitamin B6
By their chemical nature, the substances of the vitamin B6 group are pyridine derivatives. It is a white crystalline substance, highly soluble in water and alcohol.
Enemies: long-term storage, water, food processing, alcohol, estrogens.
Food Sources of Vitamin B6
The best natural sources of pyridoxine: brewer's yeast, wheat bran, wheat ovary, liver, kidney, heart, melon, cabbage, black molasses, milk, eggs, beef, cauliflower, garlic, asparagus, broccoli, cod, tuna, Brussels sprouts.
Daily requirement for vitamin B6
Measured in mg. Adults are recommended to take 1.6-2.0 mg daily; pregnant women need to increase the dose.
The table shows more detailed data on the daily requirement of pyridoxine:
| Age/gender | Daily requirement (mg) |
| Infants 0-6 months | 0,5 |
| Children from 6 months to 1 year | 0,9 |
| Children from 1 year to 3 years | 1,0 |
| Children 4-6 years old | 1,3 |
| Children 7-10 years old | 1,6 |
| Teenagers boys 11-14 years old | 1,8 |
| Teenagers girls 11-14 years old | 1,6 |
| Boys 15-18 years old | 2,0 |
| Girls 15-18 years old | 1,7 |
| Men 19-59 years old | 2,0 |
| Women 19-59 years old | 1,8 |
| Men 60-75 years old | 2,2 |
| Women 60-75 years old | 2,0 |
| Men over 75 years old | 2,3 |
| Women over 75 years old | 2,1 |
| Pregnant women | 2,1 |
| Women breastfeeding | 2,3 |
Beneficial properties of vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 promotes proper absorption of protein and fat. Promotes the conversion of tryptophan, an essential amino acid, into niacin. Helps prevent various nerve and skin disorders. Relieves nausea. Promotes proper synthesis of nucleic acids that prevent aging. Reduces nighttime muscle spasms, calf muscle cramps, numbness of the hands, and certain forms of neuritis of the extremities. Acts as a natural diuretic.
People who consume large amounts of protein need this vitamin (calorizer). Vitamin B6 can reduce insulin requirements in diabetics and, if the dosage is not adjusted, can lead to low blood sugar.
Pyridoxine is useful for the following diseases:
- Leukopenia;
- Anemia;
- Toxicosis during pregnancy;
- Meniere's disease;
- Air and sea sickness;
- Hepatitis;
- Diseases of the nervous system;
- Various skin diseases.
Harmful properties of vitamin B6
Pyridoxine is well tolerated in all forms. Has very low toxicity. People with individual intolerance to pyridoxine may develop allergic reactions in the form of urticaria. It can only cause harm if taken for a long time in very large doses. In this case, symptoms occur: numbness of the limbs, tingling, a feeling of squeezing, loss of sensation.
Vitamin B6 absorption
Vitamin B6 is well absorbed by the body, and its excess is excreted in the urine. It is excreted 8 hours after administration and, like all B vitamins, must be replenished, but if there is not enough magnesium in the body, the absorption of the vitamin noticeably worsens.
Vitamin B6 deficiency in the body
Symptoms of vitamin B6 deficiency:
- Drowsiness, irritability, lethargy;
- Loss of appetite, nausea;
- Dry skin above the eyebrows, around the eyes, on the neck;
- Cracks and sores in the corners of the mouth;
- Patchy hair loss;
- Insomnia;
- Depression;
- Flatulence;
- The appearance of kidney stones;
- Conjunctivitis;
- Stomatitis.
The following symptoms of pyridoxine deficiency are typical for infants:
- Increased excitability;
- Convulsions resembling epilepsy;
- Stunted growth;
- Gastrointestinal disorders.
Diseases caused by B6 deficiency: anemia, seborrheic dermatitis, glossitis.
Excess vitamin B6 in the body
Pyridoxine is generally well tolerated in all forms and is rapidly excreted naturally in the urine. But long-term use of large doses of vitamin B6 can cause harm. Daily doses ranging from 2-10 grams may cause neurological disorders. Possible symptoms of excessive intake of vitamin B6 are restlessness during sleep and excessively vivid dream memories (calorizer). More than 500 mg per day is not recommended.
Interaction of vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) with other substances
Pyridoxine is necessary for proper absorption of B12. Necessary for the formation of hydrochloric acid and magnesium compounds.
People with arthritis who are being treated with penicillamine should take supplements of this vitamin.
Supplements of this vitamin should not be taken by those taking levodopa for Parkinson's disease.
Vitamin B6, together with vitamins , and B12, has a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system, prevents the occurrence of ischemia, atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction.
See more about vitamin B6 in the video “Organic Chemistry. Vitamin B6"
Author: Marina L. (especially for Calorizator.ru) Copying this article in whole or in part is prohibited.
Discuss on the forum
How does a noticeable lack of pyridoxine manifest?
Timely consumption of this beneficial element or injections of vitamin B6 will help restore well-being with the following symptoms:
- noticeable drowsiness and increased irritability;
- unmotivated loss of appetite and attacks of nausea;
- drying of the skin in the eye area and neck;
- appearing skin lesions in the corners of the lips;
- focal hair loss and depression;
- increased flatulence, lethargy and sleep disturbance;
- depression with sudden mood swings.
In children under 3 years of age, pyridoxine deficiency is manifested by an excited state, convulsive spasms and disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
Daily requirement
When planning your diet, you should consider the following pyridoxine rate:
- An adult in good health needs 2-2.5 mg of B6 per day . On average, this is equivalent to eating 0.6 kg of bananas or 0.3 kg of fish.
- Children immediately after birth and up to six months need 0.2-0.3 mg .
- With age, the need for the element increases. So, from the age of six months the body needs 0.5 mg , and by 8-10 years already 1.5 mg per day .
- The body of women during lactation and pregnancy requires 2.5-3.0 mg of vitamin per day.
The need for pyridoxine increases in the following cases:
- While taking birth control pills or medications containing estrogen.
- During pregnancy, when the body synthesizes increased amounts of estrogen.
- While on a diet. Often the inability to lose weight is caused by a deficiency of this useful element.
- During the period of taking steroids (including cortisone).
- 14 days before the start of the menstrual cycle.
- In adolescence, when the fat glands are in the active stage of work.
- When playing sports or heavy physical labor, and so on.
Pyridoxine and its interaction with other components
The combination of B6 and B12 has a positive effect on the absorption of magnesium and the formation of useful hydrochloric acid in the body.
Most often, this element is included in complex preparations containing several components and B vitamins, which ensures beauty and health for every person and child.
Lack of pyridoxine is associated with dieting and improper preparation of the daily diet, lack of food of plant and animal origin.
Pyridoxine in nature
The vitamin is widely distributed in nature and is found in large quantities in many fruits, vegetables and meat products:
- meat: chicken, chicken, pork, veal liver, fish;
- fruits: bananas, avocados, prunes;
- vegetables: spinach, carrots, potatoes;
- grains and legumes;
- dairy products and eggs;
- nuts: pistachio nuts, hazelnuts.
During storage, processing and cooking, the loss of vitamin can reach 50%
Processing and cooking of plant sources has the least waste because they are rich in pyridoxine, which is much more stable than the pyridoxal and pyridoxamine present in animal sources.
The danger of drug overdose
Pyridoxine does not tend to accumulate in the body. Evacuated through the kidneys.
Reference! Water-soluble vitamins do not cause hypervitaminosis. Their excess is simply removed from the body!
Consuming doses greater than 500 mg per day is not toxic to the body. But a large one-time intake of a substance into the body (200-5000 mg) can cause a reaction:
- Allergic;
- Ataxia;
- Loss of sensitivity, numbness;
- Trembling of limbs;
- Paresthesia - tingling in the palms and soles.
Carefully! It has been proven that megadoses of the vitamin stimulate the growth of pathogenic bacteria: staphylococci, lactic acid bacteria.
What is dangerous about an overdose of vitamin B6 and what symptoms appear?