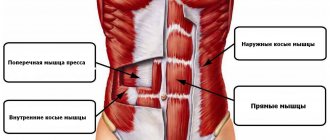
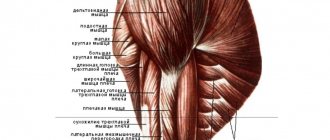
After training, muscles hurt due to overtraining, exposure to lactic acid, aseptic inflammation of the fibers, and injury. In most cases, such pain is considered normal. If it lasts more than a week, help is required.
How long have you had this pain syndrome?
- A few days (25%, 569 Votes)
- First day (21%, 479 Votes)
- Several months (12%, 273 Votes)
- Week (10%, 232 Votes)
- Several weeks (10%, 229 Votes)
- About a month (8%, 188 Votes)
- Chronic form (7%, 154 Votes)
- About a year (6%, 125 Votes)
Total voters: 2 250
Loading …
Use search Are you having a problem? Enter “Symptom” or “Name of the disease” into the form, press Enter and you will find out all the treatment for this problem or disease.
Why do muscles hurt after training?
Painful discomfort after physical exercise is normal, with the exception of acute pain of high intensity.
In this case, we can talk about injury. During sports activity, under the influence of metabolic processes, glucose contained in muscle tissue is converted into lactic acid. She's harmless. However, it causes a burning sensation. With a large number, there is a possibility of limited mobility.
The next day, the aseptic inflammatory process in the fibers begins. It is associated with microtears. Pathogenic microorganisms do not take part in this. This type of pain is called delayed pain.
It takes several days for full recovery. Therefore, when a specialist prepares a training program, he selects the number of classes and a set of exercises with the goal that at least a week passes between loads on the same muscle group.
Everyone has their own body. To make it easier to recover muscle tissue, you need to exercise regularly. Before the complex itself, you need to do a warm-up and stretching, paying attention to warming up those muscles that will bear the main load. Use light weight.
You need to choose your diet. Eat according to the schedule.
Food must correspond to the purpose of training:
- The task in losing weight is to eat in small portions five to six times a day, following the regime;
- to pump up muscles, give definition - you need a high-calorie diet with a predominance of animal protein.
Recommended Products:
- Animal meat (pork, beef).
- Chicken eggs.
- Fish.
It is acceptable to take nutritional supplements (a person’s convictions do not accept the consumption of animal products).
Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) play an indispensable role in building a sculpted figure and recovering from muscle pain.
Before starting to use BCAAs, you should consult with a bodybuilding specialist. Like any pharmaceutical drug, it has indications and contraindications for use.
Many beginners want to follow famous fitness bloggers. But a subscription will not save you from trial and error on your own. Your muscles will ache – that’s a fact. The main thing is to understand when it’s time to see a doctor and identify the hidden causes of illness.
Prevention of abdominal muscle strain
To avoid such injuries, experts recommend following some rules:
- It is imperative to warm up before starting physical exercise.
- Do not overexert yourself when doing exercises.
- Do not lift heavy objects suddenly.
- You should stop exercising if you feel tired.
- It is necessary to strengthen the abdominal muscles by performing special exercises.
There are also a number of exercises that can strengthen your abdominal muscles, which will help you avoid straining and tearing your abdominal muscles in the future.
A pulled abdominal muscle can be a fairly serious injury. At the same time, if the human body is prepared and physically strong, which regular exercise can achieve, the likelihood of such an injury is practically absent. Therefore, it is very important to play sports from a young age. And here we are not talking about any serious physical activity. It will be quite enough if you at least do certain exercises at home.
source
What to do if you have muscle pain after exercise
Methods for relieving muscle pain:
- the use of water procedures (contrast shower, warm bath);
- massage (light rubbing achieves the effect of increasing blood flow, accelerating metabolic processes, including the removal of lactic acid and restoration of fibers);
- the use of ointments and creams that have an anti-inflammatory effect and irritants;
- swimming in the pool (the procedure should last at least 10-15 minutes);
- light warm-up to accelerate blood flow in the muscles (done only with your own weight).
If the sensation lasts more than a week or increases in intensity, you need to visit a doctor. It is likely that the fibers are damaged and severely traumatized.
What to do?
There are not many treatments for headaches after sports. Both medicinal pharmaceutical products and traditional methods are used. The most effective are:
- taking a painkiller that will dilate blood vessels and reduce spasms: Pentalgin, Analgin or Spazgan;
- when the above-mentioned remedies are not available, No-shpa or Citramon will do;
- It is recommended to go to bed - this is the most harmless treatment, especially if you are very tired.
What is indicated by dull, pulling, aching or sharp pain?
Muscle soreness can manifest itself in a variety of symptoms, be concentrated in different parts of the body, or affect the entire person. It may bother you constantly or appear when you move. It all depends on the main reason for its occurrence.
Most often, disturbing muscle pain (myalgia) after exercise appears in the following cases:
- Injury.
- Stretching.
- Excessive physical activity.
- Intense sports training.
- Virus, flu.
- Hypothermia.
- Neurosis.
- Stress.
- Rheumatism.
- Inactivity.
Myalgia, accompanied by decreased performance, fatigue, cramps and numbness of the limbs, impaired motor function - the consequences of changing weather.
Myositis is an inflammation of muscle tissue, manifested by swelling and redness of the skin in the affected area. The pain is concentrated in one muscle and does not spread further.
The strength of its manifestation increases with movement, tension, and exposure to cold. The nature of pain also responds to changes in weather conditions.
Leg myalgia is caused by:
- Injury.
- Disease of the joints and spine.
- Sedentary or standing work. Unpleasant sensations in the legs are dull, aching, stabbing in nature.
- Prolonged immobility of the lower extremities. Painful negative sensations occur due to the formation of blood stagnation.
- Thrombophlebitis. The pain is of a burning nature, concentrated in the calves.
- Arterial diseases: atherosclerosis, endarteritis. The sensation intensifies when walking, and subsides at rest.
The back feels unwell in the following cases:
- Pathologies of the spine.
- Overvoltage. Often associated with the performance of work duties.
- Stagnation of blood as a result of being in the same position for a long time.
- Mechanical injury.
- Inflammation.
- Wrong massage. Impact on pain points.
The cause of myalgia in the back area can also be the anatomical features of a person. These are flat feet, asymmetry of the pelvic bones, and a shortened leg.
Soreness in the collar area is caused by excessive strain, injury or disease:
- Osteochondrosis.
- Oncology.
- Infectious lesion.
Malaise that occurs after overexertion or unusual stress for a person lasts several days.
The muscles in the hands are susceptible to infection and inflammation.
Often the pain is concentrated in the upper extremities due to:
- Tendon sprain.
- Rheumatism.
Malaise spreading throughout the body indicates in most cases that a viral infection has entered the body. This condition is typical for influenza.
Weak trapezius muscles
In some cases, the cause of neck pain may be excessively weak (or stretched) trapezius muscles. Weak trapezius shifts the load directly from the muscles of the shoulders and upper back to the cervical spine. Let us recall that the correct technique for performing upper rows in a simulator (analogous to pull-ups) involves bringing together and lowering the shoulder blades at the lowest point of the trajectory.
To independently assess the condition of this muscle group, go to the mirror and assess the position of your collarbone:
- Position A - weak and stretched trapezius muscles
- Position B - the position of the shoulder blades is too low, the trapezius may be tightened
- Position C is the correct position. The upper and lower trapezius muscles are in balance, and the trapezius itself is slightly tense.
https://youtu.be/VEvdQnMnUbE
When you need to see a doctor urgently, which specialist will help?
Pain can be relieved by taking painkillers, folk remedies, and using massage. But there are certain moments when contacting a medical facility is mandatory. Ignoring the body's signals about pathologies can lead to severe irreversible consequences.
Alarming manifestations:
- Unbearable pain that occurs when receiving physical injury. A doctor's examination is required. Only he, through examinations, can accurately determine the nature of the damage and establish a course of treatment. It is possible to take a painkiller first.
- Advanced age. Failure to consult a doctor for muscle ailments or lack of treatment will create a risk for older citizens of developing a chronic form of the disease.
- Soreness lasting more than five days. It is necessary to exclude serious injuries and determine the cause of the pain.
- Inflammation. Myositis in its progressive form can lead to muscle atrophy.
Only a doctor can diagnose the cause of pain, identify concomitant diseases, and prescribe a course of treatment. To do this, he gets acquainted with the patient’s medical history, determines symptomatic manifestations, localization and intensity of pain, and the presence of changes in the skin. During the initial examination, he conducts tests to make a conclusion about neurological abnormalities.
In addition to the general examination, he prescribes special diagnostic methods:
- ultrasonography;
- radiography;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- CT.
If you suspect the presence of specific pathologies, you can make an appointment directly with a doctor specializing in this field. Myalgia is provoked by various diseases.
Doctors who diagnose and treat it include:
- Traumatologist - orthopedist. If myositis, osteoarthritis or osteoporosis is suspected.
- Traumatologist. After being injured.
- Surgeon. In case of complicated injury associated with a violation of the integrity of muscles, bones, tendons, and ligaments.
- Neurologist. For osteochondrosis, periodic convulsions.
- Rheumatologist. For gout, rheumatic polyarthralgia.
- Therapist. For secondary pain arising from an acute respiratory disease.
- Endocrinologist. For diabetes mellitus, the consequences of obesity.
- Infectious disease specialist. For meningitis, encephalitis, and other diseases associated with infection.
- Phlebologist. For varicose veins, thrombophlebitis.
- Angiologist. For atherosclerosis, Raynaud's syndrome.
- Gynecologist. For diseases of the reproductive system.
- Gastroenterologist. When symptoms of ulceration or failure of the normal functioning of the digestive system occur.
For advice, you can initially contact a therapist, who will identify health problems and refer you to a specialist.
Prolapse of internal organs: How to treat
The disease primarily affects narrow-shouldered and thin-boned asthenics with overly extensible connective tissue. Their insides can sink due to constant physical strain and chronic fatigue, when neuromuscular tone decreases. Prolapse of the stomach, kidneys, transverse colon, and pelvic organs is most often observed.
Depending on which organ is omitted, certain features of the clinical picture of the disease are revealed. But any form of prolapse is characterized by complaints of constipation, decreased appetite, decreased performance, and sleep disturbances.
The pain appears over time, gradually and intensifies towards the end of the working day, while at the same time it is weaker in a horizontal position. As muscle strength decreases, the ligamentous apparatus weakens, the balance created by the pressure of the internal organs on each other is disturbed, and the lower abdomen protrudes.
Abdominal adipose tissue plays a certain role in maintaining the normal position of organs. With significant weight loss, the layer of adipose tissue decreases and the entire burden of the internal organs falls on the muscles.
Intermittent aching and nagging pain in the abdomen may indicate prolapse of the stomach and intestines. Unpleasant sensations usually occur in an upright position and subside when you lie down.
When the kidneys prolapse, pain in the lumbar region bothers you.
If it is accompanied by a nagging pain in the lower abdomen and sacrum, episodes of urinary incontinence appear when coughing, sneezing, laughing, or physical exertion; prolapse of the uterus and vagina is possible, which sometimes ends with their loss.
IF THE OPERATION COULD NOT BE AVOIDED...
Today, the usual solution is surgery, however, as practice shows, there is a possibility of relapse, depending on many reasons, and it is impossible to take into account and prevent all factors.
If, unfortunately, you had to undergo surgery, then after some time it will still be necessary to perform exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, because the body is even more weakened by surgical intervention, which means it requires constant attention and systematic strengthening so that there is no need for repeated operations.
Don't rely on a bandage - it will only make the problem worse.
After a temporary improvement, which can last 1–2 years, the symptoms of the disease begin to bother you with triple strength: pain increases, constipation and nausea that cannot be treated appear.
General weakness, increased fatigue and irritability occur, and sleep is disturbed. It is already very difficult to help: the muscles, accustomed to inactivity under the bandage, have completely atrophied and are not able to provide the slightest support to the sagging organs.
Prolapse of internal organs is very often associated with problems of the spine - so first of all start with it. It is necessary to check the condition of the spine.
What should you do from gymnastics? Pump up the abdominal muscles, back muscles, oblique abdominal muscles, intercostal muscles.
The exercises for this are very different: twisting and bending back and forth from different positions and at different angles, the total number of movements performed per day should be about 1000.
SPECIAL EXERCISES WILL HELP
Countless people have successfully avoided pelvic organ prolapse surgery by undergoing several sessions of abdominal muscle therapy. In general, the task is to, against the background of general strengthening of the body and its psycho-emotional state, increase the tone of the muscles of the pelvic floor, abdominal wall, lumbar region, and improve the functional state of the digestive organs.
To strengthen the muscles of the pelvic floor, abdominals, lumbar region and diaphragm, increase the motor function of the gastrointestinal tract, tone the ligamentous apparatus of internal organs, and activate redox processes in the body, special exercises are performed.
- Lying on your back, on a couch with your head raised by 10-12 cm, perform static breathing exercises (diaphragmatic, full breathing). Perform the movements rhythmically, at an average pace, full amplitude, rhythmic breathing.
- Lying on your back, diaphragmatic breathing. Exercises for the lower extremities - free and with tension.
- Lying on your right side. Diaphragmatic breathing, limb movements. The same on the left side.
- Knee-wrist, knee-elbow position. Exercises for the muscles of the limbs and torso.
- Lying on your stomach. Exercises to strengthen the back muscles (movements of the lower limbs and lower torso).
- Lying on your back, diaphragmatic breathing. Exercises for all muscles of the lower extremities and torso (without increasing pressure in the upper third of the abdominal cavity, the transition from a supine position to a sitting position is excluded).
The duration of all exercises is 15 - 20 minutes. Exercises can be performed with each leg separately. The range of motion is full.
At the final stage, exercises are performed for small and medium-sized muscles of the limbs and breathing exercises.
Static (diaphragmatic, full) and dynamic breathing exercises involving arms and legs. Exercises for the muscles of the trunk and lower extremities with an emphasis on the muscles of the pelvic floor, abdominal wall, lower back, and diaphragm. Standing on the shoulders (“birch tree”). Exercises for the lower extremities. Sitting on a chair. Exercises for the muscles of the limbs and torso. When walking with arm movements, perform breathing exercises. The exercises should be simple; when performing them, the abdominal organs should shift towards the diaphragm - these are movements of the lower limbs and torso with lifting of its lower end.
Physical exercises must be performed on an inclined plane with the foot end raised by 10-12 cm, unless there are contraindications.
The first 6-8 weeks - lying on your back, on your side, on your stomach, standing on all fours.
Starting from the 6-8th week, after achieving a lasting positive result (improved subjective state, appetite, sleep, performance, normalization of stool), exercises are introduced into the complex to develop posture in the initial standing position, excluding bending the torso forward.
During the course of treatment, it is advisable to use no more than three individualized sets of exercises, changing them no earlier than after 1-2 months of training.
The duration of classes during the 1st week is 15-20 minutes once a day; 2-3 weeks - 20-30 minutes twice a day; for 4-8 weeks and beyond - 30-40 minutes twice a day.
When the position of the lowered organ approaches normal, classes are carried out once a day. I recommend lifting things from the floor after sitting down; When getting out of bed, you must first turn on your side, then simultaneously lower your legs and raise your torso. For one year, I do not recommend bending the body forward, jumping, skipping, or running. To activate the motor function of the gastrointestinal tract, massage of the lumbosacral region, colon massage, and self-massage of the abdomen are indicated.
A FEW MORE USEFUL EXERCISES:
- Sitting on the mat, keep your back straight, bend your arms at the elbows, as if running. In this case, you need to exhale and draw in your stomach and small pelvis (pelvic floor muscles). Exhale - “ha-a-a-a-a-a.” And, moving only with straight legs, begin to move on your buttocks. First forward, then back.
- The next exercise is related to anti-gravity action. Lie on your back, put your hands behind your head, bend your knees and rest your feet (legs slightly apart). On the count of “one,” lift your pelvis up, pull in your stomach “ha-a-a-a,” and touch your knees. So: inhale - spread your knees, exhale - bring your knees together. Perform such inhalation and exhalation at least three times. Now lower yourself to the starting position. Rest and repeat again.
- Another exercise taken from yoga. Imagine that you are standing (or sitting on a chair), leaning forward, resting your hands on your knees. Take a deep breath, then exhale with your head tilted, after exhaling, hold your breath. Try to make several breathing movements deeply, but without air, while holding your breath, while relaxing your abdominal muscles. There should be an active retraction of the abdominal organs into the chest, the stomach seems to stick to the spine. As the chest expands, negative pressure should pull the abdominal organs inward. During one breath-hold (after exhalation), you need to make several of these supposed breathing movements. Each time the abdominal organs will rise and fall (5 – 10 times). If something hurts you, do not do this exercise, wait until it goes away, you need to do it on an empty stomach, best in the morning on an empty stomach or 3-4 hours after eating. In total, such “retractions” need to be done 30-40 times over several breath holds, but reach this number gradually, waiting for all the pain in the stomach to go away.
WE TIGHTEN THE PELVIC ORGANS
When you pulled in your stomach, you probably noticed that your lower abdomen didn’t pull in and didn’t participate in the gymnastics. But it would be nice to get rid of ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids, endometriosis, prostatitis, prostate adenomas, prolapses and prolapses, incontinence, hemorrhoids and other problems.
A significant addition needs to be made to the previous exercise - pulling up the upper pelvic organs so that they fall into the zone of action of the negative pressure created by the chest. This is done with a strong contraction of the pelvic muscles. We repeat several times. From now on and forever we do both of these exercises together.
You can have a specific effect on the pelvic organs with the following exercise: inhale deeply with your head tilted forward, exhale and hold your breath, use your chest to pull in your stomach and leave it in that position, strongly contract and relax only the pelvic muscles several times, lifting and lowering the organs. Repeat a couple of times. It is important to monitor your breathing and your abdominal muscles. This helps restore and elevate the pelvic organs.
Special breathing exercises are useful. They should be performed before going to bed in a lying position. Take a deep breath and then exhale as much air as possible. Repeat one more time. This exercise “puts” the organs in place, and also strengthens the abdominal muscles and makes the waist slimmer. As a result, the use of such methods of traditional medicine allows you to normalize the balance of the muscular corset that holds the internal organ, and normalize the location of the organ, as well as straighten your posture, get rid of pelvic pain, excess weight, back pain, and feel healthier, stronger, and younger.
WHAT CAUSES GASTROPTOSIS
Now I will focus more specifically on the problems of prolapse of the stomach and intestines - gastroptosis. The main cause of acquired gastroptosis is a sharp weakening of the muscle tone of the abdominal wall. This can occur due to rapid weight loss, after removal of a large tumor or pumping of fluid from the abdominal cavity, and in women also after a long or rapid labor.
In addition, women are at risk of developing gastric prolapse when lifting heavy bags, and men are at risk of weightlifting and jumping from heights.
Lifting weights leads to stretching of the ligaments that fix the stomach and weakening the tone of the muscle wall of the stomach. As a result, the stomach moves below its normal position.
There are three degrees of gastroptosis: initial, moderate and severe - with a pronounced downward displacement of the stomach.
Changing the correct position of the stomach complicates its digestive function, impairs peristalsis and the movement of food into the intestines. At the same time, the condition of the valves that separate the stomach cavity from the esophagus and the duodenum is disrupted.
Due to incomplete closure of the valves, air enters the stomach through the esophagus, which causes belching, and bile is released from the duodenum. Bile causes heartburn, and also corrodes the gastric mucosa and causes the development of erosive gastritis and stomach ulcers.
A number of symptoms may indicate prolapse of the stomach:
Impaired gastric motility causes bloating and rumbling in the abdomen, leading to a feeling of fullness even when eating a small amount of food. Due to slow digestion of food, bad breath appears, stool disturbances occur - either prolonged constipation or loose stools in the form of diarrhea.
Gastroptosis can be accompanied by changes in appetite - an aversion to food appears or, conversely, a “ravenous appetite” develops against the background of weight loss and unhealthy thinness. Urination becomes more frequent.
When symptoms worsen, severe pain appears in the abdomen, and the temperature may rise. Sometimes gastroptosis occurs after severe weight loss, removal of large tumors in the abdominal cavity, or after childbirth, especially in women who have given birth many times.
Long-term protein starvation and vitamin deficiency can lead to prolapse of the stomach. Mild disease is usually asymptomatic.
But after eating, especially a large meal, there is a feeling of heaviness, bloating, and a feeling of fullness in the epigastric region. It's about fat.
The slag masses between the abdominal organs disappear very quickly, and as a result, prolapse of the stomach may actually appear.
During this period, you need to eat more salads from cucumbers, red cabbage, bananas, honey, blueberries, and cherries.
HOW TO RAISE YOUR STOMACH
I recommend starting treatment with exercises to elevate the stomach.
Classes are carried out while lying on a couch with legs raised. In this position, the stomach returns to its “rightful” place. Perform the exercises at a calm pace, without jerks or sudden movements.
Do not start therapeutic exercises: in the later stages and with some concomitant diseases, it is strictly contraindicated.
Starting position: lying on your back, arms along your body.
1. Raise your straight legs one at a time without holding your breath (4-5 times each).
2. Bend your knees. Raise your pelvis, resting on your feet, elbows, and the back of your head, forming a “half-bridge” (4-5 times).
3. Inhale, bend your knee and, as you exhale, pull your hands towards your stomach (4-5 times each).
4. As you inhale, raise both legs, and as you exhale, lower them (4-5 times).
5. Imitation of cycling (4-5 times).
6. Raise and lower your arms (6-8 times). Breathing is voluntary.
7. Inhale, as you exhale, turn your legs bent at the knees towards you and to the right, return to i. p. Then repeat the same thing, but with a turn to the left (4-5 times in each direction).
8. Inhale, and as you exhale, pull both legs toward your stomach with your hands (4-8 times).
Finish your sessions with a light self-massage of the abdomen. Do it while lying on your back, bending your knees, and moving your arms clockwise. After exercise, try to ensure that the abdominal organs are in a normal position for 15-20 minutes. To do this, simply lie on the couch with your legs elevated. The duration of training in the first three weeks is 10-15 minutes once a day, and later - 15 minutes 2-3 times a day.
WILL HELP THE INTESTINES... A BALL OF WOOL THREAD
More specifically about colonoprosis - prolapse of the large intestine. As a rule, other underlying organs are also involved in the pathological process when the stomach prolapses. A sinking stomach puts pressure on the small and large intestines. Patients with colon prolapse are bothered by pain in the lower abdomen, bloating, and prolonged persistent constipation.
To treat and restore the correct position of organs, in addition to herbal medicine, I recommend acupressure and acupuncture.
It is imperative to follow the diet. The food should be light, but satisfying; after each meal you need to lie down for a while.
Small meals are recommended – 5-6 times a day in small portions.
Physical activity should be limited during treatment.
When intestinal prolapse occurs, there is an old method: take a ball of woolen thread, 20 centimeters in diameter. Lie on your stomach, place a ball in the navel area and roll it under your weight around the navel for 5-10 minutes.
Gradually the intestines fall into place.
There is also a method of abdominal massage, when the internal organs are lifted with your hands and pulled out with large cans.
Another ancient method: you need to smear the stomach with vegetable oil, put 2 potatoes cut in half around the navel, and stick matches into them, 5-6 in each, and set fire to these matches. Next, take a liter jar with a wide neck and place it so that the matches are inside. The matches will burn out the oxygen and most of the belly will be pulled into the jar. You can move this jar clockwise; it moves easily through the oil. And thus, not only the stomach, intestines, but also the genitals come into place.
A FEW TIPS FOR PREVENTING PROPRESSION OF INTERNAL ORGANS:
- learn not to be nervous, learn to relax;
- lead a lifestyle taking into account your natural constitution;
- eat according to your natural constitution: either maintain the digestive “fire” of the stomach, or, conversely, pacify it;
- periodically eliminate stagnation of energy and blood in the body with the help of simple physical exercises, massage, acupuncture, cupping and other procedures, avoid lifting heavy objects.
Do not forget that if the internal organs are prolapsed, it is prohibited to carry heavy objects in your hands or backpacks, or to perform household and housework associated with great physical effort.
I also recommend to everyone the technique developed by Professor S.M. Bubnovsky.
To ensure that the impact was directed, he developed a system of special simulators that make it possible to create an “anti-gravity” mode, that is, allowing the patient to take the starting position in which the pelvis is above the level of the lumbar region.
These are the most common simulators. And the technique is unique, tested by me personally. At the first stage, it requires the mandatory assistance of an instructor; in the future, it is quite possible for a person to study independently.
Also remember that movement is life, you just need to learn how to use it correctly! published econet.ru
If you have any questions, ask them here
PS And remember, just by changing your consciousness, we are changing the world together! © econet
Did you like the article? Write your opinion in the comments. Subscribe to our FB:
source
Painkillers
Analgesics are designed to combat the painful condition.
The most common and frequently used of them:
- Metamizole. Preparations based on it: Analgin, Sulperin. Has anti-inflammatory, antipyretic effect. Relieves mild, mild discomfort. Available in different forms: tablets, suppositories, capsules, injection solutions. Valid for up to six hours. Contraindicated for use during pregnancy and lactation. Obstacles to choosing Metamizole include liver disease and individual intolerance to the components of the drug.
- Ketorolac. Derivative drugs: Ketanov, Ketolong, Ketalgin, Ketoprofen. A potent drug that has powerful analgesic properties and relieves fever. Produced in tablets and in the form of solutions for injection. Pain relief for up to eight hours. It has side effects that include migraines, nausea, increased blood pressure, swelling, and allergies. Not recommended for children, nursing and pregnant women. Not suitable for ulcer sufferers during exacerbation of the disease, or asthmatics.
- Dexalgin (Dexketoprofen). Relieves myalgia, prevents the progression of myositis, reduces high fever. Effective for eight hours. Available in tablets and injections. When side effects occur, it causes hypertension, allergies, heartburn, migraines, and loss of sleep. The list of contraindications for the use of the drug includes ulcers, bleeding, kidney, liver pathologies, pregnancy, breastfeeding, sensitivity to components.
- Aspirin (Acetylsalicylic acid). Eliminates fever, malaise, myositis. Available in plain and effervescent tablets, soluble in water. The therapeutic effect lasts three hours. Contraindications to taking the medicine include categories of people suffering from a lack of vitamin K in the body, changes in blood composition, and a tendency to bleed. For women carrying a child, the drug is dangerous.
- Lornoxicam. Preparations that contain it: Xefocam, Zornica. Treats rheumatism, inflammatory processes. Available in tablet form and powder for diluting a solution for injections. Effective for eight hours. Contraindicated for expectant and young nursing mothers. Not recommended for patients with pathologies of the heart, kidneys, liver, or ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Riabal. Available in the form of tablets, solution for injection, syrup. Contraindicated in glaucoma.
- No-shpa. Antispasmodic. Allowed for use even during pregnancy.
- Papaverine. Reduces tense smooth muscle tone. Has an antispasmodic effect.
NSAIDs are also used as painkillers. They not only have an analgesic effect, but also treat and eliminate the very cause of pain.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed for treatment in cases where discomfort is the result of inflammation in the body.
The main painkillers of this group:
- Paracetamol. Derivatives: Dolomin, Efferalgan, Panadol. Used for arthritis, neuralgia, migraine, myalgia.
- Indomethacin. Antirheumatic medicine. Eliminates swelling, heat, inflammation.
- Ibuprofen. Analogs: Nurofen, Ibufen. Effective in the initial stages of disease development.
- Nimesulide. Derivatives: Nimesil, Nise, Nimid. Fights inflammation, pain, protects cartilage tissue from destruction.
- Meloxicam. A powerful analgesic and anti-inflammatory agent. Analogues: Movalis, Revmaxikam.
Among the painkillers, ointments and gels are used to relieve pain symptoms:
- Diclofenac;
- Voltaren;
- Indomethacin;
- Ketoprofen;
- Bystrumgel;
- Ketonal gel;
- Fastumgel;
- Nise gel.
Gel-form preparations are easy to use and effective in treatment. They can be used independently, without a doctor's prescription.
Degrees of abdominal muscle stretch
Experts distinguish 3 degrees of abdominal wall muscle strain:
- Moderate, when mild pain subsides within a few days.
- Average degree. Symptoms go away within a couple of weeks. In this case, patients require qualified medical care. Recovery of such patients can be observed after 3-6 weeks.
- Abdominal muscle rupture. In this situation, the patient experiences excessive pain on the left or right side of the abdomen. In this case, the stretched muscle can no longer contract. This type of lesion occurs due to very strong pressure on the rectus abdominal wall muscles. Typically, the rupture occurs in the connecting bridge of the muscles that make up the wall of the abdominal cavity. In some circumstances, when there is a rupture of the abdominal wall with displacement of internal organs, urgent surgical intervention is required. Treatment of such patients can take an average of 3 months.
Prevention as an effective method to prevent pain
Basic preventive methods to prevent muscle abnormalities include:
- limiting heavy physical activity;
- maintaining emotional calm;
- maintaining an active lifestyle;
- timely treatment of diseases, including those of infectious origin.
Maintaining constant muscle tone will help prevent increased pain associated with sports activities during training. This requires regular exercises for different muscle groups and physical therapy exercises.
After suffering from infectious, rheumatoid, neurological pathologies, the prevention of their relapse is following the doctor’s recommendations and eating in accordance with the established diet.
In order to ease the stress on muscles during training, it is recommended to take a hot bath with sea salt. To achieve a similar effect, athletes use ointments specially created based on turpentine, apple cider vinegar or badger fat.
Honey compresses, which are applied to the disturbing area at night, wrapped in a blanket, also have a beneficial effect on muscle relaxation.
It is recommended to leave spasmed muscles alone for several days, protect them from possible stress, and allow them to relax.
Exercises to strengthen the trapezius
Below are four simple exercises to strengthen the trapezius and back of the neck muscles. Developing these muscles will allow you to perform pull-ups without pain. However, remember that when performing any trapezius exercises, the neck should always be in a neutral position - the gaze should be directed strictly in front of you, and not at the side of the mirror.
1. Reverse flyes on blocks while standing. Exercise for the middle part of the trapezius muscles. At the extreme point of the movement, the shoulder blades should be brought together (imagine as if you were holding a pencil between them). Using a moderate weight, perform 3-4 sets of 12-15 reps.
2. Shrugs with dumbbells. Exercise for the upper trapezius muscles. Stand up straight, take dumbbells in your hands, raise your shoulders as high as possible, then slowly lower them down. Do not make any additional rotational movements with your shoulders. Perform 3-4 sets of 12-15 repetitions.
3. Alternate raising of arms while lying on your stomach . An exercise to stretch the trapezius and lower back muscles. Lying on the floor with your stomach down, extend both arms forward, then lift your left arm and right leg. Hold for 15-20 seconds, then switch legs and arms. Perform alternately for 1-2 minutes.
4. Lying arm raises. An exercise to stretch the lower trapezius muscles and lower back muscles. Lying on the floor with your stomach down, spread your arms to the sides, lift your legs and head, then squeeze your shoulder blades together as much as possible. Hold for 15-20 seconds and lower yourself down. Perform for 1-2 minutes.
What does sudden pain mean?
Occurring suddenly, without any special external reasons, it may indicate the development of diseases:
- Myositis. The location of the lesion is the part of the limbs located below the knee. A dull, growing wave appears as a result of a complication that has arisen after suffering a viral infection or physical exercises that are unusual for the patient.
- Intervertebral hernia. The attack covers the lumbar area and spreads to the hips. The leg becomes completely or partially numb.
- Neuralgia. A shooting, pronounced wave. Localized in the thigh, the cause is pinched nerve endings. It subsides at rest, but intensifies with careless or sudden movement of the leg.
- Osteomyelitis. The pain is unbearable in its intensity. They occur after the formation of purulent foci against the background of bone tissue infection.
- Convulsive syndrome. It manifests itself as stiffness, an aching sensation that increases over time. Occurs due to dehydration, lack of calcium and magnesium in the body.
- Fibromyalgia. The lesion covers the calves. The wave is dull, wandering.
The main symptom of such diseases is myalgia. A specific deviation can be determined by additionally exhibiting other characteristics characteristic of it. Correct and timely diagnosis of the condition can only be carried out by a doctor.
Asymmetrical pain sensations
In some cases, neck pain occurs on only one side - left or right. Such sensations most often accompany myositis. If a person is blown on one side, that is where he experiences pain. Sometimes the pain syndrome on the left or right can be so intense that the patient turns his entire body in one direction. Such sensations can occur after an accident, blow, sprain, and can even be present behind the ear. In some cases, neck pain indicates poor circulation or heart pathologies. Thus, one of the manifestations of angina pectoris is chest discomfort, which is felt on the left and radiates to the arm and cervical spine. It may also be present behind the ear. Inflammatory processes and swelling provoke pinching of the vessels that are responsible for feeding the nervous system. Reduced blood supply leads to chronic inflammation. This is what provokes the increase in pain syndrome of asymmetric localization - on the left or on the right. The cause of this condition is often bursitis of the shoulder joint. When the joint capsules become inflamed, the pain is localized not only in the affected area, but also affects all tissues that are connected to this area. In this case, discomfort is felt not only in the neck, but also in the muscles, ligaments, tendons, and behind the ear. If the inflammation affects only one shoulder, then pain in the neck will be felt only on a certain side - left or right.
Why does your neck hurt and what to do?
Almost every person experiences neck pain at least once. This causes us a lot of inconvenience and restrictions, and there can be a lot of reasons for this. Here we have tried to highlight all the main causes, systematize the symptoms, thereby helping you understand the nature of possible pain in order to understand what measures to take.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia
Vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD) is a disturbance in the functioning of a person’s autonomic functions. The reason may be:
- hereditary factors;
- mental disorders;
- somatic disorders;
- damage to the nervous system.
Typically, VSD is directly related to diseases of the musculoskeletal system, therefore, with this diagnosis, one of the main symptoms is neck pain.
But the cause must be sought in another disease, often osteochondrosis or arthrosis. Elimination of the main cause of neck pain serves as a successful key to further treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes
A lymph node is an organ of the human lymphatic system that acts as a filter in the body. There are several groups of lymph nodes in the body that perform various protective functions.
One of these groups is the cervical lymph nodes, which protect the body from infections and tumors. Due to any infection, inflammation of the lymph nodes (lymphadenitis) occurs. When the cervical lymph nodes are affected, a person feels pain in this area. As a rule, inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes occurs due to infections of the ENT organs.
In addition to neck pain, symptoms of this disease are:
- heat;
- general weakness;
- headache.
The lymph nodes in the neck cannot become inflamed and hurt on their own, so if a person complains of similar symptoms, you need to look for the source of inflammation that caused the damage to the lymph nodes.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes can be divided into 3 types:
- The lymph node is clearly not enlarged, and pain in the neck is felt only when palpated with fingers.
- Pain in the neck is felt in a calm state, and an enlarged lymph node is visually detected.
- With purulent inflammation, in addition to pain in the neck, redness of the skin in the area of the lymph node is observed.
Treatment of lymph nodes is carried out on an outpatient basis, after examination by a doctor. Self-medication in this case is very dangerous. Antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are usually prescribed, and it is also recommended to avoid physical activity during treatment.
Intervertebral hernia
Intervertebral hernia occurs due to displacement of the intervertebral discs and their protrusion into the spinal canal. When a hernia occurs in the cervical spine, a person feels a shooting pain in the neck, radiating to the shoulder joints. Dizziness and high blood pressure may also bother you.
The human spine consists of 24 vertebrae, which are connected by intervertebral discs, and includes 5 parts: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal.
Cervical hernia is difficult to diagnose because this area of the spine is quite small. However, if you experience the symptoms described, it is necessary to get tested before undergoing treatment. After all, for example, heating a hernia is strictly prohibited.
If a herniated disc is not treated, it can lead to serious complications:
- chronic bronchitis;
- radiculitis;
- gastritis.
In a mild form, a cervical hernia is treated with massages and physiotherapeutic procedures. The operation is shown in a more advanced form.
Myalgia
Myalgia is muscle pain due to hypertonicity of muscle cells. Almost every person encounters this phenomenon in everyday life. Usually myalgia appears as a result of excessive physical exertion, injury, hypothermia, and stress. The pain is aching and pressing in nature and increases with palpation.
Neck myalgia is the most common variant of this disease. Neck pain can be acute or chronic. Treatment of myalgia is complex and is aimed, first of all, at identifying and eliminating the underlying disease.
Maintenance therapy is the relief of pain and inflammation: mainly, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of ointments, gels, and tablets. In especially severe cases, intramuscular administration of drugs is required. Physiotherapeutic procedures also alleviate the condition.
Myositis
Myositis is inflammation of the muscles, leading to the formation of nodules in the muscle fibers. The reason for this phenomenon may be:
- infections;
- convulsions;
- hypothermia;
- injuries;
- permanent tension of one muscle group.
Myositis of the cervical area is manifested by severe pain, aggravated by palpation. Sometimes there is redness of the skin in the area of inflammation, swelling and hardening of muscle tissue, and general muscle weakness. In particularly severe and advanced cases, muscle atrophy may develop as a result of myositis. Neck myositis is also dangerous because it affects the muscles of the esophagus and larynx.
Myositis can easily be confused with other diseases, so for an accurate diagnosis you need to see a doctor. During treatment, it is first necessary to limit physical activity. Also used for myositis:
- warming ointments;
- massages;
- anti-inflammatory drugs.
If the cause is determined to be a bacterial infection, the use of antibiotics is necessary.
Occipital neuralgia
With neuralgia, irritation or compression of the occipital nerve occurs - this is the reason why the neck hurts in the back, in the back of the head, and severe headaches appear, radiating behind the ears and in the eye area. This phenomenon can easily be confused with migraine.
Mostly one-sided pain occurs, since the occipital nerves are located on the right and left sides, in pairs (there are 4 in total). Bilateral occipital nerve involvement is uncommon.
Neuralgia occurs as a result of such diseases:
- hypothermia of the head;
- tumor process of the occipital region;
- prolonged overload of the neck muscles;
- injuries of the cervical spine;
- infectious diseases;
- diabetes;
- osteochondrosis.
Diagnosing neuralgia is quite difficult, since there can be many causes of headache and neck pain. Magnetic resonance and computed tomography, as well as radiography, are used for diagnosis.
There are two options for treating this disease:
- drug treatment;
- surgical intervention.
With conservative (medicinal) treatment, pain relief is expected; it involves massage, thermal procedures, and anticonvulsants. A successful method of eliminating occipital neuralgia is considered to be a blockade using steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Tumors in the cervical spine
A tumor in the cervical spine occurs due to the growth of malignant cells; in addition to bone tissue, the bone marrow is affected. The complexity of the disease is that the disease is deadly, but it is difficult to diagnose in the early stages due to mild symptoms.
Patients may attribute pain that occurs in the neck to hernias or osteochondrosis. With tumor formations, neck pain can radiate to the thoracic region and upper extremities, and over time it can manifest itself throughout the spine. In general, with cancerous tumors there is a rapid deterioration in the general condition.
With this diagnosis, any delay is fraught with dangerous consequences, so if you have the slightest suspicion and discover similar symptoms, consult a doctor immediately!
During diagnosis, in addition to tomographic studies, spinal cord puncture is performed. Treatment includes radiation and chemotherapy, as well as surgical removal of tumors.
Spondylosis
Spondylosis is a chronic disease of the spine, which is accompanied by deformation of the vertebrae due to the proliferation of bone tissue and the formation of spines and protrusions. It can occur in up to 80% of people with age due to the natural wear and tear of the vertebrae. Also, the causes of spondylosis can be static overloads and injuries of the spine, metabolic disorders.
Cervical spondylosis is the most common form of this disease. Symptoms include pain in the neck, back of the head and decreased mobility of the vertebrae.
Spondylosis can be detected using radiography. The earlier the presence of the disease is detected, the more effective conservative treatment will be, because it only stops the process of further growth of bone formations. Anti-inflammatory and painkillers are prescribed to relieve pain. Manual therapy, massages, physical therapy, and acupuncture are also effective.
Displacement of the vertebrae in the cervical spine
Vertebral displacement is a pathological condition in which there is a shift and rotation of the vertebrae.
The cervical vertebrae are most susceptible to this phenomenon, the reasons may be:
- spinal injuries;
- sudden changes in temperature;
- long stay in an unnatural position;
- age-related changes in the spine;
- congenital pathologies;
- in newborns - birth trauma.
When the vertebrae in the cervical spine are displaced, neck pain, headache, sleep disturbance, and chronic fatigue are observed. Diagnosis is carried out using radiography, magnetic resonance and computed tomography. During treatment, the first step is to limit head movement using a neck brace. Patients are also prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs, reflexology, therapeutic exercises and manual therapy.
Uncovertebral arthrosis
Uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical region is a chronic degenerative-dystrophic disease, which is manifested by the destruction of the layers of cartilage tissue between the vertebrae. Because of this, pain appears in the neck, which is usually localized around the problem vertebra, and a crunch in the neck may also appear. In the early stages, neck pain occurs when turning the head or lifting heavy objects.
If you immediately consult a doctor after detecting these symptoms, you can eliminate all problems within a couple of weeks. And if you neglect treatment, the disease will only progress.
The causes of uncovertebral arthrosis are:
- cervical injuries;
- hip dislocations;
- flat feet;
- physical inactivity;
- excess weight;
- consequences of polio.
Diagnostics familiar to diseases of the spine are used: computer and magnetic resonance imaging, radiography. Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis and is aimed mainly at relieving pain syndromes and providing rest to the cervical spine (fixed with a bandage). Painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and medications to improve blood flow are prescribed.
Important in treatment are drugs that accelerate the restoration of cartilage tissue, the so-called chondroprotectors. In addition, physical therapy is indicated.