The importance of vitamin B1 for people is undeniable. Doctors say that situations are increasingly encountered when there is an urgent need for the administration of this substance. With thiamine deficiency, the risk of developing serious pathologies of the endocrine, nervous or brain systems increases, which include thyrotoxicosis, pancreatitis, Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome or brain damage. In such cases, the drug Thiamine hydrochloride is used.
This is a synthetic analogue belonging to water-soluble vitamins. When prescribed, patients have many questions regarding Thiamine hydrochloride - what kind of vitamin it is, are there any side effects when using it, are there any contraindications, etc. The medication is used for medical reasons to compensate for B1 deficiency. As with any other medications, when using the drug, you should strictly follow the instructions for use. We will now tell you in detail about the features of using the medication.
General information
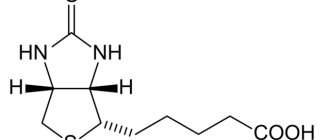
Thiamine hydrochloride is a synthetic form of vitamin B1, disulfide, and belongs to the category of drugs. The foreign name for the substance is Thiamine hydrochloride.
Chemical formula – C12H18Cl2N4OS.
It is a crystalline powder, colorless or white, with a faint odor. It is soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol and insoluble in ethers.
International name: Thiamine. Thiamine chloride, as well as similar preparations with the prefix “VIAL” or “Bromide” are all analogues of natural vitamin B1, which are trade names for the same substance and are obtained in the process of chemical synthesis of thiamine. Medicines have various dosage forms, are unstable to alkaline and neutral environments, but are not destroyed when exposed to an acidic environment.
History of the discovery of vitamin B1
Vitamin B1 in tablets and ampoules was already obtained in modern laboratories, and the first mention of this asset was associated with the search for a cure for a disease called beriberi, which often affected residents of Eastern countries. Its manifestations included mental disorders, muscle atrophy and the development of heart failure.
At the beginning of the 20th century, the Dutch pathologist Christian Eijkman suggested that rice bran contains a number of useful substances that cure Beriberi disease. This research led to the discovery of vitamins. And in 1911, Casimir Funk isolated a biological active from the components of rice bran - the substance helped overcome the symptoms of beriberi due to the nitrogen content in the molecules. More than 20 years later, Dr. Williams deduced the chemical formula of modern vitamin B1 in tablets, the name of which was given “thiamine,” which marked the beginning of the production and appearance of vitamin B1 in pharmacies .
There are other names for vitamin B1, including aneurin, thiovitamin, thiamine pyrophosphate.
Composition, in what forms it is produced
Thiamine comes in various forms, such as powder or ampoule liquid for parenteral administration, as well as tablets. The medicine has several manufacturers:
- Dalkhimpharm (RF);
- JSC BZMP, Borisov Medicinal Products Plant (Belarus);
- JSC Khimpharm, Yerevan chemical and pharmaceutical company BIOTEK (Armenia);
- Moskhimfarmpreparaty im. Semash N. A. (RF);
- Thiamine-VIAL, Shandong Shenglu Pharmaceutical (China).
The powder or solution for injection contains 50 mg of thiamine, which is the active ingredient. The auxiliary components are water for injection, unithiol. The ampoule contains 1 ml of the drug - this is a standard single dose, and the package contains 10 ampoules. In pharmacology, there is also a complex drug - Neurogamma, which, in addition to thiamine, contains pyridoxine.
Preparations containing thiamine
As mentioned above, preparations with vitamin B1 are available in ampoules and tablets. Thiamine hydrochloride solution or powder is sold in glass containers, from which an essence in the form of cocarboxylase is prepared. There are drugs made in the form of suppositories, for example, Korilip and Korilip-Neo. Vitamin B1 for oral administration is produced in the form of tablets, capsules or dragees. They contain thiamine hydrochloride, phosphothiamine or benfotiamine. There are a large number of dietary supplements with high thiamine content on the market. The most famous among them is brewer's yeast.
Mechanism of action
The pharmacological action of the drug is aimed at replenishing the deficiency of vitamin B1. Pharmacodynamics is the regulation of metabolic carbohydrate, lipid or protein processes. Thiamine after intramuscular administration under the influence of metabolic processes is converted into cocarboxylase, a coenzyme of many enzymatic reactions. After only a quarter of an hour, the drug is detected in the blood, and after half an hour - in nerve tissues, heart muscle and liver.
As a result of treatment, a complex effect is ensured, since Thiamine has a versatile effect.
- Has an immunomodulatory effect.
- Has N-anticholinergic properties.
- Normalizes metabolic rate.
- Stimulates nerve impulse transmission, increasing its speed.
- Neutralizes products of cross-lipid oxidation.
The drug is metabolized in the liver tissues and excreted through the intestines and kidneys. The drug has a tendency to accumulate in organs with a parenchymal structure, is contained in low concentrations in plasma, is completely absorbed, and is unstable to heat.
The doctor talks about all the beneficial properties of thiamine in simple language in this video:
Vitamin B1 in foods
In view of the benefits of vitamin B1, knowledge of the list of products that contain the active will allow you to create a balanced diet to obtain the maximum amount of useful substances through food.
The leaders in the list of dietary components, which foods contain vitamin B1, include:
- pine nut kernels;
- Brown rice;
- sunflower seeds;
- pork;
- pistachios;
- green peas;
- peanut;
- lentils;
- oat groats;
- buckwheat;
- millet;
- offal;
- wholemeal flour;
- eggs;
- asparagus;
- potato;
- cauliflower;
- oranges;
- legumes;
- pumpkin;
- broccoli;
- spinach;
- seaweed.
The daily intake of vitamin B1 differs depending on age, gender and physiological state:
- adults – up to 2.1 milligrams;
- elderly people – up to 1.4 milligrams;
- for women - up to 1.5 milligrams; in case of pregnancy and lactation, the dosage increases by 0.4 and 0.6 milligrams, respectively;
- children - from 0.3 to 1.0 milligrams, taking into account age.
Indications for use
Thiamine has a wide range of uses, but is especially recommended for children and is indicated for adults for conditions such as:
- vitamin deficiency or hypovitaminosis B1, including in patients who are on hemodialysis, tube feeding, or have malabsorption syndrome;
- increased need for vitamins, which is especially important during pregnancy or while breastfeeding a child;
- neuralgia – for various neuritis and radiculitis, for the treatment of complete/incomplete paralysis, hemorrhagic polioencephalitis, etc.;
- gastroenterological disorders - decreased intestinal motility or mucous gastric defects;
- excessive hormonal activity of the thyroid gland;
- IHD or metabolic myocardial damage;
- stay on chronic hemodialysis or long-term parenteral nutrition;
- severe liver function disorders;
- chronic alcohol dependence;
- various dermatoses in combination with neurotrophic changes - atopic dermatitis or eczema, psoriasis and lichen planus, herpetic infection;
- metabolic failures - with impaired lipid, protein or carbohydrate metabolism:
- tachycardia or neuroses of the cardiovascular system, abnormalities in the coronary circulation.
The drug is often used in toxicology and otolaryngology, narcology and other medical fields. In complex treatment, it is effective for nervous system hyperexcitability, intestinal atony, amnestic syndrome, memory impairment or psychological disorders. Thiamine is usually not used in monotherapy; it is often prescribed in combination with other medications.
The drug is not contraindicated for renal or hepatic disorders, but the dosage must be adjusted by a doctor.
- Pregnant patients, as well as women breastfeeding, can take Thiamine only as prescribed by a doctor in recommended dosages.
- For elderly people with impaired absorption of the gastrointestinal tract, the vitamin is recommended to be administered only parenterally.
- For children, the drug is prescribed in courses with Thiamine bromide, since in this form of the drug there is less activity of the active ingredient.
- If renal function is impaired, vitamin B1 therapy stops pathological processes in this organ in people suffering from diabetes. In diabetics, the renal vessels are often affected, which provokes the development of organ failure and loss of proteins by the body, and Thiamine therapy prevents proteinuria.
- Liver disorders often develop against the background of prolonged alcohol abuse, as a result of which the full absorption of vitamin substances is impaired, and with thiamine deficiency, the liver system neutralizes toxic substances more slowly, they accumulate in the body and poison it. Therefore, additional parenteral administration of B1 is especially necessary here.
When prescribing thiamine therapy, it is necessary to take into account the peculiarities of this vitamin associated with its destruction at high temperatures, frequent allergic reactions when administered by injection, and the combination of Thiamine with glucose when prescribed for hemorrhagic polioencephalitis.
Why take vitamin B1?
The large number of beneficial properties of vitamin B1 allows the drug to be used as a primary or additional means to combat the following pathologies and conditions:
- disorders of the cardiovascular and nervous systems;
- when prescribing a course of diuretic medications to combat heart failure and hypertension;
- normalization of the central nervous system, combating neurological disorders;
- treatment of dermatitis, including psoriasis;
- combating depression;
- prevention of the development of Alzheimer's disease;
- normalization of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and the fight against ulcers, pancreatitis, enteritis;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- prevention of exposure to chemical reagents on the body during specific work.
Contraindications and precautions
Thiamine medications have a number of restrictions on their use. Contraindications:
- with increased hypersensitivity to the components of the drug or intolerance to it;
- hypertension;
- hyperacidity of the stomach or duodenum;
- ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract.
Thiamine injections are prescribed to patients only if the small intestinal absorption of vitamin components is impaired, as well as if there is insufficient or absent effectiveness of taking tablet forms of the drug. Injection therapy is also justified when an urgent, immediate effect is needed. Begin by administering low doses, gradually increasing them under medical supervision.
Intramuscular, intravenous, and subcutaneous administration are allowed, but injections into the subcutaneous tissue are extremely painful, which is associated with the low pH of the injected solution. When prescribing thiamine injections to menopausal women, it is important to take into account the increased likelihood of side effects. Also, such vitamin therapy is prescribed with caution to allergy sufferers; a sensitivity test is required.
The combination of thiamine therapy with alcohol consumption is strictly unacceptable. The reasons for the ban are related to the weakening of the therapeutic effect of Thiamine and the acceleration of its elimination and destruction under the influence of alcohol.
Beneficial properties of thiamine
Just like any other vitamin, thiamine can have a positive effect on the human body. Some of them include:
- Improving immune functions.
- Accelerating growth in young children.
- Maintaining normal gastrointestinal muscles.
- Improvement of mental and physical activity.
- Slowing down the aging of both tissues and skin.
- Protection from the harmful effects of nature.
- Participation in the creation of blood cells.
If you take into account all the listed properties, you can immediately understand how important thiamine really is in the human body. Some call this substance the “vitamin.”
How to take, dosage
When prescribing Thiamine, you should strictly follow the instructions for use. Dosages are individually selected by the doctor, although there are average values. Tablet forms are taken according to the following scheme:
- for adults – 10 mg up to 5 times a day;
- children under 3 years of age - 5 mg 1 time per day;
- 3-8 year old patients – 5 mg 3 times a day;
- after 8 years – 10 mg up to 3 times a day.
The instructions for use of Thiamine hydrochloride specify that injections are administered deep into muscle tissue:
- adults and children from 7 years of age, 1 ml;
- children 1-7 years old – 0.5 ml;
- up to a year, the dosage of injections is 0.25 ml of thiamine.
The duration of thiamine therapy is determined by the indications for which it is prescribed, but usually treatment lasts about 10-30 days. The daily dose for parenteral administration is 1 ml, and for oral administration – 50 mg. The diluted dose should be used immediately after preparing the injection solution.
Features of suction and output
After consuming vitamin-rich foods, thiamine is absorbed into the bloodstream through the walls of the gastrointestinal tract. At the same time, the volume of thiamine that penetrates into the blood through the intestines in a certain time period is limited. Scientists have proven that the element is capable of penetrating in a dosage of 9-10 mg . This volume is called the maximum daily norm. The remaining part is passed out along with the “stool” and urine.
If there are problems with the gastrointestinal tract (colitis, duodenal diseases, ulcers), thiamine penetrates into the blood more slowly, and the body receives a reduced portion of the beneficial element.
As soon as the vitamin enters the blood, it spreads throughout the body, reaching tissues and organs, and then to brain cells. After it reaches its destination, thiamine performs its assigned functions (mentioned above). Next, the process of phosphorylation occurs, and the element itself is destroyed in the main filter of the human body - the liver. Metabolites (substances that are produced during the reaction) are processed by the kidneys and excreted.
Adverse and allergic reactions
Sometimes symptoms develop during thiamine therapy:
- allergic reactions such as itching and hives;
- in severe cases with thiamine intolerance, the development of Quincke's edema or anaphylactic shock is likely;
- hypersweating;
- tachycardia;
- excessive pain at the injection site.
If the dosages are followed according to the instructions and medical prescriptions, then the likelihood of developing side effects is negligible.
Role in the body
Thanks to thiamine, oxidation of carbohydrates occurs, or more precisely, their breakdown products. It also participates in the formation of fatty (polyunsaturated) acids.
Aneurin is one of the most important elements in the human body. Many believe that it is very important for nerve cells. This component promotes optimal functioning of the brain, endocrine and cardiovascular systems. In addition, it is used by the body to synthesize the substance acetylchone. It characterizes itself as a transmitter of nervous excitation.
Thiamine helps optimize the acidity of gastric juice. It is also necessary for the normal functioning of the entire intestines and stomach.
In addition, aneurin helps to increase the body's resistance to various infectious agents. Thanks to thiamine, not only digestion improves, but also heart and muscle function. Thiamine plays an important role in growth processes.
Thiamine takes an active part in hematopoiesis and its processes.
Thanks to it, blood circulation improves. The important role of aneurin also includes its property as a strong antioxidant, which helps strengthen the body’s defense against rapid aging processes and against various harmful and toxic substances. These include drinking alcohol and smoking.
If there is a deficiency of the element in the human body, serious problems with vital processes may begin. A lack of thiamine is reflected by its characteristic symptoms, namely: when the level of aneurin in the blood decreases, memory problems, frequent fatigue and depression (in an advanced state) occur.
Forgetfulness is very common, in some cases trembling in the hands and sometimes in other parts of the body. In addition, thiamine deficiency can cause a person to become more closed and unsure of himself, too restless and irritable.
The consequences of a lack of vitamin B1 also include insomnia and deterioration in sleep quality, frequent headaches, and increased fatigue. Many people who have low levels of aneurin in the blood report that they constantly lack appetite and experience muscle pain.
Among other things, deficiency is manifested by a burning sensation and soreness of the calf muscles.
Drug interactions
To exclude the development of side effects, it is necessary to take into account the peculiarities of the interaction of Thiamine with other medications.
- Simultaneous injection use with cyanocobalamin or pyridoxine (B12 and B6, respectively) is contraindicated. It’s just that the former increases the risk of allergic reactions, and B6 makes it difficult to convert thiamine into a bioactive form.
- Thiamine should not be mixed with streptomycin or penicillin, since these antibiotics are destroyed by the vitamin.
- It is forbidden to mix nicotinic acid with Thiamine, otherwise B1 will be destroyed.
- The vitamin reduces the effect of anaprilin and sleeping pills, phentolamine and sympatholytics, redergam and suxamethonium iodide.
Daily norm
An adult in good health should receive about three grams of the substance every day, otherwise, with a deficiency, various problems will begin to arise in the body. But there is a certain group of people in the world who need to consume it much more. This includes:
- Childhood.
- Hyperfunction of the thyroid gland.
- Period during pregnancy.
- Great mental and physical stress.
- Elderly people.
There is no need to worry that an overdose can lead to bad consequences. Vitamin B1 is quickly eliminated by the body.
Some negative effects can only occur if a person is given injections with a high content of thiamine. Symptoms include elevated body temperature, an allergic reaction (rash, etc.), muscle spasms.
In this case, it is recommended to temporarily stop using injections and consult a specialist.
Thiamine content in products, mg per hundred grams:
| Soybean meal | 2,20 |
| Potato | 0,11 |
| Kidneys, liver | 0,35 |
| Yeast | 1 |
| Fish | 0,11 |
| Oatmeal, buckwheat, millet cereals | 0,45 |
| Green peas | 0,35 |
| Dairy | 0,04 |
Cases of overdose
If you exceed the dosage recommended by the doctor and the instructions, then patients develop overdose symptoms, which manifest themselves:
- excessive sweating;
- shortness of breath;
- sudden jumps in blood pressure;
- nausea and vomiting reactions;
- stool disorders;
- nervous system hyperexcitability;
- extremely rarely - confusion or attacks of convulsive muscle contractions.
Treatment of overdose involves a symptomatic approach and is carried out in a hospital setting.
Deficiency Symptoms
A person should urgently consult a doctor if he discovers the following symptoms of thiamine deficiency:
- heart pain;
- deterioration of concentration and memory;
- the occurrence of depression;
- decreased immune function;
- insomnia;
- headache;
- reduced mental abilities;
- dyspnea;
- increased nervousness or irritability;
- frequent self-doubt;
- poor appetite.
If a person experiences at least two of the above symptoms, then it is recommended to consult a doctor who will prescribe a comprehensive examination, as a result of which it will be possible to identify the presence of any problems and try to eliminate them. In a neglected state, it is better not to self-medicate.
Benefits of Vitamin B1
The benefit of vitamin B1 is that it is a substance of vitality and energy. It is impossible to imagine a healthy person without it. Thiamine promotes proper growth and development of people of any age. The substance is an indispensable component of therapy during depression and stress. Used to prevent urolithiasis. Affects the proper functioning of the heart and stomach. The chemical compound has a great effect on memory and increases attention. Helps with the assimilation of new material. B1 is also indispensable for women's health. It regulates hormonal levels during surges and strengthens the nervous system. Thiamine has a good effect on appetite, increasing desire. Thiamine is especially useful for athletes. Has a beneficial effect on active mobility of the limbs.
Vitamin B1 has a beneficial effect on external manifestations. The processes of premature aging slow down and complexion improves. It’s not for nothing that thiamine is used in cosmetology to combat the first signs of aging. Reduces the likelihood of dermatological diseases such as inflammation, acne, psoriasis, dermatitis, etc. It has a beneficial effect on the condition of the hair, making it smooth and shiny, strengthening the roots. The vitamin blocks the negative effects of alcohol and smoking. The compound has a good effect on the digestive system and relieves toothache.
Pros:
- strengthens the nervous and cardiovascular system;
- helps produce gastric juice;
- promotes carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
Thiamine promotes protein glycation. This process makes the skin loose, which accelerates the aging process, leading to wrinkles. Vitamin B1 fights diseases such as Alzheimer's disease. Prevents distraction and forgetfulness.
Since the chemical compound is water-soluble, it is not able to accumulate in the body, causing poisoning in excess. Up to 30 mg of vitamin can be retained in tissues.
A significant advantage of thiamine is its availability. Vitamin B1 can be bought at any pharmacy, and the cost will be a pittance. With proper use of the vitamin, you can prevent many health problems and get rid of existing ailments.