Properties and benefits
Nicotinic acid primarily acts as a preventive substance that helps fight the possible risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. With its help, cholesterol levels in the blood and tissues are regulated. At the same time, malignant cholesterol is initially destroyed. It can clog blood vessels, making them obstructed. This is very dangerous for the athlete’s health, since during intense training the heart may not be able to withstand the load.
After destroying “bad” cholesterol, nicotinic acid begins to regulate regular cholesterol. It should always be present in the body at a certain concentration, but if it increases, a person may suffer from obesity.
Nicotinic acid helps break down harmful lipoproteins . In many athletes, blood pressure rises precisely because of the high content of lipoproteins in the blood. These substances can also cause blood thrombosis.
General characteristics in the video:
Vitamins in bodybuilding
Today I want to talk about vitamins.
It just so happens that this topic is avoided not only by novice athletes, but, often, by professional coaches as well. But it is vitamins that help improve the quality of your workouts, physical and emotional activity. In this article I will try to tell you as clearly as possible about vitamins, what they are and what functions they perform, what you need to include in your diet, and how to increase their level in the body.
Vitamins. What are they and why are they given little time?
You all know very well about such nutrients as proteins, fats and carbohydrates. But not everyone knows that the digestibility of these elements and their effectiveness directly depend on vitamins and minerals. The consequence of such ignorance is often a lack of microelements and inhibition of recovery in your muscles.
We will now try to figure out why vitamins play one of the most important roles.
| Wikipedia: |
| Vitamins (from the Latin vita - “life” and amine) are a group of low-molecular organic compounds of relatively simple structure and diverse chemical nature. This is a group of organic substances combined by chemical nature, united on the basis of their absolute necessity for a heterotrophic organism as an integral part of food. Autotrophic organisms also need vitamins, obtaining them either through synthesis or from the environment. Thus, vitamins are part of the nutrient media for growing phytoplankton organisms. Most vitamins are coenzymes or their precursors. |
The main functions of vitamins are:
- the launch of biochemical reactions on which the growth and preservation of muscles depends - i.e. these are catalysts for hypertrophy processes;
- regulation of metabolic processes;
- assistance in energy synthesis;
- regulation of neuromuscular activity
- protecting cells from destruction.
- strengthening the bone frame.
As already mentioned, novice athletes greatly underestimate the role of vitamins, although they greatly increase the activity of enzymes that are involved in the process of protein synthesis. In other words, if you lack vitamins, you simply will not be able to build yourself a beautiful, sculpted body, because all the elements supplied with food, such as proteins, fats and carbohydrates, will lie as dead weight in the body and no “transformations” will occur with them.
It doesn’t matter whether you want to gain weight or lose weight, you still need to build muscle to build a beautiful and sculpted body. And here you should remember that any process of hypertrophy is accompanied by the release of energy, and it directly depends on vitamins.
There are 13 vitamins in total and they are classified according to the nature of absorption into:
- fat-soluble (A, D, E, K);
- water-soluble (B and C);
Fat-soluble vitamins can be stored in the body and do not require daily intake if the body stores them in sufficient quantities. Such vitamins can accumulate in the body, especially in the liver, to toxic levels.
Water-soluble vitamins include vitamin B complex (B1, B2, B3, etc.), as well as folic/pantothenic acid and biotin. They, with the exception of vitamin B12, do not accumulate in the body and are practically not soluble in fats, and excesses are excreted in the urine.
Since muscle cells are mainly composed of water, the greater the athlete's mass, the more vitamins can be dissolved in his muscles. This is why athletes have a higher need for water-soluble vitamins than ordinary people.
The table below presents each specific type, its functions and in which products it is contained.
Water-soluble vitamins:
Fat-soluble vitamins:
Considering that our body is not able to synthesize the necessary vitamins on its own, but can only get them from food, this table will help you find out which vitamins you are missing and correctly calculate the required dosage
After analyzing the table, you will conclude that your diet must include:
- milk, cottage cheese, sour cream, eggs;
- grain bread, bran, cereal porridge;
- liver, sea fish, seafood, lean poultry meat;
- legumes, seeds, nuts, oils (fish oil, flaxseed, mustard);
- citrus fruits, berries, herbs.
By including or increasing the dosage of the above products, you will feel a powerful surge of strength, and working weights and heavy workouts will be much easier.
Now let's talk about the practical side of using vitamins, namely...
It is necessary to constantly adjust the percentage of vitamins you consume, for example, if carbohydrates predominate in the diet, then increased consumption of vitamin B1 is required, but if the main components are proteins of plant origin, then attention should be paid to vitamin PP (B3).
The most effective method of consuming vitamins in bodybuilding is considered to be combined, i.e. when a combination occurs, the interaction of individual vitamins occurs, and the phenomenon of synergy occurs (increased positive effect). For example, the following combination of vitamins allows you to achieve synergy:
- B1, B2 and PP;
- B12, B6 and C;
- B1, B2, B6 and C;
- S and R.
In general, it is generally accepted that fruits contain more vitamins than animal products, but this is not the case, and to confirm this, I suggest you read the following table.
Values close to the norm for an athlete training with weights are highlighted in blue.
Analyzing this table, we can conclude that beef/pork liver, and not fruit, has the richest content of vitamins. They are only ahead of animal products in terms of vitamin C content.
Based on this, you should not assume that fruits are the most promising and balanced source of vitamins; this is far from the case.
When people talk about vitamins in bodybuilding, they most often mean special vitamin-mineral complexes or pharmaceutical preparations in their pure form.
Below we will list 10 pharmacy vitamins and complexes that are necessary for muscle growth.
- Cobalamin (vitamin B12)
Provides carbohydrate metabolism and maintenance of nervous system tissue (spinal cord and nerves that transmit signals from the brain to muscle tissue).
Stimulation of muscles by nerve cells is an important step in muscle contraction, coordination and growth.
B12 is only available in animal products such as beef, chicken, fish, pork, etc.
- Biotin
Plays a critical role in amino acid metabolism and energy production from a variety of sources.
Bodybuilders who eat raw egg whites get a substance called Advin. This substance blocks the absorption of biotin.
Sources of biotin include: egg yolk, liver, kidney, pancreas, milk, soy and barley.
- Riboflavin (vitamin B2)
Actively participates in three main processes:
1) glucose metabolism, 2) fatty acid oxidation 3) hydrogen shuttling, through the Krebs cycle (known as the citric acid cycle, where certain molecules are broken down into energy in the form of ATP).
For bodybuilding, riboflavin is associated with protein metabolism. There is a strong relationship between lean body mass and a riboflavin diet.
Foods enriched with riboflavin: liver, almonds, soy nuts, seafood, milk and other dairy products, eggs.
- Vitamin A
Vitamin A improves vision. Important in protein synthesis (muscle growth). Participates in the production of glycogen (a form of energy for intensive body activity). Is of great importance in preparing for competitions
Power sources: there are many of them (see the link below and click the button at the very top, under the table of contents). What foods provide vitamin A? Please note that milk is mentioned once again. Of the five, milk is mentioned in four essential vitamins. What is this, a coincidence? I think not?
- Vitamin E
Being a powerful antioxidant, it takes part in the protection of cell membranes. Restores and promotes muscle cell growth, directly dependent on healthy cell membranes.
The most common food sources containing vitamin E are various vegetable oils, nuts, green leafy vegetables, and fortified cereals.
- Niacin (vitamin B3)
Participates in sixty metabolic processes associated with energy production.
Nicotinic acid, in the form of niacin, causes vasodilation, which helps you look more vascular on stage. However, large doses of nicotinic acid sharply impair the body's ability to mobilize and burn fat.
Food sources containing niacin include turkey (the body uses the amino acid tryptophan to create niacin), dairy products, poultry, fish, lean meats, nuts and eggs.
- Vitamin D
Vitamin D is necessary for the absorption of calcium and phosphorus. If adequate muscle calcium stores are not available, you will not achieve full, tight muscle contractions.
Fast and powerful muscle contractions are provided by phosphorus. Phosphorus is also necessary for the synthesis of ATP.
Food sources: Skim or low-fat milk.
- Thiamine (vitamin B1)
Essential for protein metabolism and growth.
It is directly involved in the formation of hemoglobin, which is a protein contained in red blood cells that provides oxygen to the working muscles of the body.
With increasing load and duration of sports exercises, intensive oxygen supply becomes increasingly important.
The more you increase the amount of exercise, its intensity and duration, the more thiamine you need.
Food sources of thiamine: green peas, spinach, liver, beef, pork, navy beans, nuts, pinto beans, bananas, soybeans, Goji berries, whole grain and fortified cereals, bread, yeast, brown rice bran and legumes.
- Pyridoxine (vitamin B6)
It is the only vitamin directly linked to protein intake. The more protein you consume, the more vitamin B6 you need.
Vitamin B6 promotes protein metabolism, growth and utilization of carbohydrates.
Key foods containing vitamin B6 include avocados, nuts, liver, chicken, fish, green beans, lettuce, wheat germ, nutritional yeast, sea vegetables and bananas.
- Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C)
Enhances muscle cell repair and growth and is an antioxidant.
Participates in the formation of collagen, being the main component of connective tissue (connective tissue holds your bones and muscles together). When you lift heavier weights, you place stress on your muscular structure. If your connective tissue is not strong enough, you have a fairly high chance of injury.
Helps with iron absorption. With iron deficiency, the amount of oxygen contained in hemoglobin decreases, which significantly reduces muscle performance.
Dissolves very quickly in water. Since a muscle cell consists mainly of water, the larger an athlete’s muscle mass becomes, the more vitamin C dissolves, and the concentration of this substance in the body’s tissues decreases. Thus, the bodybuilder's body requires a significant increase in vitamin C.
Helps in the formation and release of steroid hormones, including the anabolic hormone testosterone.
The main sources of vitamin C are citrus fruits and fruit juices.
So there you have it, the 10 most important vitamins for sports. If you are an athlete, you should eat a lot anyway, and the more of the above foods you eat to ensure that all these vitamins are regularly present in your diet, the less problems you will have.
However, if you feel your diet needs some support, you can also take a multivitamin with your meals, but remember that getting your vitamins from natural sources is always best. However, once you understand the critical importance of vitamin C in bodybuilding, you can benefit from its support in its pure form.
Finally, pay attention to how many times milk or dairy products are listed as the main source of the above vitamins.
Therefore, three or four glasses of milk a day will definitely be beneficial for your body. If you are lactose intolerant, you may consider purchasing lactose-free milk, which tastes no different from regular milk, but it is milk with the addition of a lactose-neutralizing ingredient. How to pump up your arms, chest, chest, lose weight, gain mass
Indications for use
Due to the fact that nicotinic acid effectively fights malignant cholesterol and lipoproteins, it is often prescribed to people who have had or will have problems with the cardiovascular system. Moreover, nicotinic acid has shown good results in the treatment of diabetes and obesity, so it should be taken by people suffering from these diseases.
But this does not mean that nicotinic acid will be effective only in the fight against serious diseases. It can also contribute to a slight reduction in body weight by burning all the unhealthy fats.
Weightlifters should definitely take niacin as an additional supplement. The fact is that it will help protect bones from developing arthritis. Many professional athletes in their old age begin to suffer greatly from this disease, so you need to think about protecting yourself from it in advance.
Nicotinic acid can be prescribed together with other medications as a complex therapy to help heal injured joints and ligaments.
It is also used for hair growth:
And for weight loss:
What are the dangers of excess and deficiency of vitamin B3?
The significance of the biological role of niacin described above already suggests that its deficiency is fraught with a real disaster for our health. Vitamin B3 deficiency can be caused by a poor diet that lacks niacin or the amino acid tryptophan, from which it can be synthesized within the body.
Other reasons may be prolonged stress, alcoholism or enterocolitis, which does not allow vitamins to be absorbed in the intestines. Hypovitaminosis RR will manifest itself as gastrointestinal disorders, diarrhea, nausea, swelling of the tongue, lack of appetite, dry skin and dermatitis, insomnia, lethargy and decreased performance, and thinness.
However, you should not abuse pharmaceutical preparations of niacin for sports or cosmetic purposes (the vasodilating effect of nicotine is used, for example, to give a fresh look to the face or hair growth). An excess of it in the body is also dangerous and leads to allergic rashes and itching, visual disturbances, digestion, migraines, yellowing of the skin, and over time – to liver damage.
Instructions for use
The daily requirement for this substance depends on the number of calories that the athlete receives through food. There should be 6.6 mg of nicotinic acid per 1000 kcal. In the presence of certain diseases, such as diabetes, the dosage of acid may be increased. On average, women need to get 14 mg of niacin, and men – 16 mg.
But how to take nicotinic acid in tablet form? What is the dosage? Usually prescribed from 0.02 to 1 g at a time . You need to drink 3 of these tablets per day immediately after meals.
Nicotinic acid (niacin) for the treatment of atherosclerosis and cleansing of blood vessels
Nicotinic acid, or niacin (vitamin PP, vitamin B3) is a chemical compound that takes part in lipid metabolism, regulates redox processes and cholesterol levels in the body.
Nicotinic acid for atherosclerosis is used to normalize fat, protein, carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism, to stimulate brain function, and also as rehabilitation therapy after a stroke.
The effectiveness of nicotinic acid in atherosclerosis
According to studies conducted in the American Mayo Clinic network, taking this vitamin for atherosclerosis has a positive effect on blood cholesterol levels, namely, it reduces “bad” cholesterol and increases “good” cholesterol by 30%, which means it reduces the risk of atherosclerosis. Regular consumption of niacin blocks a process in the body called lipolysis, when triglycerides leave fat tissue and enter the bloodstream.
Other American studies have shown that nicotine can lower blood pressure in people suffering from cardiovascular diseases, atherosclerosis and hypertension, but does not affect blood pressure if it is within the normal range.
Nicotinic acid is a vasodilator, capable of dissolving and removing cholesterol plaques and blood clots, therefore it is often used in therapy for cerebral atherosclerosis.
Effect on the cardiovascular system and other organs
The benefit of nicotinic acid for the blood vessels of the brain lies in its ability to dilate blood vessels, which eliminates circulatory disorders, improves blood flow, cleanses blood vessels of cholesterol deposits, and, as a result, reduces the risk of atherosclerosis. Also, nicotine can strengthen the walls of blood vessels, thereby reducing the quantitative level of insoluble fibrin proteins, and therefore reducing the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in the veins and arteries, thereby eliminating the factor of vascular pathology.
In addition, the use of vitamin PP stimulates the production of hormones in the adrenal glands, which strengthens immunity to various inflammatory and allergic pathologies.
In addition, nicotinic acid has the following effects on the body:
- Thins the blood.
- Stimulates digestion processes in the stomach and intestines.
- Strengthens the immune system, reduces the susceptibility to viral diseases.
- Reduces blood sugar levels, which is especially useful for diabetics.
- Improves psycho-emotional state, eliminates symptoms of nervous disorders and depressive states.
- Reduces total cholesterol levels and normalizes high blood pressure.
- Stimulates the work of glands in the gastrointestinal tract, improves peristalsis.
In turn, a lack of this vitamin in the body can lead to the development of depression, frequent headaches, memory loss, increased fatigue, decreased performance, foggy consciousness, nausea, upset stomach, various skin disorders, namely rashes, itching, dryness, irritation.
How to take niacin
The release form of nicotinic acid comes in two types - tablets and a solution for parenteral administration, that is, in the form of injections.
For the treatment of vascular atherosclerosis, nicotinic acid preparations are prescribed subcutaneously, intramuscularly and intravenously in small doses, which increase over time. This is necessary to give the body the opportunity to get used to the new substance.
Most often, in case of atherosclerosis, a course of taking niacin begins with a dose of 50 mg, gradually increasing to 3-4 g. It is in this amount that it has the most effective effect in reducing lipid levels.
Higher doses of this drug for atherosclerosis are not recommended, as they are addictive.
In tablet form, nicotinic acid is taken three times a day after meals in the amount of 1-2 tablets. The maximum daily dose is 6 tablets. For people with increased secretion of gastric juice, it is recommended to take the vitamin with plenty of warm milk.
Possible contraindications for taking vitamin PP for atherosclerosis include the following factors:
- For gout, atherosclerosis and hypertension, intravenous administration of the drug is contraindicated.
- Age up to 2 years.
- Peptic ulcer disease.
- Diabetes mellitus, hepatitis, cirrhosis.
- Bleeding.
- Brain hemorrhage.
- Kidney failure.
- In children under 10 years of age, the drug is used under the strict supervision of the attending physician.
- For pregnant and breastfeeding women, the ratio of possible benefits to risks to the fetus is assessed.
- Individual intolerance to niacin or auxiliary agents in the composition of the drug.
Possible side effects
Typically, preparations containing niacin are well tolerated by patients with atherosclerosis, and possible side effects of nicotinic acid are short-term and go away on their own after a couple of days.
However, niacin is still a drug, which means it has few side effects, so you should never self-medicate.
Since the action of the nicotinic acid drug stimulates the body's production of histamine, side effects may manifest itself in the form of the following symptoms:
- Redness on the skin, most often on the face and upper torso, as well as a slight burning and tingling sensation - a condition medically known as flushing.
- Gout.
- Reduced pressure.
- Dizziness, blurred vision.
- Increased secretion of gastric juice.
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, such as flatulence, heartburn, bloating.
- Itching.
- Hives.
With uncontrolled intake of nicotinic acid for atherosclerosis in large doses, the following side effects may develop:
- Development of liver diseases.
- Stomach upsets and irritation of its mucous membrane.
- Vomit.
- Anorexia.
- Heart rhythm disturbances, arrhythmia.
- Increased blood sugar levels.
- Feeling of tingling, burning and goosebumps on the skin.
Contraindications
Nicotinic acid is contraindicated for those people who have individual sensitivity to this substance. You should also not take vitamin complexes if:
- atherosclerosis;
- hypertension;
- stomach ulcer in the acute stage;
- gout;
- hepatitis;
- liver cirrhosis;
- diabetes mellitus
Dumbbells for Women: What Weight is Best for Beginners? How quickly do you increase the load?
You can watch the correct leg press technique in the simulator on video here - /silovye/yagoditsy/zhim-nogami-v-trenazhere-pod-uglom.html.
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, you should consult a specialist about the advisability of using such supplements.
How, by whom and why was niacin discovered?
For centuries, in countries where the basis of nutrition is corn grains (Italy, Spain, Argentina), people have suffered from pellagra. To date, scientists have managed to almost completely eradicate this disease. Scientists Funk and Goldberger made a great contribution to the study of the causes of pellagra. They admitted the existence of a certain substance that causes illness in people. In addition, in 1914, R. N. Funk noticed that pellagra mainly affects poor people, whose diet contains a lot of corn, but almost completely lacks milk, meat, and eggs. It became clear that people who get sick mostly are people whose diet lacks a certain component.
In 1937, nicotinic acid was synthesized for the first time in laboratory conditions. Much time has passed since then, and today the usual niacin can be purchased at every pharmacy.
View gallery
Consequences
If nicotinic acid enters the body in normal quantities, then the athlete will soon notice improvements in metabolism. This will affect his physical fitness, as the amount of subcutaneous fat will begin to decrease.
In addition, the concentration of malignant and normal cholesterol in the blood and tissues will significantly decrease. This will greatly reduce the risk of heart disease and obesity.
However, it is important to remember that niacin should be taken with caution, otherwise it will cause side effects. With long-term use, liver dystrophy, a decrease in the body's tolerance to glucose, and a feeling of constant heat are possible. Some people experience constant headaches and dizziness.
An overdose of nicotinic acid causes a side effect in which the blood begins to rush to the face, turning it pink. Arrhythmia is observed, itching, nausea and vomiting appear. Due to possible serious consequences, you should read the instructions before taking dietary supplements.
Why is niacin so effective?
Excellent results in the fight against atherosclerosis with the help of this vitamin were achieved thanks to its mechanism of action on the body. As soon as nicotinic acid enters the body, the synthesis of lipoprotein lipase increases. This leads to the fact that the amount of “good” cholesterol increases, and the rate of synthesis of “bad” cholesterol decreases. But first you need to understand how cholesterol is categorized:
- Good cholesterol or high density lipoprotein. They contain a lot of protein and little fat. They participate in the process of building blood vessels and organs and destroy atherosclerotic plaques.
- Bad cholesterol or low density lipoproteins. These substances consist of 70% fat, clog blood vessels and provoke various diseases.
Under the influence of nicotinic acid (niacin), the triglyceride content in the body decreases, therefore the synthesis of low-density lipoproteins decreases. Free fatty acids begin to enter the liver, where they are further processed. But there were some negative effects. When taking nicotinic acid, the production of prostaglandins increases. Because of this, the patient’s skin begins to turn red, because the vessels dilate. If this causes great discomfort to a person, the doctor may prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They will reduce the synthesis of elements that dilate blood vessels.
What products or preparations contain
Nicotinic acid is found in liver, meat, fish, poultry, nuts and beans . It can also be obtained from bread and wholemeal cereals. But in case of serious deficiency of this substance, it is necessary to take special biological supplements. They will help quickly replenish the lack of niacin, allowing athletes to quickly return to their usual training regimen.
Nicotinic acid is sold in all pharmacies. It can be produced in the form of various nutritional supplements, vitamin complexes and even injection solutions. Most often, athletes use vitamin complexes Opti-Men from Optimum Nutrition and Opti-Women from the same manufacturer. They contain over 75 beneficial ingredients, so athletes don't need to take anything extra. The complex also contains nicotinic acid.
If an athlete lacks nicotinic acid, he can use Niacin from NOW. Each capsule of the drug contains 500 mg of nicotinic acid.
Foods Rich in Vitamin B3
Products of plant origin:
- peanut
- legumes
- broccoli
- buckwheat
- ginseng
- Cayenne pepper
- potato
- raspberry leaves
- carrot
- peppermint
- oats
- dog-rose fruit
- parsley
- tomatoes
- cereal products
- wheat sprouts
- dates
- sorrel
Animal products:
- white meat chicken
- beef liver
- milk
- meat
- kidneys
- fish
- cheese
- eggs
Why do bodybuilders need B9?
B vitamins are responsible for metabolism and normal absorption of nutrients. Folates were no exception. One of the main tasks of folic acid is to control hematopoiesis, red blood cell production, tissue renewal, and DNA and RNA synthesis. The substance promotes rapid weight growth due to improved protein absorption and accelerated cell division.
There are several more reasons why folic acid is used in bodybuilding:
- the vitamin helps you achieve a feeling of fullness faster and avoid overeating;
- folates are involved in the synthesis of serotonin, which is responsible for calming the nervous system;
- Due to its effect on the production of norepinephrine, folic acid allows you to maintain vigor and increased performance, and it is easier to cope with stress and the consequences of serious training;
- The substance accelerates metabolism, so it helps you lose weight faster.
Supplements based on vitamin B9 are recommended for use not only by those who are involved in bodybuilding or other sports professionally. For amateurs, it will help maintain a good mood and enjoy training.
You cannot select dietary supplements containing B9 on your own. It is advisable that the doctor calculate the dose based on age, body characteristics and type of physical activity.
pharmachologic effect
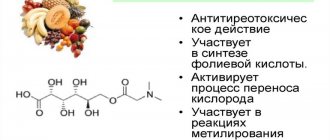
Vitamin, hypolipidemic and specific antipellagritic agent. In the body, nicotinic acid is converted into nicotinamide, which binds to coenzymes codehydrogenase I and II (NAD and NADP), which transport hydrogen, and participates in the metabolism of fats, proteins, amino acids, purines, tissue respiration, glycogenolysis, and biosynthesis processes.
Normalizes the concentration of blood lipoproteins; in large doses (3-4 g/day) reduces the concentration of total cholesterol, LDL, reduces the cholesterol/phospholipid index, increases the content of HDL, which has an antiatherogenic effect. The hypocholesterolemic effect appears within a few days, and a decrease in triglycerides occurs within a few hours after administration[1]. However, clinical trials of statin therapy in combination with high doses of niacin conducted by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute[5][ not in source
], showed that although patients taking niacin plus a statin had increased HDL levels and decreased triglycerides compared with patients taking the statin alone, the incidence of heart attacks was no different between the two groups [
unspecified 1551 days
][6 ].
Dilates small blood vessels (including the brain), improves microcirculation, has a weak anticoagulant effect, increasing the fibrinolytic activity of the blood. It has detoxifying properties[7].
Nicotinamide, unlike nicotinic acid, does not have a pronounced vasodilator effect, and when it is used, there is no redness of the skin or a feeling of a rush of blood to the head.[8]
Dosage
Vitamin B in bodybuilding, like any other substances, sports nutrition, must be taken in the required daily dosages.
- B1 - 1.5 mg.
- B2 - 1.8 mg.
- B3 - 15-20 mg.
- B5 - 5 mg.
- B6 - 2-2.5 mg.
- B7 - 50 mcg.
- B9 - 400 mcg.
- B12 - 2-3 mcg.
For increased activity during training, the dosage can be increased several times. However, you should always read the instructions for use of each specific drug.
special instructions
To prevent hypovitaminosis RR, a balanced diet is most preferable; treatment requires additional administration of vitamin PP. Foods rich in vitamin PP are yeast, liver, nuts, egg yolk, milk, fish, chicken, meat, legumes, buckwheat, unrefined grains, green vegetables, ground nuts, any protein food containing tryptophan. Heat treatment of milk does not change the content of vitamin PP in it.
During long-term treatment (especially when prescribed not as a vitamin drug), it is necessary to monitor liver function. To prevent liver complications, it is recommended to include foods rich in methionine (cottage cheese) in the diet, or use methionine, lipoic acid and other lipotropic drugs.
It is not advisable to use for the correction of dyslipidemia in patients with diabetes mellitus.
To reduce the irritating effect on the gastrointestinal mucosa, it is recommended to take the drug with milk.[1]
Biosynthesis
Synthesis of niacin (melatonin, serotonin) from tryptophan
In the liver, biosynthesis of niacin from the essential amino acid tryptophan is possible; the synthesis of one milligram of niacin requires about 60 mg of tryptophan - this is the niacin equivalent.[10] The five-membered aromatic heterocycle of tryptophan is cleaved and rearranged with the amino group of tryptophan into the six-membered heterocycle of niacin. The reactions that convert tryptophan into NAD require riboflavin (vitamin B2), vitamin B6, and iron.
Every year, the chemical industry synthesizes millions of kilograms of niacin from 3-methylpyridine.
Is it possible to speed up hair growth using niacin?
What girls can’t come up with in the fight for gorgeous hair. Several years ago, the Internet was full of “miracle reviews” about nicotinic acid, which claimed that after a course of this vitamin their hair began to grow like never before.
Similar cases have actually been recorded in medicine. Nicotinic acid dilates blood vessels even when applied to the scalp - due to this, the effect of stimulating the work of hair follicles is achieved. But the speed of hair growth is limited by physiology: no matter how hard you try, no matter what you rub into the roots, it is simply impossible to accelerate hair growth beyond three centimeters per month.
View gallery
Many girls are happy to add an ampoule of vitamin to a regular mask. This stimulates hair growth and helps strengthen it. Reviews of nicotinic acid for hair are mostly enthusiastic; its effect is really good for alopecia.