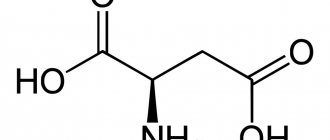
Saturated fatty acids (SFAs) are carbon chains whose number of atoms varies from 4 to 30 or more.
The general formula of compounds in this series is CH3 (CH2)nCOOH.
Over the past three decades, it has been believed that saturated fatty acids are harmful to human health because they are responsible for the development of heart and vascular diseases. New scientific discoveries have contributed to a reassessment of the role of compounds. Today it has been established that in moderate quantities (15 grams per day) they do not pose a threat to health, but on the contrary have a beneficial effect on the functioning of internal organs: they participate in thermoregulation of the body, improve the condition of hair and skin.
Types of fats
Triglycerides consist of fatty acids and glycerol (trihydric alcohol). The former, in turn, are classified according to the number of double bonds between carbohydrate atoms. If they are absent, such acids are called saturated; if they are present, they are called unsaturated.
Conventionally, all fats are divided into three groups.
Saturated (ultimate). These are fatty acids whose molecules are saturated with hydrogen. They enter the body with sausages, dairy, meat products, butter, and eggs. Saturated fats have a solid consistency due to the elongated chains along a straight line and tightly adjacent to each other. Due to this packaging, the melting point of triglycerides increases. They participate in the structure of cells and saturate the body with energy. Saturated fats in small quantities (15 grams per day) are needed by the body. If a person stops eating them, the cells begin to synthesize them from other foods, but this is an extra burden on the internal organs. An excess of saturated fatty acids in the body increases cholesterol levels in the blood, contributes to the accumulation of excess weight, the development of heart disease, and creates a predisposition to cancer.
Unsaturated (unsaturated). These are essential fats that enter the human body along with plant foods (nuts, corn, olive, sunflower, flaxseed oils). These include oleic, arachidonic, linoleic and linolenic acid. Unlike saturated triglycerides, unsaturated ones have a “liquid” consistency and do not solidify in the refrigerator. Depending on the number of bonds between carbohydrate atoms, monounsaturated (Omega-9) and polyunsaturated compounds (Omega-3, Omega-6) are distinguished. This category of triglycerides improves protein synthesis, the condition of cell membranes, and insulin sensitivity. In addition, it removes bad cholesterol, protects the heart and blood vessels from fatty plaques, and increases the number of good lipids. The human body does not produce unsaturated fats, so they must be supplied regularly through food.
Trans fats. This is the most harmful type of triglycerides, which is obtained by processing hydrogen under pressure or heating vegetable oil. At room temperature, trans fats freeze well. They are found in margarine, dressing, potato chips, frozen pizza, store-bought cookies and fast food products. To increase shelf life, food industry manufacturers include up to 50% trans fats in canned and confectionery products. However, they do not provide value to the human body, but on the contrary, they are harmful. The danger of trans fats: they disrupt metabolism, change insulin metabolism, lead to obesity, and the appearance of coronary heart disease.
The daily fat intake for women under 40 years of age is 85–110 grams, for men – 100–150. For older people, it is recommended to limit consumption to 70 grams per day. Remember, the diet should be 90% dominated by unsaturated fatty acids and only 10% should be limited triglycerides.
How to achieve the desired balance between acids in your daily menu
When choosing food products for your daily diet, you should know where and in what proportions a particular acid group predominates.
- Omega-3 predominates in oil products: olive, sunflower, flaxseed, rapeseed oils.
- Omega-6, due to its affinity with saturated acids, predominates in natural animal proteins: all types of meat, milk, eggs.
- Omega-9 is found in large quantities in nuts, legumes and whole grains.
https://youtu.be/8CG9p9Iejko
Chemical properties
The name of fatty acids depends on the name of the corresponding hydrocarbons. Today, there are 34 main compounds that are used in human everyday life. In saturated fatty acids, two hydrogen atoms are bonded to each carbon atom of the chain: CH2-CH2.
Popular ones:
- butane, CH3(CH2)2COOH;
- nylon, CH3(CH2)4COOH;
- caprylic, CH3(CH2)6COOH;
- capric, CH3(CH2)8COOH;
- lauric, CH3(CH2)10COOH;
- myristic, CH3(CH2)12COOH;
- palmitic, CH3(CH2)14COOH;
- stearic, CH3(CH2)16COOH;
- Laceric, CH3(CH2)30COOH.
Most saturated fatty acids contain an even number of carbon atoms. They dissolve well in petroleum ether, acetone, diethyl ether, and chloroform. High molecular weight compounds do not form solutions in cold alcohol. At the same time, they are resistant to oxidizing agents and halogens.
In organic solvents, the solubility of saturated acids increases with increasing temperature and decreases with increasing molecular weight. When they enter the blood, such triglycerides merge and form spherical substances, which are deposited “in reserve” in adipose tissue. This reaction is associated with the emergence of the myth that extreme acids lead to blockage of arteries and should be completely excluded from the diet. In fact, diseases of the cardiovascular system arise as a result of a combination of factors: poor lifestyle, lack of physical activity, abuse of high-calorie junk food.
Remember, a balanced diet enriched with saturated fatty acids will not affect your figure, but, on the contrary, will benefit your health. At the same time, their unlimited consumption will negatively affect the functioning of internal organs and systems.
How is the world fighting dangerous trans fats?
Scientists recently compared the trans fat content of products commonly prepared with margarines and palm oil from 25 countries. It turned out that Denmark is in last place. In 2004, Denmark became the first country to ban partially hydrogenated oils and artificial trans fats from the diet. The law regulating this states that the content of trans fats should not exceed 2% of the total fat in the product. In the United States, a law was passed in 2006 according to which product packaging must indicate how much trans fat it contains. According to a study published in the 2013 WHO Bulletin, policies implemented in Brazil, Canada, Denmark, the Netherlands, the Republic of Korea and the United States) over the past two decades have made progress in eliminating trans fats from food. By 2020, the United States plans to completely eliminate trans fats from foods. Considering this, as well as the fact that in Russia the content of trans fats in products is not regulated in any way by law, and manufacturers do not indicate it on packaging, it is likely that trans fats unclaimed on the American market will pour into our country.
Therefore, be careful! It is possible and necessary to reduce your consumption of trans fats. First of all, read the ingredients of the products you buy. If any hydrogenated or partially hydrogenated oil is listed as an ingredient, the product contains trans fats .
Importance for the body
The main biological function of saturated fatty acids is to supply the body with energy.
To maintain vital functions, they should always be present in the diet in moderation (15 grams per day). Properties of saturated fatty acids:
- charge the body with energy;
- participate in tissue regulation, hormone synthesis, testosterone production in men;
- form cell membranes;
- ensure the absorption of microelements and vitamins A, , , ;
- normalize the menstrual cycle in women;
- improve reproductive function;
- create a layer of fat that protects internal organs;
- regulate processes in the nervous system;
- participate in the production of estrogen in women;
- protect the body from hypothermia.
To maintain health, nutritionists recommend including foods containing saturated fats in your daily menu. They should account for up to 10% of calories from the total daily diet. This is 15 - 20 grams of the compound per day. Preference should be given to the following “healthy” products: cattle liver, fish, dairy products, eggs.
Consumption of saturated fatty acids is increased by:
- pulmonary diseases (pneumonia, bronchitis, tuberculosis);
- strong physical activity;
- treatment of gastritis, duodenal ulcer, stomach;
- removal of stones from the urinary/gallbladder, liver;
- general exhaustion of the body;
- pregnancy, breastfeeding;
- living in the Far North;
- the onset of the cold season, when additional energy is spent on heating the body.
Reduce the amount of saturated fatty acids in the following cases:
- for cardiovascular diseases;
- excess body weight (with 15 “extra” kilograms);
- diabetes mellitus;
- high cholesterol levels;
- reducing the body's energy consumption (during the hot season, on vacation, during sedentary work).
With insufficient intake of saturated fatty acids, a person develops characteristic symptoms:
- body weight decreases;
- the functioning of the nervous system is disrupted;
- labor productivity falls;
- hormonal imbalance occurs;
- the condition of nails, hair, skin worsens;
- infertility occurs.
Signs of an excess of compounds in the body:
- increased blood pressure, cardiac dysfunction;
- the appearance of symptoms of atherosclerosis;
- formation of stones in the gall bladder, kidneys;
- increased cholesterol, which leads to the appearance of fatty plaques in blood vessels.
Remember, saturated fatty acids are eaten in moderation, not exceeding the daily allowance. Only in this way can the body extract maximum benefit from them without accumulating toxins and without being “overloaded.”
To quickly digest fats, it is recommended to consume them with herbs, herbs and vegetables.
The danger of acid deficiency for the human body
Assessing the important role of acids in the formation of the body of any living creature, it is difficult to underestimate the lack of these substances. A deficiency of omega acids can lead a person to a number of serious diseases:
- Autoimmune pathologies: autoimmune thyroiditis, nonspecific immunodeficiency conditions, allergic reactions, especially of seasonal origin, herpetic exacerbations.
- Hormonal abnormalities: Basedow's disease, hypertrophy of the thymus gland in adulthood, dysmenorrhea in women, hypospermia and aspermia in men, infertility, anorexia, decreased serotonin levels.
- Digestive disorders: poor absorption of nutrients, hypoacid gastritis, impaired bile production, appendicitis, dysbacteriosis.
- Central nervous system disorders: impaired attention, memory, depression, irritability, tearfulness.
- Blood function disorders: iron deficiency anemia, blood clotting disorders, decrease in the total level of leukocytes.
- Oncological diseases: leukemia, brain oncology, gastrointestinal oncology, endocrine system oncology are predominantly developing.
- Disorders of the skeletal system: osteoporosis, acceleration of degenerative processes, arthrosis destruction, thinning of cartilaginous layers.
- Lack of omega acids in pregnant women: complexly leads to delays in mental and physical development in the fetus.
The ability to achieve the correct balance of fatty acids is an experience comparable to alchemy. Omega acids are essential components of any organic tissue. Nature does not tolerate shortages or excess; only when true balance is achieved will the most valuable thing that every living organism has - its life and health - be preserved.
Sources of Saturated Fatty Acids
The largest amount of EFAs is concentrated in products of animal origin (meat, poultry, cream) and vegetable oils (palm, coconut). In addition, the human body receives saturated fats from cheeses, confectionery, sausages, and cookies.
Today it is difficult to find a product containing one type of triglyceride. They are in combination (saturated and unsaturated fatty acids and cholesterol are concentrated in lard and butter).
The largest amount of EFA (up to 25%) is contained in palmitic acid.
It has a hypercholesterolemic effect, so the intake of products that contain it should be limited (palm oil, cow oil, lard, beeswax, sperm whale spermaceti).
Table No. 1 “Natural sources of saturated fatty acids”
| Product name | Content of NSF per 100 grams of volume, grams |
| Butter | 47 |
| Hard cheeses (30%) | 19,2 |
| Duck (with skin) | 15,7 |
| Raw smoked sausage | 14,9 |
| Olive oil | 13,3 |
| Processed cheese | 12,8 |
| Sour cream 20% | 12,0 |
| Goose (with skin) | 11,8 |
| Cottage cheese 18% | 10,9 |
| Corn oil | 10,6 |
| Lamb without fat | 10,4 |
| Boiled fatty sausage | 10,1 |
| Sunflower oil | 10,0 |
| Walnuts | 7,0 |
| Low-fat boiled sausage | 6,8 |
| Beef without fat | 6,7 |
| Ice cream | 6.3 |
| Cottage cheese 9% | 5,4 |
| Pork meat | 4,3 |
| Fish medium fat content 8% | 3,0 |
| Milk 3% | 2,0 |
| Chicken (fillet) | 1,0 |
| Low-fat fish (2% fat) | 0,5 |
| Sliced loaf | 0,44 |
| Rye bread | 0,4 |
| Low-fat cottage cheese | 0,3 |
Foods containing the highest concentration of saturated fatty acids:
- fast food;
- cream;
- palm, coconut oil;
- chocolate;
- confectionery;
- lard;
- chicken fat;
- ice cream made from full-fat cow's milk;
- cheese;
- cocoa butter.
To maintain heart health and stay slim, it is recommended to choose foods with less fat. Otherwise, problems with blood vessels, excess weight, and sludge in the body cannot be avoided.
Remember, triglycerides with a high melting point are the most harmful to humans. To digest and eliminate waste from a roasted piece of fatty beef or pork, the body will require five hours and significant energy costs than to digest chicken or turkey. Therefore, it is better to give preference to poultry fat.
What other foods contain unsaturated fats?
Seeds and nuts are ideal foods high in unsaturated fatty acids. You can't eat a lot of butter, can you? And they can be safely used as a snack, which will additionally serve your body as a source of vitamins and other important microelements. Read more in the article The healthiest nuts and their properties.
Areas of application
- In cosmetology. Saturated fatty acids are included in dermatotropic products, creams, and ointments. Palmitic acid is used as a structure former, emulsifier, and emollient. Lauric acid is used as an antiseptic in skin care products. Caprylic acid normalizes the acidity of the epidermis, saturates it with oxygen, and prevents the growth of yeast fungi.
- In household chemicals. NLCs are used in the manufacture of toilet soaps and detergents. Lauric acid serves as a foaming catalyst. Oils containing stearic, myristic and palmitic compounds are used in soap making for the preparation of solid products, lubricating oils, and plasticizers. Stearic acid is used in the production of rubber, as a softener, and in the creation of candles.
- In the food industry. Used as food additives under the symbol E570. Saturated fatty acids act as a glazing agent, defoamer, emulsifier, and foam stabilizer.
- In dietary supplements and medications. Lauric and myristic acids exhibit fungicidal, viricidal, and bactericidal activity, inhibiting the growth of yeast fungi and pathogenic microflora. They are able to enhance the antibacterial effect of antibiotics in the intestines, which increases the effectiveness of treatment of viral-bacterial acute intestinal infections. Presumably, caprylic acid maintains a normal balance of microorganisms in the genitourinary system. However, these properties are not used in drugs. When lauric and myristic acids interact with bacterial and viral antigens, they act as immunological stimulants, helping to increase the body’s immune response to the introduction of an intestinal pathogen. Despite this, fatty acids are included in medicines and dietary supplements exclusively as excipients.
- In poultry farming, livestock farming. Butanoic acid increases the productive life of the sow, maintains microecological balance, improves the absorption of nutrients and the growth of intestinal villi in the body of livestock. In addition, it prevents oxidative stress, exhibits anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory properties, therefore it is used in the creation of feed additives in poultry and livestock farming.
Foods that contain dangerous trans fats
- margarine
- cream
- butter
- mayonnaise and sauces based on it
- any fast food
- breaded fish fingers or cutlets
- chips
- popcorn
- cakes with icing
- chocolate candies
- cakes with whipped vegetable cream
- gingerbread
- cookie
- ice cream
- puff pastry products
- instant food products (cubes, noodles)
As already written above, domestic manufacturers and some foreign ones do not indicate the content of trans fats on the packaging. Now, going into any store or fast food chain, it is almost impossible to independently distinguish the presence of harmful trans fats in products. However, there are components whose names indicate that they contain trans fats.
Names of trans fats on packaging
• margarine • confectionery fat • cocoa butter substitute • vegetable fat and vegetable fat; • hydrogenated oil • milk fat substitute • powdered hydrogenated fat • “milk, curd or cheese product with vegetable fats”
Are there alternatives to trans fats that you can eat?
It is almost impossible to eliminate all trans fats from the foods you buy. But there is a norm for their consumption according to WHO - less than 1% of the daily intake of fat or about 2 grams. In addition, many dangerous trans fats can be replaced. For example, for cooking, use olive oil rather than margarine and butter. To avoid the temptation to use mayonnaise, use low-fat sour cream, olive oil and wine vinegar, lemon juice. If you cannot resist eating mayonnaise, use homemade mayonnaise. For a light snack that replaces chips, a tasty alternative is pita bread or pita bread wrapped in vegetables, cheese and lean chicken. It is worth remembering that it is impossible to give up fats 100%, since they are involved in building cells. And only a balanced diet allows you to maintain or improve your health.
***
In conclusion, some tips when choosing oil.
When choosing oil, keep the following in mind:
• always check the expiration date of the oil (6 months from the date of extraction) • the shelf life of oil without preservatives is 4 months. Oil can be stored for a longer time only with the addition of artificial antioxidants; if opened, the shelf life for refined oil is 4 months, for unrefined oil – 2 months. • make sure that the oil is in a dark container (if in a transparent plastic container, then pour it into a dark glass container) • the smaller the bottle you buy, the better • linseed oil oxidizes faster • if smoke appears above the surface of the vegetable oil when heated, it means It began the formation of toxic compounds harmful and dangerous to the human body. Therefore, vegetable oil cannot be heated above 160 - 170⁰С. • salt does not dissolve in vegetable oil, so first the salad is salted and waited until the vegetables give juice, and only then seasoned with oil.
Basic NLCs
Different authors indicate differently which acids are considered fatty acids. We will look at the most basic of them:
- Propionic acid (formula - CH3-CH2-COOH). It is formed during the metabolic breakdown of fatty acids with an odd number of carbon atoms, as well as some amino acids. In nature it is found in oil. Since it prevents the growth of mold and some bacteria, propionic acid, the formula of which we already know, is often used as a preservative in the production of foods that humans consume. For example, in bakery production it is used in the form of sodium and calcium salts.
- Butyric acid (formula CH3—(CH2)2—COOH). It is one of the most important and is formed naturally in the intestines. This fatty acid promotes intestinal self-regulation and also supplies energy to epithelial cells. It creates an acidic environment in which conditions become unfavorable for the development of pathogenic microflora. Butyric acid, the formula of which is known to us, has an anti-inflammatory effect, helps stop the development of cancer cells, and increases appetite. It also helps stop metabolic disorders and increases local immunity.
- Valeric acid (formula CH3—(CH2)3—COOH). It has a mild antispasmodic effect. Like oil, it activates colon motility, affecting the nerve endings of the intestine and stimulating smooth muscle cells. Acid is formed as a consequence of the metabolism of microorganisms in the colon. Valeric acid, the formula of which was given above, arises as a result of the activity of bacteria that are part of the intestinal microflora.
- Caproic acid (formula CH3—(CH2)4—COOH). In nature, this acid can be found in palm oil and animal fats. There is especially a lot of it in butter. It has a detrimental effect on many pathogenic bacteria, even those that are resistant to antibodies. Caproic acid (formula listed above) plays an important role in the human body. It has antiallergic activity and improves liver function.
NLC - what is it?
Before considering the role of saturated fatty acids (SFAs), let's find out what they are. NLCs are solids that melt at high temperatures. They are most often absorbed by the human body without the participation of bile acids, and therefore have high nutritional value. But excess saturated fats are always stored in the body as reserves. EFAs give the fats they contain a pleasant taste. They also contain lecithin, vitamins A and D, cholesterol, and saturate cells with energy.
For the last thirty years, it has been generally accepted that the content of saturated fatty acids in the body causes great harm to it, as they contribute to the development of diseases of the cardiovascular system. Thanks to new scientific discoveries, it has become clear that they do not pose a danger; on the contrary, they have a good effect on the functioning of internal organs. They also take part in thermoregulation and improve the condition of hair and skin. Even cholesterol is vital for the human body, as it takes part in the synthesis of vitamin D and hormonal processes. With all this, the body should have saturated fatty acids in moderation. Their benefits and harm will be discussed below.
Harm
Some EFAs of animal origin are directly associated with the occurrence of severe inflammatory diseases. The risk especially increases when acids enter the human body in large quantities. Thus, consuming large portions of fat can cause an acute inflammatory process; discomfort occurs within a short period of time after eating. It is also possible for cholesterol to accumulate in large quantities, which is dangerous for the cardiovascular system.
What should you eat?
First of all, you need a balanced diet that is rich in fatty acids. Healthy foods rich in EFAs - eggs, fish and organ meats - are preferable. In the daily diet, no more than ten percent of calories should be allocated to fatty acids, that is, fifteen or twenty grams. The best option is to consume fats that are included in foods that have a large number of beneficial properties, for example, seaweed, olives, nuts, fish and others.
Natural butter is considered a good choice; lard is recommended to be consumed salted in small quantities. Refined oils and their substitutes bring the least benefit. Unrefined oils cannot be subjected to heat treatment. In addition, you need to remember that fats should not be stored in the sun, open air or light.
Not all chocolates are created equal
So, if you eat quality chocolate (containing 60-70% cocoa) rather than confectionery chocolate made with lots of sugar and hydrogenated or partially hydrogenated oils, you are really helping your health.
The darker or more natural the chocolate, the higher the amount of polyphenols it contains. For comparison, dark chocolate has about two and a half times more antioxidants than milk chocolate. Other compounds found in dark chocolate also help strengthen the heart, lower cholesterol and prevent cardiovascular disease.
Plant sterols, compounds found in vegetable oils, grains and fruits, may help lower blood cholesterol levels. Many foods are fortified with plant sterols to improve their ability to lower bad cholesterol. Chocolate is one of those products that initially contain plant sterols.
The cocoa beans from which real chocolate is derived are a natural product and therefore contain many chemicals that can interact with the human body. For example, chocolate contains caffeine, and we all know what caffeine does in the body.
When is it recommended to increase EFA intake?
Saturated fatty acids are recommended to be consumed in a certain amount, but in some cases their dose can be increased. These include the following factors:
- severe diseases of the respiratory system;
- great physical activity;
- in the treatment of the digestive system;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- in the cold season, as well as for people who live in the Far North;
- some diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
For rapid absorption, fats must be consumed with vegetables, herbs and herbs. It is best to use natural products that contain them and also contain most of the beneficial components.