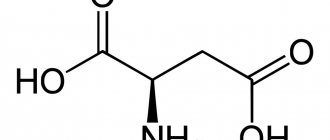
Isoleucine belongs to the amino acids with a branched molecular structure. There are three substances of this type in the human body: isoleucine itself, valine and leucine.
They are considered essential, since it is believed that a person is unable to survive without a regular supply of these substances. Branched-chain amino acids help maintain muscle glycogen stores (a storage form of carbohydrates that can be converted into energy) and prevent muscle protein breakdown during exercise. They also promote muscle recovery, maintain stable energy levels, and help regulate blood sugar levels.
general characteristics
Amino acids in the human body serve as the basis for the production of proteins, antibodies, are used to maintain the immune system, and also contribute to the production of hormones. Isoleucine is an essential amino acid, that is, the human body is not able to create it independently from other types of molecules, which, by the way, cannot be said about plants and microorganisms. They can produce this beneficial amino acid from pyruvic acid.
One of the main functions of isoleucine is the production of proteins. This means that the amino acid is the basis material for proteins. The significance of this amino acid is already evidenced by the fact that together with leucine and valine, isoleucine makes up about 35% of all muscle fiber in the body. This amino acid is an invariable participant in the process of energy exchange, including at the cellular level. In addition, isoleucine protects the body from excessive serotonin production by limiting tryptophan's access to brain cells.
Entering the human body along with food, isoleucine requires the presence of a certain amount of enzymes that contribute to the decarboxylation of the amino acid.
This is perhaps the most well-known amino acid. And all thanks to its ability to increase endurance, restore and heal muscle tissue after damage. It is especially important for athletes and bodybuilders, since its main role is to promote rapid recovery after severe physical stress.
The main reserves of isoleucine are concentrated in muscle tissue. This substance is necessary to prevent muscle atrophy and recovery after surgery or injury. This amino acid is also useful for increasing muscle protein levels. Although isoleucine does not promote glycogen synthesis, it can significantly increase the use of glucose during exercise.
Isoleucine affects the human body in several aspects simultaneously. It is necessary as an auxiliary substance for wound healing, at the same time it plays the role of a stimulant of the immune system, supplies additional energy and promotes the formation of hemoglobin.
Humans use isoleucine as a “building material” for two other types of molecules – glucose and the ketone body. Glucose, as a rule, enters the body along with food. The human body can create glucose from fats and amino acids, including isoleucine.
Amino acid functions and benefits:
- prevents the destruction of muscle proteins during physical activity;
- increases energy, increases endurance, helps restore muscle tissue;
- useful for maintaining glucose levels;
- ensures normal growth in children;
- supports the female body during menopause.
In addition, it has been experimentally proven that isoleucine has antibacterial properties. At least this ability is manifested in the intestines. The result of the study showed that 2 g of this substance can cure acute diarrhea in children.
Biological role of leucine
Leucine plays an important role in many processes. It performs the following functions:
- slows down catabolic processes in muscles;
- accelerates the synthesis of protein molecules, which helps build muscle mass;
- reduces blood sugar levels;
- provides a balance of nitrogen and nitrogenous compounds, which is necessary for protein and carbohydrate metabolism;
- prevents excess serotonin synthesis, which helps reduce fatigue and accelerate recovery after exercise.
A normal level of leucine in the blood strengthens the immune system, promotes wound healing, and accelerates recovery from injuries. The body uses it as a source of energy.
Reception features
In order for the body to get the maximum benefit from isoleucine, it is important to remember that it should be taken with two other branched chain amino acids (in combination with leucine and valine). The ideal proportion should be: 2 mg of leucine and valine per 1 mg of isoleucine.
People with kidney and liver dysfunction, disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, or an allergy to isoleucine should consult a doctor before taking a dietary supplement, as excessive consumption of the amino acid may aggravate their painful condition. In addition, nutritionists also recommend that people who consume a lot of protein “cut back” on isoleucine portions.
On the contrary, it is necessary to increase the consumption of the substance in case of damage to internal organs or muscles, people with psycho-emotional disorders, people with frequent hypoglycemia or anorexia. You can also get rid of muscle tremors using this amino acid.
Application in sports
During intense physical activity, the body requires more raw materials to build muscle fibers and extract energy. In sports, especially in strength sports, for example, bodybuilding, powerlifting, crossfit, taking leucine is a common practice.
It is necessary to reduce the intensity of catabolism and accelerate anabolic processes. Typically, the amino acid is taken in the form of sports supplements containing a BCAA complex. It contains three essential amino acids - leucine, isoleucine and valine.
In such dietary supplements, the ratio of components is 2:1:1 (leucine, its isomer and valine, respectively); some manufacturers increase the content of the former by two or even four times.
This amino acid is used by athletes both to build muscle mass and to lose weight. In addition, taking leucine increases energy potential, which is necessary for improving athletic performance.
Deficiency and excess: what are the dangers
Isoleucine deficiency causes symptoms in the body similar to hypoglycemia. A deficiency of the amino acid can result in headaches, dizziness, fatigue, depression, confusion, irritability, weakened immunity and muscle wasting. By the way, many people suffering from mental and physical disorders are diagnosed with insufficient levels of isoleucine.
Excess isoleucine is no less dangerous for humans. An amino acid in a particularly high concentration can, at best, manifest itself as a banal allergy. But there are also more serious consequences. For example, the so-called “sticky blood” (too thick), an increase in the concentration of ammonia and free radicals are also consequences of excessive saturation of the body with amino acids.
Who needs it and why?
Keeping to my promise to talk simply about complex things, I will not list how many amino acids there are and what important functions each of them is responsible for for the body.
Information about the significance of this army can be generalized and said that it is involved in the synthesis of protein - the main building material of the body, is responsible for the release of energy, the production of hormones and enzymes, affects the functioning of the nervous system, fat metabolism, immunity and beauty.
Even a generalized idea convincingly speaks of the significance of the substances we are discussing. Now it remains to understand where they come from in the human body. To do this, let's turn to the scientific classification. For our purpose, the one that divides organic compounds into two types is interesting:
- Replaceable ones that the body is able to reproduce itself.
- Essential , which are not synthesized in the body.
A person can only get the second group from food, so it is important to enrich the daily diet with foods that contain a sufficient amount of essential amino acids.
Amino acid in food
Almost all protein-rich foods can provide a person with isoleucine.
Animal sources: beef, chicken, liver, fish (sea), turkey, lamb, eggs, dairy products, cheese.
Plant sources: soy products, beans, peas, beans, chickpeas, rice, rye, corn, nuts, pumpkin seeds, lentils, buckwheat, peanuts, leafy greens (chard, spinach, watercress), cabbage, Borodino bread.
About 400 g of beef meat or the same amount of poultry can provide a daily portion of isoleucine. Vegetarians can get their daily requirement of amino acids from 350 g of beans or walnuts, or from 800 g of buckwheat. For this reason, people on a buckwheat diet need not worry about a possible isoleucine deficiency.
Best materials of the month
- Why you can't go on a diet on your own
- 21 tips on how to avoid buying stale food
- How to keep vegetables and fruits fresh: simple tricks
- How to curb your sweet cravings: 7 unexpected products
- Scientists say youth can be extended
And since these foods are traditional in the diet of most people, the risk of developing an amino acid deficiency is low. The exception is those whose body does not accept proteins from food, and people whose diet does not contain enough protein foods. In this case, there is a reason to resort to consuming isoleucine in the form of a bioactive food supplement. To achieve maximum benefits from taking the amino acid, it is important to take it in combination with valine and leucine.
Foods rich in amino acids
For the full functioning of our body, each person should know which products contain organic compounds:
- Eggs - they will give us BCAA, methionine and phenylalanine. They are absorbed with a bang, guaranteeing protein nutrition for the body.
- Dairy products provide humans with arginine, valine, lysine, phenylalanine and tryptophan.
- White meat – contains BCAA, histidine, lysine, phenylalanine and tryptophan.
- Fish is an excellent source of protein that is easily absorbed by the body. Rich in methionine, phenylalanine and BCAA.
Many people believe that protein can only be obtained from animal products. This is not true. Plant foods are also rich in it and are a source of organic compounds:
ARTICLES ON THE TOPIC:
- How many amino acids are there in a protein molecule?
- Essential amino acids for humans: list and in which foods they are contained
- Why are amino acids needed during training for women?
- Legumes are rich in phenylalanine, leucine, valine, methionine, tryptophan and threonine.
- Cereals - will give the body leucine, valine, histidine and isoleucine.
- Nuts and seeds – provide arginine, threonine, isoleucine, histidine and lysine.
I would like to highlight quinoa separately. This cereal is not as popular as the usual buckwheat and millet, but in vain.
Because per 100 grams of product there are about 14 grams of protein. Therefore, quinoa is indispensable for vegetarians and perfect for meat eaters. Let's also not forget about Orthodox fasts, which prohibit eating meat, fish and dairy products several times a year.
For convenience, I suggest familiarizing yourself with the list of products in the form of a table. You can
.
Side effects and harm
- In rare cases: allergic reactions - eczema, dermatitis, conjunctivitis.
- Amino acid intolerance: nausea, vomiting, sleep disturbance, headache, fever.
- An overdose of the substance causes nausea, vomiting, organic acidemia, a specific smell of sweat and urine, convulsions, respiratory and heart rhythm disturbances, and renal failure.
- Apathy, blood thickening, increased ammonia levels and general poisoning of the body are possible.
Who was the first to discover the amino acid isoleucine?
The first to obtain the amino acid isoleucine in 1904 was the German chemist Felix Ehrlich from fibrin, a protein that is formed in blood plasma. The scientist also conducted experiments trying to separate amino acids with branched side chains. As a result, he discovered that one part of isoleucine dissolves in 55 parts of methanol at 17º. This discovery later helped other researchers synthesize valine.
In the course of this work, Felix Ehrlich discovered that the compound he isolated was very similar in chemical composition to leucine, but differed from it in a number of chemical properties (solubility, melting point, solubility of copper salt).
Already in the middle of the 20th century, active use of the new substance in medicine began. Pharmaceutical companies began to produce isoleucine in large quantities. Today, the global production of this amino acid exceeds 150 thousand tons per year.
How to take in bodybuilding
The norm of isoleucine for a person is calculated by the formula: 50-70 mg per kilogram of weight.
BCAA contains isoleucine in an average amount of 1-2 grams per serving. The complex must be taken according to the instructions, without exceeding the maximum dosage.
When doing bodybuilding, the need for isoleucine increases to 4-6 grams per day.
- It is recommended to take one serving of BCAAs before training, half an hour or during, and a second serving immediately after completing the load.
- On rest days, you can take a serving of BCAAs in the morning, and a second during the day between meals.
Isoleucine Research: BCAA Applications
Immediately after its discovery, this branched-chain amino acid was studied extensively. Recently, large studies of leucine have been carried out abroad. Along with this, the complex use of BCAAs was studied. It turned out that leucine and valine slightly suppressed the absorption of glucose in the animals' bodies. At the same time, isoleucine normalized the absorption of carbohydrates by cells. In addition, it turned out that isoleucine, like leucine, stimulates the production of insulin in the body.
In another study, rats were given a supplement containing leucine, cysteine, methionine, valine, and large amounts of isoleucine. After a course of taking this drug by rodents, scientists conducted an oral test (blood test for sugar). It turned out that the blood glucose levels in the animals decreased. These studies have shown that the use of isoleucine alone or as part of BCAA supplements improves glucose uptake into muscles.
Contraindications
- Impaired excretion of isoleucine.
- Acidosis.
- Chronic kidney diseases.
- Diseases of the cardiorespiratory system and heart rhythm disturbances.
When taking isoleucine, it is prohibited to take vitamin B9 (folic acid), the amino acid reduces the concentration of B9 in the blood.
Although there is information that drugs with isoleucine are harmless to pregnant women and the fetus, it is still necessary to take any drugs strictly as prescribed by the doctor!