Minus 24 kg without leaving home! A Muscovite who lost weight in quarantine “blew up” Russia with her recipe
Vitamin B12 is an important element necessary for the normal functioning of all processes occurring in the body. To provide yourself with a daily dose of this substance, it is important to know which foods contain it.
Proper nutrition and a balanced diet will help you do without special expensive supplements and significantly help your own body.
General characteristics of vitamin B12
According to the chemical structure, vitamin B12 cobalamin has a complex structure. Presented in the form of a ring, inside of which a cobalt ion is located, with the help of which vitamin B12 performs its functions. It is otherwise called cyanocobalamin (this is its most common form). It is produced by archaea (protozoan microorganisms without a nucleus) and bacteria. Cobalamin dissolves quickly in water, so it is used for intravenous administration. After treatment at high temperatures it does not collapse.
In the human body it accumulates in the liver. With a reduced intake of the element from food, it is released from it and distributed to the organs. Intestinal microorganisms synthesize B12 in low quantities. When the intake of vitamin cyanocobalamin into the body is low, its active action begins.
The element is destroyed when there is a sharp change in the acid-base balance, or when a large amount of alcohol or drugs containing female sex hormones enter the body.
The benefits and harms of a microelement depend on its concentration in the body. To have a positive effect, B12 must be within the age norm.
What foods contain vitamin B12 - list of foods
The human body is not able to produce this vitamin on its own, so it is so important to know which foods contain it. To avoid the above symptoms and improve your health, it is important to add this vitamin to your diet daily.
So, foods rich in B12 (amount of mcg per 100 g of product):
- beef (especially beef liver - 60 mcg);
- pork - 30;
- chicken - 16.5;
- lamb - 2;
- mackerel, sardine, salmon - 12;
- octopus - 20;
- cheeses - 1-1.4;
- eggs - 0.5;
- sour cream - 0.4;
Products that contain vitamin B12 are mainly of animal origin, since it is preserved much better in the body of living creatures.
Plant products
Vitamin B12 significantly lower quantities in food products of plant origin than in meat. This is due to the peculiarity of its synthesis.
The content of the substance in plant foods depends on the conditions of its growth: soil, development of the system of microorganisms, etc. It can be contained in kelp, apples , as well as Asian cuisine: tofu, tempeh, miso.
This microelement is found in mushrooms: champignons 0.1-0.4 mcg.
Vitamin B12 is most found in food artificially fortified with it, if we talk about food of plant origin. People who don't eat meat or dairy can also get it from brewer's yeast, breakfast cereals and special supplements.
Beneficial properties and its effects on the body
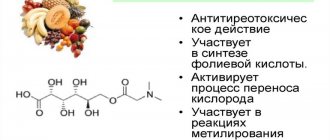
How is B12 useful, what does it affect, what are the indications for taking medications high in vitamin content:
- Increasing cellular composition by stimulating the formation of DNA and RNA in cells. The action occurs together with carotene, which turns into an active form, becoming involved in metabolic processes.
- Increasing the number of red blood cells, helping to eliminate anemia, hypoxia (oxygen starvation) in tissues.
- Enhanced regeneration (renewal) of mucous membranes, blood cells, and skin.
- Formation of nerve fibers, conduction of nerve impulses through them. Stimulates the function of nerve cells, improving memory, attention, concentration. Prevents premature death of neurons, reducing the risk of senile dementia.
- Eliminates insomnia. Helps the body get used to sudden changes in time of day. The action occurs due to the production of methionine.
- Acceleration of fat, carbohydrate, protein metabolism. Increases energy levels in cells.
- For children, vitamin B12 contributes to normal growth of the body. By accelerating metabolism, appetite improves.
- Strengthening the immune response to the introduction of a pathogenic microorganism (bacteria, fungi, protozoa).
- In men, it stimulates sperm production.
- Women during pregnancy need to double their dose of vitamin B12 along with folic acid for normal development of the fetal nervous system.
Where does B12 come from in herbivores?
These creatures have two sources of B12. Let's simulate such a situation for ourselves. The cow eats grass. And along with unwashed greens, various bacteria enter the body, as well as worms, which are also food of animal origin.
Yummy!..
Moreover, (it’s awkward to write about this, but since we are discussing such a serious issue, we have to “open all cards”!) Vegetarian animals in their natural habitat obtain B12 from their own feces. Let's call this phenomenon the scientific term - “coprophagia”.
Scientists have proven the fact that coprophagous animals (dogs, rats, mice, monkeys, rabbits, chinchillas) try to get the nutrients they need in this way.
In young individuals of these animals, the intestinal microflora is not yet able to fully break down plants. This is why semi-digested food (in other words, excrement) is a valuable source of vitamins and minerals, including B12.
For people, this option for obtaining this vitamin is, of course, not acceptable. But those of our ancestors who did not yet know what fire was hardly had any idea about sanitary and hygienic standards. In other words, washing fruits and vegetables has played such a cruel joke on humanity. In addition, few people now fertilize their crops with manure, but in vain!
But let's return to our vitamin B12. It turns out that vegans and raw foodists cannot obtain it by any natural means. Marketers have taken this fact into account and with great enthusiasm produce various ethical products enriched with B12: breakfast cereals, snacks, bread, cereals and other industrial items. You can easily find them in large supermarkets and online stores with the appropriate focus.
However, a person who wants to eat only live foods is unlikely to buy the listed products. What's the solution then? There is only one - look for natural vitamin complexes and preparations with B12.
Back to contents
B12 preparations
If cyanocobalamin deficiency is caused by an alimentary (food) factor, doctors advise applying a diet, giving advice on the nutritional system, including meat, fish, and dairy products. If the cause is pregnancy or illness (anemia, inflammation of the liver or kidneys, neuralgia, malabsorption in the intestine), medications are used.
Doctors advise using multivitamin complexes in tablet form. Injections are stressful for the body; they only administer a few B vitamins.
- Cyanocobalamin (B12). Indicated for patients with anemia, inflammatory liver diseases, neuralgia. It is administered by injection (subcutaneous, intravenous, intralumbar). Sold in 1 ml ampoules containing a solution with the element. Increases the number of red blood cells, speeds up metabolism. Activates the blood coagulation system. Reduces the amount of cholesterol. Increases the regenerative ability of tissues.
- Cobamamide. It is a metabolic agent that is a derivative of cyanocobalamin. Available in ampoules. Accumulates in the liver and takes part in enzymatic reactions. Necessary for the synthesis of methionine, RNA, DNA. Used for nervous disorders and decreased muscle function. Stimulates food reflexes. Normalizes the pH of biological fluids (blood, urine). Cobamamide is administered intravenously and intramuscularly.
- Milgamma. Contains several groups of vitamin B. It transforms into an active form inside cells, where it causes a therapeutic effect. It is used for disorders of the nervous system (myalgia, radiculopathy).
- Neuromultivitis. Used to treat various diseases of the nervous system. The drug rarely causes side effects: nausea, dizziness, skin rashes. Neuromultivit is not prescribed to pregnant and lactating women, since it has recently appeared on the pharmacological market. Take in tablet form, 2-3 times a day.
- Multi-Tabs. Contains all B vitamins. It is easily absorbed in the body, completely satisfying. Used in tablet form during pregnancy, lactation, children over 10 years of age and adults.
These drugs are taken in strict dosages. Exceeding B12 levels increases the risk of blood clots. This is fraught with stroke, heart attack, and massive blockage of blood vessels inside organs.
Causes and symptoms of deficiency
The body excretes cyanocobalamin in bile. Its destruction takes a long time.
A lack of vitamin B12 occurs with a long-term refusal of foods containing it - meat, liver, fish, milk, eggs. The preservative E200 can also cause the destruction of cyanocobalamin.
The reason for the deficiency is a violation of its absorption in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - atrophic gastritis, enterocolitis, helminthic infestations.
Regular deficiency for 5-6 years is the cause of the development of B12 deficiency anemia. The pathological condition disrupts the formation of deoxyribonucleic acid, the metabolism of fatty acids, reduces the level of red blood cells and hemoglobin, and affects the gastrointestinal tract and central nervous system. This type of anemia causes diseases of the liver, kidneys, and blood.
Other causes of B12 deficiency anemia are taking medications for seizures, birth control, and excessive consumption of foods containing yeast.
Diseases of the stomach, biliary tract, and intestines cause secondary vitamin deficiency due to a decrease in the production of cyanocobalamin by intestinal microflora.
Even with a sufficient intake of foods containing vitamin B12, it is poorly absorbed if the body does not produce enough intrinsic factor (Castle factor) - an enzyme that interacts with the inactive form of cyanocobalamin from food and converts it into the active (digestible) form.
In old age, Castle factor is practically not produced due to reduced synthesis of acids in the body. In this case, the doctor prescribes injections instead of cyanocobalamin tablets. Including acidic plant foods - berries, fruits, vegetables - in the diet helps maintain the required level of acid production in the body.
Some vitamins are antagonists. Therefore, you cannot mix vitamins B12 and B1, B2, B6, and ascorbic acid in one syringe - they are destroyed by the cobalt ion, which contains the cyanocobalamin molecule.
The following signs indicate vitamin B12 deficiency:
- increased fatigue, drowsiness, depression;
- headache, dizziness;
- irritability;
- lack of appetite;
- numbness of the limbs;
- weakening and hair loss;
- grayish or yellowish complexion.
Excess cyanocobalamin
Eating foods containing vitamin B12 does not cause excess. In case of an overdose of vitamin complexes, allergic reactions are possible.
An excess causes nervous excitement, rapid heartbeat (tachycardia), and pain in the heart area.
Excess is possible with chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, chronic renal failure, leukemia.