What is calcium and why is it important?
Calcium is a mineral that the body needs for many functions, including building and maintaining bones and teeth, blood clotting, transmitting nerve impulses, and regulating heart rate. About 99% of calcium in the body is stored in bones and teeth, the remaining 1% is found in blood, muscles and other tissues.
Experts emphasize the importance of consuming enough calcium. The general recommendation is about 1,000 mg per day for adults 19 to 50 years of age . This amount is optimal to maintain normal body function and also reduce the risk of osteoporosis, a condition that makes bones weak and brittle.
According to a Harvard University study, the body gets the calcium it needs in two ways.
- The first is to eat foods or supplements that contain calcium.
- The second is to extract calcium reserves from the body, primarily from the bones. This is done to restore the level of the mineral in the blood and support body functions that depend on calcium. Borrowing from bones occurs “on credit”: if a sufficient amount of the mineral subsequently enters the body, bone tissue is restored.
However, if a person's diet is low in calcium, the process of bone loss continues. This is why osteoporosis occurs even in young people.
Since there is very little of the mineral in the blood, a blood test for calcium would not be the best option. You can donate blood and monitor the level of parathyroid hormone , an increase in which indicates a deficiency of this microelement.
Signs of calcium deficiency in the body
The mineral is also responsible for the proper functioning of the body, is involved in blood clotting, normalizes the excitability of nervous tissue and muscle contraction. It also supplies nutrients to the cells of the human body, regulates acid and alkaline balance. Therefore, it is necessary to regularly consume foods that contain calcium.
Let's look at the signs of a lack of this mineral in the human body:
- Severe fatigue.
- Hair becomes dry and dull.
- Nails break.
- Skin problems.
- Poor dental condition.
- Muscle spasms, cramps at night.
- Spastic colitis.
- Constipation.
- Insomnia.
- Numbness of the limbs.
These are the very first signs of a mineral deficiency. The above problems can still be solved by consuming foods containing calcium. The longer the body experiences a lack of a mineral, the worse the consequences. Let's look at the more serious consequences of shortages:
- Osteoporosis. With this disease, the strength of bone tissue decreases greatly, which leads to bone fractures and age-related deformities. To prevent it, it is important to undergo examinations, monitor blood counts and take tests.
- Contraction of the heart muscle. This leads to improper functioning of the heart and surges in blood pressure. Also to heart failure.
- If there is a lack of calcium-containing foods, blood clotting may be impaired. The gums begin to bleed.
- Immunity declines. A person begins to get sick often, and chronic diseases worsen.
- Calcium deficiency in children is dangerous. Since at an early age the bone skeleton is not yet fully formed, this leads to deformation. Therefore, the mineral is necessary for proper structure.
- Calcium plays an important role for pregnant women. The development of the baby’s muscle, bone and nervous system depends on its content.
Features of assimilation
The process of calcium absorption in the body involves many vitamins, minerals and acids, which can either improve or impair absorption. The following have a negative effect on mineral absorption:
- age (children absorb 60%, adults - 45-50%, and in adulthood - 15-20%);
- oxalic acid, which is part of vegetables, for example, spinach, rhubarb, sprouted wheat grains;
- phosphoric acid, found in carbonated drinks;
- refined sugar, especially in combination with fats;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (chronic pancreatitis, constipation, cholelithiasis, reduced stomach acidity);
- dysfunction of the parathyroid gland (hypoparathyroidism);
- decreased production of sex hormones.
To improve calcium absorption, it is necessary to ensure a regular intake of vitamins and minerals such as:
- Vitamin D - increases the number of macronutrient transport proteins from the intestines into the bloodstream. Vitamin D is produced in the body under the influence of sunlight and also comes from food (milk, fish, butter, meat).
- Vitamin C - promotes the beneficial effects of calcium on the condition of the skin, nails, hair and cartilage tissue.
- Magnesium – ensures even distribution of the mineral, increasing bone density. Sources of magnesium are cereals (buckwheat, millet, oatmeal) and nuts (almonds, cashews).
- Phosphorus – strengthens bones and teeth as a result of the formation of a crystalline molecular compound with calcium. The largest amount of phosphorus is found in meat, fish, seeds, eggs and cheese.
Also, the process of calcium absorption is beneficially affected by physical activity, for example, running or strength exercises, which stimulate bone formation processes and contribute to the uniform strengthening of bone tissue.
It should be remembered that not only a deficiency, but also an excess of these nutrients can negatively affect calcium metabolism, for example, lead to the formation of kidney stones or the deposition of salts in the joints.
Daily value of calcium
- Children under 3 years old - 600 mg
- Children from 4 to 10 years - 800 mg
- Children from 10 to 13 years old - 1000 mg
- Adolescents from 13 to 16 years old - 1200 mg
- Youth 16 and older - 1000 mg
- Adults from 25 to 50 years - from 800 to 1200 mg
During pregnancy
Lack of calcium during pregnancy can lead to the development of gestosis - a dangerous disease accompanied by high blood pressure, leading to impaired fetal development in the third trimester of pregnancy, as well as to the destruction of teeth and bones, and is accompanied by muscle cramps, swelling, and hair loss.
In cases where calcium from food is not properly absorbed, calcium single preparations, combined calcium preparations with vitamin D, magnesium and zinc, or multivitamins with a complex complex of microelements are prescribed.
In old age
After 50 years of age, the risk of developing osteoporosis increases, a disease that causes a decrease in the mass and density of bones, which become brittle and prone to frequent fractures as a result of a lack of calcium. To prevent osteoporosis it is necessary:
- use a calcium diet;
- engage in physical exercise to maintain stress on the bones, stimulating mineralization;
- take vitamin complexes;
- reduce the amount of table salt;
- reduce meat consumption, as the mineral is used in the process of protein breakdown.
https://youtu.be/G_RGB7RGsh0
Fruits and berries
Fruits are ideal plant-based foods. There are opinions that the human body initially, in primitive times, was “tuned” only to feed on them. Today, “fruit eating” is very popular, when a person consumes exclusively this food. By the way, there are about 300 types of such products in the world. Fruits contain large amounts of water, vitamins, and carbohydrates. Fructose, the sugar found in them, is perfectly absorbed. It enriches the body with useful substances. Based on the content of vitamins, sugar and microelements, fruits can be divided into several categories:
- Sweet: bananas, dates, papaya, etc.
- Semi-acid: apricots, pears, apples, plums, etc.
- Sour: tangerines, oranges, lemons, pineapples, etc.
It is best if all three categories of fruits are present in the diet. But thermally processed fruits (jams, jams, compotes, etc.) are many times inferior to their fresh counterparts in quality and quantity of nutrients. You should completely stop using them. Berries are very similar to fruits in their composition, but they contain much more amino acids. The most useful: lingonberries, cranberries, currants, blueberries, blueberries, strawberries, cherries and raspberries.
Calcium paradox
It is generally accepted that the best source of calcium is milk, but this is far from true. Scientists have recorded an amazing phenomenon: the incidence of osteoporotic fractures was highest in countries where they consumed the most dairy products, calcium and protein. This phenomenon has been described as the "calcium paradox". The effect may have been due to excess exposure to animal protein, which may have outweighed the benefits of calcium intake.
An extensive 12-year study of 78,000 women found that those who drank more milk had more broken bones than those who drank it infrequently. Another study sought to establish a link between veganism and bone loss in postmenopausal women.
For comparison, we took two female groups with different types of diets: one was vegan, and the other was omnivore. The study results showed that there was no difference in bone loss between the groups. In addition, no significant differences were recorded in terms of height, weight or age of the subjects.
What are proteins?
Twenty amino acids are divided into two main groups: essential and non-essential.
Essential amino acids:
- valine
- methionine
- leucine
- isoleucine
- phenylalanine
- lysine
- tryptophan
- threonine
- histidine
Essential amino acids:
- arginine
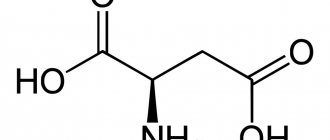
- glutamic acid
- glycine
- aspartic acid
- serine
- cysteine
- tyrosine
- alanine
- proline
- glutamine
- asparagine
Calcium in plant foods
For many years we have been told that osteoporosis is a disease of milk deficiency, but no one tells us that you can get a lot of calcium from a balanced vegetarian diet. It is easy to saturate your body with this mineral by eating enough legumes and leafy greens. Here is a list of plant products with the richest calcium content.
- Legumes (beans, soybeans, peas, lentils)
- Seaweed
- Leafy greens (kale, vegetable tops)
- Cabbage (broccoli, Chinese cabbage, white cabbage)
- Nuts (almonds)
- Seeds (sesame, poppy, flax, chia, sunflower)
- Oranges
- Dried fruits (raisins, prunes, figs, dried apricots)
- Dried herbs (dill, basil, marjoram, thyme, oregano, mint, rosemary)
Legumes
Legumes such as beans and lentils contain significant amounts of fiber, protein and micronutrients. They also boast high amounts of iron, zinc, folic acid, magnesium and potassium. Some varieties are also rich in calcium.
Winged beans have the highest amount of calcium among legumes. A 200-gram serving of cooked winged beans contains 184 mg of calcium, which is 18% of the RDI (19).
White beans are also a good source of calcium - a 200g serving of cooked white beans contains 146mg of this mineral, which is 14% of the RDI. Other beans and lentils contain lower amounts of this mineral, at 4-6% of the RDA per serving (20, 21, 22).
Research shows that legumes may help lower LDL cholesterol (“bad cholesterol”) and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes (23).
Summary:
Legumes are highly nutritious, and one 200 gram serving of cooked winged beans provides 24% of the RDA for calcium.
Seaweed
Adding seaweed to your diet is another way to increase your calcium intake.
Wakame—the variety typically eaten raw—provides about 126 mg or 12% of the DV per cup (80 grams). You can find it in most Asian supermarkets or sushi restaurants.
Seaweed, which can be eaten raw or dried, is another popular option. One cup (80 grams) of raw kelp—which you can add to salads and main dishes—provides about 14% of your calcium requirement. Dried kelp flakes can also be used as a seasoning.
However, seaweed may also contain high levels of heavy metals. Some varieties, such as spirulina and chlorella, may contain excessive amounts of iodine per serving (18, 19).
While iodine is essential for proper thyroid function, consuming too much can be harmful. For these reasons, seaweed should not be consumed too often or in large quantities (20).
Some types of seaweed are rich in calcium. However, some seaweed may also contain heavy metals and excessively high levels of iodine, both of which can have negative health effects.
Vegetables
Calcium is found primarily in green leafy vegetables such as parsley, cabbage, spinach, basil, and broccoli.
Basil, both fresh and dried, differs from other vegetables in its large amount of calcium, as well as the presence of mineral, essential, tannins and acids. The benefits of basil include a beneficial effect on the functioning of the nervous, cardiovascular and skeletal systems.
Products Ca (mg) per 100 g
| Basil | 370 |
| Parsley | 245 |
| Olives | 96 |
| White cabbage | 210 |
| Kale | 150 |
| Broccoli | 105 |
| Green onion | 98 |
| Garlic | 181 |
| Stewed spinach | 141 |
| Sun-dried tomatoes | 110 |
| Arugula | 160 |
Some fruits
Some varieties of fruit contain good amounts of minerals. Therefore, they can also be considered plant sources of calcium.
For example, raw figs provide 18 mg in 1 piece - or about 2% of the norm. Dried figs offer slightly less, at about 13 mg.
Oranges are another fruit high in calcium. They contain about 48–65 mg, or 5–7% of the value for a medium-sized fruit, depending on the variety.
Blackcurrants, blackberries and raspberries complete the list.
Blackcurrants contain about 65 mg of calcium per cup (110 grams)—or about 7% of the normal value. While blackberries and raspberries give you 32-44 mg per cup (145 grams and 125 grams, respectively).
In addition to calcium, these fruits also offer a good dose of fiber, vitamin C and a variety of other vitamins and minerals.
Figs, oranges, blackcurrants and blackberries are worth adding to your diet. These are fruits high in easily digestible calcium.
Nuts and seeds
Seeds and nuts are foods rich in calcium, as well as protein, fats (Omega 3), copper, iron and manganese, and are beneficial for heart disease, bone disease, and insulin resistance.
Poppy seeds are high in calcium, manganese, chromium, copper, proteins, polyunsaturated fatty acids and vitamins C, E, D, K and group B. Poppy prevents demineralization of bone tissue and tooth decay, and also promotes bone restoration after fractures.
Products Ca (mg) per 100 g
| Sesame | 900 |
| Poppy | 1450 |
| Cashew | 290 |
| Almond | 250 |
| Pine nuts | 250 |
| Brazilian nut | 160 |
| Pistachios | 130 |
| Hazelnut | 123 |
| Sunflower seeds | 100 |
| Caraway | 789 |
| Mustard seeds | 266 |
| Mustard seeds | 245 |
| Flax seeds | 255 |
Spices and herbs
| No. | Name of herbal product | Amount of calcium contained in the product (per 100 g) |
| 1. | Fresh thyme | 405 mg |
| 2. | Dried spearmint | 1488 mg |
| 3. | Ground black pepper | 443 mg |
| 4. | Ground savory | 2132 mg |
| 5. | Fresh coriander | 68 mg |
| 6. | Dried marjoram | 1990 mg |
| 7. | Fresh parsley | 138 mg |
| 8. | Dried thyme | 1890 mg |
| 9. | Ground red pepper | 148 mg |
| 10. | Dried dill | 1784 mg |
| 11. | Fresh curly mint | 199 mg |
| 12. | Celery seeds | 1767 mg |
| 13. | Fresh dill | 208 mg |
| 14. | Ground sage | 1652 mg |
| 15. | Ground white pepper | 265 mg |
| 16. | Dried oregano (oregano) | 1597 mg |
| 17. | Grape leaves | 363 mg |
| 18. | Dill seeds | 1515 mg |
| 19. | Ground cloves | 632 mg |
| 20. | Dried cilantro | 1246 mg |
| 21. | Cumin seeds | 689 mg |
| 22. | Fennel seeds | 1196 mg |
| 23. | Coriander seeds | 709 mg |
| 24. | Dried parsley | 1140 mg |
| 25. | Bay leaf | 834 mg |
| 26. | Dried tarragon | 1139 mg |
| 27. | Ground cinnamon | 1102 mg |
Cereals
| No. | Name of herbal product | Amount of calcium contained in the product (per 100 g) |
| 1. | Wheat bread | 138 mg |
| 2. | Wheat bread toast | 165 mg |
| 3. | Whole grain wheat bread | 107 mg |
| 4. | Wheat bread with germ | 89 mg |
| 5. | Wheat bran | 73 mg |
Plant-based protein: benefits and advantages
To summarize the previous conversation, we summarize all the benefits of protein obtained from plant products:
- amino acids inside the protein have a positive effect on the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- protein strengthens the immune system, increasing resistance to irritants;
- stimulates the production of “good” cholesterol in the blood, reducing “harmful” (this cannot be said about animal protein);
- helps restore intestinal microflora;
- maintains normal weight;
- improves metabolism due to easy digestibility;
- does not produce toxins;
- does not cause allergic reactions;
- has a beneficial effect on the condition of the epithelium - skin and hair;
- resistant to heat treatment;
- In addition to protein, the products contain vitamins and microelements that enhance their benefits and also help the immune system, heart, blood vessels, nervous system and bone tissue.
Plant protein is indicated for the prevention of atherosclerosis, obesity, and diabetes. In addition, the presence of antioxidants in protein products also suggests that, to some extent, protein protects against cancer.
Protein is vital for cells, and if it is lacking, a person may feel unwell. Among the symptoms, doctors name muscle weakness, dizziness, memory loss, apathy, irritability and a general decrease in immunity. Of course, these symptoms are not particularly specific, and if they occur, you should consult a specialist.
You also need to take into account that there is a daily protein intake for an adult. It is equal to 60–120 grams and includes both plant and animal protein. You should not overuse these products, as this can harm digestion. In addition, the norm depends on the individual characteristics of the body, age and type of activity of the person. For example, for teenagers this figure will be 210–270 grams, because their body is actively developing.
Green smoothies
Green smoothies are a discovery in themselves!
They were first invented by Victoria Butenko, a raw foodist with 12 years of experience. She had been looking for a long time for a method by which she could eat a lot of greens, since greens are one of the healthiest foods on Earth for humans.
Here we consider greens as a source of calcium; let me remind you which greens contain calcium:
- 100 grams of basil contain 370 mg of calcium,
- 100 g parsley – 245 mg
- 100 g of celery – 240 mg
- 100 g dill – 223 mg
- 100 grams of watercress – 180 mg
Mix all this in smoothies with fruits or berries and you will get a wonderful vitamin drink that is full of calcium.
Green smoothie recipe
- We take 4 small bunches - 2 parsley, 2 dill, two celery sprigs (you can throw them in the form of greens, if you have them), put them in a blender.
- Add some kind of fruit, I like bananas and oranges, if desired, it can be grapefruit or something else.
- So, put 3-4 bananas and 1 peeled orange into the blender
- Add 1-1.5 glasses of water
- Mix everything in a blender for at least 2 minutes.
- If you do everything like I did, you will get about 1 liter of cocktail.
- Believe me, it's very tasty!
Cereals
Cereals are also food products of plant origin. This group includes wheat, rye, oats and other types. They have been used by humans for many centuries. At first they were cooked whole, then they began to grind and bake various baked goods. But over time, more and more research scientists are coming to the conclusion that cereal porridges cause fermentation, and excessive consumption of bread contributes to weight gain.
Of course, we will not be able to completely eliminate these plant-based foods from our diet. But it’s worth using some tips:
- Grains must be consumed unprocessed. That is, the diet should not contain any cereals, semolina, etc.
- You must combine them with vegetables and fruits. This refers to the correct balance of these products in the diet.
- It is better to eat cereals in the morning. They contain a lot of carbohydrates necessary for normal activity and vigor throughout the day.
Vitamin salad of white cabbage and broccoli
- We cut the onion into half rings , preferably red, but this is not important. Place the onion in a bowl, rinse it several times with cold water, pour in lemon juice and honey, pepper with hot red pepper and let it stand while we make the salad.
- Finely chop young (loose) white cabbage , leaves only, sprinkle a little sea salt on top, squeeze the cabbage with your hands so that it gives a little juice, softens and salts. Place in a deep bowl.
- Finely chop the broccoli - both the stem and the leaves, raw, not boiled. As it is! Put it in a bowl.
- Finely chop the tomatoes into squares.
- We cut the garlic (if you like it spicier), but this is not for everybody and is optional.
- Finely chop 1 bunch of dill .
- In a separate bowl, mix lemon juice , about half a lemon and honey. Stir until the honey is completely dissolved, then add more hot red pepper. You can mix it all with a blender.
- Then we put it in a bowl with the cabbage - first the broccoli, then the tomatoes, then the onions, garlic, dill and pour it all over with sunflower oil and our lemon juice.
- Mix everything with your hands so that the sauce covers the entire salad.
- Throw a good pinch of raw sunflower seeds on top.
Sources
- https://myhandbook.com/gde-iskat-kalcij-v-rastitelnyx-produktax/
- https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5a0c331186516515bab4e163/5daafc643639e600af7a4761
- https://zabolevanija.net/produkty-s-vysokim-soderzhaniem-kaltsiya/
- https://aif.ru/food/diet/zdorovye_kosti_v_postnye_dni_rastitelnye_istochniki_kalciya
- https://foodismedicine.ru/15-produktov-soderzhashhih-kaltsij-v-bolshom-kolichestve/
- https://foodformula.ru/pitanie/top-10-rastitelnyh-istochnikov-kaltsiya/
- https://BestLavka.ru/tablica-soderzhanija-kalcija-v-rastitelnyh-produktah/
- https://kerimovanatalia.ru/kalciy-rastitelnogo-proiskhozhdeniya/
[collapse]