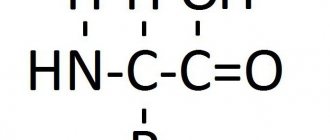Most diseases are associated with metabolic disorders in the body, the main cause of which is a deficiency of potassium and magnesium. Lack of microelements leads to weakness and nervous excitability, excess weight gain, insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle, etc. “Aspark” helps to replenish the deficiency of potassium and magnesium. The compounds of organic substances and aspartic acid included in the drug have a complex effect.
The drug has a beneficial effect on the myocardium and heart muscle, helps normalize blood pressure, metabolism and gastrointestinal function. "Asparkam" is recommended for children, adults and pregnant women.
Composition and release form
The drug is produced under several names, each of which necessarily contains the word “asparkam”: “Asparkam-farmak”, “Asparkam-ROS”, “Asparkam-L” and others. This means that they all have the same dosage formula, but are produced by different manufacturers. Release forms may also differ.
Chemical composition:
- Tablets in a package of 10-50 pcs. 1 tablet contains active substances: magnesium aspartate 175 mg, potassium aspartate 175 ml. The tablet is white, flat, and has a dividing line along its diameter.
- Solution in ampoules for injection of 5, 10 and 20 ml. Substance in liquid form: magnesium and calcium ions in the aspartate compound.
- The liquid form of the drug is a solution for a dropper. The composition is identical to the solution for injection and is available in tubes of 200 and 400 ml.
Excipients are: corn starch for tablets (as a binder), distilled water and sorbitol are added to solutions.
Asparkam's analogs
Such complexes include:
- Potassium and magnesium aspartate (Asparticacid);
- Aspangin;
- Asparkad;Asparkam-L;
- Asparkam-AKOS;
- Asparkam-Ros;
- Asparkam-UBF;
- Asparkam-Farmak;
- Asparkam-Verein;
- Pamaton;
- Panangin.
All of these drugs contain the same main active ingredients. The names are different due to different manufacturers.
Video: “Asparkam or Panangin?”
Therapeutic effect
The active ingredients of the drug are potassium and magnesium. The main effect of Asparkam is the replenishment of ions of organic substances and microelements, which have a positive effect on metabolism. The mineral elements K and Mg play an important role in the functioning of internal organs and the entire body:
- Magnesium (Mg). It is one of the main elements responsible for bone formation, energy and carbohydrate metabolism. It has a sedative effect, due to which it is successfully used in neurology and for the treatment of mental illnesses. The intensity of blood supply to the heart muscle depends on the amount of magnesium ions in the blood. In addition, this macroelement tends to enhance metabolic processes.
- Potassium (K). All intracellular metabolic processes in the body occur with the direct participation of this macroelement. Potassium salts affect the formation of soft tissues and their condition. It is deservedly called the “heart” element - the frequency of contraction of the heart muscle and fibers in the myocardium depends on its presence in the blood. Potassium in the blood provides oxygen to the brain and maintains blood pressure levels. The metal also prevents the accumulation of sodium salts in blood vessels, which are one of the main causes of atherosclerosis.
The drug "Asparkam" gives a mixed therapeutic effect, which is due to the combination of microelements. The compound of magnesium and potassium is part of a number of enzymes that regulate glycolysis and maintain cellular concentration at the required level.
Aspartate helps K and Mg ions penetrate the cell membrane better. “Asparkam” is well absorbed and easily excreted through the gastrointestinal tract, urinary system and sweat glands.
The active effect of the drug is achieved within 2 hours after administration.
Why do you need to take Asparkam tablets every day and constantly?
The human body consists of many elements that are presented in the periodic table. The ratio in which they are found in the body affects its vital functions. The same applies to the content of potassium and magnesium in the body, that is, without these components the body will not be able to function normally.
The balance of water and salt in the body depends on the content of potassium and sodium in the body. For this reason, potassium-containing drugs should be used with extreme caution. After all, an excess of potassium can upset this very balance, and this can lead to the most unforeseen consequences.
Potassium is involved in the transmission of impulses from nerve endings, and the state of the heart muscle largely depends on it.
If the potassium content in the body is insufficient, this can cause the development of cardiovascular pathology, and this in some cases even ends in the death of the patient.
If a person has an imbalance of magnesium and potassium in the body, this can lead to hypertension and sometimes stroke. Magnesium transmits nerve impulses, takes part in energy production, and also synthesizes protein. Even by the width of the lumen and the tone of the tissue in the muscles, one can judge how much magnesium is contained in the body.
Magnesium has a sedative effect and is often used by neurologists and psychiatrists. Therefore, the use of magnesium should be careful, especially in cases where it is necessary to concentrate.
In what cases is it recommended?
An insufficient amount of Mg in the body leads to disruption of mineral metabolism, the functioning of the adrenal glands, and an increase in the risk factor for the development of the initial stages of diabetes mellitus and cancer. A constant lack of magnesium ions in the blood leads to diseases of the cardiovascular system and disturbances in the functioning of the genitourinary system.
A deficiency of another equally important element, potassium, leads to rapid loss of energy, weakness and the development of chronic fatigue syndrome. As a result of a lack of K, hypokalemia develops - a condition that contributes to the development of renal failure, the appearance of arrhythmia and tachycardia.
Look at the same topic: An innovative product on the market of bioactive supplements B lite
The use of Asparkam helps to quickly eliminate the lack of important minerals and stabilize the functioning of the body and internal organs.
The drug is also recommended for use as a preventative measure, especially in cases of large fluid losses and insufficient intake of essential substances with food. Most often this can be observed during strict diets, constant stressful situations, intensive growth, recovery and during pregnancy.
Modern Pharmaceuticals of Russia
Asparkam, tablets 175 mg + 175 mg
Trade name: Asparkam International non-proprietary or generic name:
Potassium and magnesium aspartate.
Dosage form:
Tablets
Description:
Round flat-cylindrical tablets of white color with a chamfer and a score.
ATC code:
A12СХ
Pharmacotherapeutic group:
Potassium and magnesium preparation.
Pharmacological action:
The most important intracellular cations of potassium (K+) and magnesium (Mg++) play a key role in the functioning of numerous enzymes, in the formation of bonds between macromolecules and intracellular structures and in the mechanism of muscle contractility.
The intra- and extracellular ratio of potassium, calcium, sodium and magnesium ions affects myocardial contractility. Endogenous aspartate acts as a conductor of ions: it has a high affinity for cells, due to the slight dissociation of its salts, ions in the form of complex compounds penetrate into the cell. Magnesium aspartate and potassium aspartate improve myocardial metabolism. Lack of magnesium/potassium predisposes to the development of arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries, arrhythmias and metabolic changes in the myocardium. Pharmacokinetics
Potassium and magnesium aspartates are intensively absorbed in the intestine, mainly in the small intestine.
Excreted by the kidneys. Indications for use:
To eliminate potassium and magnesium deficiency as part of combination therapy for various manifestations of coronary heart disease (including acute myocardial infarction);
chronic heart failure; heart rhythm disturbances (including arrhythmias caused by an overdose of cardiac glycosides). Contraindications:
Hypersensitivity to any of the constituent components of the drug, acute and chronic renal failure, hyperkalemia, hypermagnesemia, Addison's disease, atrioventricular block I-III degree, shock (including cardiogenic) (blood pressure less than 90 mm Hg), violation amino acid metabolism, myasthenia gravis, hemolysis, acute metabolic acidosis, dehydration state, age under 18 years (efficacy and safety have not been established).
With caution:
Pregnancy (especially in the first trimester of pregnancy) and breastfeeding.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding:
Use is possible if the potential benefit to the mother outweighs the possible risk to the fetus.
Potassium and magnesium aspartate passes into breast milk.
If it is necessary to take the drug during breastfeeding, breastfeeding should be stopped. Directions for use and dosage:
Before use, you should consult your doctor.
Take orally, without chewing and with plenty of water.
Asparkam should be taken after meals, because... the acidic environment of the stomach reduces its effectiveness.
Adults are prescribed 1-2 tablets 3 times a day.
The course of treatment is 3-4 weeks. If necessary, the course is repeated. Side effects:
Possible nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, discomfort or burning sensation in the epigastric region (in patients with anacid gastritis or cholecystitis), atrioventricular block, paradoxical reaction (increased number of extrasystoles), hyperkalemia (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, paresthesia), hypermagnesemia (facial redness, thirst, decreased blood pressure, hyporeflexia, respiratory depression, convulsions).
Overdose
The risk of symptoms of hyperkalemia and hypermagnesemia increases.
Symptoms of hyperkalemia:
increased fatigue, myasthenia gravis, paresthesia, confusion, heart rhythm disturbances (bradycardia, atrioventricular block, arrhythmias, cardiac arrest).
Symptoms of hypermagnesemia:
decreased neuromuscular excitability, nausea, vomiting, lethargy, decreased blood pressure.
With a sharp increase in the content of magnesium ions in the blood: inhibition of deep tendon reflexes, respiratory paralysis, coma. Treatment: symptomatic therapy - intravenous administration of calcium chloride at a dose of 100 mg/min, if necessary - hemodialysis. Interaction with other drugs:
Pharmacodynamic interactions.
When used together with potassium-sparing diuretics (triamterene, spironolactone), beta-blockers, cyclosporine, heparin, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, the risk of developing hyperkalemia up to the development of arrhythmia and asystole increases. The simultaneous use of potassium supplements with glucocorticosteroids eliminates the hypokalemia caused by the latter. Potassium reduces the undesirable effects of cardiac glycosides. Asparkam enhances the negative dromo- and bathmotropic effects of antiarrhythmic drugs. Magnesium reduces the effects of neomycin, polymyxin B, tetracycline and streptomycin. Anesthetics increase the inhibitory effect of magnesium preparations on the central nervous system; when used simultaneously with atracuronium, decamethonium, succinyl chloride and suxamethonium, neuromuscular blockade may be enhanced. Calcitriol increases the content of magnesium in the blood plasma, calcium supplements reduce the effects of magnesium supplements.
Pharmacokinetic interaction.
Medicines that have an astringent and enveloping effect reduce the absorption of magnesium and potassium aspartate in the gastrointestinal tract, therefore it is necessary to maintain a three-hour interval between oral administration of Asparka with the above medications.
Special instructions:
Patients with diseases accompanied by hyperkalemia require special attention: regular monitoring of potassium levels in the blood plasma is necessary.
Effect on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery:
No studies have been conducted.
No effect is expected on the ability to drive vehicles or operate mechanisms that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions. Release form:
Release form. Tablets, 175 mg + 175 mg.
8, 10, 20, 25 tablets in a blister pack (blister) made of polyvinyl chloride film and aluminum foil.
10 tablets in a contour-free packaging made of polyethylene-coated packaging paper.
50, 100 tablets in polyethylene jars.
Labels made of label or writing paper or labels made of self-adhesive paper are glued onto polyethylene cans.
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 or 10 contour packages or 1 polyethylene jar together with instructions for medical use are placed in a box of cardboard.
It is allowed to pack 500, 700 or 1000 contour packages together with an equal number of instructions for medical use in corrugated cardboard boxes (for hospitals).
Storage conditions:
At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Keep out of the reach of children. Shelf life:
3 years.
Do not use the drug after the expiration date indicated on the package.
Dispensing conditions:
Without a prescription.
Sport
When regularly playing sports, the body is subjected to increased stress, which can result in a deficiency of vital substances. Heavy sweating and physical activity lead to large quantities of not only liquids being removed from the body, but also various inorganic substances: ions of K, Mg, Na, Fe and other metals.
To restore balance and to prevent disturbances in the functioning of the body, it is recommended to take Asparkam tablets. Intravenous injections should only be carried out under the supervision of a physician to prevent an overdose of the drug.
Why is Asparkam needed during a diet?
Many nutritional systems recommended for weight loss are based on the principle of reducing the amount of food consumed, removing large amounts of fluid and eliminating carbohydrates from the diet. As a result, the body begins to experience stress, which leads to the loss of extra pounds. However, disturbances in electrolyte metabolism, resulting from a lack of essential minerals in food, can provoke the development of various pathologies.
As a result of strict diets, such as buckwheat, protein or drying the body, a deficiency of vital substances occurs in the body. This leads to the fact that after completing the diet, the lost kilograms return. In addition, as a result of such strict weight loss measures, irreversible processes in the body can begin in the form of kidney disease, heart muscle disease, etc.
Nutritionists recommend combining the process of losing weight with taking Asparkam or other medications that are its analogues. This will help not only normalize metabolism, which will promote weight loss, but also replenish the lack of minerals.
Properties
They are caused by the combined effect of potassium and magnesium on the heart muscle and help restore it after a heart attack. K+ improves the contractility of the heart, reducing excitability and improving muscle conduction. It expands the lumen of the great vessels of the heart. Magnesium stimulates the synthesis of amino acids necessary to compensate for the defect in muscle tissue and stimulates cell division, promoting rapid regeneration.
These properties are used in the treatment of glaucoma and high intracranial pressure. Normalization of metabolism and electrolyte balance relieves almost all negative symptoms associated with vascular overload. A side effect is accelerated muscle growth, which has proven important for athletes. Therefore, Asparkam is quite popular in strength sports.
Preventive actions
If there is a lack of minerals in the body, or there are one or more signs of macronutrient deficiency, you can start taking Asparkam tablets as a preventive measure.
The result will be more effective if the use of the drug is combined with a therapeutic diet, which must include food products containing K and Mg.
These include:
- Prunes;
- Nuts (any);
- Rye bread;
- Baked potatoes in their jackets (with skins), etc.
The duration of the course of preventive measures is determined individually (depending on the general state of health). Recommended intake: 1 Asparkam tablet per day during or after meals.
Symptoms and signs of potassium and magnesium deficiency
At the first symptoms that indicate a deficiency of essential macroelements in the blood, you should start taking the drug Asparkam or its analogues. The use of the drug is also recommended after prolonged physical activity, when playing sports and during weight loss.
Hypomagnesemia
The most obvious sign of magnesium deficiency is paresthesia - loss of sensitivity.
It manifests itself as itching, slight tingling on the skin, a sharp change in thermal conditions, painful cold or “goosebumps”.
Other signs are:
- Insomnia;
- Fast fatiguability;
- Decreased appetite;
- Stomach upset;
- Vomit;
- Constipation.
A lack of magnesium contributes to the appearance of deficiency of other minerals, including potassium. Determining hypomagnesemia is a complex process. Often in blood serum tests the amount of magnesium may be sufficient: 0.74 mmol/L for children, 0.8 mmol/L for pregnant women and 0.005 mmol/L for adults.
A pathological condition can only be determined in accordance with general signs, which are:
- Congenital pathologies of electrolyte metabolism disorders;
- Strict diet, fasting;
- Lack of thyroid hormones;
- Kidney failure;
- Chronic pyelonephritis.
A decrease in the amount of Mg in the body can be observed as a result of taking certain medications, long-term treatment, or sudden weight loss. In all of the above cases, Asparkam is prescribed to restore metabolism.
See the same topic: Effective use of Amfepramone to combat obesity
Hypokalemia
A lack of potassium results in muscle weakness and dehydration. Cramps and spasms of the lower extremities, depression and causeless fatigue are the first signals that the level of K in the blood has decreased. Among the obvious signs of hypokalemia: dry skin, brittle hair and nails.
If you do not take Asparkam and do not increase the amount of potassium-containing foods in your diet, peptic ulcers and gastritis may develop.
Hypokalemia is diagnosed if the potassium level in the blood is less than 3.5 mmol/L. The reasons for this may be:
- Diets and lack of substances in food;
- Loss of macronutrients due to vomiting and diarrhea;
- Taking certain medications;
- Long-term use of corticosteroids;
- Insulin administration;
- Renovascular hypertension;
- Congenital diseases;
- Oncology;
- Blood transfusion;
- Stress.
In all cases, the medication Asparkam is prescribed. The therapy includes a special diet with increased consumption of foods that are sources of the mineral potassium.
Indications for use
Diagnosis is carried out in the form of detailed tests, which are prescribed at the first signs of disturbances in electrolyte metabolism.
Diagnoses for which it is recommended to start taking Asparkam are: hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia.
Medical indications are:
- Cardiac ischemia;
- Poor circulation;
- Shock, stress, depression;
- Changes in heart rate;
- Epilepsy;
- Gout;
- Glaucoma;
- Metabolic disorder.
Treatment of children
If there is a lack of potassium in the child’s blood, he is recommended to take the medication “Asparkam”. The drug replenishes the deficiency of the substance not only in the blood, but also in the cells. This helps reduce the risk of developing heart and myocardial diseases.
Common causes of K loss are diarrhea and vomiting, as well as chronic kidney and liver diseases. Treatment with such a strong diuretic drug as Diacarb, which is prescribed to reduce intracranial pressure, can also lead to the leaching of most of the potassium from the body. To restore mineral reserves, Asparkam is most often prescribed. However, these medications should only be taken under the supervision of a specialist.
"Diacarb" and "Asparkam" can be used to treat children only after consultation with the attending physician. The dosage of medications is calculated by a neurologist taking into account his age, weight and specifics of the disease. If necessary, the dosage can be adjusted. In some cases, your doctor may stop treatment with these drugs.
How to use asparkam correctly?
But before using the drug for this purpose, it is worth studying all the pros and cons.
Our body uses magnesium to help and restore the central nervous system . Potassium improves the functioning of blood vessels and the heart, and helps muscles work. Microelements in combination normalize and regulate the balance of salt and water in the body, helping to cope with excessive swelling. Due to this effect that Asparkam gives, the indicators on the scales become lower. But a person does not lose weight in the generally accepted sense of the word, but simply gets rid of excess fluid in the body. The drug has no effect on the amount of fat in the body and should not be taken as a means to combat excess weight.
Metabolism is a rather complex process that can slow down when taking medications. The reverse process of acceleration, with an excess of microelements in the body, has not been proven by science. In general, the components of the drug can help improve the well-being of those losing weight. But not a single medical representative will recommend Asparkam to you to combat excess weight.
The accompanying instructions for the drug indicate that Asparkam is not recommended for use by breastfeeding women, pregnant women, or children. Since the effect that the medicine has on the human body has not yet been fully studied. If the patient is from the above category, then one doctor can decide to prescribe a course of treatment with this drug.
Most drugs should be taken with caution by older people, but since heart disease is much more common in older people, there is no restriction on taking Asparkam for them.
If Asparkam is still prescribed, it must be taken three times a day, two tablets after each meal.
Treatment and prevention with asparkam
Sometimes a medicine is prescribed not for treatment, but for the purpose of prevention. Then the dose should be halved - one tablet three times a day, preferably after an equal period of time. For prophylactic purposes, the course of taking the medicine lasts up to a month.
In case of illness, tablets should not be taken for longer than 10 days . Although there are situations when taking Asparkam is resumed, but only as prescribed by the attending physician.
As mentioned above, the patient can receive the drug not only orally, but also intravenously and intramuscularly. But only after consultation and agreement on the dosage with your doctor.
Particular attention should be paid to intravenous and intramuscular administration of the drug.
To carry out the procedure, 30 ml of Asparkam is diluted with saline or glucose solution exactly according to the instructions. The dose of the finished substance for an adult ranges from 10-20 ml. The attending physician determines the number of injections per day.
Intravenous administration of the drug does not tolerate speed. This can have very negative consequences.
A maximum of 25 drops per minute is allowed for administration in the system. When administering the drug into a vein, no more than 5 milliliters per 60 seconds is allowed.
In the category of patients with long-term medication use, it is necessary to constantly monitor the content of potassium and magnesium in the body, monitor the hemostasis of electrolytes, and also conduct a timely electrocardiogram.
Like every drug, Asparkam, in addition to its indications, also has contraindications.
Instructions for use
Asparkam tablets are taken 3 times a day during or immediately after meals, 2 tablets. Recommended course of treatment: 30 days. If necessary, therapy can be repeated.
Intravenous injections are performed on an outpatient basis or in a hospital setting. The solution should be injected into a vein by drip (25 drops per minute) or stream (5 ml per minute). Dosage for an adult patient: 10-20 ml 1-2 times a day, depending on the diagnosis and doctor’s prescription. For injections or ciliates, the product is diluted with 0.9% sodium chloride or a 0.5% glucose solution (20 ml of Asparkam per 100-200 ml of excipient).
Children are prescribed only in tablet form.
Reception regimen:
- 0-12 months: 0.25 pcs. 1 appointment;
- 1-3 years: 0.5 pcs. 1 time per day;
- 4-6 years: 1/2 pcs. 2 times a day;
- 7-10 years: 0.5 pcs. 3 times every 6-8 hours;
- 11 to 12 years: 1 pc. every 12 hours;
- 13 to 16 years old: 1 piece. 2 times a day;
- 16 years and above: 1 pc. 3 times.
Instructions: how exactly is it recommended to take Asparkam
The Asparkam tablet should be consumed as a whole, without crushing or chewing it. It is recommended to drink it with water in the amount of 200 grams. It is best to take Asparkam after meals, otherwise its effectiveness will be affected by the content of juice in the stomach.
It is enough for an adult to take Asparkam 2 tablets three times a day, sometimes the doctor may prescribe three tablets at one time. How long the course of treatment will take will depend on the patient's condition and how he will respond to treatment. As a rule, Asparkam is taken for 3-4 weeks and then the course of treatment is repeated after 1-3 months.
If the time for taking Asparkam was missed, the drug should be taken as soon as you remember. However, you should not take a double dose of the drug if it is time for the next dose. A double dose of Asparkam will still not be absorbed by the body and will simply be excreted through the urine or gastrointestinal tract.
Contraindications
The main contraindication to taking this drug is individual intolerance or an allergic reaction to the active substances.
Therapy with Asparkam should be abandoned if:
- Dehydration;
- Atrioventricular block;
- Renal failure accompanied by hyperkalemia;
- Severe myasthenia.
Contraindications for hypomagnesemia:
- Hypermagnesemia:
- Arterial hypotension;
- Depression of the respiratory center;
- Prenatal period;
- Acute appendicitis;
- Rectal bleeding;
- Intestinal obstruction;
- Dehydration;
- Myasthenia;
- Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum.
Side effects
Side effects of the drug occur in rare cases.
With long-term use or incorrect dosage, the following may occur:
- Digestive tract disorders: nausea, vomiting, dry mouth. When changing the dosage, the side effects disappear;
- Myocardial conduction disturbances, decreased blood pressure, atrioventricular block. Malfunctions in the functioning of the cardiovascular system may also occur;
- Disorders of the central and peripheral nervous system;
- Potassium-magnesium metabolism disorders;
- Allergic reactions;
- Holding your breath.
Look at the same topic: Highly effective drug Liprina to reduce appetite
In many ways, the side effects of the drug appear depending on the individual reaction of the body or due to improper use of the drug. If you feel unwell, you should consult a doctor immediately.
Side effects
Asparkam has not only positive side effects, but also negative ones. They are visualized by the following symptoms:
Feeling weak, tired, dizzy.
- Muscle weakness.
- Skin rashes.
- Nausea.
- Dyspepsia.
- Dry mouth.
- Bloating.
- Hypotension.
- Hyperhidrosis.
- Dyspnea.
- Vein thrombosis.
In addition, an overdose is possible, which manifests itself:
- hyperkalemia;
- hypermagnesemia;
- crimson cheeks;
- thirst;
- arrhythmia;
- convulsions;
- arterial hypotension;
- heart blockades;
- depression of the respiratory center in the brain.
These symptoms require consultation with a doctor. In general, long-term use of Asparkam requires monitoring of electrolyte levels, because:
- the absolute safety of the drug has not been proven;
- when combined with tetracyclines, iron and fluorine, the medicine inhibits their absorption (the interval between medications must be at least three hours);
- there is a risk of developing hyperkalemia.
Interaction with other drugs
The simultaneous use of several medications can cause adverse reactions and reduce their therapeutic effectiveness.
Compatibility and possible risks should be discussed with your doctor. To avoid side effects and other complications, you should not change the dosage of medications yourself.
- It is not recommended to take anesthetic drugs in combination with Asparkam. Taking drugs together may lead to increased neuromuscular blockade.
- Antiarrhythmic drugs and Asparkam should be taken separately. When medications interact with each other, they can cause side effects.
- Antibiotics of the tetracycline group and preparations containing iron and sodium fluoride. When taken together with Asparkam, a slowdown in the absorption of the drug into the blood may occur. For effectiveness, it is recommended to take medications with a time difference of at least 3 hours.
- Cardiac glycosides are prescribed in complex therapy for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. In combination with Asparkam, they reduce the risk of adverse reactions and enhance the therapeutic effect.
Application of asparkam
The drug belongs to the category of relatively affordable drugs . In pharmacies it can be found in several varieties:
- pills,
- injection,
- solution for intravenous administration.
Despite the low cost, this is a serious, potent medicine. It is not recommended to prescribe it yourself without consulting a doctor. After prescription, you must thoroughly read the accompanying information that comes with the tablets in order to avoid consequences that will ruin the entire treatment.
Analogs and price
- “Asparkam-UBF” is a medicinal product that has a composition of active substances identical to “Asparkam”. It has a beneficial effect on the heart muscle and is recommended as an adjuvant in the treatment of diseases of the heart and blood vessels. Contraindicated in case of low blood pressure, chronic kidney and liver diseases. Recommended dosage: 3 times a day after meals. Available in tablets of 10 pcs. packaged. Price on the domestic market - from 24 rubles.
- "Panangin" is a pharmaceutical analogue of "Asparkam" produced (Hungary), which contains the same active substances. It differs in the percentage of potassium aspartate and magnesium aspartate (158 g and 140 g, respectively). Recommended for the treatment of arrhythmia and prevention of myocardial infarction, prescribed to eliminate adverse reactions of cardiac glycosides. Recommended daily dose: 9 tablets. Dosage regimen: 3 tablets 3 times a day. The medicine is available in tablets, the price per pack is 50 pcs. — from 136 rub.
- Potassium and magnesium aspartate solution. The German-made drug is an analogue of the domestic “Asparkam”. Release form: 500 ml bottle. Recommended as an antiarrhythmic agent and to replenish electrolyte deficiency. It is used in complex treatment and as an independent therapeutic agent. Bottle price: from 266 rubles.
https://youtu.be/5UiHDAcum80
Effect of taking
Beginning athletes are wondering whether it is possible to drink Asparkam? – Yes, it is useful for a number of areas of the body’s life. The main reason for taking it is to normalize metabolism; for this purpose, the composition contains potassium and magnesium in aspartate form. The action of potassium is to restore healthy metabolism. Due to the special composition of the drug, muscle mass increases, fatigue is eliminated and endurance is slightly increased.
Asparkam is used in bodybuilding to normalize heart rate
Magnesium and bodybuilding are interrelated concepts, because with a deficiency of the substance, protein metabolism is disrupted. When there is enough magnesium, the process of weight gain improves.
Magnesium can be used separately in bodybuilding to achieve some of the described effects, but it is important to follow the overall dosage of the drug. The effect of magnesium will not increase with increasing concentration of the substance; excess minerals will be excreted from the system through the kidneys. Magnesium in bodybuilding is important to cover deficiencies and prevent complications associated with them. But overdose with long-term use can lead to the same dangerous consequences.
During training, a lot of water is consumed, which, when it leaves the body, captures potassium and magnesium ions. Based on the increased rate of mineral removal, the need for an additional source of substances arises. More often, Asparkam tablets are used for this purpose.
Taking Asparkam is often carried out with the aim of reducing body weight by eliminating part of the fluid and fat deposits.