Cycling[edit | edit code]
"Guide to creating a sports diet"
Registered Dietitian Renee McGregor, 2016
Bike racing has grown in popularity over the past few years; The legacy of the London Olympics was the record number of cycling events held and attended.
Cycling can take the form of one-day races, ranging in distance from a few to several hundred kilometers, such as time trials or the London-Brighton cycle race. They can also be multi-stage events, such as the Tour de France or Cape Epic, during which athletes cover enormous distances over several days.
Cycling requires strength and endurance, although the body's anaerobic capacity is equally important to take off, climb hills and sprint to the finish line at the limit. A competent training program includes sessions that focus on all of the above aspects, as shown in Table. 3.3.
Table 3.3. Standard cycling schedule
| Day of the week | Intensity |
| Monday | 60 minutes, high intensity |
| Tuesday | 60 minutes, low intensity; restorative riding that strengthens the aerobic base |
| Wednesday | Rest or strength training |
| Thursday | 80 minutes, high intensity |
| Friday | 90 minutes, moderate intensity riding at a constant speed |
| Saturday | Rest or strength training |
| Sunday | 3 or more hours of low/moderate intensity endurance riding |
Depending on the event for which professional athletes are preparing, during peak training periods they travel 400-800 km per week.
Serious recreational cyclists try to cover about 240-320 km per week in preparation for a specific event. With all that said, eating plans are of paramount importance, especially if you also have to juggle work and family life. So let's look at some examples of workouts and the needs of the athletes who perform them.
What muscles are used when riding a bicycle?
When it comes to the muscles that cycling trains, the leg muscles are the most basic. But still there are many more of them. So, let's see what muscles work during cycling:
Legs
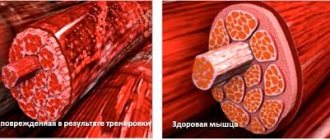
When riding a bicycle, all leg muscles are used. We rotate the pedals, setting the bike in motion - the legs are loaded the most, but the type of load is constantly changing and different muscles are worked this way. As you extend your foot while pressing the pedal, your calf muscles and hamstrings are activated. When climbing uphill, when the cyclist presses the pedal hard, the quadriceps of the thighs are pumped well. And when the leg rises up along with the pedal, the hamstrings are involved in the work.
The gluteal muscles do not go unloaded either, working in tandem with the quadriceps - they are responsible for maintaining balance. The small iliacus muscle, located in the groin area, helps to straighten the hips and bend the leg at the knee. Of all the muscles, it is one of the most vulnerable, so if you experience any discomfort in this area, you should take a break.
Get ready for the cycling season with an intensive training course from Hollywood trainer Jim Barcena. Read more about the course here.
Press
According to Tatyana Borzenkova, for comfortable cycling, strong abdominal muscles are simply necessary - they are the ones who keep the back straight and are responsible for tilting the body forward.
Back
All back muscles work when training on a bicycle to maintain balance. For example, during turns, a cyclist actually works with the latissimus dorsi muscles. This load helps improve muscle tone. But those who have back problems should be careful with cycling loads. They need to be especially careful about proper fit.
Arms and shoulders
The muscles of the shoulder girdle will also receive a certain load while cycling, but the chest and arms cannot be worked only by cycling. If you need visible results, it is recommended to combine cycling training with appropriate gymnastics with dumbbells.
Low-intensity training[edit | edit code]
Regardless of the distance you choose, low-intensity recovery cycling always follows the same format. It should not last more than 60 minutes at a leisurely pace at approximately 50% of your maximum heart rate. In addition, it strengthens overall aerobic endurance. At this pace, you should be able to pedal and carry on a conversation without strain. After the trip, you will feel a surge of energy, as a result of which it would be wise to place such a session between two more intense ones.
Dietary requirements[edit | edit code]
Low-intensity riding at a leisurely pace does not require a special source of energy, provided it does not exceed 60 minutes. It is optimal to do this early in the morning on an empty stomach, since your body will take everything it needs from fat or glycogen stores. In other words, you can ride a bike at a leisurely pace at any time convenient for you, but there is no need for a special “refueling” before training.
On a day when you plan to ride at a leisurely pace, the maximum requirement for carbohydrates is 3 g/kg body weight, and for proteins - 3-4 servings of 0.25 g/kg body weight (during the day). In order to adhere to this norm, three meals a day are enough - fist-sized portions of complex carbohydrates (oatmeal, sweet potatoes, root vegetables, legumes) and a handful of proteins (eggs, chicken, fish). All this is complemented by fresh salad or vegetables in unlimited quantities. Fruits or vegetables are suitable as a snack.
Nutrition for professional cyclists
We found out how professional cyclists train.
But it is quite obvious that without proper nutrition it is impossible to count on serious success. Often, athletes must travel at least one hundred miles throughout the day during a race. Imagine what amount of energy must be in the body so that it can work normally all this time. Cyclists eat a large amount of fruits, vegetables, rice, potatoes, and pasta. All of these foods are excellent sources of carbohydrates. However, to recover after a race or workout, you need to provide your body with protein compounds. Athletes themselves often admit that sometimes they even indulge in fast food, but this is due to necessity. The bulk of the food consumed by cyclists is healthy and wholesome.
During the race, it is necessary to maintain fluid balance and also replenish energy reserves. For this purpose, special bars and gels are used that supply protein compounds and carbohydrates to the body. Note that during training they act in the same way, because the duration of the classes is not inferior in duration to the race, and sometimes even exceeds it.
It is mandatory to have a bottle of liquid on your bike to avoid dehydration. During competitions or training, athletes do not drink plain water, but special drinks containing a complex of electrolytes, and sometimes caffeine. Before the start of the race, each athlete receives a musette bag containing energy bars, gels, small sandwiches and even cakes.
On average, cyclists burn about five thousand calories during one stage of a multi-day race. At the same time, the energy value of the daily diet is a maximum of three thousand. This suggests that athletes can consume any product and not worry about it. However, cyclists are known for their obsession with body weight.
They often weigh their portions to make it easier to stick to their caloric intake goals. They also often step on the scale after a race to determine the amount of food and water they need to consume to regain body weight. During the off-season, a rider’s body weight can exceed the competition weight by a maximum of five kilos. But they rarely think about it, because after the start of the training process everything will return to normal. To monitor their diet, professional cyclists turn to nutritionists for help.
A few words need to be said about restoration. After hard training or a race, this is extremely important. To do this, they do light cycling, during which the body recovers faster and blood flow normalizes. Athletes devote at least eight hours to sleep, and some try to find time to take a nap, even after training, if their training schedule allows it.
After completing a race or training, it is imperative to consume recovery sports cocktails, which contain protein compounds and carbohydrates. After some time, a full meal follows to speed up the regenerative processes in the body. Each team has massage therapists who help with recovery. It is known that thanks to massage, the processes of utilization of lactic acid are accelerated.
Moderate intensity training[edit | edit code]
Moderate-intensity cycling sessions are usually done at a “steady state”, varying in time from 60 to 90 minutes. It's faster than your leisurely pace. You should still be able to carry on a conversation, but not too fluently. If you are using a heart rate monitor, it should operate at 60-70% of your maximum heart rate.
You can do these sessions on the road or on a turbo or stationary bike, but be sure to maintain the right intensity.
Dietary requirements[edit | edit code]
A moderate intensity session is harder than a leisurely ride, but you're still in your comfort zone. The daily requirement for carbohydrates is a maximum of 5 g/kg BW, and for proteins - 0.25 g/kg BW four times a day. The moderate exercise nutrition plans presented in Chapter 2 show what these needs look like in practical terms, and also take into account what time of day you ride.
If you are an experienced cyclist, you will have no problem doing this session early in the morning on an empty stomach, just remember to drink enough fluids and exercise for no more than 60 minutes. If the session is expected to be longer than 60-90 minutes or is planned the next day after a strenuous workout, you will need to refuel before running. Here are some great options:
- banana;
- 1-2 slices of malt bread;
- 1 toast;
- a small jar of low-fat Greek yogurt with 1-2 teaspoons of honey.
Be sure to think about how you will recover after the trip. Calculate portions based on the fact that you need 1 g/kg body weight of carbohydrates and 0.25 g/kg body weight of protein, and do not forget about the time frame.
If this is your only training session of the day, try to schedule a recovery meal or snack within 2 hours of your run. Most likely, it will be needed for the next meal. For example, you leave home in a steady state before breakfast at 6:30 and return at 7:30. Today you are not supposed to have any more training. The most important thing is a good restorative breakfast, say Bircher muesli with blueberries (see recipe p. 193) or pita with omelette (see recipe p. 200), by 9:30. You can eat immediately upon returning, or you can take a shower first.
If you have another workout coming up in the next 12 hours and you don't eat right after your race, you'll need a recovery option like a tropical smoothie within 30 minutes (see recipe on page 284), and after 2 hours after it - a substantial meal.
Training programs
We would like to point out that drawing up any training plan is an individual process that takes into account many factors. To build a training process, taking into account the runner’s goals, you need to contact a qualified trainer
Below are examples of interval training that can be effective training tools for any amateur runner.
Every amateur runner should start their workout with a light jog (warm-up) lasting 10 minutes and stretching the main muscle groups. At the end of the workout, you also need to do a cool-down in the form of a 10-minute easy run at a low heart rate.
There are two categories of interval training programs: for beginner runners and for experienced runners.
For Beginner Runners
- Fast 1000 meters (pulse zone 130-150 beats per minute);
- Jogging 800 meters (pulse zone 100-120 beats per minute).
Repeat 4-5 intervals.
For experienced runners
- Fast 1000 meters (pulse zone 140-160 beats per minute);
- Jogging 600 meters (pulse zone 110-130 beats per minute).
Repeat 6-8 intervals.
Pay special attention to including fartlek in your training plan.
- Preparatory (basic) fartlek.
During a long workout, speed up for 1 minute every 6 or 7 minutes. The acceleration pace should be 10 to 20 seconds per kilometer faster than the normal pace of the “slow” portion of your long workout.
- Standard fartlek.
Perform this type of training in a standard athletics stadium. You need to perform 5-7 fast segments of 400 meters at a pace that will be approximately 20-30% slower than the maximum pace. Accelerations are performed through a 400 meter segment, which will be slightly slower than the fast segment, by about 5-10 seconds.
Maximum pace 5 min/km. The fast section should be run at a pace of 5:10 min/km)
Video about fartlek and variable running
https://youtu.be/AT7ARFtHhsA
https://youtu.be/Qa51qbrYYH4
If you decide to set ambitious goals for yourself, then you will definitely need to choose a starting point. And a preparation plan for any competition should be an integral part of the path to achieving sports goals.
Endurance training[edit | edit code]
Endurance cycling is paramount for those preparing for an event that lasts a full day or several days. The duration of time in the saddle should be increased with each week of training. Such trips develop endurance and help maintain good aerobic fitness. You should move at a leisurely or moderate pace. You should be able to carry on a conversation for a long time. If you cannot talk, then the tension is too great.
Several program options
- 3.5 hour ride at a leisurely pace with a quick finish;
- 4-hour drive through hilly terrain;
- A 5 hour ride at a leisurely pace with a quick finish.
Endurance cycling requires adequate nutrition as glycogen stores will be completely depleted. You'll need to prepare 24 hours before your trip and eat enough carbohydrates both beforehand and during your workout.
Dietary requirements[edit | edit code]
The key strategy is to consume small portions of carbohydrates in the 24 hours leading up to your workout at every meal and snack. During this 24-hour period you will need them in the amount of 5-7 g/kg body weight. Try to stick to fist-sized portions; meals (a total of 4-6 of them per day) should contain complex carbohydrates. In practice it will look like this:
- 50 g oatmeal;
- banana;
- fist-sized portion of sweet potato;
- 3-4 oatcakes;
- a fist-sized portion of boiled rice/couscous;
- toast.
The “little and often” principle is very important because it ensures more efficient storage of glycogen and does not cause stomach discomfort or problems during long rides. Such a scheme, which has become a habit, will be useful for the day of the competition. Go through the endurance training plans presented in Chapter 2 to reinforce your knowledge of this type of nutrition. Once you've decided what you'll eat before training, think about your needs during the race. They depend on how exactly you plan to practice.
Remember that such sessions are not high-intensity, so the body does not need carbohydrates as a source of “fuel”. By using the nutritional principles described earlier in this section, you will ensure that you have full glycogen stores. They will provide you with energy for approximately 1.5-2 hours at a low/moderate intensity pace. Once these reserves are depleted, the body will switch to fat so you can keep moving. Since carbohydrates are not a necessary source of energy in this situation, I always advise people to choose foods that they will want to snack on while running. Such a duration requires not only physical, but also mental stress, and if you have just a little something tasty with you, there will be a significant incentive to successfully reach the finish line.
Clue
For an endurance cycling ride longer than 3 hours, you will need 60g of carbohydrates per hour. Try eating fast-releasing energy foods, such as energy gels, gelatin candies, dried fruit, every 45 minutes, alternating with slow-releasing energy foods, such as yeast extract sandwiches, banana and nut butter sandwiches (see recipe on page 275), sweet potato brownies (see recipe on page 272) or salted peanuts.
Hydration[edit | edit code]
In hot weather, take electrolytes (see page 40) or add table salt to squash at the rate of 1L teaspoon per 500ml. This will prevent it from being lost through sweat and help the body retain water. If you prefer to use energy drinks or squash with added sugar, remember that these are sources of carbohydrates and you will need to adjust your diet accordingly. The body can process a maximum of 90 grams of carbohydrates per hour, so consuming excess carbohydrates can cause stomach discomfort and other problems in some people.
What kind of lifestyle do professional cyclists lead?
The competitive stage in cycling lasts from January to October.
Among all sports, cyclists have the longest season. To stay in peak shape all this time, professional cyclists need to adhere to a given pace of life. They must not only show results, but also have time to recover. During the season, athletes have to travel frequently, but they do not have time to appreciate the beauty of the places in which they find themselves. Frequent flights are extremely tiring and after them you need to spend time adapting. During the off-season, many athletes travel with their families.
During the season, all athletes' thoughts are aimed at results. They are required to participate in various promotional events and meet with team sponsors. They often have to give interviews for various media. Before the start of the race, a team meeting is held to discuss strategy. All these activities significantly reduce the amount of free time.
However, a professional must remain so in everything, and his lifestyle is adapted to his career. Almost every professional athlete has his own business, which he will take up closely after his career ends. While the cyclist is participating in competitions, he rarely sees his family and all his thoughts are aimed at winning the next race.
For more information on training professional cyclists, see the following story:
High intensity training[edit | edit code]
These workouts are performed at levels very close to or above lactate threshold. The goal of such sessions is to increase the lactate threshold, that is, to be able to run faster and longer. Here are three high-intensity training programs.
- 5x8 Hill Workout: This involves a 5-minute uphill and downhill recovery, repeated 8 times with a 10-minute warm-up and cool-down at a leisurely pace. Such training increases strength and endurance and requires a lot of effort; you won't be able to carry on a conversation while climbing a mountain.
- 5x5 Flat Intervals: This is riding at the limit at approximately 80-90% of your maximum heart rate for 5 minutes followed by a 90 second recovery, repeating the cycle 5 times with a 10 minute warm up and cool down in the riding format. at a leisurely pace. This session can also be done on a bike or turbo trainer.
- 60-Minute Threshold Riding: Warm up by riding leisurely for 10 minutes, then increase the pace to 75% of your maximum heart rate, which is close to your lactate threshold. Hold this load for 40 minutes. At this threshold pace, you should maintain the ability to speak, but with great difficulty, pronouncing no more than 3-5 words in one breath. To cool down, ride at a leisurely pace for 10 minutes. Again, this session can be performed on a bike or turbo trainer.
Dietary requirements[edit | edit code]
During high-intensity workouts, the body needs to get carbohydrates, otherwise you will not be able to perform such sessions. The daily requirement for carbohydrates is at least 5 g/kg body weight in women and 7 g/kg body weight in men. This is approximately 5-7 fist-sized servings, divided among meals and snacks. In addition, you will need 4-6 fistful-sized servings of protein (that is, 0.25 g/kg body weight each).
If you plan to do high-intensity sessions in the morning, make sure to include carbohydrates in your main meal the night before. Calculate your serving size based on the fact that you need 1-2 g/kg BW. Additionally, eat a similar-sized breakfast at least 1-2 hours before your workout.
If you plan to do your sessions in the evenings, make sure you consume 1g/kg body weight of carbohydrates at breakfast, lunch and afternoon snack before starting your session.
Refer to the sample high-intensity training nutrition plans presented in Chapter 2 to determine how you should meet your needs based on the time of day you plan to exercise.
After a hard workout, recovery plays a huge role. If you have another workout scheduled within the next 12 hours, recovery should occur within the first half hour after the end of the workout and include 1.2 g/kg body weight of fast-acting carbohydrates and 0.25 g/kg body weight of easily digestible proteins in liquid form - great Flavored milk or mocha shake will do (see recipe on page 285).
If the next workout is scheduled no earlier than 12 hours after the previous one, recovery should occur in the first 2 hours after the end of exercise and include 1.2 g/kg body weight of carbohydrates and 0.25 g/kg body weight of proteins. Try chilli con carne with lentils and beans (see recipe on page 240).
Exercise bike exercises: answers to all questions
Training on an exercise bike is an aerobic exercise aimed at burning calories and strengthening the muscle corset. The movements can be performed with different intensities and durations, depending on the desired result. The main source of energy during exercise is oxygen, which has a beneficial effect on cells, providing them with nutrition from the inside.
Exercise bike classes are suitable for both men and women who have problems with excess weight.
The main advantage of an exercise bike is its versatility and accessibility. You can install the structure even at home and practice at any convenient time. If other family members live in the house, they will also be able to evaluate the purchase and take part in the training.
Benefit for health
Diligent pedaling will diversify your morning exercises or completely replace going to the gym. Saturating the body with oxygen and prolonged measured exercise has a beneficial effect on all organ systems and also helps solve a number of problems. The main useful functions of the exercise bike:
- develops leg muscles;
- makes joints mobile and strengthens ligaments;
- improves the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- normalizes breathing;
- increases the body's endurance;
- promotes figure correction;
- burns fat;
- accelerates blood circulation;
- calms the nervous system, relieves stress.
An intense workout on an exercise bike will give you sound sleep and a good mood for the whole day.
Exercise bike for weight loss
In order to reduce your proportions and get rid of excess calories, exercise on an exercise bike should be targeted. All movements must be performed slowly and smoothly. Efficiency is achieved through prolonged exposure to problem areas.
ADVICE! Selecting the minimum load in the simulator settings will help you maintain your strength and increase the training period.
On average, about 400–700 kcal are burned in 1 hour of exercise on an exercise bike. If you follow the program daily, you can lose from 3 to 5 kg per week, which is about 10–15 kg per month. Much depends on factors such as initial weight, balanced diet, drinking regimen, and compliance with all training rules.
Impact on legs
During cycling exercises, the muscles of the legs, buttocks, abs and waist are worked. The first ones are the most vulnerable. Intense and frequent training gives the calves relief, increasing their volume. To maintain a feminine silhouette and give your legs slimness, you should stick to a calm pace. Before training, the muscles are warmed up, and at the end, stretching is performed.
Planning a weekly training schedule[edit | edit code]
While it's important to eat according to your type of training each day, you should definitely consider how all your meals will fit together throughout the week. In table 3.4 Tuesday, Wednesday and Saturday are days of low-intensity exercise; the body does not need carbohydrates to produce energy. But each of these days precedes a day with high-intensity exercise or endurance riding, which means that you will have to take care of the “fuel” entering the body in advance. To do this, it will be enough to eat a meal rich in carbohydrates on Tuesday and Wednesday evenings, as well as small regular portions on Saturday. Additionally, as you prepare for Monday's high-intensity session, you'll need to pay special attention to recovery on Sunday by eating meals or snacks containing protein and carbohydrates every 2-3 hours.
Table 3.4. Sample weekly training schedule
| Day of the week | Intensity |
| Monday | 60 minutes, high intensity |
| Tuesday | 60 minutes, low intensity; restorative riding that strengthens the aerobic base |
| Wednesday | Rest |
| Thursday | 80 minutes, high intensity |
| Friday | 90 minutes, moderate intensity riding at a constant speed |
| Saturday | Rest |
| Sunday | 3-hour (or longer) low to moderate intensity endurance riding |
Proper nutrition
A cyclist's diet directly depends on the intensity of the workout. If you are going to train at low to moderate intensity, your normal daily diet will be sufficient; no additional refueling will be required before leaving the house. But if you have to drive a long distance, you need to take care of additional sources of energy.
To do this, during the day before training, you need to eat fist-sized portions of food, so as not to create excessive stress on the digestive system, and two hours before leaving the house, avoid food altogether. During long rides, it is useful to alternate foods rich in glycogen with foods rich in quickly digestible carbohydrates. These snacks should be done every 45 minutes. For example, you can eat a gelatin candy, and next time - a handful of nuts or a previously stored candy bar. In this case, you need to pay attention to the calorie content of “sports” bars and drinks, and if necessary, divide them into portions. To maintain hydration, you can add half a spoon of table salt to smoothies or plain water. Do not drink a lot to wet your throat, two or three sips will be enough.
After training, you are allowed to drink up to a liter of water, and a few hours later eat a full, healthy lunch.
Case from practice[edit | edit code]
One of my clients was a man who initially came to me because he biked 56km to work but was unsure whether he was meeting his self-imposed demands. Ideally, he would like to go to work like this every day, but he only managed to do it three times a week. By Wednesday evening he was so tired that he was unable to get on his bike. He was constantly tormented by a feeling of hunger; he could not lose several stubborn kilograms, despite the fact that this man traveled more than 160 km in a week. This was his typical diet.
- Before the morning drive
A bowl of breakfast cereal - At work, after shower,
Bacon sandwich, bag of crisps at desk - Lunch
2 rolls with chicken, mayonnaise and salad; large chocolate bar - Before the day's ride
: A cereal bar and a handful of gelatin candies - At home
Large portion of pasta with sauce, cheese and garlic bread; ice cream bowl; crackers and cheese
The main problem was that the client's diet was "reactive", as I call them. The man chose the wrong foods high in fast carbohydrates, which explained the fluctuations in blood sugar levels. As a result, he had a strong need for sweets and a constant feeling of fatigue.
The first thing we discussed was recovery. I explained that the right foods for recovery after a morning commute should help immediately replenish glycogen. This will provide the body with a supply of “fuel” for the return trip. In addition, I recommended that the client include more complex carbohydrates and lean proteins in his daily diet to maintain stable blood sugar levels and energy levels, as well as provide the body with important nutrients to meet exercise needs.
Example of an adjusted daily diet
- Before your morning ride
Smoothie - At work, after a shower
, at the table, 300-500 ml of chocolate milk, a whole wheat bagel with peanut butter and banana or something similar - Lunch
Jacket potatoes with tuna and salad, yogurt - Mid-day
2 buns and 75g mixed nuts - After the return trip
500 ml of milk - 18:30
Main meal followed by natural yoghurt with fruit and honey - 21:30
Hot chocolate with oatcakes and peanut butter
Initially, the client was not sure that changes in the diet would have any effect on his “insatiable hunger,” as he himself put it. However, a few weeks later the man reported amazing improvements. His performance, energy and concentration have noticeably increased.
Principles of cycling training
The basic principles of effective cycling training for weight loss are:
It is recommended to do muscle stretching exercises before and after the trip.
- Systematicity. To correct your figure, you need to exercise at least 3 times a week. There is no need to train every day, because restoration of muscle fibers requires at least a day. In between classes, you can do light exercises and stretching. If cycling is only possible 1-2 times a week, the missed lesson should be replaced with fitness, dancing, Pilates or another sport.
- Increasing duration. The first workouts should last no more than 15-20 minutes. The duration of the load increases by 5-10 minutes each time, which allows you to gradually strengthen the muscles and tendons, avoiding injuries, sprains and severe soreness.
- Optimal load intensity. The intensity of the load is determined by the speed of movement, heart rate (HR) and pedaling. A calm pace does not allow you to thoroughly work out your muscles and stimulate fat burning, so while cycling you need to monitor your heart rate, increasing the speed as your heart rate decreases. The recommended pedaling frequency is 90 times per minute.
- Protection from damage. Special sportswear, gloves, knee pads, elbow pads and a helmet will help avoid injuries and chafing during cycling. The areas at risk when pedaling are the knee joints, the iliopsoas muscle and the Achilles tendon. If you experience pain in your legs, you should stop exercising. If the pain intensifies over time and is accompanied by other symptoms (swelling, redness), you should consult a traumatologist or surgeon.
- Proper breathing during exercise. Excessive and labored breathing can lead to stabbing pain in the side and a decrease in the intensity of the exercise. You need to breathe regularly, through your nose, with a frequency of about 1 inhalation or exhalation per 2 revolutions of the pedals (one for each leg). Before climbing, it is recommended to increase the frequency of inhalations in advance, since moving uphill requires a larger volume of oxygen.
Changing the intensity and type of exercise has a beneficial effect on the weight loss process. For example, you can climb steep hills at a brisk pace while walking your bike alongside you. This load allows you to maintain a high heart rate and avoid excessive stress on the joints and ligaments.
Cycling can be replaced by exercise on an exercise bike. To maintain muscle tone and activate blood circulation, 20-25 minutes of exercise at an average pace is enough, and to lose weight you need at least 40-50 minutes of exercise at least 3-4 times a week. The effectiveness of an exercise bike is lower than that of cycling.
Before exercising on a bicycle or exercise bike, you should do a warm-up - swinging and rotating your legs, squats, etc. After training, a cool-down is required - a set of exercises to stretch the muscles and reduce the level of stress hormones.
The cool-down after cardio consists of aerobic exercise with a gradual decrease in heart rate (for example, running or brisk walking) for 5-7 minutes and a 5-minute stretching of the muscles being loaded (hips, legs, obliques).
Loads and results
choose the load depending on your goals.
The final result of training depends on the load.
- to pump up the muscles, use high resistance, the muscles work the entire cycle;
- For weight loss, choose a medium resistance level.
How is training intensity determined?
The intensity of the workout depends on the selected speed:
- light - 15–16 km/h;
- average - 19–20 km/h;
- moderate - 22–25 km/h;
- high - 27–30 km/h;
- very high - from 35 km/h.
Interval training for weight loss
alternate between fast and slow paces.
This weight loss system is suitable for an exercise bike. Interval riding will reduce the risk of fatigue injuries and allow you to complete more repetitions in less time.
This is a good way to combat fat stores because it burns more fat than monotonous exercise. The point is to alternate between fast and slow tempos.
The fast phase lasts no longer than 60 seconds, which does not allow the body to move into the comfort zone.
Research results confirm the effectiveness of this type of training. Scientists conducted studies and found that women who periodically increased their pace by 8-12 seconds lost more body fat in 20 minutes than those who exercised monotonously for 40 minutes. Reviews of people losing weight on an exercise bike can be found here.
Interval riding helps you lose weight not only in your legs, but also in your stomach, although it seems that the abs are not involved in such loads. The method is suitable for those who do not have time to train 4-5 times a week - in this case, 3 times a week is enough.
| Phase duration, seconds | Phase name | Load level |
| 300 | Warming up | Lightweight |
| 30 | Sprint | High |
| 60 | Rest | Average |
| 30 | Sprint | High |
| 60 | Rest | Average |
| 45 | Sprint | High |
| 60 | Rest | Average |
| 45 | Sprint | High |
| 60 | Rest | Average |
| 60 | Sprint | High |
| 60 | Recovery | Average |
| 60 | Sprint | High |
| 60 | Recovery | Average |
| 30 | Sprint | High |
| 60 | Recovery | Average |
| 30 | Sprint | High |
| 60 | Recovery | Average |
| 45 | Sprint | High |
| 60 | Recovery | Average |
| 45 | Sprint | High |
| 60 | Recovery | Average |
| 60 | Sprint | High |
| 60 | Recovery | Average |
| 60 | Sprint | High |
| 60 | Recovery | Average |
| 240 | Completion | Lightweight |
Beginners can begin interval training after mastering the initial training program.
Interval training is prohibited due to health problems. Contraindications include a weak heart and chronic diseases. Therefore, before a cycle of classes, consult a doctor about whether it is possible to conduct classes in this mode. Such training is carried out in courses. After a month of interval training, they switch to uniform training, and after another month the course is repeated.
Burn fat with cardio training:
How to do the bicycle exercise
Lie on the floor on your back, raise your hips to a right angle in your pelvis and bend your knees.
Lift your shoulder blades off the floor, tighten your abs tightly and do not relax until the end of the exercise. Imagine that someone is going to hit you in the stomach.
Place your hands behind your head and spread your elbows to the sides. There is no need to clasp your hands or press your palms on the back of your head - your fingers only lightly touch your head.
Alternately bend and straighten your legs, as if pedaling a bicycle. At the same time, turn your body and reach your elbow towards the opposite knee.
Do not try to touch your knee, the main thing is to turn your body to the side in the maximum accessible range.
The best workouts for weight loss[edit | edit code]
https://youtube.com/watch?v=XdPXePMmB8U%3F
Yuzhakov Anton HOW TO EAT AND TRAIN TO GET RESULTS
It has been scientifically proven that aerobic training (or cardio training) is most effective for burning fat and creating a ripped figure in men and women. In the long term, vigorous physical activity has a greater impact on weight maintenance than diet. Aerobic training strengthens the cardiovascular system, increases endurance and performance of the body, and improves mental state. Aerobic training speeds up recovery from mental stress and increases resistance to stress. This aerobic training program is universal; using it, you can create an individual training program that suits you best.
The study showed that interval cardio training (3 times a week, 20 minutes each, excluding a 10-minute warm-up) allows you to reduce weight by about 1.5 kg in 3 months of training. According to the results of the study by M. Heydari, fat loss was 2 kg, while a slight increase in muscle mass was observed (+ 0.5 kg of muscle). Strength training produces worse results. It is worth noting that these tests were conducted on volunteers who did not change their usual diet and daily routine. Read more:
workouts and metabolism acceleration.
Thus, training contributes only 15-20%
contribution to building a figure,
50% is diet
,
25% is sports nutrition and pharmacology
. High-quality results can be obtained much faster if you use an integrated approach.
How to improve your aerobic training results?