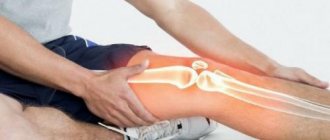
Round mix or circular mixed training
January 29, 2020, 10:43
It’s difficult for an unprepared person, not initiated into the art of fitness and the wisdom of group exercises, to understand different types of training, decide which one he needs and what is the advantage of one type of training over others, but we will try to help you the initial stage - general information, benefits and distinctive features. Of course, when you come to the gym in Chertanovo “Inferno” you will receive advice from a professional trainer who will tell you how and what is best to do based on your goals, but you need to have a general idea, for example, about Round mix training or mixed circuit training. Thus, at the initial stage you will be able to understand what type of training this is and “what it comes with.”
So, Round mix or circular mixed training is a set of exercises that involves training in a cyclic order, where a break takes a minimum of time. As for the area of influence, when working in Round mix, individual muscles are occupied, and the main load is directed to them. As a positive effect, Round Mix ensures the development of the body's endurance and activates metabolic processes for more active burning of fat deposits. The undoubted advantage of the result of these classes will be a significant increase in the physical strength of the student, acceleration of metabolic processes, work on relief, a positive effect on the cardiovascular system, as well as the opportunity to attend classes for both beginners and people who have been involved in fitness for many years. One thing should be clearly understood - it will not be possible to build muscle mass with such training; it was not created for that at all. Both men and women can do circular mixed training.
Let's figure out what the Round mix process is. As elsewhere, a warm-up is provided here, and the load increases. Then there are exercises aimed at burning fat cells; it is the cyclic order of execution, coupled with minimal breaks, that is the essence of these exercises; there is very little time left for a break. At first you may think that doing exercises with a Round mix instructor is quite difficult, but by the second or third lesson you will get into the rhythm and be satisfied with the result.
Basics
From a user's point of view, these two package installation options are not very different. Both Deb and Rpm files are just archives created using the ar utility. These archives include program files, executable files, libraries, or configuration files. In addition, each package includes metadata from the package management system, which is what distinguishes rpm and deb. The actual package files differ mainly in this, but there is also a package management system. And there are already much more differences in the database.
Let's take a closer look at each package management system, and then compare what's special about them and whether rpm or deb is better.
https://youtu.be/M7zPNDSswKI
Where to do Round mix
Today, few gyms offer round mix and there are a limited number of professional instructors for this type of group programs, but it is in the group training hall in Chertanovo “Inferno” that you can attend this type of training. At your service is a professional, responsive trainer interested in the results of each student, a spacious, bright hall equipped with everything necessary, a convenient location of our club between the Prazhskaya and Yangelya stations in the Southern Administrative District of Moscow, spacious free parking, as well as convenient training times. You will definitely like it with us!
RPM (Red Hat Package Manager)
As we have already said, RPM is a package manager used in operating systems based on Red Hat, this is the entire branch of distributions: Fedora, OpenSUSE, Red Hat, CentOS, etc. Initially, this package manager was developed at Red Hat back in 1997 and only for their distribution, but then it spread to other operating systems. Instead of regular compression, gzip compression using the cpio algorithm and a special archive file format are used here, we will look at it below. Here, in comparison with rpm or deb, the first seems better, but not everything is so simple, if the system does not have the necessary utilities, then you will not be able to unpack such a package. In addition to cpio, other compression algorithms can be used, for example, lzma or xz. Recently, all software is signed with keys for authentication, so RPM supports signing using GPG and MD5. PatchRPMs or DeltaRPMs technology allows you to intelligently update RPM packages without high traffic costs.
Although it is said that the rpm file is a regular archive, this is not entirely true. At the beginning of the file there is a header that identifies the file as an rpm archive, then there is a signature to verify the integrity and authenticity of the file. Next comes the header, which contains information about the package itself, version, architecture, list of files, etc. And only after all this comes the archive itself with the package files.
Several different package managers can be used to work with RPM, these are the universal rpm utility, the zypper package manager in OpenSUSE, dnf in Fedora, urpmi in Mageia, yum in many Fedora-based distributions.
Let's look at the main features of RPM:
- Automatic dependency resolution is correct in most cases
- The archive file has a special format
- Implementation of dependencies with the choice of dependency on package1 or package2 is not supported.
- Recommended packages are not supported
- Allows you to configure a dependency on a file rather than a package
- All data about installed packages is stored in the database, so if necessary, you can check the checksums
- Scenarios are supported both before and after installation of programs
- The SRPM format is supported, which contains the program sources, all patches with assembly instructions, allowing you to build the program from the sources on the local machine.
- Excellent support for Multilib packages
conclusions
Despite minor differences in the process of processing packages and working with software, these systems are very similar and it will be very difficult to choose which is better, deb or rpm. After all, they perform the same functions, just the technology is slightly different. There are also noteworthy features. Users with slow Internet will find the delta RPM packages feature very useful, which allows you to update only the modified part of the package, and beginners will benefit from the ability to automatically install recommended packages in deb. If you know other differences between rpm and deb, write in the comments!
Related posts:
No similar posts
Convenient additions to RPM[edit | edit code]
There are several programs that allow you to automatically resolve dependencies when installing packages. Here are some of the most famous:
- apt-rpm, a port of APT originally developed by Conectiva, then significantly modified by the ALT Linux Team and continues to be developed;
- apt4rpm, a later port of APT than apt-rpm;
- smart, available for many distributions;
- urpmi, used in Mandriva Linux;
- zypper, used in SuSE;
- yum, developed in Yellow Dog Linux, is also used in Fedora, ASP Linux, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (from version 5.0, and CentOS, Scientific Linux distributions based on it).
Graphical interfaces for RPM are PackageKit and Synaptic.
Sooner or later we have to install software not from official repositories. Not all packages are available there, and the newest versions of newly released programs are not always available. Very often, developers post packages for the most popular distributions on their official website. Usually these are deb and rpm. The latter is a little less common, but if you're using a Red Hat-based distribution, this is the package format you need. You can also often find libraries and other components online that are not available in packaged repositories.
SSD as an alternative
When developing modern computer platforms, the use of hard drives with platters and a spindle is abandoned. Today, solid-state drives are used, which have no moving parts at all. The "innards" of these drives are chips on a circuit board. Such devices work like regular flash drives, but the performance and speed of data access in them is very high and far exceeds the performance of standard HDD drives. In addition, they are quiet, very light and consume little energy. The high price is the only drawback. A 1 TB 7200 RPM HDD will cost less than a 128 or 256 GB SSD.
If we draw an analogy, the difference between an SSD and a HDD is approximately the same as the difference between a regular DVD and a flash drive. They have already moved away from disks, and today only flash drives are mainly used.
What is a pump: general information
Pump is a kind of workout, which is a kind of mixture of intense aerobics and strength training for bodybuilders. You can exercise not only in the gym, but also in a free home environment. In this case, training can be collective or personal and performed under the strict supervision of a trainer.
The first training of this kind was conducted by New Zealand resident and big fan of weightlifting Phillip Mills. This happened in the 90s. Since then, fitness enthusiasts have added super-effective exercise to their knowledge base.
Concept
The abbreviation RPM (Rounds per minute) in Russian is literally translated as “Revolutions per minute”. This unit indicates the rotation speed of the spindle of the hard drive, but the concept itself does not mean anything to the average user. The RPM of the hard drive plays a role in system performance, and the higher the rotation speed, the faster the entire system will run. Most often, this parameter is indicated in the specifications for a hard drive, and between two hard drives, it is advisable to choose the one with a higher RPM.
If you take two disks identical in all respects, but with different spindle speeds, you can immediately notice a significant difference in system performance.
Disadvantages of High Speed
Of course, high RPM ensures high system performance as a whole, but there are also disadvantages. The faster the spindle rotates, the hotter the disk itself heats up, and the more noisy it operates. Also, such hard drives consume more electricity. However, modern technologies make it possible to set the RPM and reduce energy consumption and noise by reducing the spindle speed. Performance losses are compensated by a special data caching algorithm.
How it works?
To understand more precisely what RPM is, it is necessary to understand the operating principle of the device itself. When certain information is requested, the magnetic head unit moves to the requested track. This requires a certain amount of time to search (Seek latency). After the read heads move to the desired sector, you must wait until the disks rotate so that the desired area is under the read head. This period of time is called rotation delay. It is this parameter that depends on the spindle rotation speed, and the higher it is, the lower the rotation delay will be.
Both delays (spindle movement and disk rotation) determine the speed of system access to data. Many performance testing programs calculate this parameter and display it under the “Access to data time” lines. This allows you to determine the real speed of the disk. This parameter directly affects the performance of the entire system. Today there are many powerful laptops that are equipped with powerful video cards and processors, and a large amount of RAM. But at the same time, very slow hard drives with a rotation speed of 5400 rpm are used together with good hardware. As a result, all these powerful components do not work at full capacity due to low data access speeds. So the RPM of the disk is important along with the processor frequency and the video card bus width.
Examples [edit | edit code]
- rpm -Uhv package.rpm
— If the package package is available, it will be updated, if not, it will be installed. - rpm -qa –queryformat '%010 %-%-% '
- Lists all installed packages and their sizes. - rpm -q –queryformat % package.rpm
is the name of the distribution in which the package is installed (option -q for a package installed on the system, option -qp for an uninstalled one). - rpm -qa |
grep xx - list of packages where the combination "xx" appears. - rpm -q –whatprov > Supported Linux distributions [ edit | edit code]
Below is a list of some of the most famous RPM-based distributions:
(This is not a complete list. See the list of Linux distributions for more options)
How to find out the spindle speed?
Determining this parameter is as easy as pie - it is always indicated on a sticker on the device itself. Just open the case of your system unit and look at the sticker. There may be a lot of confusing options, but there is always one of the following lines:
- HDD RPM: 5400.
- RPM: 7200.
- RPM: 10000.
If the hard drive is hidden under the laptop case, which is quite difficult to open, then you can use a special hardware testing program.
The following are popular:
- Crystalmark.
- Aida64.
- Speccy.
They are available for downloading from the Internet completely free of charge. By running one of these programs, you can quickly find information about your storage device. There the hard drive parameters will be displayed in detail. We are primarily interested in the “Rotation Rate” line and the value opposite it. In the Russian version of the Aida64 program, you need to click on “Data storage” – “Windows data storage” on the left side, then in the upper part you need to select the hard drive, after which information about it will appear below, including the line “Rotation speed”.
Package names [edit | edit code]
Each RPM package has a name, which consists of several parts:
- The name of the program;
- Program version;
- The number of the released version (the number of times the program of the same version has been rebuilt). Also often used to refer to the distribution for which this package is compiled, for example, mdv
(Mandriva Linux) or
fc4
(Fedora Core 4); - The architecture for which the package is built (i386, ppc, etc.)
The assembled package usually has a name format like this:
Sometimes the package includes source codes. Such packages do not contain architecture information; it is replaced by src
. For example:
Libraries are most often distributed in two separate packages. The first contains the assembled code, the second (usually -devel
) contains header files and other files needed by developers.
It is necessary to ensure that the versions of these two packages match, otherwise the libraries may not work correctly. Packages with the noarch.rpm
do not depend on a specific computer architecture. They usually contain graphics and texts used by other programs.
Installing RPM file in GUI
If you use OpenSUSE this is very easy. The universal YaST system configurator, among other things, allows you to install rpm packages. You can do this using the file manager by selecting the context menu item for the file open with Yast or by running the command:
yast2 -i package_name.rpm
In Fedora, you can use the distribution's application manager for the same purposes. Previously, there were several more universal utilities for solving this problem, but now they are all outdated.