To strengthen joints and ligaments. How to strengthen joints and ligaments?
We should not think that joints are ideal mechanisms that will work flawlessly throughout our lives. If you expose them to loads, but do not strengthen them in any way, then over time the cartilage will wear out. We should start with what are joints and ligaments? Ligaments are weakly elastic in structure and therefore they are often subject to stretching. They perform a connecting function and connect bones to each other. Joints provide movement of body parts and consist of cartilage tissue with synovial fluid, which fills the cavity of the cartilaginous bursa. The shoulder joints are by nature very vulnerable due to their fragile structure. Joints do not like being overstrained or improperly loaded, pushed into extreme positions, etc. Often joints fail due to prolonged overload. For prevention, it is recommended to follow a proper diet, take special supplements, and also perform a series of physical exercises and, most importantly, always do a warm-up. Now we have access to drugs that work to restore cartilage surfaces. The diet must contain vitamins: E, B6 and C, and as for minerals, the diet must contain: magnesium, zinc, selenium and niacin. There are special preparations that include the entire range of vitamins and substances that joints need. Supplements that strengthen the structure of joints and ligaments:
- Chondroitin and Glucosamine sulfate
- Collagen can be taken in the form of gelatin
- Combined with calcium and vitamin D
To strengthen joints and ligaments, static exercises are necessary - this is when the muscles are under constant long-term tension, while their movement is practically absent. There is also static dynamics - this is when the muscles are tense, but have a small range of motion. The deciding factor here is technique, not weight.
Use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and prescription medications with caution
Exercise machines have their advantages. For example, they will be useful for beginners who do not have good balance during weight-bearing exercises.
However, simulators force you to move in a strictly certain way and do not allow your joints to work freely. Try replacing exercise machines with exercises with barbells, dumbbells, or cables on a cable machine.
Often, weightlifters and powerlifters take anti-inflammatory or analgesic medications before training to get rid of dull, aching joint pain.
By numbing the pain, you only make it worse. Instead of treating your sore joints, you continue to train at high intensity and with poor technique. In addition, regular use of painkillers is bad for the liver.
Read more: Rich Piana at 18, photo of the athlete in his youth
How to restore joints and ligaments. How to strengthen joints and ligaments
Healthy joints and ligaments are the key to the longevity of any athlete; accordingly, you need to know everything about the prevention of their diseases. This knowledge will allow you to avoid various injuries that often occur in athletes who, while training, withstand physical loads of varying severity. In the future, such injuries are fraught with chronic diseases that affect the decline in athletic performance.
There are ways to prevent injuries, as well as treat existing ones. To do this, you need to use special medications that help strengthen ligaments and joints. When starting to take them, it is worth clarifying what the purpose and function of joints and ligaments is. Joints are cartilage tissue consisting of synovial fluid that fills the cavity of the joint capsule. Their main function is to ensure smooth movements of body parts. Ligaments are tissues that connect bones to each other.
What methods exist to help strengthen ligaments and joints?
Their health can be effectively maintained if preventive measures are taken in a timely manner to prevent the consequences that arise from heavy physical activity. Treatment is usually difficult, recovery takes time, and surgery is often required to restore normal function. Periodic preventive measures will help preserve the functionality of ligaments and joints for a long time, which will certainly affect athletic achievements.
Prevention includes warming up before training and using strengthening supplements. Currently, the proven additives that bring the greatest effect are:
- chondroitin sulfate, it is produced by the cartilage tissue of the joint and is a component of synovial fluid;
- glucosamine sulfate is a component of chondroitin sulfate. Its lack in synovial fluid causes chondroitin deficiency. This reduces its quality and a crunching sound appears when moving. Because of this, supplements almost always contain components such as chondroitin and glucosamine sulfate;
- Collagen is the main component of connective tissues, it has a beneficial effect on the skin;
- calcium and vitamin D - most often they are taken at the same time, since the latter promotes the rapid absorption of calcium. A lack of vitamin D provokes inflammation and various types of disorders.
In addition to the main components listed, supplements that help strengthen ligaments and joints may contain:
- Methylsulfonylmethane or MSM - serves only to reduce pain and inflammation. It does not affect the recovery process in any way;
- Omega-3 fats, which improve the function of joint mobility and improve the recovery process. They also relieve pain;
- Shark cartilage – quite commonly used in supplements, contains collagen, calcium and glucosamine at the same time. But the use of these components will be more effective if they are used separately;
- vitamins B, C, E and minerals do not significantly affect the recovery process.
Activities to strengthen ligaments and joints should be carried out 2-3 times a year for 1 or 3 months. The duration of the course depends on the load and condition of the patient. These measures must necessarily include the use of drugs with chondroitin and glucosamine sulfate. It will not be superfluous to use omega-3, collagen, vitamins and minerals.
You can use a combination of the above components, choosing the optimal preventive course specifically for yourself. Glucosamine sulfate and chondroitin must be taken for a month to feel their effects, as they have cumulative properties.
If the ligaments and joints are in a neglected state, not only supplements are needed, but also special gymnastic exercises. It is also worth temporarily limiting the load on sore joints and ligaments. Be sure that everything will work out.
Complex. Home
The previous complex is usually performed in the gym. But this is how you can strengthen your wrist for striking at home. The techniques here are not complicated. To carry them out, you may only need a comfortable mat, for example, the one used for yoga.
The method “How to strengthen your wrists at home” has the following algorithm:
- Position: lying on your fists. The entire load should be placed on their impact zone: Make a fist. Secure your thumb.
- The initial position of the fists to each other is parallel. They swing smoothly. Then the fist needs to be deployed, as if preparing an uppercut. It is better to pump up your hands in order. This is a great way to strengthen your fists and wrists.
- Do push-ups on your fingers. First for everyone. Then reduce the number of fingers involved. The limit of skill is push-ups on one finger. This technique should be given 5-7 minutes a day. This is a powerful strengthening for the fingers and wrists. When you can do push-ups even on 2-3 fingers, this will be a sign of solid strengthening of your wrist for striking.
Strengthening joints and ligaments exercises. Method #1: Physical Activity
Before starting any gymnastics, you should warm up the ligaments and muscles by warming up (for example, walking in place). This helps to increase blood circulation in the tissues, they become more elastic, are not injured and tolerate stress well.
It is better to start the complex with static exercises (muscle tension with a small range of motion) that strengthen the ligaments of the knee joint. They are performed until fatigue and noticeable discomfort in the muscles appear. If pain occurs, it is better to avoid exercise:
- Sit on a chair, bend your foot at a right angle to your leg, raise and lower your leg (in small movements, at an angle of 10–15 degrees). It is more effective to perform similar exercises to strengthen the knee joint with weights.
- Lie on the floor, straighten your legs, lift (15–20 cm from the floor) and hold your straight leg suspended (as long as possible). Repeat 10 times.
- Lie on your side, lift (15–20 cm from the floor) and hold your straight leg suspended (as long as possible). Repeat 10 times.
Illustration of exercises from the list above: 1 – knee extension with a training loop; 2 – alternate leg lifts while lying on your back; 3 – leg lift while lying on your side
Exercises to stretch ligaments and muscles:
- Spread your feet shoulder-width apart, bend over, trying to touch your feet with your palms and clasp them with your hands. Do not bend your knees, stay in this position (as long as you can). Repeat the exercise 10 times.
- Sit on the floor, spread your straight legs to the sides slightly wider than your shoulders. Grab your feet with your hands, lean forward with small movements, trying to “lay” your torso between your legs. Relax, repeat the exercise 10 times.
- Stand on one leg (you can lean on the back of a chair), bend the other at the knee, and bring it back. Grasp your foot with your hand and, with small movements, pull it up towards your buttocks (as far as you can). Repeat 10 times.
Stretching exercises: 1 – bending towards the feet from a standing position; 2 – leg stretching from a sitting position; 3 – front thigh stretch
Exercises to strengthen the ligaments of the knee joint and thigh muscles (repeat each 10 times):
- Squat down slowly, with your feet slightly wider than shoulder-width apart and keeping your pelvis at a right angle to the floor (a few seconds).
- Climb the stairs up and down (forward, backward, sideways). The same exercise can be performed with a wooden stand.
- From a standing position, take a large step forward while simultaneously lowering your other leg to your knee (lunge). Tighten your thigh and buttock muscles (hold this position as long as you can). Make sure your knees are bent at right angles.
Illustration of exercises from the list above: 1 – squats; 2 – going up and down the stairs; 3 – forward lunges
To strengthen the knees, some yoga asanas are very effective (Utkatasana on toes, supported on a wall, and others); exercise on various exercise machines, running, swimming, and race walking help well.
Special exercises
Both before playing sports and after an injury, surgery requires special exercises that will help strengthen the ligaments, which will help not only restore the function of the joint, but also avoid knee instability and sprains.
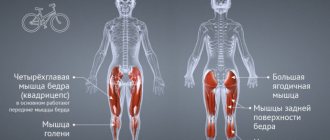
Exercises for developing the knee joint, stretching actions, as well as training that strengthens the muscles of the lower leg and thigh help with this.
To pump up the quadriceps muscles, the following exercise is suitable . From a standing position we take a step forward. Lower your buttocks down until your working leg forms a right angle. At the same time, we try to touch the floor with the knee of the second limb. Having completed up to 10 repetitions, we move on to working the second leg.
It is impossible to strengthen the ligaments without working the popliteus muscle. Walking up stairs helps work this muscle, which can be imitated by using a step, any hill, or even a chair.
The best exercise for weak ligaments is squats. The main thing is to follow the technique so as not to harm your knees. Any squats are performed with the buttocks pulled back so that the hips form a straight line in relation to the floor. If such exercises are difficult, you can do partial squats or use a support.
Jumping also affects the condition of the ligaments. You can train with a skipping rope, on the steppe, or using regular jumps. To avoid injuring your knees, especially after surgery, you need to land on slightly bent legs.
Important! During exacerbations of arthrosis, it is not advisable to conduct intensive training until the inflammatory processes have completely subsided.
Yoga also helps with weak ligaments. Yoga exercises are gentle. Therefore, they can be carried out both after the removal of the cast and in the presence of arthrosis. Yoga has many positions and movements that involve stretching and warming up the knee.
Doctors recommend that patients who have undergone any surgery or been injured exercise their joints in water. Swimming or water aerobics helps strengthen ligaments and muscles without overloading the joint.
There are quite popular and simple ways to strengthen the joint, which are available to patients of different ages and with any joint condition. These are regular walks that can be practiced daily.
Vitamins for athletes' joints. Vitamins for ligaments and joints of athletes
Vitamins for joints: rating of the best supplements from sports nutrition and pharmacies for athletes
The normal functioning of joints plays an important role in the life of any person. Healthy joints allow you to spend time actively and play sports. However, joints are parts of our body that are subject to constant wear and tear. With normal functioning of the body and with a sufficient amount of nutrients, joints are able to work for a long time. Athletes are especially susceptible to wear and tear on their joints because they regularly subject them to high levels of stress. Therefore, vitamins for joints may eventually become an athlete’s essential item.
What vitamins for joints and ligaments do athletes need during exercise?
To maintain or restore the function of joints and ligaments, there are sports supplements and vitamin complexes aimed at protecting joints. Sports supplements are also necessary for people after suffering injuries such as fractures, dislocations or sprains. The human body is able to restore itself after injury, but only if it receives the right amount of essential vitamins and other substances. Joints require attention as you get older, so older adults should take supplements to prevent and protect against potential problems. Taking such complexes allows you to delay the onset of age-related changes and ensure active longevity.
The most common substances in chondroprotective sports nutrition supplements are the following: chondroitin, glucosamine, hyaluronic acid, methylsulfonylmethane or MSM, collagen hydrolysate. These substances help strengthen cartilage tissue, reduce inflammation, increase elasticity and mobility of joints, ligaments, cartilage, and also improve joint lubrication.
Vitamins for joints and bones
In a large abundance of microelements there are substances, the deficiency of which worsens the condition of joint tissues. Their list contains vitamins such as:
- Vitamin C - helps improve the elasticity of vascular walls, thins the blood, and blood thickening is the cause of many joint diseases and hemorrhages in them. Vitamin C is also involved in the synthesis of collagen, which is very important for joint health, because it is the main element of joint tissue.
- Vitamin D is a vitamin that is also called a prohormone. This element strengthens cartilage and bone tissue.
- Vitamin E is a joint protector from the negative effects of free radicals that destroy joints. It also helps in the regeneration of cartilage tissue.
- Vitamin B1 - this vitamin normalizes carbohydrate metabolism, and carbohydrates are part of the building material for all cells of the body, and it is also contained in cartilage tissue. In the absence of the required amount of carbohydrates, the aging process of joints may begin earlier.
- Vitamins B5 and B6 – help strengthen collagen fibers and reduce pain from the inflammatory process.
- Vitamin B12 – has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Vitamin A is responsible for the proper formation of cartilage.
Carrying out treatment in a sanatorium
After surgery or long-term treatment of arthrosis and other diseases of the knee, rehabilitation measures are required. It is advisable to engage in such treatment in a rehabilitation center or specialized sanatorium. There are quite good sanatoriums, both in Russia and in Belarus and Crimea, where special programs are offered for the restoration and strengthening of the knee joint.
The sanatorium carries out all the activities in a complex, which allows not only to strengthen the ligaments, but also to improve the health of the body and restore motor abilities. Specialized sanatoriums for the treatment of arthrosis offer balneotherapy, mud treatment, and physiotherapeutic procedures.
In addition, in any sanatorium where rehabilitation after surgery takes place or arthrosis is treated, special therapeutic sets of exercises are provided, which can be carried out both individually and in groups. Sanatoriums also offer exercise classes and swimming pools.
Recuperation in a specialized sanatorium helps restore the joint after surgery, strengthen the ligamentous apparatus, and forget about exacerbations of arthrosis for a long time.
Proper nutrition
Along with regular exercise therapy, it is recommended to follow a proper diet. Basic nutritional recommendations:
- The menu should include foods enriched with large amounts of collagen and gelatin. Elderly people and athletes at risk are recommended to consume jellied dishes and jellied meat, jellies and jellies.
- The diet must contain foods that contain substances that have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. This includes green tea, fresh fruits, nuts, vegetable oils.
- The body must receive the required amount of calcium and vitamin D per day. Sources of these elements are fermented milk products, fish and eggs.
It is necessary to avoid smoked meats and marinades, fried and fatty foods, products that contain preservatives and various additives of chemical origin. If you have problems with excess weight, you will definitely need to go on a diet and get rid of excess pounds. Excess body weight puts even more stress on your joints, increasing the likelihood of injury.
Never do leg extensions in a seated position.
Stay away from seated leg extensions if you have knee pain.
Even better, don’t do them at all, even if your knees are fine. Since this is an unnatural movement for the knee joints. Because they are designed by nature to work together with the entire leg from a standing position on the floor. If you have had an anterior cruciate ligament sprain or rupture (a fairly common sports injury), then doing leg extensions in a machine is simply stupid. What's the matter? This exercise is an open kinetic chain movement, meaning the leg does not stand on the ground, but moves freely in the air. It is important to remember that the knees work best in conjunction with the muscles and joints of the legs. And leg extensions in the machine, unlike squats, remove all other joints from the movement. As a result, strong quadriceps create a lot of torque and stress on the anterior cruciate ligament and the entire knee joint.
Alternate training to failure with recovery periods
Weight itself is not as harmful to joints as disruption of movement mechanics during lifting. Unfortunately, training to failure is often accompanied by deviations from correct technique.
Recent research has shown that muscle hypertrophy depends more on the amount of time spent under tension than on doing a small number of repetitions with the highest possible weight.
It is better to do 12 slow repetitions with a lighter weight, during which the muscles are constantly under tension, than 6 fast repetitions with the heaviest weight possible.
“Some weightlifters like to train with heavy weights and work until their muscles fail every workout. This is what most intensity-increasing techniques are designed to do, says Escalante. “If you always train to the maximum, you will have to sacrifice something, and that sacrifice will be your joints.”
The best way to avoid this is to alternate the load. Your muscles will experience stress, but this will be combined with periods of recovery - less intense training.
Escalante is a big fan of wave-based training patterns. Instead of dedicating multiple weeks to super-heavy and light recovery workouts, he prefers to alternate these periods within one training week.
Most powerlifters try to build muscle with a regular 8-12 rep workout, but sometimes they try lifting as much weight as they can and end up adding an extra 20-30 pounds to the barbell. This leads to a significant increase in stress on muscles and connective tissues.
Escalante also notes that after intense training, tendons and ligaments grow more slowly than muscles. They can become a weak link in your body, putting you at high risk of injury.
Take care of your joints, do not neglect warming up and do not train to failure every time, otherwise you will have to finish your journey in strength sports much earlier than you planned.