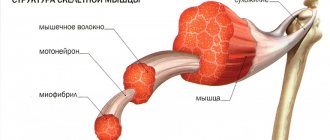
Carbohydrates. What to choose during exercise
Carbohydrate drinks, intended for consumption during and immediately after training, are included in the diet of athletes of various sports, both speed-strength and those requiring general endurance, which is not surprising, since carbohydrates are energy, and energy is a necessary condition for any movement. Similar products are offered to us by many sports nutrition manufacturers, and their composition is by no means complicated - a mixture of different types of carbohydrates, or even just one of them. What exactly can we find on the label with the composition: sucrose, fructose, dextrose, maltodextrin and amylopectin (Vitargo). It would seem that it is not so important what type of carbohydrates we consume during exercise, because they will all eventually turn into glucose, but not everything is so simple. The metabolic characteristics of various carbohydrates and their structure can significantly influence the rate of restoration of the body's energy potential. Let's look at each of the above types of carbohydrates.
Sucrose (or simply sugar in everyday life) is a disaccharide consisting of two monosaccharides: α-glucose and β-fructose. Sucrose, entering the intestines, is quickly broken down into glucose and fructose, which are then absorbed into the blood. Therefore, in its effect, sucrose is equivalent to a mixture of 50% glucose and 50% fructose. The presence of fructose in sugar is its main disadvantage - for reasons that will be indicated below. Other disadvantages include poor tolerance to the gastrointestinal tract during exercise, but the advantage is its ultra-low cost and availability - sugar can be bought at any store.
Fructose is a monosaccharide (isomer of glucose). The metabolism of fructose in the body is different from the metabolism of glucose. Unlike glucose, which serves as a universal source of energy, fructose is not absorbed by insulin-dependent tissues (including muscle), and no other cells of the human body, except sperm, can use it directly. Fructose can be converted into liver glycogen, but cannot be converted into muscle glycogen. In connection with the above, during intense physical activity its benefit in providing energy for muscle activity is small. Fructose is relatively inexpensive and available, usually sold in the health food section of grocery supermarkets.
Dextrose is nothing more than glucose in dry form. An excellent source of energy during exercise, but much less accessible than sucrose or fructose. The pharmaceutical form in the form of tablets is very inconvenient, since a lot of these tablets must be used at one time. It is also worth considering that at high concentrations in an aqueous solution (more than 5%), dextrose can cause heaviness in the stomach and belching.
Maltodextrin is starch enzymatically broken down into large pieces (dextrins), and when maltodextrin is completely broken down, glucose is formed. The advantage is its relatively low rate of breakdown in the digestive system, thereby ensuring a long and uniform supply of glucose to the body. Maltodextrin is cheap to produce, easily digestible and does not cause gastric complications, has virtually no taste, which makes it convenient for preparing training drinks, which is why it is so common in various sports nutrition products, especially gainers. You can purchase it in its pure form only in bags weighing 25 kg or more, intended for the needs of the food industry, or in sports nutrition stores in the form of so-called. carbohydrate complexes, for example CARBO PLUS from UNIVERSAL NUTRITION, which contains exclusively maltodextrin.
Amylopectin is a branched polysaccharide formed by glucose residues. It is part of starch (usually 70–90%), and in the so-called waxy varieties of corn, barley, and rice, starch consists only of amylopectin. Widely known in the world of sports nutrition under the patented name “Vitargo®”. From the moment sports scientists from Stockholm established that Vitargo restores glycogen levels after exercise much faster than any other type of carbohydrate and passes through the stomach faster, it immediately found its way into the diet of professional athletes from a variety of sports. Just as whey isolate is considered the most valuable among proteins, Vitargo is considered the most valuable among carbohydrates. It has a number of advantages, which led to its wild popularity: it is in the stomach only for a short period of time, it is absorbed very quickly and easily, therefore it does not cause discomfort during physical activity (which is typical for sugar and dextrose), it can be used in concentration above 5–8%, that is, more than twice as high as recommended for carbohydrate drinks based on sucrose or maltodextrin, does not absorb water from the body’s reserves, but on the contrary, increases the flow of water into the blood, acting as a kind of pump during the athlete’s physical activity. It is interesting that initially “Vitargo” gained particular popularity among representatives of sports that require the manifestation of general and strength endurance, such as cross-country skiing, biathlon, cycling, American football, marathon, and only later it was “tried” by security forces: bodybuilders and powerlifters. It is known that Russian pro-bodybuilder Leonid Istomin used Vitargo during carbohydrate loading before competitions, noting that this type of carbohydrate does not cause problems with absorption and fluid retention in the intestines, which is very important during loading. And one of the most titled powerlifters in Russia, eleven-time world champion and seventeen-time European champion Konstantin Pavlov, used Vitargo throughout his preparation for the European Bench Press Championship in Terni, Italy, where he actually became the winner once again. Vladimir Kravtsov, “Uncle Vova,” has Vitargo as one of his favorite types of carbohydrates, which he uses constantly. Currently, amylopectin can be found in various sports nutrition products from a variety of manufacturers. Complex manufacturing technology also determines the high cost of the product; perhaps this is its only disadvantage.
Thus, based on the choice of carbohydrate product that you are going to use during or after your workouts, you must take into account that different types of carbohydrates will support the energy of muscle activity in different ways, and your digestive system, which works at low speed during exercise ", will also react to them differently. It is believed that when using sugar, fructose or dextrose in a drink, their concentration should not exceed 5%, maltodextrin - 8%, Vitargo - 15%.
Amylopectin is one of the complex carbohydrates found in food starch. In bodybuilding, it is used to increase the flow of energy necessary for the growth and development of muscle tissue and muscles. From a chemical point of view, it is a polysaccharide that is formed by several glucose molecules. In food it can be found in maize, rice, wheat, starch from the waxy plant, potatoes, and waxy varieties of corn. It is of great value to the athlete, so many sports nutrition manufacturers have paid attention to creating a supplement that is freeze-dried amylopectin. We will tell you in this material how effective amylopectin is for improving performance and fueling an athlete’s body, and how to take it.
Action and benefits of amylopectin
Bodybuilders use it to optimize muscle glycogen levels. With this starch-like substrate, various carbon drinks are prepared to increase energy reserves. Thanks to amylopectin:
- You can increase the operating time under heavy loads.
- The athlete's body is fueled with the necessary substances during physical exercise.
- Muscles recover faster, protein is synthesized more actively.
The main advantages of the supplement also include the following:
- Its molecules take water from reserves, acting like a pump, thereby increasing the flow of fluid into the vessels and blood, and with it transferring nutrients to the muscles. Therefore, it can be used in combination with supplements such as glutamine, BCAA, creatine and others, which will only benefit their effectiveness and speed.
- This high-molecular, complex, ultra-fast carbohydrate in cocktails is perceived by athletes much better than maltodextrin or sugar, because it is absorbed in a matter of minutes, without causing a feeling of discomfort, excessive satiety, or bloating. And this is very important, because physical activity with a bloated stomach is an extremely unpleasant sensation. Plus, such training will bring neither satisfaction nor benefit. Since it is quickly digested, you can drink it immediately before going to the gym during the workout itself and even after it.
- It will not reduce your activity due to the release of insulin, as can happen in the case of sucrose or dextrose, but on the contrary, it will increase it. Suitable even for use during a pre-competition diet.
- It speeds up the fat burning process, helps fats break down and be eliminated. A sufficient amount of complex carbohydrates promotes the oxidation of fat cells to final products.
Because of all of the above, it is popular in almost all sports where endurance is important, for which a stable level of glycogen in muscle tissue is responsible.
Insulin and bodybuilding
The article discusses the different types of carbohydrates and how the body regulates blood glucose levels.
Unbridled enthusiasm is a characteristic feature of many aspiring bodybuilders. This irrepressible enthusiasm is accompanied by an insatiable thirst for knowledge.
Unfortunately, newcomers absorb any information and misinformation like a sponge.
They eagerly embrace training programs published in glossy "muscle" magazines, recommended by "experienced" athletes and those willing to give advice.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates provide energy to the human brain, central nervous system (CNS) and muscle cells in the form of glucose (blood sugar). Carbohydrates can be divided into simple and complex carbohydrates.
Simple carbohydrates
Simple carbohydrates are sugars whose organic structure bonds are easily destroyed during digestion. Sugars are classified as monosaccharides (mono = one) or disaccharides (di = two).
Monosaccharides include glucose, galactose and fructose. Disaccharides are molecules consisting of two monosaccharides. These include maltose (malt sazar - two glucose residues), sucrose (fructose and glucose), lactose (galactose and glucose). Our body can only absorb monosaccharides into the blood.
Complex carbohydrates
Complex carbohydrates are polysaccharides (poly = many) found in starch and fiber. Starch is a polysaccharide that humans can digest, but it must be broken down into monosaccharides before it can be digested. how they will be absorbed into the blood.
Polysaccharides can also be linear (amylose, one of the main polysaccharides of starch, consists of from 400 to several thousand glucose molecules) or branched (amylopectin consists of several hundred glucose molecules).
Glycogen (glucose stored in muscles) has a structure similar to amylopectin.
Cellulose is the fiber in vegetables that the human digestive tract cannot digest.
How the body uses carbohydrates
Once digested and absorbed through the intestinal wall, the body can use glucose in the following ways.
- The body can use the glucose directly in the mitochondria, releasing carbon dioxide, water and energy.
- If glucose is not needed right away, it can be converted into glycogen by the liver or muscles.
Muscle glycogen supplies energy only to the muscles. Glycogen in the liver can support energy in any part of the body.
- Any glucose that enters the body after being saturated with glycogen is processed by the liver into fat and accumulates in adipose tissue.
The level and pattern of stored fat depends on many factors, but is generally related to whether a person consumes more calories than he burns.
The connection between sugar and blood
Our body regulates blood glucose levels. When blood sugar levels rise, the pancreas releases insulin. If the sugar level is too low, then glucagon (a hyperglycemic hormone from the pancreas) is released.
Pancreas
Monitors blood glucose concentrations
| When blood glucose levels are high, insulin is released | When blood glucose levels are low, glucagon is released |
| Signals: fat and muscle cells to take up glucose This lowers blood glucose levels to normal levels Occurs immediately after eating | Signals: The liver breaks down glycogen and releases glucose into the blood This raises blood glucose levels to normal levels Occurs between meals |
Applicable to bodybuilding
It is important for bodybuilders to understand that when insulin levels are high, the body stores excess glucose as additional body weight. Unfortunately, your body doesn't care at all whether the mass is muscle or fat. It is important to understand the difference in carbohydrates and their use by muscle tissue
Enzymes in muscles are able to digest starch, which breaks down into usable glucose
It is important to understand the difference in carbohydrates and how they are used by muscle tissue. Enzymes in muscles are able to digest starch, which breaks down into usable glucose
The liver contains intermediate enzymes that convert glucose, fructose, galactose, amino acids and other metabolic products into glycogen stores.
Comments:
How to take amylopectin?
The glycemic index of the sports supplement amylopectin ranges from 100 to 135%, depending on the manufacturer.
It is an exception from complex carbohydrates, since it is very quickly absorbed into the bloodstream, which allows it to be treated as a simple carbohydrate when taken. This remedy should be used in the following way:
- One minute of intense strength training should take between half and a gram of the supplement. Therefore, if your stay in the hall takes an hour, then the drink is prepared with 30–60 g of the product. You can start from the lower limit and gradually rise, and if you have experience and the body accepts it well, then you can immediately use an average or high norm (40–60 g).
- It must be dissolved in clean water without gas, stirring well so that no sticky lumps remain.
- If your goal is to gain weight, then close the carbohydrate window with a cocktail, that is, drink it immediately after completing the exercise.
- A drink with only this additive or a whole combination of different ones can be drunk little by little throughout the entire lesson. If you come to the training room with a slight feeling of hunger, so that your last meal is two to three hours before, then all the calories you drink will go towards endurance and energy, without being stored as excess weight.
- If you are expecting an extremely intense, long-term load with very heavy weights and relief work, then it is recommended to take it half an hour before class (30 g) and during (40–50 g).
During the drying period, athletes sometimes use this powder so that they have enough energy not to abandon their training.
In this case, no more than 20 grams of product are used per session. Also, you should take this into account by adjusting your carbohydrate diet so that fat burning does not stop. In addition to preparing a drink with only amylopectin, it can be combined with a number of other components. The most popular cocktails among famous bodybuilders are those containing:
- BCAA - from 15 to 30 g;
- amylopectin from 50 to 80 g;
- creatine 10–15 g;
- glutamine from 10 to 20 grams.
Also, arginine, citrulline malate, beta-alanine and others are often added. In order to find out in more detail which recipe will be most effective in your case, you can seek advice from professionals in this field.
What is starch Properties and application
2). Its molecular weight reaches 1-6 million.
Rice. 2. Branched macromolecule of amylopectin (colored circles are places of branching of side chains)
Amylopectin is a branched polysaccharide, in the chains of which D-glucopyranose residues are linked by α(1,4)-glycosidic bonds, and at branching points by α(1,6)-bonds. Between the branch points there are 20-25 glucose residues.
Hydrolysis of starch in the gastrointestinal tract occurs under the action of enzymes that cleave α(1,4)- and α(1,6)-glycosidic bonds. The end products of hydrolysis are glucose and maltose.
Glycogen. In animal organisms, this polysaccharide is a structural and functional analogue of plant starch. It is similar in structure to amylopectin, but has even greater chain branching. Typically, between branch points there are 10-12, sometimes even 6, glucose units. Conventionally, we can say that the branching of the glycogen macromolecule is twice that of amylopectin. Strong branching helps glycogen perform its energy function, since only with a plurality of terminal residues can rapid cleavage of the required number of glucose molecules be ensured.
The molecular weight of glycogen is unusually large and reaches 100 million. This size of macromolecules helps perform the function of a reserve carbohydrate. Thus, the glycogen macromolecule, due to its large size, does not pass through the membrane and remains inside the cell until the need for energy arises.
Hydrolysis of glycogen in an acidic environment occurs very easily with a quantitative yield of glucose. This is used in tissue analysis for glycogen content based on the amount of glucose formed.
Similar to glycogen in animal organisms, amylopectin, which has a less branched structure, plays the same role as a reserve polysaccharide in plants. This is due to the fact that metabolic processes occur much more slowly in plants and do not require a rapid influx of energy, as is sometimes necessary for an animal organism (stressful situations, physical or mental tension).
Cellulose. This polysaccharide, also called fiber, is the most common plant polysaccharide. Cellulose has great mechanical strength and serves as a support material for plants. Wood contains 50-70% cellulose; Cotton is almost pure cellulose. Cellulose is an important raw material for a number of industries (pulp and paper, textiles, etc.).
Cellulose is a linear polysaccharide in which D-glucopyranose residues are linked by β(1,4)-glycosidic bonds. The disaccharide moiety of cellulose is cellobiose.
The macromolecular chain has no branches; it contains 2.5-12 thousand glucose residues, which corresponds to a molecular weight of 400 thousand to 1-2 million.
The β-configuration of the anomeric carbon atom results in the cellulose macromolecule having a strictly linear structure. This is facilitated by the formation of hydrogen bonds within the chain, as well as between neighboring chains.
This packing of chains provides high mechanical strength, fibrousness, insolubility in water and chemical inertness, which makes cellulose an excellent material for building plant cell walls. Cellulose is not broken down by ordinary enzymes of the gastrointestinal tract, but is necessary for normal nutrition as a ballast substance.
The ether derivatives of cellulose are of great practical importance: acetates (artificial silk), nitrates (explosives, colloxylin) and others (viscose fiber, cellophane).
Previous1234567891011121314Next
Date added: 2015-05-26; ;
Contraindications to the use of amylopectin in bodybuilding
This drug should not be taken if:
- Individual intolerance and allergic reaction to components.
- Pregnant at any stage.
- Nursing mothers
- Children and adolescents who have not yet turned eighteen years old.
Before you start improving your body with the help of this complex carbohydrate, you should consult with a trainer and a nutritionist.
Only they will be able to say with confidence how useful the supplement will be for you and whether its use will cause any harm. The price of amylopectin in Russia is from 350 rubles, and in Ukraine from 150 hryvnia.
Ivan Vodyanov answers questions about amylopectin in the following video:
Amylopectin is the most widely used carbohydrate by elite athletes, ideal for fitness professionals or endurance athletes. This carbohydrate has been the subject of scientific research demonstrating its ability to assimilate and recharge glycogen stores faster and more effectively than any other available glucose polymer composition on the market.
Amylopectin promotes muscle growth, increases energy, and improves performance. It prevents, ensures immediate carbohydrate assimilation to increase energy levels and replenish muscle glycogen. Amylopectin recharges glycogen faster and more effectively than any other glucose composition on the market and is the most recognized carbohydrate by professional athletes. This carbohydrate spends very little time in the stomach, does not cause discomfort or upset, and has no side effects. Benefits of Amylopectin:
- Promotes muscle growth.
- Increases energy.
- Improves performance.
- Prevents overtraining syndrome.
- Provides instant assimilation of carbohydrates.
- Quickly replenishes muscle glycogen.
- Does not cause discomfort or side effects.
Being in nature and receiving
Starch is formed during photosynthesis as a result of the polymerization of glucose:
- 6CO2 + 6H2O (light, chlorophyll) → C6H12O6 + 6O2;
- nC6H12O6 → (C6H10O5)n + nH2O.
Starch is the main component of plant seeds. It is used as an energy reserve. The most starch is found in the endosperm of cereals (up to 85%) and in potato tubers (20%).
Starch is found in cells in the form of grains, the shape of which depends on the type of plant. Starch grains are layered grains. They grow by laying new layers of starch on old layers. Grains are deposited in special plant cells (types of leucoplasts) - amyloplasts.
Rice. 3. Examples of starch grains.
In food and industrial chemistry, starch is most often isolated from potatoes. To do this, the tubers are crushed, washed and settled. The starch that floats to the surface is collected, washed and dried until crystals form.
Starch is not synthesized in the body of animals. A similar energy substance in animal cells is glycogen.
Product Features
Amylopectin is a highly branched glucose polymer found in plants
. This is one of the two components of starch - amylose. It is easily soluble in water.
The reason for their relative digestion rates is due to the fact that the enzymes have greater access to glucose subunits in a highly branched structure.
Due to its molecular weight, amylopectin is absorbed by the intestines faster than dextrose or maltodextrin - “fast carbohydrates”, which, in turn, leads to a significant increase in glycogen content.
Amylopectin is a carbohydrate from waxy corn, potato starch, rice or wheat.
Due to its high amylopectin content, waxy corn is considered an extremely fast-acting carbohydrate and is sold by manufacturing companies in powdered form. Due to the rapid absorption of amylopectin in the body, bodybuilders often use waxy corn to quickly release glycogen levels after a workout. (Glycogen is the stored form of carbohydrates in muscle tissue)
. Some companies claim that waxy corn is absorbed 70-80% faster than other popular sugars such as dextrose or maltodextrin.
Sports nutrition products containing amylopectin
Vitargo® is a unique, patented carbohydrate specifically designed for elite athletes to effectively supply the body with readily available muscle energy (glycogen). Vitargo® has undergone clinical trials at the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, which have shown that it has unique characteristics compared to other sports carbohydrate drinks on the market today. Tests have proven that Vitargo® restores glycogen levels faster and passes through the stomach faster.
It consists of amylopectin, obtained from specially modified corn starch (WMS), with a very high molecular weight (> 500,000). Element has virtually no taste, easily dissolves in water, and is easily combined with creatine, BCAA and/or arginine. WMS is the latest development in the sports nutrition industry; it is a complex carbohydrate that easily passes through the digestive system and goes directly to the muscles. An unrivaled glycogen source, Element works amazingly fast (much faster than dextrose). Can be taken pre- or post-workout, or as a supplement to regular meals or protein shakes.
- An indispensable tool when preparing for competitions
- Replenishes glycogen stores almost instantly
- Helps deliver BCAA to muscles extremely quickly
Brands
Amylopectin Vit.O.Best.
Amylopectin Vit.O.Best
is a high-purity, high-quality supplement containing amylopectin, a highly effective carbohydrate.
Contains 100% pure amylopectin and no other carbohydrates or sweeteners. Promotes accelerated recharge of muscle glycogen. Vit.O.Best
is a well-known company engaged in the production of a new generation of products. This company develops innovative formulas and produces high quality supplements with the best raw materials available in the market at a very affordable price.
Max Muscle Sports
MMSN
introduces
Max ACM
with a
Triple Carb Matrix
with three different molecular weight carbohydrates including pure waxy corn starch (amylopectin), maltodextrin and trehalose. Max ACM is designed to support glycogen production, which provides essential energy for bodybuilding.
Geneticlab AMYLOPECTIN (amylopectin) 1000gr
Geneticlab nutrition
– manufacturer of high quality products. Amylopectin from this manufacturer in one serving (33 g) contains: B. - 0.1 g; F. - 0 g; U. - 28.1 g. In one serving - 112 kcal.
For aldoses and ketoses.
Monosaccharides
otherwise called
monosae
.
According to the chemical composition, monoses are either polyhydroxyaldehydes or polyhydroxyketones. Monosaccharides that contain an aldehyde group () are called aldoses
, and a ketone group () are called
ketoses.
A characteristic feature of the carbohydrate class
is the presence of
at least two hydroxyl groups and one carbonyl (aldehyde or ketone) group
.
Therefore, the simplest carbohydrate must contain three carbon atoms. Based on the number of carbon atoms, monosaccharides are called trioses, tetroses, pentoses, hexoses
etc.
The name monoz takes into account both the number of carbon atoms and the presence of an aldehyde or ketone group. For example, monosaccharides containing 6 carbon atoms and an aldehyde group are called aldohexoses
, but if they contain a keto group, then
ketohexoses.
Scientific and practical article by the speaker of the II International Fitness Convention “T..R.I.U.M.F.” Sofia Kiryukhina
Every day there are more and more supporters of proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle. People began to pay more attention to their own health and appearance. Often on the Internet you can find information from doctors, trainers and fitness models that starch is the cause of numerous diseases associated with metabolic disorders. People thoughtlessly believe this and are interested in what foods contain starch and try to protect themselves from consuming it. Is starch really that bad?
Since ancient times, starches have been the most commonly consumed type of carbohydrate and an important source of energy for many people; our ancestors obtained many nutrients and micronutrients from starchy foods. The main sources of starch are legumes, wheat, corn, rice, and potatoes. Currently, starch is widely used in various branches of the food industry (confectionery, bakery, sausage, etc.), which confirms the relevance of this topic. After all, many of the foods that we eat today in one form or another contain starch, so we need to figure out which starch is healthy and in which foods, and when it should be avoided.
The purpose of this work: to analyze the starch content in various food products.
Starch consists of glucose molecules and is a complex carbohydrate in which two types of polymers are present: amylose and amylopectin, the only difference is that amylopectin consists of branched glucose molecules, has a branched structure , is easily broken down into smaller parts during digestion and is more intense increases blood sugar levels and, as a result, insulin levels (prevails in glycemic starches), and amylose consists of linear or slightly branched chains, takes a long time to digest (found mainly in resistant starches) . Depending on which polymer predominates, starches are divided into glycemic, which are easily digested, and resistant.
Glycemic starches are broken down in the gastrointestinal tract by the action of amylase secreted by the pancreas and, depending on the rate of digestion, are considered either fast or slow digestible. For example, mashed potatoes are considered to be quickly and completely digested in the small intestine, since the starch in it is in a gelatinized state. Slowly but completely digestible starches are found, for example, in pasta, especially those prepared according to the classic Italian recipe, that is, al dente, this allows the starch to dissolve in the body for a long time, gradually turning into glucose.
The most beneficial for the human body is resistant starch. According to the study: consumption of resistant starches improves a number of human physiological indicators: glycemic and insulin index, blood lipid composition, increases the feeling of satiety. The thing is that such starch is not available for fermentation in the small intestine. However, once in the large intestine and rectum, it becomes available for fermentation, thus the physiological functionality of such starches is similar to dietary fiber.
Confirmation of this is the following: from 1 g of resistant starches the body is able to extract only 2 kcal - despite the fact that in 1 g of carbohydrates (and starches are carbohydrates) there are always about 4 kcal, all because carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, and bacteria are not able to break down to glucose, it breaks down to butyric and other short-chain fatty acids - it turns not into sugar, but into a very healthy fat. The type of carbohydrates and starches we eat determines how many calories we get, just compare potato chips to boiled potatoes, a chocolate cereal bar to oatmeal.
There are four types of resistant starch:
RS1-Starches contained in products that have a hard fibrous shell that cannot be broken down by enzymes in the gastrointestinal tract. Contained in legumes, whole grains, seeds. However, canned beans and peas contain almost no resistant starch.
| Resistant starch content in products | |
| Name | Resistant starch content (g) per 100 g of product |
| Raw oats | 11.8g. |
| Oatmeal, raw | 11 |
| Wheat germ flakes | 6.1g. |
| Boiled white beans | 4.0g. |
| Chickpeas, cooked | 3.0g. |
| Lentils, cooked | 3.5g. |
| Peas, cooked | 3.0g. |
| Barley | 2.2g. |
| Beans, cooked | 2.0g. |
| Canned beans or peas | 0g. |
RS2 - Starches that enzymes in the human digestive system cannot break down into proteins, fats and carbohydrates. This includes raw potatoes and unripe bananas, corn, with a high amylose content. For example, unripe banana fruits contain 4g. resistant starch per 100g, which turns into regular starch when ripe.
You should be careful with corn, since the amount of resistant starch also depends on the quality of the product and the variety. For example, some varieties of corn contain less than 1% amylose (for example, waxy corn). Other types of corn, on the contrary, contain from 55 to 80% amylose, but they are very rarely grown, since the higher the amylose content, the lower crop yield, on average corn contains 15-20% resistant starch.
RS3- “Retrograde” starches, their peculiarity is that when they cool, they change their structure and again become more resistant to digestion. Formed in bread, cereals (corn flakes, cooked and cooled potatoes, cold rice, chilled pasta, crackers, etc.), the proportion of resistant starch in such products is in small quantities - no more than 5%.
| Resistant starch content in products | |
| Name | Resistant starch content (g) per 100 g of product |
| Italian bread, toast | 4.5g. |
| Rye bread | 3.8g. |
| Muesli | 3.5g. |
| Cornflakes | 3.0g |
| Corn tortilla | 2.5g. |
| Pearl barley | 2,3 |
| Sourdough bread | 2.2g |
| Cooked millet | 1.8g. |
| Shredded wheat | 1.5g. |
| Wheat pasta | 1.6g. |
| Pita, wheat | 1.0g. |
| Bran | 0.8g. |
| Whole wheat bread | 0.7 g. |
| Croissants, scones, granola bar, sugar cookies. | <0.2 g. |
Various varieties of rice contain from 0.5 to 4.5% resistant starch, approximately 1 - 3.5 g of resistant starch per 100 g, brown rice - 1.7 g. The consistency of cooked rice and its gloss are determined mainly by the amylose ratio - amylopectin" in starch. If rice is crumbly after cooking, then it contains a high or medium amount of amylase, resistant starch, and low-amylose rice is sticky or semi-crumbly. Most often, short grain rice has less amylose, which is why it clumps. But you can increase the content of resistant starch in rice, which was proven by Sudhair James, a student at the Sri Lankan College of Chemical Sciences, for this you need to cook the rice with the addition of a small amount of fat, for example, coconut oil, let it cool and put it in the refrigerator for 12 hours, this procedure increases the resistant starch content of rice by 10 times.
Consider potatoes - one of the main sources of resistant starch, but only when cooked correctly, for example, freshly cooked potatoes contain 1.6 grams of resistant starch per 100g, and sweet potatoes 1.8 g. However, cooking and subsequent cooling of potatoes or sweet potato leads to an almost twofold increase in resistant starch, which is 5 grams per 100 grams of product, almost no starch is lost in potatoes during the frying process, but, as noted earlier, there is almost no resistant starch in mashed potatoes, it turns into glycemic.
| Resistant starch content of potatoes and sweet potatoes | |
| Name | Resistant starch content (g) per 100 g of product |
| Boiled potatoes | 1.6g. |
| Boiled sweet potato | 1.8g. |
| Boiled and cooled potatoes or sweet potatoes | 5.0g. |
| Potato chips | 3.5g. |
| Mashed potatoes | 0 g. |
To get the maximum effect from resistant starches, you need to consume them in the least processed form possible; heating destroys complex starches, so a number of popular tips become important: soaking or sprouting cereals significantly shortens their cooking time and preserves complex carbohydrates intact. Only proper preparation and consumption of foods containing resistant starch kills precancerous cells in the intestines,” says Janine Higgins, Ph.D., a researcher at the University of Colorado Cancer Center. (Proper use is at room temperature or below.)
There is another type of resistant starch, RS4, which does not occur naturally but is produced industrially.
In the modern world, products are increasingly processed, so now starch with a high content of amylose or amylopectin is obtained from various starch-containing products. For example, cereal starch can contain from 15% to 28% amylose, corn starch consists of 75–80% amylopectin and only 20–25% amylose, tuber starches (potatoes, for example) contain 17–22% amylose, while in legume starches (lentils, beans, chickpeas...) there is much more of it - from 33 to 66%.
In the process of preparing baked goods, premium wheat flour is most often used to improve the quality of flour products; such flour consists of almost only amylopectin, which means it is a “fast carbohydrate”. Research conducted at the Belgorod Scientific Research Institute of Agriculture of the Russian Agricultural Academy and the Belgorod State National Research University has established that finished products made from wheat flour with low amylose content are resistant to staling. Often they even use waxy wheat flour, the peculiarity of which is the absence of amylose in its starch composition, which increases the period of preservation of freshness of products. Special varieties of grains and corn (waxy, waxy), as well as barley (Swedish company Swecarb AB, Vitargo brand) containing only amylopectin of the required size. Instant porridges and semolina also contain a lot of similar starch.
The same applies to jelly, which is made from starch, most often potato or corn. Starch gelatinizes during the preparation of jelly; if this happens more strongly, then the amylose content is lower and the better it can be broken down by alpha-amylases, digestive firmants, i.e. in fact, when starch is heated, we obtain pure glucose.
But the real danger lies in refined and modified starch. It will not give the body anything from which it could benefit; it is in such a substance that there is a lack of dietary fiber, which is so necessary for the body, and too few useful substances, but it gives the human body energy and does not overload the gastrointestinal tract. Modified starches have found application in various branches of the food industry. For example, in the production of baby food, modified starch from 3 to 6% is used: rice, corn or potato; it is modified so that such starch breaks down faster into glucose and does not cause digestive problems in the child.
In Russia, native starches are used in the production of meat products: potato, wheat and imported tapioca; the structure of such starches includes predominantly a polysaccharide - branched amylopectin, which quickly breaks down and increases the level of glucose in the blood.
Starch is used in sports nutrition for various purposes. Carbohydrate drinks are made from amylopectin, so as not to “overload” the gastrointestinal tract and allow the rapid entry of carbohydrates into the bloodstream during training; such carbohydrates replenish glycogen losses 70% faster (Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology (Scand. J. Gastroenterol 2000; 35: 1143-1149 .) and the European Journal of Applied Physiology (Eur J Appl Physiol 81: 346-351.) In nutrition, the feature of longer digestion of amylose polymers is used on the contrary to give carbohydrates “longitude”, i.e. more prolonged digestion. There are tricks to this “longitude” "I can also lengthen it chemically. For example, a starch has been developed with the difficult-to-pronounce name Hydroxypropyl distraction phosphate, abbreviated as HDP-starch.
In the modern world, there is a tendency to reduce the consumption of resistant starches. This is explained by the widespread use of industrially processed products that contain significantly less of this starch. People eat chips instead of potatoes, oat bars instead of oatmeal, burgers instead of meat. The minimum intake of resistant starch is 10 grams per day, but it can go up to 50 grams. By adding resistant starch to your diet, after just four weeks you can see that insulin sensitivity increases by 33-50 percent (Nutrients. 2013). Resistant starches alleviate the condition of constipation, excitable bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis. A study by Australian scientists showed that indigestible starch may help offset the effect of frequent consumption of red meat, which increases the risk of developing bowel cancer. The results of the work were published in the journal Cancer Prevention Research). Resistant starches help you feel full.
To summarize, I would like to say that resistant starch is necessary for our body, as it has many beneficial properties, so anyone who cares about their health needs to add to their diet: legumes, grains, potatoes, unripe bananas and other foods high in amylose and limit consumption of processed foods such as cereal bars. Particular attention should be paid to the process of preparing starch-containing products so as not to lose resistant starch, the most valuable for our body, during processing.
General composition
As already mentioned, both amylose and amylopectin are polymers of alpha-glucose. The difference is that the amylose molecule has a linear structure, while amylopectin has a branched structure. The first is a soluble fraction of starch, amylopectin is not, and in general, starch in water is a colloidal solution (sol), in which the dissolved part of the substance is in equilibrium with the undissolved part.
Here, for comparison, the general structural formulas of amylose and amylopectin are given.
Amylose is soluble due to the formation of micelles - these are several molecules assembled together in such a way that their hydrophobic ends are hidden inward, and their hydrophilic ends are hidden outward for contact with water. They are in equilibrium with molecules that are not assembled into such aggregates.
Amylopectin is also capable of forming micellar solutions, but to a much lesser extent, and therefore is practically insoluble in cold water.
Amylose and amylopectin in starch are in a ratio of approximately 20% of the former to 80% of the latter. This indicator depends on how it was obtained (the percentages are also different in different starch-containing plants).
As already mentioned, only amylose can dissolve in cold water, and even then partially, but in hot water a paste is formed from starch - a more or less homogeneous sticky mass of swollen individual starch grains.
Benefits of Geneticlab Amylopectine 1000gr
Amylopectine does not contain sugar, so it does not allow you to gain fat mass and does not interfere with the removal of excess fluid from the body. It triggers the process of protein synthesis, which ensures the growth of muscle tissue, even when following a low-carb diet. It is instantly and completely absorbed by the body and does not cause a feeling of heaviness or bloating in the stomach. This makes it an ideal sports nutrition to take before and during physical activity. Does not contain maltodextrin. By purchasing it in our online store, you become a member of the bonus program.
Compound:
amylopectin starch from waxy corn.
Serving Size: 2 scoops (33 g) Servings per container: 30
Contents of one serving:
Protein: 0.3 g (0.4%*) Fat: 0.2 g (0.24%*) Carbohydrates: 27.6 g (7.56%*)
* - percentage of the recommended level of daily consumption according to TR CU 022/2011, Appendix 2.
Energy value:
113 kcal/ 475 kJ
Recommendations for use:
Mix 1 serving with desired amount of liquid in shaker. The number of servings depends on your carbohydrate needs. Before use, consult a specialist. The duration of taking the product is not limited.
Contraindications: individual intolerance to the ingredients. It is not recommended for use by pregnant women and during lactation.
You can ask any question you are interested in about the product or the work of the store.
Our qualified specialists will definitely help you.
Amylose
Amylose consists of glucose molecules linked together via 1,4-hydroxyl bonds. It is a long, unbranched polymer with an average of 200 individual glucose molecules.
In starch, the amylose chain is coiled: the diameter of the “windows” in it is approximately 0.5 nanometers. Thanks to them, amylose is able to form complexes, inclusion compounds of the “guest-host” type. These include the well-known reaction of starch with iodine: the amylose molecule is the “host”, the iodine molecule is the “guest”, placed inside the spiral. The complex has an intense blue color and is used to detect both iodine and starch.
The percentage of amylose in starch can vary from plant to plant. In wheat and corn it is typically 19-24% by weight. Rice starch contains 17% of it, while apple starch contains only amylose - 100% mass fraction.
In the paste, amylose forms the soluble part, and this is used in analytical chemistry to separate starch into fractions. Another way to fractionate starch is to precipitate amylose in the form of complexes with butanol or thymol in boiling solutions with water or dimethyl sulfoxide. In chromatography, the property of amylose to adsorb on cellulose (in the presence of urea and ethanol) can be used.
Amylopectin 1000 gr
Amylopectin - used in bodybuilding to optimize the amount of glycogen in muscles.
Amylopectin is a complex, high-molecular, long-chain carbohydrate. Simply put, this starch-like substrate provides energy for growth and development.
From a chemist's point of view, it is a polysaccharide formed by several glucose molecules. Contained in waxy varieties of corn, in potato and maize starch, as well as in some varieties of rice and wheat.
- increase the duration of work under load, provide long-term training;
- provide nutrition to the athlete during training.
accelerate muscle recovery, have a positive effect on protein synthesis;