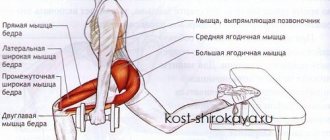
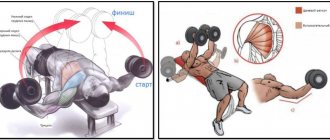
Technique for performing a chest push while standing in fitness
This is an excellent movement for developing the muscles of the shoulder, legs and back.
On average, an athlete can gain more than ten kilos of quality mass in a year thanks to the chest press. Of course, for this it is necessary to perform it in strict accordance with the technique and take it seriously. This movement is quite popular in weightlifting, where it is divided into two phases when performed. First you need to lift the projectile onto your chest, thereby working the muscles of the legs and back, and then perform a push for the shoulder girdle. Now we will talk about the technique of this magnificent movement.
Stage 1
Squat down into the position you want to take when performing a deadlift. The only difference is the grip. In this case, it is necessary to use a different grip. Make sure your back is straight and there is a natural arch in your lower back. Lift the projectile using only the force of your legs. After the bar passes the knee joints, detonate the projectile.
Stage 2
Straighten your body and use your shoulders to give the projectile momentum to move upward.
Stage 3
Turn your hands and sit under the projectile. Be careful, as the bar may already begin to move downwards. After taking the projectile to your chest, straighten up completely.
Stage 4
Bend your knees and push upward, working not only with your arms, but also with your legs. Raise the apparatus above your head and lower the barbell. The entire movement is performed without pauses between stages.
Exercises for leg muscles
All athletes know how difficult it is to build leg muscles. Almost no one likes it, but they need to be trained. In most cases, in beginners, the leg muscles are poorly developed and this is due to several reasons. But now we won’t talk about them, but will give advice on how to quickly pump up your legs.
- Try to work on your leg muscles on the first training day of each week and dedicate a separate session for this.
- It is better to pump the quadriceps using the pumping effect, which means performing 12 to 15 repetitions per set. For the muscles of the buttocks and hamstrings, it is better to use a small number of repetitions, from 4 to 6, and work with heavy weight.
- At the end of each training week, pay special attention to your hamstrings.
- Find time to do specific leg training once a week.
- This class requires you to jump on high pedestals, perform sprints at a powerful pace, and jump up and forward.
Bench press exercise
Many pro-athletes have noticed that when performing a bench press, the muscles of the upper back are in a state of static tension.
This helps improve hand stabilization. The triceps are subjected to a similar load in the initial phase of movement, thereby helping to keep the elbow joints at an angle of 90 degrees. To increase the load on these muscles, it is necessary to force them to contract intensively. This can be achieved by placing a ring-shaped rubber shock absorber on your wrists, twisting it in an “8” shape. Once the shock absorber is on your wrists, you can begin to press.
Deadlift exercise
This is an excellent exercise to perform for all athletes who want to achieve good results. At the same time, it is quite traumatic and you have probably heard about it. Deadlifts are more dangerous for athletes with poorly developed lower back muscles. But this is an excellent exercise that still needs to be performed, for this reason we will now tell you how to reduce the risk of injury when performing it:
- The apparatus should be placed on supports just above the knee joints (this is advice for beginners).
- The initial working weight should not exceed half your body weight.
- Perform the movement no more than twice a week.
- Increase the weight by no more than 2 or 2.5 kilos. If the load turns out to be too much for you, reduce it.
- Don't work yourself to failure.
- After the working weight is equal to twice your body weight, lower the projectile down one division and again start with a weight of 0.5 of your body weight.
- Stick to this mode until the projectile is on the ground.
- When working with heavy weights, use a different grip.
First of all, you need to perfect your deadlift technique.
This is very important, since most injuries are associated precisely with the lack of technique among athletes. It is necessary to lift the projectile from the ground (stops) slowly. Once the bar is in the air, increase the speed of the projectile, but do it smoothly. After the projectile passes the level of the knee joints, the speed of the bar should be maximum.
Clinical anatomy
Deep (local) muscles
The deep muscles originate from the lumbar vertebrae and for this reason provide a stabilizing and strengthening effect to the area.
The mechanism of deep muscle function, as well as the maintenance of stability/stability, is a rather controversial issue, but it can be assumed that the transverse abdominis muscle, together with the diaphragm and pelvic floor muscles (PFM), can act as a kind of container. Co-contraction of these muscles increases intra-abdominal pressure and, hypothetically, increases stability due to connections with the thoracolumbar fascia. The multifidus muscles increase the rotational stability of the lumbar spine segments in the sagittal and horizontal planes.
The normal functioning of the deep muscles is disrupted due to back pain. There is compelling evidence that specific training in motor control and specific muscle activation is effective in restoring this function.
Superficial (global) muscles
There are a number of large superficial muscles that cross several different segments of the human body, but do not directly attach to the spine. These include the rectus abdominis, external obliques, and some parts of the erector spinae muscles. These muscles act as “tension cables” that control the position of the spine. They also work together to control the movement of the spine when it experiences external stress.
Kettlebells are a great addition to basic exercises.
You can significantly increase the effectiveness of basic exercises by using kettlebells in your training program. Now we will tell you about the most effective exercises with this sports equipment, which will allow you to achieve the following effects:
- Eliminate fat reserves;
- Increase functional strength;
- Give the muscles relief.
And now about three exercises that have proven themselves to be excellent.
Gladiator
Lean sideways on your outstretched arm, and lift your free leg up, keeping it suspended. Press the kettlebell with your free hand. After completing the required number of repetitions, do the exercise on the other side.
Kettlebell Squat Press
Lower yourself into a squat, holding the exercise equipment at arm's length above your head. The second hand holds the second weight located on the ground. As you rise from the squat, press the second kettlebell upward.
Lunges
Press the two weights upward and hold the weights in your straight arms. Maintaining this position, begin to lunge while walking. After walking ten meters, turn around and move back.
Exercises to develop coordination
Below we will describe exercises that can be performed without the use of specialized exercise equipment. Daily simple exercises will not take much time, but will help you achieve good results. In addition, these exercises have a beneficial effect on many organs.
If you are too lazy to read or it’s easier for you to perceive visually, then here is a useful video that contains basic exercises for the targeted development of coordination.
Pole with ropes
This exercise helps to relax the arms, shoulders and relieve tension in the neck.
You need to stand up straight and place your feet at shoulder level. You can imagine the torso as a pillar, and the arms as ropes that are tied to it. When performing the exercise, your hands should be completely relaxed. You need to turn around an axis and fully transfer your body weight, gradually increasing speed.
Heron
When performing this exercise, you need to lean on one leg. It has been practiced for centuries in Eastern medicine and has a positive effect on the immune system, since the channels of six important internal organs are located on the feet. In addition, it prevents the development of varicose veins. It must be performed without shoes.
You need to lean on one leg, and raise the other so that the thigh is parallel to the floor (if possible, higher). If it is not possible to raise your leg high, stop at the maximum possible height.
Extend your arm with the same name as your raised leg in front of you, without fully extending it. Keep your other hand in a lowered position. Once you have reached the desired position, try to maintain your balance with your eyes closed.
Video clip
This exercise has a positive effect not only on the coordination system, but also on the entire body. It helps strengthen the spinal muscles and improves blood circulation. This exercise requires a flat surface. Initially, the exercise may cause discomfort, in which case you can use a mat.
In a sitting position, pull your legs towards your body, clasping them with your arms. It is necessary to round your back as much as possible. With a quick movement you need to lean back, roll over onto your back and return to your original position.
Hammer
The hammer exercise also has a beneficial effect on the spine, more precisely on its upper part. It is quite simple, but it is important to know when to stop. When performing this, crunching sounds may be heard, but there is no need to worry about this.
You need to lie down and clasp your shoulders with your hands, then slightly raise your upper body and begin to lightly “tap” your back on the floor.
Sphinx and Cobra
This exercise allows you to develop a good reaction and has a positive effect on the spine.
It is necessary to lie on your stomach and raise your upper body, in this case your forearms act as a support, they should be parallel to each other. Lower your shoulders, point your toes, look ahead. This exercise is called the Sphinx.
Now let's move on to Cobra. We remain in the same position as when performing the Sphinx exercise. Gradually rise up on your hands, while your spine should arch more strongly. To achieve the best results, you must perform these exercises together.
Germ
This exercise rounds the back as much as possible after strong backbends of the spine. It has a beneficial effect on the digestive organs and fights salt deposits.
You need to take a sitting position, with your legs underneath you so that your knees are close. Lower yourself forward and try to round your back as much as possible. Your arms should clasp your knees and be extended forward.
Crunches
The exercise is known to those who practice yoga. It is beneficial for the back and spinal region, and is practiced for the prevention of rheumatoid pain. Constant practice helps to increase flexibility and mobility of the spine, strengthens the nervous system, and can even reduce abdominal girth.
You need to lie on your back, with your arms at an angle of 90° to your body, and your knees bent. As you exhale, you need to twist to the right and left. At the same time, your shoulders should remain on the floor. You can stay in the twisting position for some time, depending on the body’s capabilities.
Tilts
This exercise helps strengthen the lumbar spine and stretches the tendons.
In a standing position, spread your legs as far as possible and extend your arms. Maintaining this position, lean to the left. Fix the position and do 3 cycles of inhalation and exhalation, then return to the starting position. Do the same, leaning to the right.
Now proceed to bend down, touching your ankles on the opposite leg with your hands. At the same time, you need to keep your other hand extended upward and look at it.
It is necessary to complete 3 cycles, and then move on to the other leg. After completing the exercise, it is recommended to bend back.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Why do athletes need basic exercises?
Although the effectiveness of basic movements has been proven not only by the many years of experience of a huge number of athletes, today you can increasingly come across the opinion that a base is not needed. The only exception here is the bench press, which is something you won't hear about. Here are the main reasons that make athletes refuse to perform squats, deadlifts, snatches, etc.
- Due to poor technique, you can get injured, because you have to work with heavy weights.
- Often athletes do not see progress from performing basic movements, which is again due to the lack of correct technique.
- Many bodybuilders believe that squats and deadlifts are most effective for powerlifters. It is useless to argue with the fact that much attention is paid to these exercises in powerlifting, but all pro-bodybuilders also use them during their training.
The debate about the importance of core exercises will likely never go away.
But if you have mastered the technique of these movements, then they should definitely be the basis of your program. Learn more about interesting and unusual fitness exercises from this video:
Physiological classification of physical exercises
In his daily activities - at home, at work, during physical education and sports - a person performs a wide variety of motor actions: From the point of view of physiology, a set of motor actions (movements) continuously interconnected with each other, aimed at achieving a specific goal (solving a motor problem). tasks) is an exercise.
In a competitive sports exercise, a set of motor actions (movements) is aimed at achieving the highest possible sports result (examples of sports exercises: high jump, javelin throwing, shooting, sports game, running or swimming over a certain distance).
A huge number of physical, including sports, exercises necessitate their classification. Physiological classification groups physical exercises with similar functional characteristics. On the one hand, these are exercises for the successful implementation of which, to a certain extent, similar regimes, means and methods of physical education (sports training) can be used. On the other hand, one group combines physical exercises that can be equally used in the system of physical education (sports training) to increase the functionality of the same physiological organs, systems and mechanisms, and therefore the same physical quality . Thus, the capabilities of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, which largely determine the level of endurance development, can be successfully increased by using different physical exercises of the same group: long running, cycling, swimming, cross-country skiing.
General physiological classification of physical exercises
The most general physiological classification of physical exercises can be carried out on the basis of identifying three main characteristics of the activity of the muscles performing the corresponding exercise:
1) volume of active muscle mass;
2) type of muscle contraction (static or dynamic);
3) strength or power of contractions.
Local, regional and global exercises
Depending on the volume of active muscle mass, all physical exercises are classified into local, regional and global.
Local exercises include exercises in which less than 1/3 of the total muscle mass of the body is involved (archery, pistol shooting, certain gymnastic exercises).
Regional exercises include exercises in which approximately 1/3 to 1/4 of the total muscle mass of the body is involved (gymnastic exercises performed only by the muscles of the arms and upper limbs, muscles of the torso, etc.).
Lecture 1
Physiological classification of physical exercises
Plan:
1. Physiological classification of physical exercises
2. General physiological classification of physical exercises
2.1. Local, regional and global exercises
2.2. Static and dynamic exercises
2.3. Strength, speed-strength and endurance exercises
3. Energy characteristics of physical exercises
4. Physiological classification of sports exercises
4.1 Classification of cyclic exercises
4.2 Classification of acyclic exercises
Introduction to the subject.
Sports physiology is the second part of the physiology course studied at physical education institutes. The main content of this course is the physiology of human muscular activity, a special case of which is sports activity. In the course of sports physiology, two central issues can be distinguished - the physiological characteristics of various types of sports activities and the physiological mechanisms of adaptation of the body during sports training.
WITH
athletic activity is associated, as a rule, with maximum or almost maximum tension of the leading physiological systems that ensure its implementation. The main task of sports physiology is to provide a quantitative description of the physiological reactions of individual systems and the entire organism for different types of sports activities.
IN
In his daily activities - at home, at work, during physical education and sports - a person performs a wide variety of motor actions: From the point of view of physiology, a set of motor actions (movements) continuously interconnected with each other, aimed at achieving a specific goal (solving a motor problem ), is an exercise.
IN
In a competitive sports exercise, a set of motor actions (movements) is aimed at achieving the highest possible sports result (examples of sports exercises: high jump, javelin throwing, shooting, sports game, running or swimming over a certain distance).
ABOUT
The huge number of physical, including sports, exercises necessitates their classification. Physiological classification groups physical exercises with similar functional characteristics. On the one hand, these are exercises for the successful implementation of which, to a certain extent, similar regimes, means and methods of physical education (sports training) can be used. On the other hand, one group combines physical exercises that can be equally used in the system of physical education (sports training) to increase the functionality of the same physiological organs, systems and mechanisms, and therefore the same physical quality . Thus, the capabilities of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, which largely determine the level of endurance development, can be successfully increased by using different physical exercises of the same group: long running, cycling, swimming, cross-country skiing.
N
The most general physiological classification of physical exercises can be carried out on the basis of identifying three main characteristics of muscle activity:
1
) volume of active muscle mass;
2
) type of muscle contraction (static or dynamic);
3
) strength or power of contractions.
IN
Depending on the volume of active muscle mass, all physical exercises are classified into: local, regional and global.
TO
local exercises include exercises in which less than 1/3 of the total muscle mass of the body is involved (archery, pistol shooting, certain gymnastic exercises).
TO
Regional exercises include exercises in which approximately 1/3 to 1/4 of the total muscle mass of the body takes part (gymnastic exercises performed only by the muscles of the arms and the belt of the upper limbs, muscles of the torso, etc.).
G
“Local” exercises are those in which more than 1/2 of the total muscle mass of the body is actively involved (running, rowing, cycling, etc.). The vast majority of sports exercises are global.
Course of lectures on the anatomical and physiological foundations of FC and S (p. 17)
4. Pre-start condition and warm-up.
5. Working in.
6. Steady state.
7. Fatigue.
8. Recovery.
1. General principles of physiological classification of physical exercises.
A huge number of physical and, above all, sports exercises require their classification. The physiological literature offers different methods and principles for classifying physical exercises.
Classification based on muscle volume
divides all physical exercises into
local, regional and global.
· Local exercises affect less than a third of the total muscle mass. This includes, for example, exercises with a hand expander or shooting with a pistol.
· Regional exercises affect between a third and half of all muscles. This includes some gymnastic exercises.
· Global exercises affect more than half of the muscle mass. This includes running, swimming, cross-country skiing, etc.
This classification suffers from the fact that the classes of exercises are very unequal.
Classification based on type of muscle contraction
divides exercises into
static and dynamic.
In this case, static exercises are aimed at maintaining the posture, and dynamic ones at performing movements. And here we are faced with unequal classes of exercises, since there are significantly fewer static exercises than dynamic ones.
Classification by strength and power
divides exercises into
strength and speed-strength.
In the case of strength exercises, maximum strength is manifested, and in the case of speed-strength exercises, maximum power is manifested. According to this classification, strength exercises include weightlifting exercises, and sprinting, for example, is a speed-strength exercise. By the way, according to this classification, speed-strength exercises also include endurance exercises. It turns out that a sprinter and a stayer are one and the same. True, some scientists propose to separate endurance exercises into a separate class of exercises.
The most commonly used classification is based on the structure of exercises.
According to this classification, exercises are divided into
cyclic and acyclic.
2. Classification of cyclic exercises.
Cyclic exercises are exercises with a relatively constant repetitive structure and power.
This includes all types of running, walking, swimming, cross-country skiing, speed skating, rowing, etc.
Cyclic exercises are divided into two classes: anaerobic and aerobic.
Anaerobic
exercises are characterized by the fact that they take place in a mode of oxygen deficiency in the muscles.
However, with oxygen deficiency, exercise cannot be prolonged, so anaerobic exercise is usually short-term. This includes track and field and speed skating
sprint distances.
Moreover, the shorter the distance, the higher the power of the exercise. There are anaerobic exercises of maximum, near-maximal and submaximal power.
Aerobic exercise
characterized by a normal supply of oxygen to the muscles. An exercise is considered aerobic if the anaerobic metabolic threshold (TAT) is crossed. The more trained the athlete, the higher the PANO level. The level of ANNO is most often indicated as a percentage of maximum oxygen consumption (MOC). In untrained people, the level of PANO is 40–45% of the MOC, and in high-class athletes it is 55–60%, and sometimes 70%.
Aerobic exercise is divided into five classes: low, moderate, submaximal, near-maximal and maximal aerobic power.
Low aerobic power exercises are walking at a low pace, medium aerobic power exercises are jogging. But the last three classes are long-distance running, stayer speed skating, swimming over 400 m, rowing and cycling over 4 km.
3.Classification of acyclic exercises.
To acyclic
include exercises where each new moment in time, exercise movements can have a new structure and power.
These are all types of martial arts, sports games, gymnastics, figure skating, etc.
There are four groups of such exercises: explosive, standard-variable, non-standard-variable, interval-repetitive.
Explosive exercises are characterized by the presence of one or more accentuated short-term efforts of high power.
This group includes jumping and throwing. Their important feature is their short duration.
Standard-variable exercises are characterized by the presence of complex actions - elements - combined into a continuous, strictly fixed chain.
Each element can be learned separately.
This group of exercises includes figure skating, gymnastics, synchronized swimming, acrobatics, etc.
Non-standard variable exercises or situational exercises are exercises during which periods with different character and intensity of motor activity alternate sharply and in a non-standard way.
This includes all
sports games
,
martial arts, various types of skiing.
These exercises are divided into periods of intense physical activity (work period) and intermediate periods with low intensity work.
Interval-repetitive exercises are characterized by periods that are constantly repeated over time with different intensity of work.
This group of exercises includes
biathlon and orienteering.
Such exercises are found in the training practice of many sports. For example, practicing individual elements in figure skating, techniques in martial arts, working in the gym.
Get full text
Tutors
Unified State Exam
Diploma
4.
Pre-start condition and warm-up.
The pre-start state is characterized by functional changes preceding the start of work. The significance of these changes is to prepare the body for the start of upcoming activities.
The duration of the pre-launch state may vary. It depends on the individual characteristics of the person and can last from several minutes to several days.
The nature of this phenomenon is conditioned reflex and humoral. Emotional reactions play an important role in this process. Therefore, the most dramatic functional changes are observed before competitions. Moreover, the degree of pre-start changes is directly proportional to the significance of the competition.
There are three main types of pre-launch states: state of readiness, starting fever and starting apathy.
These conditions can have completely different effects on athletic performance. A state of readiness, as a rule, leads to an increase in athletic performance. Starting fever is an unpredictable condition, fraught with either a decrease or an increase in the result. Initial apathy is a condition leading to a decrease in results.
Warm-up is used to optimize the pre-start state.
.
Warm-up is the performance of exercises that precedes performance at a competition or the main part of a training session.
Warm-up speeds up the development process and is designed to improve performance.
The effects of warming up on the body are diverse:
1) increased excitability of sensory and motor centers;
Get full text
Coursework
Unified State Exam
Diploma
2) strengthening the work of all parts of the oxygen transport system;
3) has a positive effect on thermoregulation, facilitating heat transfer and preventing overheating of the body;
4) increases body temperature and especially working muscles.
Warm-up can be general or specific
. A general warm-up can consist of various exercises, the purpose of which is to increase body temperature, excitability of the central nervous system, etc. A special warm-up is closer to the upcoming activity, its lighter version.
The meaning and role of warm-up is different for different sports. The positive effect of warming up is especially noticeable in speed-strength sports. But before long-distance running, the positive effect of warming up is much less pronounced; at high temperatures it can even be harmful.
5.
Working in.
The theory explaining the processes occurring in muscles during physical exercise was developed by the English physiologist Nobel Prize winner Archibald Hill
. According to his theory, physical work goes through several stages: 1-working in, 2-steady state, 3-fatigue. These stages are ideally described when performing cyclic exercises, especially endurance exercises.
During running-in, the following physiological processes occur:
1) setting up nervous and neurohumoral mechanisms for controlling movements and vegetative processes;
2) gradual formation of the necessary movement pattern, leading to improved coordination:
3) achieving the required level of autonomic functions that ensure this muscle activity.
Get full text
Some features are typical for working:
1. Relative slowness in the strengthening of vegetative processes and functions, which is due to the nature of nervous and humoral regulation.
2. Heterochronism - non-simultaneity in the strengthening of individual functions, since the development of the motor apparatus occurs faster than the development of the vegetative systems.
3. Direct relationship between the power of work performed and the rate of change in vegetative functions.
4. Direct dependence of the training time on the athlete’s level of training.
A few minutes after the start of intense and prolonged work, the athlete experiences a condition called “dead spot”. The appearance of this condition depends on the intensity of the start of work, the degree of training of the athlete, individual physiological characteristics, etc. This condition is characterized by severe subjective sensations: feelings of tightness in the chest, dizziness, pulsation of cerebral vessels, shortness of breath and the desire to stop working.
Objectively, this condition is expressed in increased oxygen consumption and increased release of carbon dioxide in exhaled air. The blood acquires an acidic environment, as the primary accumulation of lactic acid occurs in it.
| Due to the large volume, this material is placed on several pages: 17 |
2.2. Static and dynamic exercises
IN
According to the type of contraction of the main muscles performing this exercise, all physical exercises can be divided into static and dynamic, respectively.
TO
static exercises include, for example, maintaining a fixed pose while holding a handstand (for gymnasts) at the moment of shooting (for a shooter).
B
Most physical exercises are dynamic. These are all types of locomotion: walking, running, swimming, etc.
2.3. Strength, speed-strength and endurance exercises
When
classifying physical exercises according to the force of contraction of the leading muscle groups, two dependencies should be taken into account: “strength - speed” and “strength - duration” of muscle contraction.
IN
According to the “force - speed” relationship (Fig. 1), during dynamic contraction, the force exerted is inversely proportional to the speed of muscle shortening (the speed of movement of the moving part of the body): the greater this speed, the less the force exerted. Another formulation of this relationship: the greater the external load (resistance, weight), the lower the speed of shortening (movement) and the greater the manifested force, and vice versa, the smaller the external load, the higher the speed of movement and the less manifested muscle force. The product of force and the speed of muscle contraction determines its power (see Fig. 1).
Z
The strength-duration relationship of muscle contractions is expressed in the fact that the greater the strength (or power) of muscle contractions, the shorter their maximum duration. This is true both for local and regional static and dynamic work (Fig. 2) and for global work (Fig. 3).
By
Based on the strength and power of muscle contractions and the associated maximum duration of work, all physical exercises can be divided into three groups: strength, speed-strength (power) and endurance.
WITH
silt exercises can be considered exercises with maximum or almost maximum tension of the main muscles, which they exhibit in a static or dynamic mode at low speed - movement (with large external resistance, weight).
In Fig. 1 strength exercises correspond to the left side of the force-velocity curve. The maximum duration of exercises with maximum manifestation of strength is calculated in several seconds. Strength is the main motor quality that determines the success of strength exercises. Core
-strength (power) exercises are dynamic exercises in which the leading muscles simultaneously exhibit relatively greater strength and speed of contraction, i.e., greater power. The maximum power of muscle contraction is achieved under conditions of maximum muscle activation at a shortening rate of about 30% of the maximum for an unloaded muscle. On the strength-velocity curve, speed-strength exercises occupy a middle position - up to 50-60% of maximum speed (see Fig. 1). Muscles develop maximum power with external resistance (load) that is 30-50% of their maximum (static) strength. The maximum duration of an exercise with high power of muscle contractions is in the range from 3-5 s to 1-2 minutes - in inverse proportion to the power of muscle contractions (load). Power plays a critical role in speed-strength exercises.
U
Endurance exercises are considered to be those exercises in which the leading muscles develop contractions that are not very strong in strength and speed, but are able to maintain or repeat them for a long time - from several minutes to many hours (in inverse proportion to the strength or power of muscle contractions) . Endurance is the leading physical quality for exercises in this group.
E
Energy cost is the most important characteristic of the exercise. To determine the energy cost of physical exercise, two indicators are used: energy power and gross (total) energy consumption.
E
energetic power is the amount of energy expended on average per unit of time when performing a given exercise. It is usually measured in physical units: watts, kcal/min, kilojoules per minute, as well as in “physiological”:
With
rate of O2 consumption (ml O2/min) or in METs (metabolic equivalent), i.e. the amount of O2 consumed in 1 min per 1 kg of body weight under conditions of complete rest while lying down. 1 MET is equal to 3.5 ml O2/kg min).
IN
Total (total) energy expenditure is the amount of energy expended during the entire exercise. Gross energy expenditure (total energy cost of an exercise) can be defined as the product of average energy output and the duration of the exercise.
At
When running, the gross energy consumption to cover the same distance, within certain limits, does not depend on the speed of movement. The fact is that with an increase in speed (energy power), the time to cover a given distance decreases, and with a decrease in speed, on the contrary, it increases, so that the product of energy power and time, i.e., the total energy consumption, remains unchanged. The total energy cost of covering the same distance is higher when running than when walking (up to a speed of about 8 km/h): for each kilometer of walking distance, an average of 0.72 kcal/kg of body weight is consumed in women and 0.68 kcal /kg body weight in men, and when running, 1.08 and 0.98 kcal/kg body weight, respectively.
By
In terms of energy capacity, physical exercise is usually divided into light, moderate (medium), heavy and very heavy (Table 1).
Table 1. Classification of physical exercises by energy expenditure (kcal/min) in men and women of different ages.
| Gender and age | Exercises | |||
| moderate (average) | very heavy | |||
At
When assessing the severity of an exercise based on energy indicators, it is necessary to take into account a number of factors: the nature of the work performed (static or dynamic), the volume of active muscle mass (local, regional or global exercise), body size or weight, age, gender and degree of fitness (physical fitness) the person performing this exercise, the external conditions for performing this exercise.
T
So, if very hard local work is performed, which can last only a few tens of seconds, the rate of energy expenditure of the body does not exceed 1.2 kcal/min (Table 2). The same rate of energy consumption is typical for regional work of moderate (moderate) severity, which can be performed for many tens of minutes, and for global, but very light work (extremely slow walking on level ground), which lasts for many days in a row. Very heavy global work for women aged 50-59 years with an energy expenditure of more than 5.5 kcal/min, which can last only tens of seconds, is moderate for men 20-29 years old and can be performed by them for several hours (see table . 1).
Table 2. Classification of the severity of local, regional and global exercises by energy expenditure (kcal/min)
ABOUT
Particularly large differences in the energetic assessment of exercise severity exist between untrained people and highly trained athletes. The latter are able to perform loads with such energy costs that are inaccessible to untrained people. For athletes in the vast majority of sports, the severity of physical exercise in terms of energy (and other) indicators exceeds heavy or even very heavy loads for untrained people and is inaccessible to the latter (Table 3).
Table 3. Energy cost of various types of physical education and sports activities (according to E. M. Berkovich, N. V. Zimkin, N. I. Volkov, etc.)
| Kind of activity | Energy cost.(kcal/min) |
| Rest: lying down | |
| 18 km/h (5.0 m/s)** | |
| 23 km/h (6.3 m/s)*** | |
| 26 km/h (7.2 m/s) **** | |
| 32 km/h (8.8 m/s)***** | |
| Swimming: | |
| crawl 0.9 m/s | |
| on the back 0.6 m/s | |
| breaststroke 0.8 m/s | |
| Skiing 13 km/h | |
| Ice skating | |
| A ride on the bicycle | |
| more than 30 km/h | |
| Gymnastics | |
| trunk flexion | |
| turns on the crossbar, | |
| Volleyball (recreational) | |
| single | |
| Sport games | |
| (football, basketball, handball) |
* Corresponds to jogging speed. ** Corresponds to the speed of marathon running with a result of 2 hours. 20 minutes. *** Corresponds to the running speed of 10,000 m with a result of about 28 minutes. **** Corresponds to a running speed of 1500 m with a result of about 3 min 40 s. ***** Corresponds to the running speed of 400 m with a result of 45 s.
WITH
From a physiological point of view, the severity of the same physical exercise varies greatly depending on the conditions of its implementation (for example, in the mountains or at elevated temperatures and humidity), although its energy cost remains almost or completely the same as under normal conditions.
T
Thus, assessing the severity of an exercise using energy criteria alone is insufficient. Therefore, many classifications of physical exercises, along with energy characteristics (related to weight or body surface), also take into account a number of other physiological indicators (Table 4): rate of O2 consumption, heart rate (HR), pulmonary ventilation (PV), body temperature, respiratory coefficient (DC), lactic acid content in the blood, etc.
Table 4. Classification of physical work by energy and physiological indicators (based on data from untrained men)
| Difficulty of work | Energy capacity | Physiological indicators | Type of activity (working time limit) | ||||||||
| kcal/min* | VO2 ML/KG*MIN | VO2***, l/min | Heart rate, beats/min | Rectal temperature | Blood lactate, mg% | ||||||
| Easy job: | |||||||||||
| calm | Indefinitely | ||||||||||
| moderate | Normal work activity (up to 8 hours per day) | ||||||||||
| Average performance: optimal | Intensive work activity (8 hours a day for several weeks - seasonal work) | ||||||||||
| Hard work: intense | Physical education classes (1 - 2 hours a day, 3 times a week) | ||||||||||
| Very hard work: | |||||||||||
| maximum | Intense training (up to 1-2 hours per day) | ||||||||||
| exhausting | Competitive exercise (several minutes) | ||||||||||
- 1 kcal/min = 426.85 kgm/min = 69.767 Watt = 4.186 kJ/min. ** 1 MET = 3.5 ml, O2/kg*min - 0.0175 kcal/kg = 0.0732 KJ/kg. *** 1 l of O2 consumption = -5.05 kcal = 21.237 kJ
Very often, when making recommendations when drawing up a training program, there is a reference to certain types of exercises. As a rule, exercises are divided into basic (multi-joint) and isolating. Here you can add an intermediate type - exercises of a local nature.
Let's see how they all differ from each other.
Local and global computer networks
We live in a civilized, rapidly developing world, ruled by technology. Until recently, even the existence of a mobile phone could only be read in a science fiction book, but today it is an ordinary reality. And many amazing and unreal things predicted by science fiction writers have already come true today. For example, in Edward Bellamy's 1887 novel, the character enters a lethargic sleep at the end of the 19th century and emerges from it at the beginning of the 21st. What does he discover? There is no cash, and instead, citizens receive an amount in their own account that they can spend using a special card. Why isn't today the day for you?
Arthur C. Clarke “constructed” an artificial satellite in the mid-20th century. Similar devices are used today, for example, to transmit television signals.
And the greatest American writer of the middle of the last century, Robert Heinlein, “prophesied” the appearance of a microwave oven, a mobile phone, an ATM and “introduced” space tourism. But the main thing is that he wrote about a television news search engine - an analogue of modern Internet portals. Our science fiction writers, the Strugatsky brothers, have an analogue of the Internet: the Big Planetary Information Center - BVI. However, writers began to approach the global virtual network much earlier. In 1898, Mark Twain, in one of his stories, essentially predicted the emergence of the Internet, writing about a device with which one could observe each other and learn a wide variety of news. At the same time, the necessary information was displayed on the TV screen, which was invented only in the next century.
Today we cannot imagine our life without computers and the Internet. Almost every person, without leaving home, can pay for services, make purchases, communicate with relatives and friends via video calling, and much more. And in all these actions one of the main information processes is involved - the process of information transfer.
Questions:
· What is a computer network?
· What network is called local?
· What is a global network?
Information is transmitted from source to receiver in the form of a certain set of signs, symbols, signals.
To quickly learn new material, it is best to obtain information from several sources. For example, use computer technologies that allow you to listen to explanations of new material and perceive audio signals, as well as look at the screen and perceive information visually. The transmitted sequence of signals, symbols, signs is called a message
.
But how are messages transmitted? To do this, a communication channel is established that provides a connection between the transmitter and receiver. Link
is a system of technical means and signal propagation medium for transmitting messages from a source to a receiver.
That is, classrooms are equipped so that students can watch and listen, for example, to an educational film. And absorb the information received. Speakers transmit information using sound waves, video - using light waves. In order to convey information to the receiver, it must be written down or converted in accordance with the rules specified by some code, that is, encoded
.
For many centuries, humanity used the postal service to transmit letters; in the second half of the 19th century, a device for receiving and transmitting sound was invented, which was called the telephone. And since the 30s of the 20th century, telefax began to be used to transmit images.
At the present stage of development of electronic communications, computer networks
.
The transmission and reception of information on a computer network can occur in various ways. There are two messaging modes. In the first case, the transmission and reception of messages are separated in time. In this mode, for example, sending and receiving emails is carried out. In the second case, communication occurs in real time. Communication in this mode is provided by an instant messaging tool - a messenger program
(translated from English as a messenger, courier). Such programs allow you to exchange text, voice and video messages through computer networks.
An important characteristic of a computer network is the speed of information transfer or channel capacity
is the amount of information transmitted per unit of time. This value is defined as the amount of information in bits per second, as well as in multiple units: kilobits per second (kbit/s), megabits per second (Mbit/s), gigabits per second (Gbit/s).
Naturally a question arises. How is messaging organized? A communication channel must be established, that is, computers must be connected to each other. To ensure communication between computers, they are combined into computer networks.
. There are local and global computer networks. Let's look at each of them.
Local computer network
is an association of computers at short distances from each other. As a rule, it is within one organization, enterprise, firm, educational institution. Computers connected to a local network can share access to computer resources (programs, files, folders), as well as to peripheral devices (printers, scanners, disks, modems) connected to the network. There are the following types of local networks: peer-to-peer and with a dedicated server.
Peer-to-peer
are called small local networks where all computers have equal rights, that is, each of them can use the resources of the other. In such networks, each user decides for himself which resources of his computer (programs, files or folders) to make available to the entire network.
If a large number of users are connected, then access to all computers on the network is undesirable. In such cases, the most powerful computer is allocated, which is called a server.
.
The server's hard drive stores files (data and programs), as well as peripheral equipment (printer, scanner, etc.) and makes them accessible to other computers on the network. Computers that have access to files and peripheral equipment located on the server are called clients
.
To transmit and receive signals via communication channels, each computer connected to a local network must have a special board - a network adapter. And the connection of computers to a local network is carried out via wired channels using various types of cables (for example, it can be twisted pair or optical fiber), or via wireless channels (for example, Wi-Fi).
With small computer networks everything is clear. But how do messages travel over long distances?
At arbitrarily large distances (these can be not only different countries, but also different continents), computers are also united into a network, which is called a global computer network
.
Global computer networks can be:
· Corporate
— are created to provide activities to various types of organizations that have branches in remote territories.
· Regional
— These are networks that are created within one region (for example, a country, city or region).
The most famous and extensive global computer network is the Internet. Internet
is a worldwide system of interconnected computer networks (local, regional and corporate) for storing and transmitting information around the world.
Any global computer network consists of a computer node and a communication channel. Knot
is a powerful computer that is constantly connected to the network.
Subscribers are connected to the nodes. Subscribers
are users’ personal computers or local networks.
To transmit data in global networks, the following are used: electric cable, radio communications through repeaters and communication satellites, infrared rays, modern fiber optic cable, and a regular telephone network.
An organization that provides users with a connection to the global network through their computers is called a network service provider
.
Telephone lines are actively used to connect remote users and local networks to the Internet. To increase speed, ADSL
, which in English means asymmetric digital subscriber line. This means that the available channel bandwidth is not evenly distributed between outgoing and incoming traffic. Since most users have a much larger volume of incoming traffic than outgoing traffic, the speed of incoming traffic is greater than the speed of outgoing traffic. This limitation has become more pronounced due to the spread of video communications.
Let's use an example to calculate how long it will take us to download a 700 Megabyte movie via an ADSL connection at a speed of 512,000 bits per second.
So, according to the condition, we know the ADSL connection speed - 5.1 × 105 bits per second and the movie size - 700 × 106 bytes.
Let's convert 700 × 106 bytes into bits.
This requires 700 × 106 × 8. We get approximately 5.6 × 109 bits.
As you remember, the speed of information transmission is the amount of information transmitted per unit of time, that is.
This means that to find the time required to download a movie, you need to divide the file size by the data transfer speed. or
We get approximately 104 seconds.
It turns out that the time required to download a file depends inversely on the speed. That is, the higher the data transfer speed, the less time is spent downloading the file.
Important to remember:
· The transmitted sequence of signals, symbols, signs is called a message
.
· Link
is a system of technical means and signal propagation medium for transmitting messages from a source to a receiver.
· Computer network
– these are two or more computers connected by information transmission lines.
· Local computer network
is a network that connects computers installed in the same room or building.
Computers connected to a local network can share access to computer resources, as well as to peripheral devices. There are the following types of local networks: peer-to-peer
and with
a dedicated server
.
· Global computer network
is a network in which computers are connected over arbitrarily large distances.
· Global computer networks can be corporate
and
regional
.
· The most famous and extensive global computer network is the Internet.
Basic (or multi-joint) exercises.
This is a group of exercises that use more than two large joints. A classic example of such an exercise would be the barbell squat. In this case, during the exercise, work occurs in the knee and hip joints.
Thus, when performing squats with a barbell, almost all the muscles of the body are involved - not only the legs, but also the back, and other large muscle groups. This is why it is recommended to base your training program on basic exercises - you will use many more muscles in the same time.
In addition, such exercises develop your central nervous system, giving a stronger hormonal and metabolic response, which allows you to increase muscle mass. In fact, this is an interconnected process: you can only get the best hormonal response by using heavy weights, and you can only use heavy weights in multi-joint exercises that involve the legs and back - the strongest muscle groups.
List of multi-joint exercises:
- Squats
- Deadlift
- Straight-legged deadlift, Romanian deadlift
- Bent-over barbell row
- Bench press
- Standing press
- Pull-ups
- Bent-overs with a barbell
- Hyperextension
First day at the gym: where to start
The first time is not easy for a newbie in the fitness room: the amount of information on the Internet and instructions on Youtube can easily make you feel overwhelmed. Where to begin? What to do? And, most importantly, how to exercise correctly so as not to catch the sidelong glances of other trainees? If you don’t want to become the hero of the “I can do everything myself” meme, then read a short educational program for beginners, compiled by expert methodologist of the federal network of fitness clubs X-Fit Ruslan Panov.
- All exercises are divided into 3 types: global, regional and local. They differ in the target muscle groups that are included in the work in a particular exercise, and the movements of the joints.
- Local include exercises in which less than 1/3 of the total muscle mass is involved and single-component movements are present. For example, bending or extending the arms for the biceps and, accordingly, the triceps.
- Regional ones include those where up to 50% of the muscles work and movement in 2-3 joints. Leg press in HAK, rows on horizontal and vertical blocks, some types of presses.
- Global - or otherwise basic - exercises involve more than 50% of the body's muscles and produce movements in several joints. These are all types of squats, lunges, push-ups, planks, work on the abdominal muscles.
- Have you heard the expression, “Make the base?” It's from this opera. They are present in any type of training, it doesn’t matter - functional, interval, strength. With the exception of cycling (training of varying intensity on stationary bicycles. - Esquire) and some types of dance. They can be performed in the gym, in group programs and even at home. They are widely used in everyday life, in outdoor sports and games. Thanks to them, you can not only strengthen the muscle frame, but also develop coordination, improve endurance and strength.
Why do basic exercises?
They include a large number of joints and muscles - accordingly, they are more energy-intensive. The mathematics is very simple: an isolated muscle can spend, say, 10-15 kcal per minute when performed at moderate intensity. At the same time, a basic exercise can reach up to 50 kcal - depending on the correct execution, speed and individual characteristics.
Basic exercises include:
Shutterstock / Vostock Photo
Push-ups. The exercise is aimed at the muscles of the arms, chest, back, the abs in this case acts as a stabilizer. Beginners can do it from their knees, this will reduce half the load. More advanced ones - on straight legs. In the version for those who are more advanced, the leg muscles are also involved. The most important thing in push-ups is the angle of the hands relative to the elbow and shoulder joints: the elbows should not fall out, the hands should be strictly under them. Push-ups can be done with a wide grip, where the pectoralis major and biceps are involved, or with a narrow grip - then most of the load falls on the triceps.
Shutterstock/Vostock Photo
Plank. A unique exercise that uses ALL the muscles of the body. The simplest and most effective, requiring no additional equipment, space, or equipment. If you don’t know what to do, do a plank. There are several types, depending on the level of preparedness of the trainee. Do not forget about the correct technique: on straight arms, the hands, elbows and shoulders are at the same level, on semi-bent arms - the elbow is exactly under the shoulder. The back is not slouched, the lower back is taut, and does not fall down. The knees are straight, but not “locked” or arched.
Shutterstock/Vostock Photo
Squat. In the squat, the target muscles are almost all the muscles of the legs and buttocks. The back muscles, the spinal extensors, are used as stabilizers. There are many types of exercise with different movement mechanics. You can find them and study them yourself on the X-Fit Youtube channel.
Shutterstock/Vostock Photo
Lunges. They act in a similar way to a squat. The same muscles are involved. There are different types of exercise that can be done to diversify the training process - on the spot, in a step, backward lunges, scissors.
In both squats and lunges, a lowered head, knees together, and a round back are unacceptable - all this can lead to loss of balance, injury to the knees and spine.
Expert methodologist of the federal network of fitness clubs X-Fit Ruslan Panov:
“First of all, it is necessary to control the equipment. Often beginners immediately start working at increased intensity, thinking that it is effective. But that's not true. All joints have certain vectors of movement, and if they are not followed, then the exercises become useless and even traumatic. Therefore, when we talk about starting a training journey, the most important thing to start with is setting up the technique. The study of movement technique is called biomechanics. It’s best to do this with a coach on an individual basis.”
No matter where you train - at home, in the gym, at the stadium or on the beach on vacation - include core exercises in your workout. You can build a full workout using squats, lunges, push-ups and planks. More advanced ones can use weights and increase the number of repetitions. The most important thing is the correct technique, then the lesson will be effective.
Local exercises.
The exercises of the second group include all those that, for a number of reasons, are not included in the multi-joint group, but they cannot be called isolating either. We can say that these are exercises that involve one large muscle group (legs, back).
List of local exercises:
- Lunges
- Block rows to the chest or belt
- Dumbbell row to waist
- Seated barbell press (with back support)
- Seated dumbbell press (with back support)
- In fact, this also includes pull-ups.
Isolation exercises.
This group includes exercises whose task is to isolate one muscle group as much as possible. Very often, exercises in this group are the main ones in training programs, which is not very correct for a number of reasons:
- In these exercises it is physically impossible to use large weights, which means the hormonal response will be small;
- Even if you try to lift a lot of weight, you will put excess stress on joints that are not designed to handle it like large joints;
The purpose of these exercises is to provide a pumping effect, promote sarcoplasmic hypertrophy, and increase blood supply to the muscle due to the high-repetition mode of work. You don’t have to give up these exercises, but you don’t have to put them at the forefront.
But they also have a plus - using such exercises, it is difficult to overtrain.
This group of exercises includes everything that involves small muscle groups or isolates large ones.
- Various biceps curls using barbells, dumbbells or machines;
- Various triceps extensions;
- Lifts and flyes of dumbbells on the deltas (shoulders);
- Dumbbell flyes and presses (pectoral)
- Leg exercises performed in machines (leg press, Smith machine squats)
Of course, one must understand that such a division was created, first of all, for the convenience of the trainees themselves. A number of these exercises, if desired, can be classified into other groups. For example, pull-ups definitely cannot compete in effect with squats or deadlifts, but they should still be classified as basic exercises, since their counterpart on machines - deadlifts - definitely belongs to the local group.
Also, if desired, heavy bench presses and dumbbell flyes can be classified as a local group. I classify them as an isolating group, because using heavy weights in this case is stupid - there are barbell presses for that.
Any training program is built, for the most part, from multi-joint and local group exercises. It is quite possible to combine them - for example, on leg day, put the squat as the first exercise, and lunges with the barbell in place as the second. Or, when training your back, start with deadlifts, continue with pull-ups, and finish with dumbbell and block rows.
In the same way, when creating a full-body program, you can do heavy, multi-joint exercises for one muscle group (for example, deadlifts) on one day, and simpler ones (for example, barbell or dumbbell rows to the belt) on the other.
The main thing is not to make the common mistake and not build a training program only from isolation exercises, since this will be of little use.
Want to learn more about exercise selection? Download my book “FAQ on Fitness and Bodybuilding”! No spam. I send letters only on the topic.undefinedDownload the book!
The effectiveness of bodyweight training is controversial and doubtful among many professional athletes. There is an opinion that exercises without additional weights do not give excellent results. However, for those new to sports, functional training is ideal for improving strength and increasing muscle mass.
Grammar piggy bank
You have found yourself in a grammar box that stores grammar exercises. Choose any and enjoy. If you find it difficult to choose, a randomizer will help.
Thematic exercises
- Tenses
- Irregular Verbs
- Make
- Offer and Suggest
- Noun + Noun, Possessive Case and article
- Another, Other, Others
- Used to, Be Used to
- Only Singular
- There or It?
Olympiad grammar exercises
All the exercises in this section are tasks from last year’s versions of various English language Olympiads.
- Exercise 1 - the meaning of conjunctions and allied words (Eurasian Olympiad for schoolchildren 2016/17, qualifying round, grades 10–11)
- Exercise 2 - word forms (brackets) (Interregional Olympiad for schoolchildren on the basis of departmental educational organizations 2016/17, final, 11th grade)
- Exercise 3 - paraphrasing (Plekhanov Olympiad for schoolchildren 2016/17, final, grades 10–11)
- Exercise 4 - word forms, word bank (“Lomonosov” 2015/16, final, grades 10–11, option 1)
- Exercise 5 - word forms, word bank (“Lomonosov” 2015/16, final, grades 10–11, option 2)
- Exercise 6 - 20 multiple choice questions (Herzen Olympiad for schoolchildren 2015/16, qualifying round, grades 10–11)
- Exercise 7 - word forms (brackets) (Interregional Olympiad for schoolchildren on the basis of departmental educational organizations 2015/16, final, 11th grade, option 2)
- Exercise 8 - word forms (brackets) (Interregional Olympiad for schoolchildren on the basis of departmental educational organizations 2015/16, final, 11th grade, option 1)
- Exercise 9 - word forms, word bank (RANEPA 2015/16, qualifying round, grades 10–11)
- Exercise 10 - verb forms, brackets (RANEPA 2015/16, qualifying round, grades 10–11)
- Exercise 11 - mixed topics (including vocabulary), multiple choice (PVG 2014/15, final, grades 10–11)
- Exercise 12 - -ing/-ed, word order; multiple choice (RANEPA 2016/17, qualifying round, grades 10–11)
- Exercise 13 - impersonal structures; rewriting sentences (RANEPA 2016/17, qualifying round, grades 10–11)
- Exercise 14 - miscellaneous; multiple choice (Eurasian Olympiad for schoolchildren 2015/16, qualifying round, grades 10–11)
- Exercise 15 - miscellaneous; multiple choice (Eurasian Olympiad for schoolchildren 2015/16, qualifying round, grades 10–11)
- Exercise 16 - multiple choice (Plekhanov Olympiad for schoolchildren 2016/17, qualifying round, grades 10–11)
- Exercise 17 - word forms, word bank (“Lomonosov” 2016/17, final, grades 10–11, option 1)
- Exercise 18 - word forms, word bank (“Lomonosov” 2016/17, final, grades 10–11, option 2)
- Exercise 19 - word forms (brackets) (Interregional Olympiad for schoolchildren on the basis of departmental educational organizations 2017/18, final, 11th grade)
- Exercise 20 - transformations based on instructions (Herzen Olympiad 2017/18, final, grades 8–11)
- Exercise 21 - grammar terms (Eurasian Olympiad for schoolchildren 2014/15, final, grades 10–11)
- Exercise 22 - reported speech; paraphrase (RANEPA 2017/18, final, grades 10–11)
All sorts of different grammar exercises
- Sentence Translation Exercise
Pros and cons of bodyweight exercises
If you are looking to improve your body definition, then a bodyweight exercise program is right for you. But for gaining muscle, training with a large number of repetitions without weights is not suitable at all. Sports professionals often recommend a set of Tabata exercises. This functional training is good for losing weight. However, for obese people, such training can be dangerous. It is better to first consult a doctor in this case.
Benefits of functional training:
- There is no need to spend on sports equipment in the first stages of playing sports.
- You can conduct training at home or on the sports ground.
- You customize the training program to suit yourself by changing or adding exercises.
- Correction of musculoskeletal problems and postural disorders.
- When performing multi-joint exercises, several muscle groups are trained simultaneously.
There are also disadvantages to such training:
- Not suitable for overweight people.
- It is impossible to gain more muscle mass.
- In the future, there will be a need to purchase sports equipment for effective training.
When exercising without equipment, ensure proper breathing and exercise technique.
The main principle of the respiratory system when engaging in physical activity is exhalation of air during exertion and inhalation during the easy stage of exercise. If you do not adhere to the execution technique, you will not only not achieve the desired result, but you may also injure yourself. Before you start, watch videos of sports activities and evaluate the technical composition of the exercises. Also, during your first lessons, stand in front of a mirror. This will help you track your mistakes and execution technique.
There is no need to rush when doing the workout; perform all positions of the program slowly. Do not make long stops before repetitions or between approaches; during exercises, try to maximally load the muscle group on which you are doing the approach. Put in the effort and do your workout to the best of your ability.
At the end of each training session, be sure to devote 15-20 minutes to cardio exercise. If you are a beginner, do your first sessions at an average pace. There is no need to exercise at a frantic pace; it is better to maintain proper breathing and perform cardio exercises for longer. Interval running or stair climbing are ideal for this.
The effectiveness of multi-joint exercises
Multi-joint exercises with your own weight are an excellent solution for those who want to lose excess weight or add definition to their body in a short period of time. A large number of exercises are basic techniques; they are mandatory for most athletes. If you perform such workouts systematically, your strength indicators will grow more intensely.
If you don't have the opportunity to go to the gym, then training without equipment is perfect. Basic training includes the following exercises: push-ups, squats, pull-ups, lunges, etc. If it is difficult to do, for example, push-ups, you can find an analogy in an easier form. Combine basic exercises with additional exercises, try to pay attention to all muscle groups during training, namely: muscle groups of the legs, chest, back and arms.
Block similar articles
Bodyweight training program for men: effective techniques
Requirements for beginners:
- regularity of training and repeated repetition of exercises;
- optimized loads and systematic rest;
- increasing the number of approaches and repetitions for high-quality load.
To improve body quality, professional athletes recommend not only choosing good training positions, but also monitoring the rhythm of exercise. It is recommended to train with a large number of repetitions, for example, in one session, perform: 30 squats (10 repetitions for 3 sets); 18 push-ups (6 repetitions in 3 sets). Perform other exercises using the same principle.
- To increase the intensity of burpees, try to jump higher each time. (10-12 times in three sets).
- Plank, there are many variations of the exercise. Beginners should start with a 20-second plank, gradually increasing the time to 60 seconds.
- Raising your legs to the crossbar with a delay at the highest point. (15 times, three approaches).
- Push-ups on a bench with a narrow arm position will perfectly pump up the muscles of the back and shoulders. (12-15 times in three trips).
- Push-ups on parallel bars. (8-10 repetitions on each leg).
- Slow crunches will help get your abs in shape; pay attention to your breathing as you do them. Perform about 30 repetitions per workout.
- Stepping up a hill: 30 times on each leg.
- Raising legs from a lying position. (12-15 times in 3 sets).
- Lunges, in a confined space, can be performed on the spot, 30 repetitions on each leg.
Be sure to take breaks between classes and give your muscles time to rest. In untrained people, the muscular system recovers slowly; after training, do a little stretching, and before training, warm up for 10 minutes.
Principles of treatment
Here are some examples of exercises to improve lumbar motor control/core stability.
Deep muscles
In serious pathologies where deep muscle dysfunction is clearly present, we recommend that doctors first concentrate on motor control training and later move on to general strengthening exercises.
Superficial muscles
It is very important that doctors and sports specialists who undertake training of the superficial muscles of their patients have a good understanding of their pathoanatomical features, and are also able to predict what effect physical exercise will have on this. Ideally, all these exercises should be performed with correct lumbopelvic position with full control of the deep muscles. The number of repetitions and hold time may vary depending on your training goals (as long as the exercise is performed with good control).
Crunches
Lie with your back on the floor, bend your knees, arms crossed over your chest, feet pressed to the floor. Lift your shoulders off the floor and pull your torso towards your knees. Avoid full sit-ups and make sure your lower back does not lift off the floor.
Oblique crunches are performed like regular crunches, but you need to reach your shoulders towards the opposite knee.
Plank
Lie on the floor on your stomach. Keeping your torso straight (as if extended in one line), lift yourself up on your toes and elbows so that your elbows are directly under your shoulders. Stay in this position as long as you can control the correct body position. To make the exercise more difficult, you can try lifting your leg off the floor a little.
Bridge
Lie with your back on the floor, knees bent, feet on the floor. Lift your pelvis off the floor and point it up, resting your shoulders and feet on the floor. You can complicate the exercise by performing a bridge on one leg (the second leg is straightened and looking at the ceiling).
Raising legs from the "cat" position
Take a knee-elbow position, back straight. Raise one leg to horizontal level, repeat on the other leg.
Superman
The technique is the same as in the previous exercise, however, at the same time as the leg, you should raise the opposite arm to a horizontal level.
Leg raises
https://youtu.be/gSi8z1gIdC8
Lie on your back, legs straight, arms along your body, palms down. Then raise one leg 10 cm, the lower back should not come off the floor, do not let it round. Change your leg. You can make the exercise more difficult by lifting both legs at once.
A hundred
Lie on your back, legs straight, arms along your body. Then raise your legs and bend them at the knees (the bend angle at the knees and hip joints should be 90 degrees). Next, lift your hands off the floor a few centimeters and start drumming your hands on the ground (you need to hit your hands 100 times). Focus on keeping your hips and legs completely still and your back flat.
Leg extension
Lie on the floor, legs straight, arms along your body. Lift one leg off the floor, keeping the other straight and pressed to the ground, then slowly lower it. Switch legs.
There are also many exercises that can be performed with a fitball. Such training has been shown to have a better effect on neuronal activity and the trunk's ability to maintain balance than floor training. Here are tips and examples of exercises from Akuthota for core stability training:
- Study your core anatomy well.
- Emphasis on active participation.
- Increase the difficulty of deep muscle training once the patient can complete 30 repetitions with an 8-second hold.
- Pretension of the deep abdominal muscles.
- Sliding your feet along the floor with pre-tension of the deep muscles.
- Raising the legs from a supine position (with pre-tension of the deep muscles).
- Performing a bridge (with pretension of the deep muscles).
- Pretension of deep muscles while standing.
- Horizontal row with pretension of deep muscles.
- Walking with pretension of deep muscles.
- Raising the arms from the “cat” position (with pre-tension of the deep muscles).
- Lifting the legs from the “cat” position (with pre-tension of the deep muscles).
- Alternately lifting opposite legs and arms (with pre-tension of the deep muscles).
- Exercises for the quadratus lumborum and obliques (increase the difficulty if the patient can do 30 repetitions with an 8-second hold).
- Side plank with bent knees.
- Side plank with straight legs.
- Facilitation techniques for torso twisting, if necessary.
- Reduction of MTD, visualization, palpation, work with pelvic tilt, use of ultrasound.
- Functional body positions during training with core activation.