In the body of every person there is tissue that is found almost everywhere - in blood vessels, heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, diaphragm, tendons, muscles, ligaments. In some organs it is loose, in others it is dense, in some places it is less, in others it is more, but it is present everywhere. And it's called connective tissue.
Connective tissue is a complex structural and multifunctional system that unites various organs and tissues of the body into a single whole and makes up approximately 50% of body weight. It consists of an intercellular matrix and various cells (fibroblasts, chondroblasts, osteoblasts, etc.). In turn, the intercellular matrix in the body performs many functions:
- forms the framework of tissues and organs;
- serves as a kind of “biological glue” for cells;
- participates in the regulation of water-salt metabolism;
- forms highly specialized structures - teeth, tendons, cartilage, basement membranes, etc.
The basis of the intercellular matrix is collagen , a protein that accounts for about a third of all proteins in the human body (about 6% of body weight). About 40% of collagen is found in the skin, approximately 50% in skeletal tissues and only 10% in the stroma of internal organs (this term refers to structural formations that determine or fix the shape of a cell).
Collagen owes its name to the ancient Greek words “glue” (colla) and “origin” (genesis). It “glues”, or rather, holds the tissues of the body together. Any living creature on Earth has collagen - from viruses and protozoa to multicellular organisms, including humans. Collagen is not found only in plants.
Collagen is a protein made up of amino acids containing carbon, oxygen and hydrogen. Collagen is composed of various molecules that have a unique ternary configuration of three polypeptide subunits in a helix known as the alpha chain. Each chain contains about 1000 amino acids, representing the amino acid sequence consisting of glycine, proline and hydroxyproline and arginine.
How does collagen synthesis occur and what contributes to it?
Collagen synthesis is a complex enzymatic process that must be provided with the proper amount of vitamin and mineral elements. Synthesis occurs both in the cells of our connective tissue - fibroblasts, and outside them.
Thus, the formation of the most important amino acid for collagen, hydroxyproline, occurs exclusively with the help of the enzyme “proline hydroxylase”, and this enzyme is in active form only if it consists of divalent iron, and vitamin C provides divalent iron.
Vitamin C deficiency disrupts the hydroxylation process, which affects further stages of collagen formation, and is fraught with the formation of “unfinished”, loose collagen, which underlies saggy, “tired” skin...
Overdose
Even with repeated and prolonged excess of daily portions, an overdose of collagen is unlikely. Being a set of amino acids, the polypeptide simply breaks down into elements that are used to strengthen different systems and structures of the body. The human body always has somewhere to use excess protein.
If an overdose does occur, doctors suggest that it may manifest itself as diarrhea, thickening of the blood, and metabolic disorders. However, so far there are no officially known cases of excess substance.
The process of collagen destruction
In addition to synthesis, fibroblasts also destroy collagen through the enzyme “collagenase”. This is a necessary process in the body that occurs throughout life. Collagenase breaks down collagen molecules, and macrophages “capture” and “digest” these broken molecules. The amino acids formed during this process again participate in the process of synthesis of new collagen. A sort of “circulation” of collagen in the skin...
The whole problem is that after 25-30 years the process of destruction begins to prevail over the process of synthesis. And if in young skin restored collagen is about 6 kg per year, then after 35 only 3 kg of collagen is restored, moreover, damaged, fragmented collagen accumulates in the skin, unable to retain water molecules. First, wrinkles form, then ptosis (sagging skin) and fibroblast damage begin.
This is why fibroblasts need to be “helped” after 30 years.
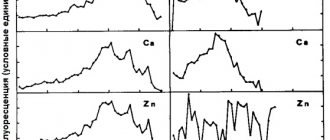
In this picture you can see the difference between the histograms showing the state of collagen in young and mature skin.
Release forms
There are several forms of UC-II collagen on the pharmaceutical market:
- Capsules. The best option for those who do not tolerate the taste and smell of the substance. The gelatin shell protects the active compound from contact with gastric juice and maintains the high therapeutic value of the drug. The supplement is absorbed within 30–40 minutes, and in rare cases it can cause belching with the taste of collagen.
- Pills. This form of protein takes the longest to break down. Pills are convenient to store, take and transport, but they all contain additional components that are not always beneficial to the body. They can cause allergies, and their large size makes them difficult to swallow.
- Powder. It is quickly and well absorbed, safe from the point of view of skin reactions, and has no auxiliary components. Requires drinking or adding to liquid. The drug is inconvenient to use outside the home: it needs to be dosed and time spent mixing.
A more serious and almost instantaneous therapeutic effect is provided by collagen in injections. The injection solution usually contains not only the polypeptide, but also many other substances: chondroitin sulfate, fermatron with gillan, hyaluronic acid. The drug is injected into the synovial area and is prescribed to patients with severe pain or elderly patients with arthrosis of the knee joint and osteoarthritis.
The liquid product relieves discomfort well, stimulates metabolism in cartilage and ligaments, normalizes the production of synovium, and improves shock absorption when walking. Injections cannot be used without a doctor's prescription.
But not only does a person lose collagen with age, there are many other reasons for this, such as:
- Active facial expressions.
- Smoking. Many of the chemicals present in tobacco smoke damage collagen and elastin in the skin. Nicotine also constricts blood vessels in the outer layer of skin, which reduces the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to the skin, compromising skin health.
- Psychological stress.
- Poor nutrition.
- High sugar consumption. Eating foods high in sugar increases the rate of glycation, which makes collagen dry, brittle and weak.
- Alcohol consumption.
- Sunlight. Ultraviolet rays from sunlight damage collagen at an increased rate, causing abnormal elastin to accumulate. Abnormal elastin leads to the formation of an enzyme that breaks down collagen. This process can lead to the formation of sun scars.
- Autoimmune disorders. Some autoimmune disorders cause the production of antibodies against collagen. Mutations in the genes responsible for encoding collagen alpha chains can affect the extracellular matrix, resulting in decreased production of normal collagen and secretion of dysfunctional mutant collagen.
- Environmental pollution.
But we must remember that this aggravates not only the quantity of collagen, but also its quality, which is important. The synthesis of this protein is carried out in fibroblasts by creating peptide bonds from amino acids (hereinafter referred to as AMK), further spiralization and the formation of a tertiary (active) structure. With proper production, the skin becomes elastic and smooth. It should be clarified that a wrinkle is a groove in the framework of which the collagen structure is destroyed.
Drugs
Type II collagen supplements can be purchased at a pharmacy or online store. But the prices there are often inflated, and the active substance is contained in minimal quantities. We recommend purchasing dietary supplements for joints on the iHerb website.
For our readers who are not yet familiar with iHerb, we offer a -10% discount on their first order. To take advantage of this advantageous offer, you need to follow this link or enter the promotional code AGK4375 in a special box when checking out your cart.
Top 6 medications with II for joints:
★★★★☆
California Gold Nutrition, CollagenUP, Unflavored, 7.26 oz. (206 g)
1 200 ₽
More details
★★★★☆
California Gold Nutrition, Collagen UP, Unflavored, 16.36 oz. (464 g)
2 550 ₽
More details
★★★★☆
California Gold Nutrition, Hydrolyzed Collagen Peptides + Vitamin C, Type 1 &…
1 350 ₽
More details
★★★★☆
Azelique, Serumdipity, Anti-Aging Collagen Facial Serum, 1...
1 500 ₽
More details
★★★★★
Lake Avenue Nutrition, Hydrolyzed Collagen Type 1 & 3, 1,000 mg, 60 Tablets
150 ₽
More details
★★★★☆
Mason Natural, Premium Collagen Cream, Pear Flavor,…
383 ₽
More details
See the full catalog of products at the link:
show all
The site is distinguished by a huge assortment of quality goods from the best manufacturers in the USA and Europe. Thousands of reviews and ratings help you choose a truly useful drug, and affordable prices (1.5–2 times lower than pharmacy prices) make the purchase even more enjoyable. Good impressions of the site are left by punctual and profitable delivery in various ways, attentive technical support working around the clock.
What are the benefits of collagen?
The helices of this protein allow the connective tissues of the human body to remain in working condition; they have such good strength that they are practically not stretchable.
The main functions and tasks of the “protein of youth”:
- Protective. Protects body tissues (for example, muscles) from mechanical damage.
- Restorative. Regenerates cells.
- Support. Strengthens the structures of organ forms. Provides elasticity of structures.
- Inhibition in the development of melanomas (these are skin tumors).
- Stimulation of the development of new cell membranes.
The consequence of a decrease in the amount of protein in the body is:
- Loss of skin elasticity, appearance of wrinkles.
- Malaise and frequent illnesses.
- Rapid fatigue.
- Periodic pain in all muscles of the body.
- Thinning and fragility of blood vessels.
- Severe overstrain of the body's muscles.
- Unintentional decrease in activity level.
- Worsening of the average condition of the body.
- Weakening and brittleness of bone tissue.
Dosage and regimen
To prevent joint diseases, it is recommended to take 5000 mg of collagen per day. This amount of substance is enough to maintain the elasticity and strength of connective tissue for a long time.
When diseases appear, the daily dose of UC-II should be increased:
- for recovery from fractures and injuries, 10,000 mg of the drug will be required;
- to eliminate pain and stiffness in arthrosis, arthritis - from 10 to 12 g of protein.
For athletes, it is recommended to increase the daily dose of the supplement to 8000 mg, dividing this amount of the substance into three doses.
Take type 2 collagen on an empty stomach, 30–60 minutes before meals. The powder is pre-mixed in water or juice; tablets and capsules are consumed as is, with a glass of liquid.
The course of treatment for joints lasts 4–6 months. The first results appear after 90 days, but therapy must be continued. With long-term consumption of protein, the health of the musculoskeletal system improves, the tone of the skin increases, wrinkles are smoothed out, and hair and nails are strengthened.
For prevention, it is recommended to take collagen once a year for 3-4 months. If it is necessary to eliminate the symptoms of articular pathology, a treatment regimen is prescribed by the doctor. During therapy, it is advisable to avoid sweets, alcohol, fats, white pastries, and refined rice. Carbohydrates are a good glycating agent. When combined with collagen, they glue fibrillar fibers together, making them stiff and brittle.
The video will tell you how to take collagen for joints:
Types of collagen
Currently, 28 of its types have been described, differing in amino acid sequence and degree of modification. But, to be honest, this makes us neither cold nor hot, because only 3 of them are industrially produced.
| Types | Genes | Tissues and organs |
| I | COL1A1, COL1A2 | Skin, tendons, bones, cornea, placenta, arteries, liver, dentin (bone substance of the tooth). |
| II | COL2A1 | Cartilage, intervertebral discs, vitreous body, cornea |
| III | COL3A1 | Arteries, uterus, fetal skin, stroma of parenchymal organs (the connective tissue basis of parenchymal organs, which include the liver, spleen, endocrine and exocrine glands, brain and others). |
Reviews about the application
According to reviews from consumers who took type II collagen in the recommended course, the drug really improves the functionality of joints, strengthens ligaments, eliminates pain and facilitates movement. Older patients note that the creaking in the knee joints has gone away, it has become easier to sit down and stand up, and climb stairs.
Athletes who use collagen as a sports nutrition or in recovery techniques after injuries speak about the high regenerative properties of the supplement. The dietary supplement accelerates the healing of damaged tissues, increases elasticity, and allows you to quickly return to training.
Doctors consider UC-II an excellent addition to physiotherapy and exercise therapy for diseases of the spine, after dislocations and fractures. According to victims, the protein stimulates bone healing, shortens the period of immobility, allows the injured limb to be used earlier, and relieves discomfort.
How to increase collagen production in the body?
Collagen is found in food, but, unfortunately, in very low concentrations. There are not enough of them for any effect to be noticeable in humans. It would be good to add gelatin-rich foods to your diet, but the choice is limited.
The highest quality sources of amino acids that make up collagen are preparations containing so-called “free amino acids”. Since free amino acids are practically ready for absorption, the receiving person’s body does not need to waste time, digestive enzymes and energy on digesting them. They are able to enter the blood in the shortest possible time, and being delivered by it to places in need of additional collagen synthesis, they are immediately included in its formation.
Side effects and allergies
Oral administration of collagen UC-II rarely causes discomfort. If you are intolerant to animal or fish proteins, a person may experience an allergic reaction with itching, rash and redness of the skin. Patients suffering from autoimmune diseases sometimes experience swelling of the face and limbs.
More often, injections of collagen preparations lead to side effects. After a long course of injections, you should be wary of the appearance of bruises, scars, pigmentation, and tissue necrosis. All these conditions can be treated, but therapy requires a lot of effort and time. Therefore, if you have joint problems, you should contact a good specialist who can eliminate the occurrence of unwanted effects.
Storage and shelf life of supplements
Tablets and capsules with collagen are kept in a dark place, out of reach of children, at room temperature. The shelf life of the drugs is 2 years. The powder requires a dry room. It is stored in tightly sealed jars for 24 months from the date of manufacture.
Great Lakes Gelatin Co., Collagen Hydrolysate, Unflavored, 16 oz (454 g)
★★★★★
from 2,083 ₽
More details
Why does women's skin age faster?
Collagen synthesis involves estrogen in women and testosterone in men. The production of these hormones stops in different ways. Testosterone takes longer to produce in men than estrogen in women. Its absence slows down collagen synthesis, which causes skin aging, weakness of muscles, bones and joints. This is why women show signs of aging earlier, while men remain youthful longer. To prevent collagen from being destroyed, you should eat right and give up bad habits (drinking alcohol, smoking). Ultraviolet radiation, illness and stress, and hormonal imbalance also contribute to the loss of collagen.