What are the benefits of creatine
Most modern researchers believe that creatine can be consumed safely. This applies not only to athletes, but also to people who want to increase their energy and metabolism.
Most studies have shown that not every person responds to this supplement in the same way. Some may experience greater results and improved health. While others deal with creatine side effects such as stomach upset and fluid retention. Below we will look at the benefits and harms of using creatine, what to expect if you are interested in how to drink creatine monohydrate and start “introducing creatine”. As well as how you can maximize your results while continuing to use this supplement safely ().
Let's start with the benefits of creatine and its uses. Why take creatine monohydrate? Benefits associated with taking this supplement include:
- Aids in protein synthesis, which increases muscle growth. Creatine also increases body weight by filling muscles with more water. Some studies have shown that one week of creatine supplementation increased body weight by approximately 1-2 kg.
- More power. The storage capacity of creatine in our muscles is limited, but it increases with increasing muscle mass. Supplements have the ability to restore ATP stores more quickly during intense physical activity, helping to maintain effort and prevent fatigue ().
- Aids in muscle recovery after exercise, such as maximizing the benefits of strength training.
- Increased performance during high-intensity interval training. Research shows that creatine monohydrate improved performance during maximal force muscle contractions, single-effort sprints, and repeated sprints.
- Neuroprotective properties (may help protect the brain) ().
- Improved cognitive functions such as increased alertness, concentration and attention.
- Reducing the severity of depressive symptoms.
- Cardioprotective properties, as creatine may help protect the heart and blood vessels. It has also been shown to support increased endurance and anaerobic cardiovascular capacity ().
- Reducing fatigue.
- Improved bone density when combined with resistance training ().
Possible beneficial effects of taking creatine
Creatine can be useful not only for athletes to improve their professional skills, but also in medicine. It is used in the complex therapy of a number of neuromuscular and neurodegenerative disorders. This includes arthritis, Parkinson's disease, chronic heart failure, and prolonged depression. This chemical compound is also often prescribed for increased mental and emotional stress.
Improved athletic performance
| Athletes Take Creatine to Increase Performance |
Creatine supplements have long been used by athletes, as they are simply irreplaceable during high-intensity exercise.
People take creatine because it allows the body to produce more energy, and with more energy, “you can do 1-2 more sets or increase the load by 2-3 kg”, and as a result, “your muscles become bigger and stronger”, So says Chad Kerksik, Ph.D., assistant professor of exercise physiology at Oklahoma State University.
In a study published in the Journal of Neurochemistry, scientists shared their opinion that regular use of creatine can increase maximum power and performance in high-intensity anaerobic exercise by up to 15%.
The creatine content in muscles directly depends on body weight and body water balance.
Another conclusion of this study was that taking creatine leads to water retention, but does not have a direct effect on the distribution of water in the body.
Creatine and Parkinson's disease
Creatine actually helps slow the progression of Parkinson's disease. Scientific experiments conducted on mice have proven that creatine prevents cell death, which is inevitable in this disease.
In a study published in the Journal of Neurochemistry, scientists concluded that "the combination of coenzyme Q (10) and creatine helps treat neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's and Huntington's disease."
Creatine is indicated for people with muscular dystrophy
Creatine may also help increase muscle mass in people suffering from muscular dystrophy.
A study conducted in Germany found that people taking creatine were able to build muscle tissue by 8.5%, compared to those who did not take it.
Dr. Rudolf Kley, a leading expert at the Ruhr University (Bochum, Germany) stated that “both short- and medium-term supplementation of creatine improves muscle strength in people with muscular dystrophies, and is generally well tolerated.”
Creatine for treating depression
For some, it will be unexpected and surprising that a popular nutritional supplement for athletes has properties that help alleviate the mental state of nervous disorders and prolonged depression.
Researchers from three different South Korean universities found that women with officially diagnosed depression who took an additional 5 grams of creatine per day in addition to a prescribed antidepressant, recovered twice as quickly as women who took only an antidepressant.
Creatine improves brain function
Researchers from the University of Sydney and Macquarie University (Australia) have scientifically proven that creatine can improve memory and intelligence.
Dr Caroline Ray, the study's principal investigator, said: “The results were very clear in both groups of people. Creatine significantly improves brain function."
Creatine in food
You can eat high-protein foods, including meat (especially beef), poultry, fish, and eggs, to get your creatine.
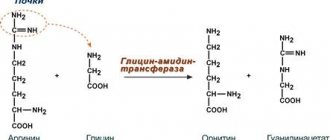
Consuming collagen protein and collagen sources like bone broth is a great way to increase your intake of the amino acids that form creatine (arginine and glycine). Meat organs such as liver and kidney have lower concentrations. Some of them can also be found in breast milk, dairy products and milk from cows/sheep/goats, as well as in the blood of humans and animals. Because vegetarians/vegans avoid the highest sources of this compound, they have been found to have lower concentrations of creatine. This can contribute to problems gaining muscle mass and strength when eating a low protein diet.
Final Thoughts
Creatine is a small peptide made up of amino acids. It is found naturally in the body, consumed from certain high-protein foods, and taken by some people, such as athletes or bodybuilders, in supplement form.
The benefits of creatine include building muscle mass, improving strength and power, reducing fatigue, improving cardiovascular health, increasing bone density and improving mood.
Why might creatine be harmful? Although it is generally safe, creatine monohydrate may cause side effects in some people, such as weight gain due to water retention, abdominal pain, diarrhea, cramping and restlessness. These effects are most likely to occur in those who take overdoses or have kidney disease.
The best way to take creatine monohydrate is to follow the dosage directions, spread the intake throughout the day, use after a workout, take with a meal containing carbohydrates and protein, and drink plenty of water when using.
How to take creatine
In order for the result to be noticeable, you need to know how to use the supplement correctly. Many people make mistakes at the beginning of their journey. But it’s better to find out everything in advance so as not to play with your health.
The approximate daily norm is 2-5 grams. The substance is mixed with carbohydrates. Many people make the mistake of taking it before training. Experts have found that it would be more correct to do this after exercise.
The powder is poorly soluble in water. Crystals are often used this way: take the required dose into your mouth and wash it down with water. But this is not very convenient. A blender and shaker come to the rescue.
Attention! The quantity cannot be determined visually. Doses are very small, it is better to use a kitchen scale. It is worth noting that not all types are consumed equally
For some, an individual dosage regimen is determined. Otherwise, creatine in sports will bring not only benefits, but also harm. There are two schemes for using monohydrate:
It is worth noting that not all types are used equally. For some, an individual dosage regimen is determined. Otherwise, creatine in sports will bring not only benefits, but also harm. There are two schemes for using monohydrate:
- 4 times a day, 5 grams in sweetened water. Later, 5-10 grams in two doses.
- 10 grams in two doses.
It is important to increase the amount of fluid you drink while taking supplements. Every 5 grams – half a liter of water
Myths about creatine
Despite the benefits of creatine during physical activity, there are myths about the dangers of this substance.
Let's look at some of them:
- has a negative effect on the liver and kidneys. Studies have shown that this component, even with long-term use, does not harm the liver and kidneys, as well as other internal organs. The main thing is to adhere to the recommended schemes;
- may cause gastrointestinal disorders. Creatine may cause minor stomach upsets. Studies have shown that such a reaction occurs in 6–7% of people who take this drug. Typically, such gastrointestinal disturbances occurred due to taking creatine above the recommended amount or when taken on an empty stomach. To reduce the likelihood of such negative manifestations, micronized creatine was developed, which is better absorbed by the human body;
- causes cramps and leads to dehydration of the body. There are no confirmed facts about this. Moreover, dietary supplements with this substance help maintain moisture levels in the body;
- may cause the development of compartment syndrome. A slight increase in blood pressure may occur due to high intake doses that exceed the recommended intake. The main causes of this disease are injuries, fractures, damage or the occurrence of inflammatory processes, tumors, which leads to disruption of circulatory processes and neurological disorders;
- Creatine leads to weight gain. At the initial stage of admission, slight weight gain may occur due to slight fluid retention in the body in the range of 0.8–2.9%. But this does not happen when taking lower doses. Taking creatine during physical strength training leads to an increase in muscle mass and a decrease in body fat mass. And these factors contribute to the formation of a beautiful athletic figure;
- promotes the occurrence of rhabdomyolysis. There is no direct evidence that this is the case. This myth appeared after a publication in the New York Times, which reported that creatine contributed to the occurrence of rhabdomyolysis in football players. Such a diagnosis may appear under constant heavy loads in a hot climate with high humidity. The football players who were exposed to this disease were in a sports camp, where they worked out for a long time every day in a hot gym with high humidity. None of the players confirmed that they consumed creatine supplements.
Video: real scientific facts and manufacturers' speculations about creatine
Creatine increases the strength and endurance of sports people, helps to increase muscle volume, which is valued by bodybuilders. This supplement, when taken correctly, does not have any side effects, except for increasing body weight due to muscle growth.
Did you know? Medicine is very interested in creatine as a substance that helps fight Parkinson's disease, as well as having a positive effect on memory and intelligence.
Experts' opinions
E. Komarov
Conducted studies indicate the beneficial properties of creatine in increasing muscle mass and regular training. This action applies to young athletes who practice exercises with a short-term, but quite intense load on the muscles. Based on this effect, creatine is prohibited by certain sports associations and is regarded as doping. For other athletes who do not participate in competitions, the supplement is quite safe at a dosage of 2-3 grams daily.
However, as an adult, creatine products will not help you build or maintain muscle mass. At the same time, the supplement becomes more difficult to digest with age, which can cause a negative reaction in internal organs. There is also no reliable data about the absolute safety of creatine; there is controversial information. To protect your body from potential negative consequences, you do not need to exceed standard dosages of creatine, use it during pregnancy and in old age.
E. Komarov, editor-in-chief of the section on health at Harvard Medical School
K. Kendal
Thanks to misleading information in the media and widespread myths among athletes, women call creatine a predominantly male option for sports nutrition. Doubts about the safety of taking such a supplement only increase due to advertising campaigns (manufacturers do not include creatine in the list of recommended women's supplements for sports).
In practice, this product is a universal option. Not only does it improve strength and overall performance, but it also helps women lose weight faster (due to the increased pace of training). However, it is worth considering lower dosages for women and not exceeding the recommended amount.
K. Kendal, nutritionist, PhD, Australian Health Association
H. Antonio
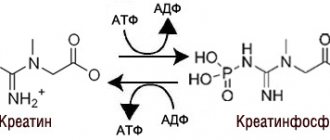
Creatine actively works as a source of quick energy for the body, which can be used during intense exercise. This mechanism is due to an increase in internal phosphocreatine reserves in muscles.
The supplement is almost the only sports nutrition option for increasing anaerobic performance, muscle mass and volume. To avoid possible side effects in the body, you should adhere to the water norm. When taking a creatine course, you should drink an additional minimum of 113 grams of water for every 3 grams of this substance.
H. Antonio, Ph.D. Nova Southeastern University, founder of the International Society of Sports Nutrition
Creatine retains water in the body
Most men constantly
Those taking a sports supplement have experienced the harmful effects of creatine. Bodybuilders note that their bodies retain water. But despite the increase in body weight, no swelling is observed, which eliminates the need to take diuretics.
Athletes also noticed that despite saving fluid, dehydration occurs due to the fact that water accumulates in the muscles. This may be accompanied by a number of undesirable reactions - impaired thermoregulation, acid-base balance disorder and disruptions in metabolic processes.
In order not to experience the harm of creatine, experienced bodybuilders recommend drinking at least three liters of water a day. This will replenish lost fluid, balance electrolyte balance and minimize the risk of unwanted effects.
Many people have noticed that creatine monohydrate can cause muscle spasms and cramps due to dehydration. To eliminate the side effect, you need to drink plenty of fluids. After this, the cramps will quickly pass.
Allergic reactions
The disadvantages of creatine do not end there. When taking the supplement, an allergic reaction may soon develop to other sports nutrition. That is, creatine monohydrate somehow helps the athlete’s body stop taking other drugs. Negative properties appeared when creatine was taken simultaneously with another supplement. How to minimize side effects in this case?
First, you need to make an appointment with an allergist and undergo an examination to find out if there is an allergen that causes all these effects.
It is very important to carefully analyze the composition of the drug before purchasing it. You should refuse to purchase if the packaging contains an ingredient that has allergic properties.
There is a widespread belief among athletes that allergy symptoms can be eliminated with special medications. And after that, continue to use sports nutrition. However, we must remember that such drugs simply hide the symptoms of the disease, but do not in any way affect their cause. It is best to completely avoid foods that pose a potential danger. Many athletes reached unimaginable athletic heights without special drugs.
Contraindications and precautions regarding use
In some cases, the harm of creatine is justified, since it is prohibited under certain conditions. The use of amino acids should be avoided in case of individual intolerance to the substance, chronic kidney diseases, gastrointestinal tract, liver and asthma.
It is not advisable to drink the product during pregnancy, lactation and puberty, as it can intensify the manifestations of acne. The use of the supplement is also contraindicated for adolescents because it disrupts the process of formation and development of the body, negatively affecting the functioning of the myocardium and hormonal system.
All athletes should know that constantly drinking creatine is prohibited. The body quickly gets used to the synthetic amino acid and stops producing it on its own.
How can you reduce the risk of negative reactions from taking creatine? To reduce the likelihood of negative effects, you must adhere to a number of recommendations:
- It is advisable for people prone to allergies to visit an allergist and undergo tests prescribed by the doctor.
- You should do your research carefully before purchasing a supplement. If the product indicated on the package contains an allergy-causing ingredient, you should not buy it.
- You should not take antihistamines together with creatine, because they will only mask the symptoms of an allergy, but will not eliminate the cause. If allergic reactions occur, it is better to stop taking the amino acid.
Despite a number of possible negative reactions, an overdose of creatine has not been recorded. Even if the supplement is abused, its components are quickly eliminated by the body through the kidneys along with excess water.
How it affects the body
Digestive system
Some gastrointestinal side effects may occur. Quite rarely, nausea, pain in the abdominal area and problems with bowel movements are observed.
Such phenomena occur due to insufficient dissolution of creatine crystals - this means that the product has not undergone the recommended purification and is of low quality. The use of a high-quality supplement, according to the manufacturer’s recommendations, minimizes such effects on the gastrointestinal tract.
New forms of creatine - citrate and malate - have maximum solubility and are suitable for people with sensitive stomachs.
Heart and blood vessels
Continuous use of creatine supplements in isolated cases leads to heart rhythm disturbances in male athletes (at increased dosages of the substance). However, this phenomenon has not been sufficiently studied, so it cannot be stated that creatine has a direct negative effect on the heart and vascular system.
Liver and kidneys
Studies have shown (Bender A, Beckers J, Schneider I, et al.) that regular supplementation of creatine for up to 2 years does not affect kidney function. Such data relate to healthy athletes who have not previously had pathologies of the excretory system. If you have chronic diseases in this area, you should consult a doctor. Otherwise, creatine may place increased stress on the kidneys due to moisture accumulation.
The substance is not metabolized in the liver and is a natural component that is produced in the body.
Water retention
The sports supplement provokes water retention in the tissues, but this does not cause significant harm to the athlete’s body. With healthy kidney function, there is no swelling or other negative manifestations. This phenomenon can only be noticed with regular weighing. During the break after a course of creatine, excess fluid will be eliminated naturally.
Effect on potency
The myth about the effect of creatine on potency is quite widespread among male athletes. This misconception was formed on the basis of analogies with hormonal supplements that directly regulate the level of sexual desire and capabilities of the male body.
Creatine does not have any side effects on potency. Even with regular and long-term use of a sports product in large dosages (for example, a “loading” plan), the athlete completely retains the natural level of hormones.
Muscletech, Essential Series, Platinum 100%, Creatine, No Additives, 400 g (14.11 oz) Price – RUB 829.77
Now Foods, Sports, Creatine Monohydrate, 750 mg, 120 capsules Price – RUB 482.28
Now Foods, Sports, Creatine Monohydrate, 2.2 lbs (1 kg) Price – RUB 1,250.73
Description and composition of the supplement
Creatine belongs to the carboxylic acids of the nitrogenous group. This substance is produced by internal organs and is natural for any person. However, such synthesis in the body is not enough, so creatine can be obtained from food and sports supplements. Athletes need this substance in large quantities, since it directly affects the training process.
When making creatine supplements, the most commonly used budget and working form is monohydrate (the effect from it comes quite quickly).
The most popular monohydrate options on iHerb:
Optimum Nutrition, Creatine Fine Powder, Unflavored, 1.32 lbs (600 g)
Price – RUB 1,227.69
Buy from a partner
Price –
Buy from a partner
Universal Nutrition, Creatine, Unflavored, 500 g, 1.1 lb (500 g)
Price – ₽925.21
Buy from a partner
Creatine brand Myprotein is also popular in Russia.
Many athletes buy creatine from the famous Chinese site Aliexpress. The following brands are popular here:
- Stenzhorn;
- healthfamily;
- MET-Rx.
Despite the lack of a specialized section, the supplement can be found using the search. You can look for creatine in these stores on Ali:
- MBHAVE'S Secret Store;
- Healthy and beautiful Store;
- InHealth Store.
This compound is presented in crystalline form.
Acids and glucose can also be added to pure creatine for better absorption. Additional ingredients significantly increase the cost of the final product, so you should carefully study the composition before purchasing (for “extra” components). Be sure to check out:
Gallery image with caption: Sports nutrition for gaining muscle mass at home Gallery image with caption: Creatine: properties of the supplement and its importance in sports nutrition Gallery image with caption: Shelf life and storage of creatine Gallery image with caption: Is it possible to mix BCAA with creatine and what could this lead to?
Who should take creatine?
Creatine is one of the most important components of sports nutrition. The amino acid is offered in its pure form and in combination with other beneficial substances. Such supplements should not be confused with steroids and anabolic steroids. Firstly, creatine intake by athletes is allowed everywhere. Secondly, this substance is non-hormonal and does not have a negative effect on health. Creatine intake is recommended for all athletes who increase the intensity of the training process and are actively involved in the gym.
The drug has no absolute contraindications and does not cause side effects if the rules of administration are followed. It is recommended to use creatine before and after training. The result appears immediately. The weightlifter feels a charge of energy and does not get tired from increasing the volume of training. It is advisable to use creatine constantly, but if this is not possible, you should ensure that it enters the body at least during the period of active training, increasing the number of approaches or increasing working weight.
Why is creatine used in amateur and professional sports?
There is still active debate about how useful creatine is in sports. For example, bodybuilders consider it an indispensable supplement that helps achieve growth and beautiful muscle definition. But for those who do not need muscles as such, and the goal of training is to lose weight or maintain current weight, creatine is not considered a necessary supplement. Why do professional athletes use it:
- to quickly achieve the muscle pumping effect;
- rapid growth of muscle mass;
- increasing anabolism;
- increasing endurance;
- accumulation of glycogen reserves;
- growth of strength indicators;
- normalization of the work of the heart muscle under heavy loads.
So, how does this amino acid affect all these indicators?
Improving body characteristics.
To begin with, this is not the main effect of creatine. We can say that this is a pleasant “side effect”, increasing strength skills by almost 35%. How it works? The fact is that with rapid muscle growth, they become saturated with fluids, which leads to greater pumping and an increased need for oxygen. After the second workout, the body begins to compensate for this condition by saturating the muscles with oxygen. As a result, glycogen production also increases here. Both of these factors directly affect the body's endurance. Now you can move on to working with heavier weights or doing more approaches. That is, starting the process of muscle growth leads to the fact that in the end the athlete becomes not only more pumped up, but also stronger.
Body water balance
. Like most other supplements, take creatine with water. When using it, daily water consumption should be 2.5-3 liters. A large amount of fluid in the body keeps the musculoskeletal system in order, reducing the likelihood of injury during training. However, there are pitfalls here: if you drink too much water, the water-salt balance is disrupted, which can lead to seizures. The problem is solved by maintaining a balance between water and salts, as well as using potassium and magnesium supplements after consultation with a specialist.
Increased muscle mass
. An interesting fact is that when using creatine, it is “dry meat” that begins to increase. Why does it happen this way? The strength indicator increases, the athlete moves on to new loads, and the muscles receive new stress. Excess glycogen is eliminated from the body along with water, the amount of which has increased significantly. At the same time, the muscles are additionally saturated with oxygen, which accelerates anabolic processes. Under high loads, creatine in the muscles begins to break down: in fact, new muscle tissue fibers begin to be built from this amino acid.
Rollback effect
. It is because of this unpleasant consequence that creatine has received persistent dislike among some athletes. Why does this even happen? Due to the high load and concentration of a large amount of amino acid in the body, metabolism tends to get rid of its excess and stops accepting new portions of dietary supplements. Therefore, after a couple of months after starting to use creatine, its effectiveness drops to zero. So there is no practical benefit to taking creatine for a long time. At least three months should pass between “loads”, during which the body will rest and adapt. Of course, all this is not without consequences. Firstly, muscle mass begins to decrease, weight falls (due to the removal of excess fluid). Secondly, rapid fatigue occurs: there is no longer a lactic acid buffer, and it quickly accumulates in the muscles. In turn, this brings a decrease in stamina.
Interesting fact: even with the rollback effect, the athlete still remains more resilient and stronger than he was before starting the creatine course.
Effect on bones
. Another benefit of “loading” with creatine is its beneficial effect on the musculoskeletal system. True, this only works on the condition that, in parallel with creatine, the athlete adheres to an appropriate diet, and also takes calcium and vitamin D3 supplements. The fact is that creatine helps calcium to be absorbed faster, which, in turn, strengthens bones, preventing serious injuries during training.
Contraindications: in what cases should you not take it?
Naturally occurring creatine has some contraindications that should be considered before use.
The supplement should not be used if:
- violations of water-salt balance;
- pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract (including temporary digestive disorders) and liver;
- diseases of the kidneys and the entire genitourinary system.
Excess creatine in the body (with multiple increases in the standard dosage) can provoke digestive problems even in healthy people.
Kinds
Before you go to a sports nutrition store, you need to understand what exactly you need for training. After all, there are many types of creatine. And each of them acts in its own way, has its own regimen and effectiveness. The benefits of each type of creatine for the body are assessed differently.
Monohydrate is the most popular and simplest type. The benefits and harms of creatine monohydrate have been revealed more than other types. It contains pure substance and water. It has pros and cons. One of the advantages is its relatively low price. However, its use causes side effects in the form of digestive tract disorders.
Citrate, phosphate, malate, tartrate - acids (citric, phosphate, lactic, tartaric) are added to these types, they help release energy. It is quickly absorbed and has more energy. The price for such pleasure is a little higher. And the concentration of creatine itself is lower.
Glutamine-taurine and magnesium contain additional magnesium and glutamine. The absorption of the main substance is facilitated and muscle strength increases. However, the dosage schedule is misleading.
HMB is a form that accelerates muscle growth, is quickly absorbed by the body and causes minimal harm to the digestive system. For this type you will have to pay the highest price.
Titrate, liquid creatine, effervescent tablets dissolve quickly in water. But their effectiveness is lower than other types.
Chewable one lasts longer. However, the price is not at all pleasing, and the concentration of creatine in these types is lower.
Non-existent side effects and harm[edit | edit code]
Currently, you can find a lot of misinformation regarding the side effects of creatine. To resolve doubts, here is a list of non-existent side effects and harms of creatine:
- Creatine does not increase blood pressure[8][9][10]
- Creatine does not reduce potency and does not lead to infertility
- Creatine is not carcinogenic
- Creatine does not overload the heart[11]
- Creatine is not addictive
And finally, it should be noted that after completing the course, the gained muscle mass is retained by 70-80%. Some weight loss (20-30%) occurs due to the removal of excess fluid.
Potential harms of creatine
Creatine is the safest and most studied supplement. However, there are several problems associated with its use.
First, it can cause bloating in large doses. Secondly, some claim that creatine is bad for your kidneys, but this claim is not backed by scientific evidence.
Is creatine bad for your kidneys?
Creatine's strong safety profile is usually overshadowed by media reports claiming it harms your kidneys—a claim that is currently not supported by scientific research.
In fact, studies involving people of different ages have shown that taking creatine supplements does not harm kidney health. Studies have used doses of 5–40 grams per day for 5 days to 5 years (, , , ).
The misconception that taking creatine damages your kidneys likely exists because creatine is known to raise creatinine levels above normal levels. Creatinine is a poor marker of kidney damage ().
Creatine supplementation has been found to be safe even for people with a high dietary protein intake, which has also been erroneously linked to kidney damage (, ).
A study conducted in people with type 2 diabetes, who may have kidney damage, found that taking 5 grams of creatine daily for 12 weeks did not impair kidney function ().
However, because research is limited, people with impaired kidney function or kidney disease should consult their doctor before taking creatine supplements.
May cause bloating
The most common complaint associated with taking creatine supplements is stomach discomfort caused by bloating.
This bloated feeling most often occurs when you first start taking this supplement during the creatine loading phase.
This loading phase involves taking large amounts of this supplement over a short period of time to saturate your muscle reserves. A typical dosage regimen involves taking 20–25 grams over 5–7 consecutive days.
During the loading phase, creatine also tends to draw water into muscle cells, resulting in weight gain. This may cause bloating ().
This bloating does not affect everyone
However, you can take precautions to avoid this by keeping your dose to 10 grams or less per serving ()
Additionally, you can always split your doses evenly throughout the day to avoid taking too much at once.
The supplement is also associated with other complaints such as diarrhea and general distress. As with bloating, you can reduce your risk of developing these symptoms by limiting your dose to 10 grams or less ().
You can find out more about bloating when taking creatine on this page - Creatine and bloating: what causes it and how to avoid it?
Creatine and disruption of natural digestion
Gastrointestinal distress is the second most common side effect experienced while taking creatine. It can manifest as abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea and flatulence. This effect occurs especially often during the stages of increased drug intake. If a large number of slowly soluble crystals of the drug accumulate in a person’s stomach, then this problem can manifest itself quite quickly. Scientists associate all problems associated with digestive disorders with poor purification of the additive. Therefore, athletes and athletes are advised to use only high-quality creatine. Today, to prevent various eating disorders, creatine is available in liquid form and in the form of micronized capsules. However, the liquid form of creatine is less effective than the capsule form.
There are other chemical forms of creatine supplement. These include crealcaine, ethyl ester and a number of similar new models. Despite the advertising, these supplements, like the classic monohydrate, can have side effects on the digestive process. Often, in order to avoid the process of indigestion, manufacturers of a new product play tricks by advising athletes to take small doses of the drug. This use of the supplement helps reduce the incidence of disorders, but the effectiveness of the drug itself also decreases. Research has proven that the doses of monohydrate and new forms must be equal to obtain the desired effect.
There are studies that indicate that creatine malate and creatine citrate can cause fewer side effects on the gastrointestinal tract. This is due to the good solubility of the drug.
About danger
Since its active use, there has been ongoing talk about whether creatine is harmful. There is a lot of discussion about the effect of the supplement on the body, its effect on the functioning of organs, as well as the functioning of the main systems in general. Let's figure out point by point whether creatine is harmful or not:
- General information. Today, the benefits of creatine are beyond doubt - it helps to increase strength and muscle mass, helps to quickly achieve muscle definition, accelerates recovery processes and plays the role of a lactic acid buffer. But with such unique functionality, the substance is absolutely safe. Tests have confirmed that there is no harm from creatine even with a significant overdose. The subjects took 25 grams of the supplement for a long time, but there were no health problems. Although, some side effects still occur.
- Water retention. Taking creatine leads to a partial decrease in kidney functionality against the background of an increase in the volume of creatine in the blood. As a result, urine formation is not as active. This phenomenon is often associated with active growth of muscle cells. Many people talk about the high risk of edema, but in practice this is not the case. Although water is retained in the body, it is in small volumes. Therefore, you should not be afraid of puffiness (and even bags under the eyes). In this way, the body adapts to a new mode of operation without harm to health. Under no circumstances take any additional medications that cause a diuretic effect. This is exactly what can pose a danger and lead to the development of dehydration. If you stop taking the supplement, your weight will not return to its previous level. In the worst case, body weight will decrease by 1.5-2 kilograms, no more. So in this regard, the benefits of creatine are incomparably higher.
- Dehydration. The fear of dehydration stems from the problem of water retention in the body. And in some cases, this phenomenon can actually cause harm. For example, the active transfer of water from blood plasma and muscle structure can lead to disruption of thermoregulation processes, metabolic disorders, and disruption of the acid-base balance. In turn, through dehydration, the body tries to return all processes to normal. In a normal training regime there is no need to be afraid of such problems. If creatine is taken during a period of active drying, then certain disruptions may well occur in the body.
- Digestion. Sometimes you can find reviews online that taking creatine leads to nausea, diarrhea, and even severe abdominal pain. Such phenomena can indeed occur, but only at the beginning of treatment. In the first few days, the body adapts to the new substance. In the future, there are usually no such side effects.
- Acne, pimples. Sometimes taking creatine can cause similar symptoms. But, as a rule, such phenomena are very rare. The main reason is the active production of testosterone in the body. This is a case where the benefits of taking a supplement may result in minor side effects. But don't worry. As a rule, in 99% of cases there are no such symptoms.
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/iJU8sIQ_CJw
Water retention[edit | edit code]
The strongest justification is for side effects that are associated with the osmotic activity of creatine; simply put, creatine consumption is associated with an increase in water retention in the body. This phenomenon occurs in almost everyone who consumes creatine, while water retention does not harm the body, and occurs as a compensatory reaction to balance the osmotic imbalance. Water retention itself is practically unnoticeable, and it can only be determined by scales; no edema or “swelling” of the face occurs in healthy people. Typically, the increase in the percentage of liquid is insignificant; on average, its volume is 0.5 - 2 liters, which cannot be determined externally or subjectively.
Do not try to limit fluid intake, and especially do not take diuretics to prevent fluid retention. By reducing the manifestations of this harmless phenomenon, you can harm the body due to dehydration.
As a rule, after stopping creatine, weight loss occurs (20 - 30% of the gain), this is associated with the removal of accumulated fluid.
When is the best time to take creatine before or after a workout?
Scientific research suggests that there is little difference in whether you take creatine before or after a workout.
In one experiment, bodybuilders took 5 grams of creatine: one group immediately before and the other after strength training for 4 weeks. Muscle mass increased in both groups and there was no significant difference between both groups 13.
The same result was found in other studies 14.
Scientists, however, suggest that it is better to take creatine immediately AFTER your workout.
Another experiment showed that taking creatine immediately before or after a workout was significantly better at stimulating muscle growth than taking it long before the workout (in the morning, for example, if the workout was in the evening) 15.
Choosing the Right Creatine Supplements
Benefits of Creatine Ethyl Ester
Creatine ethyl ester provides all the same benefits as monohydrate. But there are additional beneficial properties. This type of creatine is better absorbed by the body and does not leave you feeling bloated. It has a more bitter taste. But a small number of studies have been conducted that could confirm the effectiveness of this type of substance.
Comparison of Creatine Supplements
Because of its effectiveness and popularity, creatine is sold in various forms.
Creatine monohydrate. The most popular form of monohydrate is a pure micronized powder. It contains no calories, protein, carbohydrates or fat. More advanced forms of powder have flavoring components. The most popular flavors are grape and assorted fruit. Often other additives are added to creatine monohydrate. For example, glutamine, taurine, amino acid mixtures, or even mixtures with other types of creatine.
Creatine ethyl ester. Also sold in pure powder form. Overall, these are more expensive supplements, but prices are still kept within reasonable limits. Their effect on the human body is similar to the effect of monohydrate. Also, many products have taste differences. And mixtures of creatine ethyl ether with other substances are also sold.
Pills. Creatine tablets have a wide price range and a wide range of products. The simplest tablets consist of creatine monohydrate, there is creatine ethyl ether in capsules. Tablets are easy to swallow and a more convenient form than powder. There is no bitter taste left in the mouth, and there is no feeling of bloating. Creatine from tablets is absorbed more slowly. There are a huge number of different creatine tablets on the sports nutrition market, often also containing other additives. The ability to take the substance in tablet form is a big advantage.