The essence of the diet
The essence of a low-carbohydrate diet is to completely or partially avoid foods containing carbohydrates and significantly increase the proportion of protein and fiber in the diet. Carbohydrates in the diet are reduced to 50 grams per day, and the amount of protein, on the contrary, increases - up to 150-200 g, depending on age, body type, and level of physical activity.
The diet must include a large amount of fiber in the form of vegetables, herbs, bran, and some unsweetened fruits. By switching to a low-carbohydrate diet, an athlete forces his body to adapt to alternative energy sources. The main principle of the low-carb diet is based on the process of ketosis. Let's figure out what it is.
Biochemistry of ketosis
Any no-carb or low-carb diet (including the Atkins diet) is a ketogenic diet.
Ketosis is the process of producing fatty acids and ketone bodies from fat cells (adipocytes) for energy in the Krebs cycle.
This diet improves insulin levels in the blood, which is especially important for patients with type 2 diabetes. Since the body does not get sources of carbohydrates from food, the required amount of glucose is not formed in the blood. In conditions of its deficiency, the body urgently needs alternative sources of energy and nutrients and switches to a mode of consumption of fat accumulations to maintain a normal level of metabolism.
In the cells of adipose tissue, breakdown processes are activated. Fatty acids are formed, which enter the liver and muscle tissue, where they are oxidized and converted into acetyl-CoA (a substance necessary in the Krebs cycle) and ketones (ketone bodies).
When carbohydrates are scarce, the liver breaks down fats into fatty acids and ketones to replenish glycogen stores and provide energy—this is how ketosis occurs.
Dr. Atkins Diet
The most common and popular ketogenic low-carb diet is the Dr. Atkins diet. Already at the initial stage, it implies a strict limitation on the proportion of carbohydrates in the diet - no more than 20 grams per day. Dr. Atkins first published his diet in 1966 in Harpers Bazaar magazine.
He divided his diet into 4 stages:
- The induction or stimulating phase is a preparatory 2-week phase aimed at transitioning the body into ketosis mode (no more than 20 grams of carbohydrates per day).
- The active phase of weight loss, aimed at gradually increasing the proportion of carbohydrates in the diet (by about 10 grams per week) while maintaining the fat-burning effect.
- Transitional phase - allows you to add any food to your diet, but in strictly limited quantities 1 or 2 times a week.
- Support - by this stage, the weight should stabilize, and the diet gradually becomes more familiar. However, the proportion of carbohydrates and the size of portions must be controlled to avoid weight gain.
In case of weight gain, we return to the first stage of the diet.
Glycemic index of foods
To understand the benefits of a low-carb diet, consider the concept of a product's glycemic index (GI). In the field of sports medicine and fitness, it is customary to divide carbohydrates into simple and complex. Or fast and slow - depending on the speed of their absorption by the body.
There is a nuance: the same product can have a high, medium or even low rate of glucose absorption into the blood. It all depends on the method of thermal or mechanical processing, temperature, as well as additional impurities and additives. Therefore, in many ways, the division of carbohydrates into fast/slow will be conditional. It is more correct to divide them according to their glycemic index.
The glycemic index is an indicator of the effect of foods on blood sugar levels after consumption.
The glycemic index of a product is determined by two factors - the rate of starch breakdown and the amount of starch that will undergo breakdown. The faster starch breaks down into glucose, the faster it enters the blood, and the higher the sugar level rises.
If a large amount of glucose enters the body at once, it is not immediately used in full. Some are sent to the “fat depot”. Therefore, the same food product can have a completely different glycemic index and will be perceived differently by the body.
For example, raw carrots have a glycemic index of 20 units, and boiled carrots have a glycemic index of 50 units (like regular white bread).
Buckwheat or oatmeal have a glycemic index of 20 units, and buckwheat or oat flakes have a glycemic index of 40 units.
What carbohydrates does our body need?
To properly provide the body with nutrients, the daily diet of a person with normal physical activity should include from 300 to 500 g of carbohydrates, of which at least 30 g of fiber is a list of foods rich in fiber.
Almost all carbohydrates should be complex; simple ones are desirable only after serious physical or emotional stress and on the holiday table. Nutritionists recommend vegetables and fruits, cereals, durum pasta, whole grain bread and legumes as the main sources of carbohydrates in a healthy diet.
The features of storage, industrial and culinary processing of products are of great importance. Sometimes they can significantly increase the availability and rate of absorption of carbohydrates from foods; the difference in glycemic indices can be up to 20 points:
- Most ready-made products that you can buy in the store contain modified starch, a fast carbohydrate with a GI of 100. It is found in sausages and processed meats, in ketchups, sauces and yoghurts, and is often present in baked goods and desserts. The same products made at home will contain much less simple carbohydrates than industrial ones.
- In vegetables and fruits, the availability of sugars increases during cooking. If raw carrots have a GI of 20, then boiled carrots have a GI of 2 times higher. The same processes occur in the production of cereal flakes. The GI of corn grits increases by 20% when it is made into flakes. Thus, preference should be given to minimally processed products.
- In flour products, carbohydrates are released more slowly as the dough is stretched. Spaghetti with meat, especially slightly undercooked ones, is healthier than dumplings, despite the identical composition.
- The availability of carbohydrates decreases slightly when foods are cooled and dried. Hot pasta will increase blood glucose faster than cold pasta in a salad, and fresh bread - faster than crackers made from it. Bread crusts contain more complex carbohydrates than bread crumbs.
- Steaming and baking retain complex carbohydrates in food better than boiling and frying in oil.
- The more fiber a product contains, the slower its sugars are absorbed, which is why whole grain bread is healthier than white bread, and a whole pear is preferable to a peeled one.
- The more the product is crushed, the faster the carbohydrates it contains. The best example is mashed potatoes, which have a GI 10% higher than boiled potatoes.
https://youtu.be/ZEsXyMhPw-o
Rules and diet
On a low-carb diet, it is recommended to follow a number of rules to achieve the best results in losing weight:
- You should not exceed the permissible amount of carbohydrates in your daily diet.
- Avoid eating breaks for more than 4 hours.
- It is advisable to divide the daily diet into 5-6 meals.
- Divide all meals into 3 main meals and 2-3 snacks.
- The calorie content of a main meal should not exceed 600 kilocalories, and a snack should not exceed 200 kilocalories.
- If your workout takes place in the morning, it is advisable to first have a light protein breakfast (an omelet of 2-3 eggs).
- If your workout is in the evening, eat 2-3 hours before your workout and, if possible, avoid eating immediately after your workout. A light snack before bed with a serving of cottage cheese (or other protein product) is allowed.
- On a low-carb diet, it is not recommended to drink coffee and other caffeinated drinks. Alcohol is strictly prohibited.
- Drink at least 2-3.5 liters of clean drinking water per day.
- During a low-carbohydrate diet, it is advisable to take vitamin and mineral complexes to replenish the reserves of essential substances in the body.
Recommended Products Table
In addition to the above rules and recommendations, there is another important point. An integral part of a low-carb diet is a table of foods recommended for consumption.
Be sure to take it into account if you are interested in the result.
| Meat and meat products: | lean beef and pork, veal, rabbit meat, ham, liver, chicken, turkey, duck and goose meat |
| Fish: | salmon, salmon, trout, herring, mackerel, tuna, cod, haddock, greenling, flounder |
| Seafood: | sardines, pink salmon, halibut, crabs, squid, shrimp, mussels, oysters, scallops |
| Dairy products: | cottage cheese, sour cream, cheese, milk, kefir, fermented baked milk, natural yogurt |
| Eggs: | chicken eggs, quail eggs |
| Vegetables and greens: | all types of cabbage, tomatoes, cucumbers, lettuce, bell peppers, eggplants, zucchini, celery, garlic, onions |
| Legumes: | green peas, green beans |
| Mushrooms: | porcini mushrooms, boletus, chanterelles, morels, champignons, oyster mushrooms |
| Fats and oils: | olive oil, hemp oil, flaxseed oil, peanut oil, nuts, olives, olives, mayonnaise |
List of prohibited products
Prohibited foods on a low-carb diet include:
- bread and all types of bakery products: buns, pies, cakes, pastries, cookies;
- any sweets: sugar, honey, various syrups, popcorn, ice cream, candy, chocolate;
- sweet vegetables and vegetables containing starch: potatoes, Jerusalem artichoke, sweet corn;
- any products containing large quantities of lactose, sucrose and maltose;
- various cereals and porridges made from them with a high glycemic index: semolina porridge, rice porridge, oatmeal, corn flakes.
Indications for use
Diabetes mellitus in the absence of acidosis and concomitant diseases of internal organs.
Destination purpose
Create conditions that maintain a positive carbohydrate balance and prevent lipid metabolism disorders.
general characteristics
A diet with a protein content above the physiological norm, moderate restriction of fats and carbohydrates. Easily digestible carbohydrates are excluded. Substances with lipotropic effects are introduced into the diet. The food contains quite a lot of vegetables. Limit salt and foods containing cholesterol. Cooking is normal.
Calorie content and composition
- proteins 100-120 g
- fat 70 g
- carbohydrates 300 g
Diet
Meals six times a day, carbohydrates distributed throughout the day. During the insulin injection and 2-2.5 hours after the injection, the patient should receive food containing carbohydrates.
| Product Name | Products and types of food | |
| Featured | Excluded | |
| Meat and poultry | • Lean meats (beef, veal, lamb) and poultry, fried, stewed, boiled in one piece, as well as chopped. • Meat jelly, jellied chicken or veal. • Low-fat ham, doctor's or diabetic sausage. • Beef sausages. | • Fatty pork, beef and lamb, goose, turkey. • Fatty ham, sausages. |
| Fish | • Low-fat boiled and fried. • Filled. • Canned fish in tomato. • Lightly salted caviar. | • Fatty varieties. • Salted (herring and others). |
| Eggs | • No more than one every other day. • Protein omelet. | • Egg yolks are limited. |
| Dairy | • Milk, kefir, yogurt. • Cottage cheese 100-125 g per day. • Sour cream in limited quantities. • Mild and lightly salted cheese. | • Salty cheese. |
| Fats | • Butter. • Vegetable oil, mainly in its natural form in dishes (salads, vinaigrettes). | • Salty. • Meat - beef and lamb, lard. |
| Cereals | • Porridges made from rolled oats, buckwheat, barley, wheat, millet and pearl barley. | • Rice, semolina and pasta are not recommended. |
| Vegetables | • Potatoes strictly by weight, taking into account the carbohydrates they contain. • Carrots, beets, rutabaga, kohlrabi, green peas, green beans are included in the carbohydrate counting menu. • Vegetables containing about 5% carbohydrates: white cabbage, cauliflower, zucchini, pumpkin, asparagus, eggplant, cucumbers, tomatoes and greens without limitation. | |
| Soups | • Shchi, borscht made from prefabricated vegetables in meat broth. • Potato with pearl barley, taking into account the carbohydrates it contains. • Cold. | • Fatty broths. • Dairy with noodles and cereals. • Pea. |
| Sauces and spices | • Low-fat broth (tomato and others). • Cinnamon, cloves, pepper in moderation. | • Fatty and spicy. |
| Fruits and berries. Sweet dishes. Sweets. | • Fresh fruits and berries. • Compote of dried fruits without sugar. • Jelly without sugar. • It is recommended to replace sugar with xylitol or sorbitol. | • Grapes, bananas, dates, raisins, sugar, honey, jam, sweets. |
| Beverages | • Tea. • Natural coffee, surrogate or cocoa with milk without sugar. • Rosehip decoction. • Juices of fresh berries and fruits (except grape). • Tomato juice. | • Grape juice. • Alcoholic drinks. |
| Bread | • Wheat and rye strictly by weight, taking into account the allowed amount of carbohydrates. • Inconvenient flour products at the expense of the allowed amount of bread. | • Flour products are rich and sweet. |
What to combine with foods containing carbohydrates
The ability to combine foods correctly is the basis of a balanced diet. Any cereals and rice can be combined with vegetables and fruits. Oatmeal goes well with berries - strawberries, raspberries, and fruits - apples, plums. You can add a little dried fruit to porridge, but just a little, because they are rich in glucose. You can eat a small piece of whole grain bread along with the porridge.
Also, porridge can be consumed separately, without any addition, so as not to burden already high-calorie foods. This rule is especially relevant when losing weight. Nutritionists do not recommend cooking porridge with milk, since the calorie content of the dish increases significantly, and in addition to complex carbohydrates, simple carbohydrates are added - lactose or milk sugar.
A bad combination is combining carbohydrates with proteins and fats.
You should not eat meat products, both animals and birds (for example, sausages or cutlets), together with pasta. Fish is also not suitable. You can prepare a vegetable sauce for pasta, for example from tomatoes. Vegetables are ideal for fish, both fresh (in the form of salad) and baked or boiled (except potatoes, beets). You can also eat vegetables in any form with meat.
Poultry and eggs go well with vegetables. An omelet with vegetables or herbs is ideal for eating in the morning. Asparagus, spinach, lettuce, chard go well with meat. Vegetables and herbs go well with vegetable oils - sunflower, olive and others.
Often fruits are combined with dairy products - kefir, cottage cheese, yogurt, cream, sour cream. The fruit also goes well with nuts and seeds. It is not recommended to mix sour and sweet fruits; you should eat sour and sweet fruits separately.
You need to be very careful when combining carbohydrate foods. For example, the combination of starch and sucrose is not very successful. The breakdown of starch begins directly in the mouth and ends in the stomach. And the digestion of sugars begins only in the small intestine.
Starch will be digested first, and sucrose at the same time will cause fermentation in the stomach. Starchy foods are recommended to be consumed separately from other foods and during the daytime. Potatoes are recommended to be consumed together with pumpkin, cauliflower, carrots, and eggplants. The main condition is the exclusion of foods containing sugar.
Bread, no matter what flour it is baked from, is recommended to be consumed separately from other food products. It does not combine with jams, preserves, or butter. Flour products should be consumed separately from other products, due to the fact that baked goods themselves are quite high in calories. Combinations of dough products with eggs, meat and any other proteins are especially “dangerous”.
Bad food combinations are:
- joint consumption of cereals with tomatoes, since oxalic acid from tomatoes inhibits the absorption of starch;
- porridge should not be eaten together with fermented milk products due to differences in the duration of digestion;
- legumes (beans, peas) are not recommended to be consumed with fish due to different digestion times, but beans can be baked with vegetables;
- bread is not compatible with fermented milk products also due to different digestion times;
- It is not recommended to drink rye bread with coffee, because the substances contained in this drink interfere with the absorption of nutritional components from the bread.
Any sweets (cakes, chocolate, caramel and cakes) are recommended to be consumed as a separate dish (as dessert) and no more than 3-4 times a week.
Chocolate should not be consumed together with alcoholic beverages, because chocolate promotes the outflow of bile, and alcohol, on the contrary, prevents its release, resulting in spasm of the sphincter (passage into the duodenum) and acute pancreatitis.
The list of foods containing carbohydrates is very long. The vast majority of food products contain both simple and slow carbohydrates. These nutrients are essential for human health.
Why does the body need carbohydrates?
The human body is capable of producing carbohydrates itself, but its quantity is not enough for normal human life, so the main part comes from food. It is this substance that gives the body energy.
Carbohydrates are necessary for normal functioning:
- brain;
- muscles;
- intestines (prevent the formation of bacteria, fight constipation);
- digestion (promote the absorption of fats).
Scientists have proven that complex carbohydrates take part in protecting the body. Mucopolysaccharides cover the lungs and nasal mucosa, which prevents dust and viruses from entering the body.
Easily digestible carbohydrates have a high glycemic index. Because of this, they quickly turn into sugar, significantly increasing its concentration.
It is necessary to control the consumption of products containing this substance, since high blood glucose levels are dangerous for humans.
Excessive intake of easily digestible carbohydrates into the body threatens the development of the following diseases:
- hypertension (high blood pressure);
- stroke, heart attack and other diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- oncology;
- arthritis;
- diabetes mellitus (cells become less sensitive to insulin);
- atherosclerosis (cholesterol plaques appear);
- obesity (the body's ability to absorb sugar is lost);
- caries.
To prevent dangerous diseases, you should exclude or leave a minimum amount of fast carbohydrates in your diet..
Complex carbohydrates
Complex carbohydrates include:
- starch;
- cellulose;
- sucrose;
- glycogen.
When digested, they are broken down into simple carbohydrates (glucose, maltose) and only then absorbed. They do not have a pronounced sweetness. But since the process of their breakdown begins directly in the mouth, upon contact with saliva, a sweetish taste appears.
A distinctive feature of complex carbohydrates is that they give a feeling of fullness for a long time.
Carbohydrate diets are quite popular. The diet consists of foods rich in slow carbohydrates. Fast carbohydrates are completely excluded. The number of meals per day is about 4-6. As for liquids, you can only drink pure water or tea. It is recommended to have dinner before 19:00.
Authorized products:
- beans;
- cereals;
- vegetables;
- fruits;
- vegetable and fruit juices;
- dairy products;
- lean meat;
- whole wheat bread.
One meal should contain about 150 g of carbohydrates in total.
The benefits of the diet are that blood glucose levels are reduced. The food is quite dense, so there is no feeling of hunger, and the diet is well tolerated. Products containing complex carbohydrates. Complex carbohydrates, a list of products containing them is shown below, help reduce body weight.
| Product | Mass of carbohydrates per 100 g of product mass (g) |
| Hercules | 50 |
| Pearl barley | 66,5 |
| Brown rice | 65,1 |
| Pasta made from durum wheat | 68,4 |
| Corn | 22,5 |
| Buckwheat | 68 |
| Barley grits | 71,7 |
| Wheat bread | 53,4 |
| Beans | 54,5 |
| Soybeans | 26,5 |
| Lentils | 53,7 |
| Bran crispbread | 70,6 |
| Crackers | 72,4 |
| Pine nuts | 20 |
| Peas | 21,1 |
| Beet | 9,56 |
The entire process of digesting complex carbohydrates takes about 40-50 minutes. During this time, complex carbohydrates are broken down into simple monomers and absorbed by the body.
Types of carbohydrates and their composition
Depending on their chemical composition, carbohydrates are divided into simple and complex.
Simple ones include:
- Monosaccharides (glucose, fructose, galactose). In a complex reaction they break down to water and carbon dioxide.
- Disaccharides (sucrose, lactose, maltose). They consist of two or more monosaccharides, which are connected to each other using hydroxyl groups.
Simple carbohydrates are quickly absorbed in the body, which leads to adverse consequences.
Complex carbohydrates are made up of three or more units.
These include polysaccharides:
- Plant origin (starch, fiber).
- Animal origin (glycogen).
Before the process of food absorption begins in the body, complex carbohydrates are broken down into simple components. This requires energy and time.
List of easily digestible carbohydrates
Monosaccharides
| Name | Description | Effect |
| Glucose | A colorless crystalline monosaccharide | Upon penetration into the blood, it becomes a source of nutrition for the brain, liver, and muscles. |
| Fructose | The sweetest of all carbohydrates | Does not lead to excess sugar. Converts to glycogen faster than glucose |
| Galactose | Not found in free form, together with glucose it forms lactose | As a result of its oxidation, complex carbohydrates are burned in the body and metabolic processes are regulated |
Disaccharides
| Name | Description | Effect |
| Sucrose | Dissolves quickly. Composed of glucose and fructose | Accumulates in the body as reserve fat |
| Lactose | Milk sugar | Promotes more active absorption of B vitamins, ascorbic acid, calcium |
| Maltose | Is malt sugar. Formed during the breakdown of starch | Easily absorbed by the body, saturating it with amino acids and B vitamins. Promotes the production of energy necessary for brain function |
The benefits of carbohydrates for weight loss
Complex carbohydrates are essential when losing weight. They give you a feeling of fullness for a long time and saturate the body with a large supply of energy. There are 4.1 kilocalories per 1 g of carbohydrates.
During digestion, slow carbohydrates are broken down into monomers that feed the brain. That is, the brain receives the glucose it needs, but from healthy foods.
Cellulose, which is also a complex carbohydrate but is not digested in the human body, is necessary for the normal functioning of the digestive system and cleansing the intestines of harmful substances. Pectin substances also help cleanse the body by absorbing harmful compounds.
Where can you get easily digestible carbohydrates?
All food products whose index exceeds 65 units are considered easily digestible.
The maximum amount of carbohydrates of this type can be obtained from bread, potatoes, carbonated and alcoholic drinks, sweets, cakes, honey, cereals, etc.
Table of easily digestible foods with their calorie content
The table below shows foods containing easily digestible carbohydrates:
| Name | Kcal (100g) |
| Alcoholic drinks | From 33 |
| Bread | 250 |
| Starch | 320 |
| Honey | 300 |
| Potato | 105 |
| Dried fruits | 480 |
| Sugar | 350 |
| Carbonated drinks | 27 |
| Porridge | From 105 |
| Muesli | 320 |
| Baking | 350 |
| Rice | 360 |
Low-carbohydrate diet - rules, diet, foods and sample menu for the week
To prevent fat accumulation, you should balance the amount of carbohydrates you eat and exercise. The danger of fast carbohydrates lies not only in excess weight. They can bring many other problems:. Easily digestible carbohydrates according to their molecular structure are divided into mono- and disaccharides. The chemical monoformula is composed of carbon dioxide and water.
And a little about secrets...
Products with a glycemic index of GI exceeding 70 units contain fast carbohydrates. GI is the rate at which the body breaks down carbohydrates. Even taking into account the negative effects of fast carbohydrates, one should not conclude that they should be completely excluded from the diet. When combined correctly, products are beneficial. If you find it difficult to stick to a healthy diet on your own, it is recommended to seek help from a nutritionist. He will give professional recommendations and draw up a list of prohibited products.
A diet limiting easily digestible carbohydrates implies the normalization of healthy body activity and further weight control. Nutritionists have developed a special diet plan based on reducing carbohydrate intake. As a result, the body begins to produce energy through the slow oxidation of fats and amino acids. Such a diet allows you to get back into shape in a short time.
The daily carbohydrate intake required to maintain insulin levels is calculated as follows: 1 gram per kilogram of weight. Completely avoid smoked and fried foods. Preference is given to boiled, baked, steamed dishes. In addition to a balanced diet, you should lead an active lifestyle: physical activity is required 3-4 times a week for at least 30 minutes.
Excessive overexertion is contraindicated for people with low blood sugar. In a month, in this mode, all metabolic processes are completely restored, without the appearance of unnecessary deposits. If insulin production is normal, it is recommended to follow such a diet at least once a year, which improves well-being and promotes weight loss. Restricted diets are contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Caution is exercised in relation to the diet of children and adolescents.
What is a low-carb diet for weight loss?
If a child is obese, it is recommended that the menu be developed under the supervision of a nutritionist. Existing pathologies are taken into account, so they undergo a medical examination first.
People with type 2 diabetes require special nutrition, which should not contain fast carbohydrates. The list of diseases for which these compounds are excluded from the diet also includes:. If you are prone to edema, it is necessary to limit fluid intake and develop a gentle diet.
With impaired metabolism in the kidneys, restrictions in phosphates and calcium are possible. With the right approach, a low-carb diet should not be accompanied by loss of strength and exhaustion.
Basic principles and its variations
On the contrary, there is a surge of energy and a feeling of lightness throughout the body. Products that are high in calories are replaced with others that contain large amounts of fiber, vitamins and minerals. It can be used to determine the amount of digestible carbohydrates in food. What is this therapeutic nutrition? The general characteristic of this table is to organize the consumption of low-calorie foods, which is achieved through a combination of animal fats and carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates are organic compounds that supply the body with the energy necessary for full functioning. They are part of every tissue and cellular structure. Carbohydrates account for approximately 2.7 percent of total body weight. Without them, internal organs and systems cannot function normally. Maintaining the ratio of carbohydrates in the body becomes possible with a balanced diet, including foods containing these and other beneficial substances.
To understand why these organic compounds are so important, it is necessary to study their functions.
Carbohydrates that enter the body with food have the following range of actions: In addition, these organic compounds increase the body’s protective functions, determine blood type, and also reduce the likelihood of developing cancer pathologies. Organic substances from the carbon group are divided into two large groups - simple and complex. The former are also called fast or easily digestible, and the latter - slow.
In recent years, fat-protein diets with extremely low carbohydrate content have become very popular. Let's consider the question of what a low-carbohydrate diet is, its features and purpose. Dietary systems with carbohydrate restriction are used for various purposes: for weight loss, for diabetes mellitus, for the treatment of obesity, for hypertension.
They have a simple composition and are quickly absorbed in the body. This feature of carbohydrate leads to a sharp increase in blood glucose. The body's reaction to the consumption of simple carbohydrates is a large release of insulin, the hormone responsible for the production of pancreas.
The sugar level under the influence of insulin decreases below the standard norm. Thus, a person who has recently eaten foods rich in simple carbohydrates begins to feel hungry quite quickly.
In addition, the conversion of sugar molecules into subcutaneous fat occurs in a ratio of one to two. If you abuse food that is rich in fast carbohydrates, this will lead to the following adverse consequences: These negative effects became the main reason that these carbohydrates began to be called harmful or undesirable.
Slow organic compounds, such as fiber, glycogen, starch, act on the body in a completely different way. The substances included in this group have a complex composition, which means their absorption rate is much lower than that of fast ones. These compounds have high nutritional value and therefore the sugar concentration practically does not increase, and, consequently, a person feels full for a long time.
Since the concentration of sugar is not too high, the liver has time to process it. This means that it is almost completely converted into energy resources, and is not stored as fat. Thus, complex carbohydrates do not cause any harm to the body, that is, they are beneficial. The daily intake of an organic energy source is determined by age, gender, weight, lifestyle and some other factor.
To calculate your daily carbohydrate intake, you can use the following calculation:.
The role of easily digestible carbohydrates in the full functioning of all systems of the human body is great, since they are the main source of vital energy. However, if used uncontrolled, these compounds can be dangerous.
The resulting number will become the daily consumption rate. If your height is cm, then the amount of carbohydrates consumed per day should be grams. Excess carbohydrates entering the body with food lead to a sharp increase in the concentration of insulin in the blood and rapid formation of fats.
In other words, the cause of obesity, diabetes and other health problems associated with excess weight is carbonaceous foods. The lack of such products in the body is also harmful. If carbohydrates are supplied in limited quantities, glycogen reserves are gradually depleted, fats accumulate in the liver and various dysfunctions of this organ develop. A deficiency of this organic compound leads to increased fatigue, a general feeling of weakness, and decreased physical and intellectual activity.
When there is a lack of carbohydrates, the body receives the energy necessary to maintain vital functions from fatty tissues. The high rate of fat breakdown causes increased production of harmful catenes. This leads to acidification of the body and ketoacidotic coma. The appearance of the first signs that signal a deficiency or excess of carbohydrates should be carefully reconsidered and the daily diet should be adjusted in the future.
A properly composed menu allows you to avoid the negative consequences associated with an overdose or lack of carbon-based food. The controversy surrounding carbohydrates continues. Some nutritionists consider them harmful, while others, on the contrary, claim their beneficial properties. The human body is capable of producing carbohydrates itself, but its quantity is not enough for normal human life, so the main part comes from food.
It is this substance that gives the body energy. Scientists have proven that complex carbohydrates take part in protecting the body. Mucopolysaccharides cover the lungs and nasal mucosa, which prevents dust and viruses from entering the body. It is necessary to control the consumption of products containing this substance, since high blood glucose levels are dangerous for humans. Excessive intake of easily digestible carbohydrates into the body threatens the development of the following diseases:
To prevent dangerous diseases, you should eliminate or leave a minimum amount of fast carbohydrates in your diet. Before the process of food absorption begins in the body, complex carbohydrates are broken down into simple components. This requires energy and time. The maximum amount of carbohydrates of this type can be obtained from bread, potatoes, carbonated and alcoholic drinks, sweets, cakes, honey, cereals, etc.
A diet that excludes or limits easily digestible carbohydrates is designed to reduce weight and normalize the functioning of the body. During such a diet, the body receives energy from oxidized fats and amino acids. To maintain insulin levels, the amount of carbohydrates required is calculated from the ratio of 1 g per 1 kg of body weight.
In this case, it is advisable to consume complex carbohydrate compounds. During the day you need to drink at least 2 liters of clean water. On this day, eat the foods you want, but you shouldn’t abuse them. The glycemic index (GI) is a unit of the rate at which blood sugar rises. It directly depends on the carbohydrate content of the product. The more there are, the higher the glycemic index. Easily digestible carbohydrates have a higher GI value. After eating such foods, blood sugar rises quite quickly.
Low GI foods are considered complex and satiate the body for a long time. When following a diet, it is necessary to create a menu only from foods with a low glycemic index. Such food helps restore metabolism. Products that are compatible with each other contribute to the complete absorption of beneficial microelements found in this food.
Each product has a specific chemical composition, which determines its digestibility in the human body. All products are divided into quickly and slowly digested. Also, each food group requires its own environment in the stomach. For example, for chicken meat it should be acidic, and for mashed potatoes it should be alkaline. Carbohydrate foods are best combined with fats, vegetables, and herbs.
This combination is safe for the body and does not lead to food fermentation. Scientist William Hay proved that when simultaneous consumption of protein foods and carbohydrate foods, the alkaline environment interacts with the acidic one, as a result of which they neutralize each other. Thus, tea cannot be combined with milk, since the proteins contained in milk prevent the absorption of the beneficial properties of tea. Carb-free foods are not a myth.
Such food really exists and is the key to an effective diet and a healthy body. In its original form, meat does not contain any carbohydrates. They are formed during the cooking process due to the addition of sauce or spices. The same applies to sausages.
Before purchasing them, carefully study the composition.
Diet with limited fast carbohydrates
A diet that excludes or limits easily digestible carbohydrates is designed to reduce weight and normalize the functioning of the body. During such a diet, the body receives energy from oxidized fats and amino acids.
A diet with the exclusion or limitation of easily digestible carbohydrates is designed to reduce weight and normalize the functioning of the body
To maintain insulin levels, the amount of carbohydrates required is calculated from the ratio of 1 g per 1 kg of body weight. In this case, it is advisable to consume complex carbohydrate compounds.
The duration of the diet is 30 days, after which you need to take a break.
The following foods should be included in your diet:
- boiled meat;
- boiled eggs;
- varieties of fish rich in fats;
- nuts;
- cottage cheese;
- Brown rice.
These products should become the main components of the diet menu.
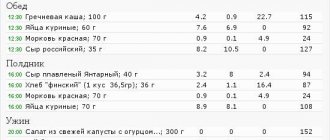
Example 1:
- Breakfast: omelette with tomatoes, coffee or tea without sugar.
- Snack: lettuce, apple, low-fat cottage cheese (mix these ingredients and add 1 teaspoon of olive oil to get a delicious dish).
- Lunch: 250-300 g of boiled chicken fillet, fresh cucumber and tomato.
- Dinner: fish baked in foil.
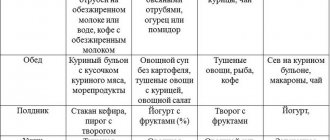
Example 2:
- Breakfast: 200 g of cottage cheese, 0.5 apples, unsweetened tea (coffee).
- Snack: fresh vegetable salad with flaxseed or olive oil dressing.
- Lunch: salad with meat, seasoned with lemon juice.
- Dinner: vegetable soup.
Example 3:
- Breakfast: 2 boiled eggs, a slice of hard cheese, coffee without sugar.
- Snack: seafood, a glass of freshly squeezed grapefruit juice.
- Lunch: broccoli soup, steamed pork.
- Dinner: stuffed squid, yogurt.
There should be a time interval of 2-3 hours between meals, and the portions should not be large . The consumption of smoked and fried foods is not allowed.
During the day you need to drink at least 2 liters of clean water. After 14 days, arrange a “holiday menu”. On this day, eat the foods you want, but you shouldn’t abuse them.
Features of diet No. 9 for type 1 and type 2 diabetes
Nutritional therapy for type 1 and type 2 diabetes is different.
- The calorie content of the daily diet must necessarily be reduced to between 2800 and 3100 kcal in order to get a positive result. This is enough in the initial stages of the disease. In the acute course of the disease (type 1 diabetes mellitus), more stringent restrictions on nutrition should be put forward, therefore the calorie content of foods consumed per day should not exceed 2300 kcal. Meals should be fractional, up to 5-6 times per day. Sweets and baked goods should be removed from the diet.
- Diet No. 9 for type 2 diabetics with a stable course of the disease is rational and has virtually no restrictions. But it should be remembered that with this form of the disease obesity often develops, so it is completely recommended to exclude foods rich in fats and easily digestible carbohydrates. Treatment may also consist of eliminating harmful foods, which is most often enough to prevent the development of complications. If there is no sugar in the urine, you can include a small amount of this product in your diet.
Return to content
Optimal diet for the day
Composition of acceptable food products of the standard diet No. 9 for diabetics
| Product name | Weight, g | Proteins % | Fat % | Carbohydrates % | ||
| Black bread | 150 | 8,7 | 0,9 | 59 | ||
| Milk | 400 | 12,5 | 14 | 19,8 | ||
| Oil | 50 | 0,5 | 42 | 0,3 | ||
| Sour cream | 100 | 2,7 | 23,8 | 3,3 | ||
| Hard cheese | 30 | 7,5 | 9 | 0,7 | ||
| Cottage cheese | 200 | 37,2 | 2,2 | 2,4 | ||
| Meat | 200 | 38 | 10 | 0,6 | ||
| Egg | 1 PC. 43-47 | 6,1 | 5,6 | 0,5 | ||
| Carrot | 200 | 1,4 | 0,5 | 14,8 | ||
| Cabbage | 300 | 3,3 | 0,5 | 12,4 | ||
| Apples | 300 | 0,8 | — | 32,7 | ||
| Buckwheat | 80 | 6,4 | 1,2 | 51,5 | ||
Medicinal properties of burdock for diabetes mellitus. Useful recipes Medicine beetle or darkling beetle - panacea or fiction? How will the bug help in the treatment of diabetes?
What are the causes and symptoms of type 1 diabetes? Read more in this article
Return to content
Glycemic index of foods
The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of the rate at which blood sugar rises. It directly depends on the carbohydrate content of the product. The more there are, the higher the glycemic index.
Scientists have identified three types of GI:
- increased – more than 70 units;
- medium – from 40 to 70 units;
- low – from 10 to 40 units.
Easily digestible carbohydrates have a higher GI value. After eating such foods, blood sugar rises quite quickly. Low GI foods are considered complex and satiate the body for a long time.
The following food group has a high glycemic index:
- alcohol (110);
- fast food (100);
- baked goods (90);
- sweets (85);
- white rice (80).
When following a diet, it is necessary to create a menu only from foods with a low glycemic index. Such food helps restore metabolism.
What is easily digestible food?
This is good quality sunlight, air, water, plant products, rich not only in light, water, oxygen, but also in fiber, vitamins, microelements, amino acids, fatty acids, and alkaline bases.
Fruits, if consumed correctly (fresh, raw, separately from other types of food, on an empty stomach, before meals), are usually digested within 30-80 minutes. Vegetables, consumed separately or in the right combination, are digested in 2 hours. At the same time, our body is adapted to their absorption both physiologically and genetically.
But when it comes to combining vegetables with other products, you need to know certain laws so as not to suffer from indigestion, gas, and discomfort, which can lead to chronic diseases. What are these laws?
Fruits and vegetables are digested in the small intestine, leaving the stomach very quickly. Bread and meat, on the contrary, must first be treated with stomach juices. When you eat meat, bread and fruits at the same time, fermentation begins in the stomach with the formation of alcohol, acetic acid and other unwanted products. It turns out that it is not the products themselves that are harmful, but their incorrect combinations.
Incompatible products, at the same time entering the stomach, disrupt the natural process of digestion and become toxic.
Why product compatibility is important
Products that are compatible with each other contribute to the complete absorption of beneficial microelements found in this food.
Each product has a specific chemical composition, which determines its digestibility in the human body. All products are divided into quickly and slowly digested.
If you eat food with different “speeds” of digestion, there will be a delay in the body of fast foods.
Also, each food group requires its own environment in the stomach. For example, for chicken meat it should be acidic, and for mashed potatoes it should be alkaline.
Carbohydrate foods are best combined with fats, vegetables, and herbs. This combination is safe for the body and does not lead to food fermentation.
Scientist William Hay proved that when simultaneous consumption of protein foods and carbohydrate foods, the alkaline environment interacts with the acidic one, as a result of which they neutralize each other.
With this process, 40% of the food remains undigested.
What foods don't go together?
Separate nutrition will greatly simplify the functioning of the human body and improve health.
Nutritionists have identified several groups of incompatible foods:
- Foods high in protein and flour products.
- Proteins of plant origin and proteins of animal origin.
- Pastries and fruits.
- Flour products and dairy products.
- Proteins and milk.
Thus, tea cannot be combined with milk, since the proteins contained in milk prevent the absorption of the beneficial properties of tea.
Avoid combining cheese with meat.
When is the best time to eat carbohydrates?
There are many opinions about the timing of carbohydrate intake. Some nutritionists believe that you can consume fast carbohydrates (all kinds of sweets, sugar, etc.) only in the first half of the day, that is, before 12 o’clock. It is recommended to eat slow carbohydrates (in the form of pasta, potatoes) between 12 and 16 hours, and all kinds of cereals for breakfast.
In the evening, it is recommended to completely avoid carbohydrate foods, except vegetables.
Other nutritionists believe that complex carbohydrates can be consumed throughout the day, and fast carbohydrates only before lunch. But there is no precise scientific research on the timing of carbohydrate consumption. That is, it has not been scientifically proven that eating foods rich in carbohydrates at night leads to weight gain faster than eating carbohydrates in the morning.
In addition, some nutritionists are of the opinion that in the evening you should not limit your food intake, because the stomach is constantly working and its work is not interrupted at night.
What foods do not contain carbohydrates?
Carb-free foods are not a myth. Such food really exists and is the key to an effective diet and a healthy body.
In its original form, meat does not contain any carbohydrates. They are formed during the cooking process due to the addition of sauce or spices. The same applies to sausages. Before purchasing them, carefully study the composition.
List of products that do not contain an energy source:
- chicken, beef, venison, pork, duck;
- shrimp, oysters, mussels, crabs;
- salmon, halibut, trout, catfish;
- butter, Guyère cheese;
- spinach, radishes, cucumbers, cabbage.
- fish oil, table salt.
Carbohydrates are found in small quantities in zucchini (7 g), cauliflower (5 g), champignons (2 g), cherry tomatoes (6 g), celery (1 g), tofu (3 g).
Signs of a lack or excess of carbohydrates
In the BJU ratio, carbohydrates occupy about 50-60%. With a carbohydrate deficiency, the following occurs:
- fatigue not only after physical activity, but also after waking up in the morning or after a long sleep;
- headaches, irritability, because the brain needs glucose for full functioning;
- chills;
- the desire to eat sweets, as the brain does not have enough glucose;
- disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system due to a lack of cellulose (fiber).
The main sign of excess carbohydrates in the diet is excess weight. With a surplus of fast carbohydrates, some of them are still absorbed, and the rest is converted into fat deposits. Eating large amounts of carbohydrates can lead to a kind of “addiction.” Some people cannot do without sweets, others cannot do without flour.
Regular consumption of large quantities of simple carbohydrates leads to the manifestation of symptoms of latent diabetes. Carbohydrates themselves do not cause disruption of insulin synthesis, but they contribute to the development of diabetes in people with a predisposition to it.
People who eat a lot of simple carbohydrates are prone to fungal diseases. It is also very difficult for such people to get rid of the fungus, because it feeds on glucose.
Disadvantages of a Low Carb Diet
The following consequences of switching to this diet can be considered harmful:
Fat burns in the flames of carbohydrates
In order for fat to be burned, it must go through a metabolic process within the mitochondria in the muscles. During aerobic fat metabolism, several processes must occur.
The product of carbohydrate metabolism (oxaloacetate) acts as the source of this metabolic reaction. It is clear that the decrease in glycogen levels that occurs with a low-carb diet will affect oxaloacetate levels and therefore the metabolic process of fat utilization.
Reducing training intensity
A low-carb diet lowers glycogen levels because the body switches to ketones for energy. Obviously, lower glycogen levels will significantly impact physical performance in the gym. Reduced glycogen levels will reduce the amount of effort you can perform during both strength and cardiovascular training.
The reduced workload during strength training means less muscle fiber work and wasting, and therefore less visible muscle growth or shrinkage if you're on a strict diet.
Reducing the workload during cardiovascular exercise will reduce the total number of calories burned and, therefore, fat.
Many reviews of low-carb diets suggest research showing that declines in physical performance are ignored because this is the time the body uses to switch to fat metabolism. But it's still ambiguous.
Reduced fiber and microelements
A low-carb diet suggests eliminating most sources of fiber, since fiber/NSP (non-starch polysaccharide) sources are also high in carbohydrates. At the same time, there may be a decrease in micronutrients (vitamins and minerals), since the most fibrous sources of carbohydrates also provide the lion's share of micronutrients.
Given that most vitamins act as coenzymes for many body functions, including energy metabolism and cell construction, it is obvious that a decrease in micronutrient levels will impede physical development.
Hypoglycemia and low testosterone levels
Although fat and cholesterol are vital nutrients in the production of anabolic hormones such as testosterone, a state of chronic hypoglycemia due to severe carbohydrate restriction has been shown to reduce the amount of luteinizing hormone and therefore reduce testosterone levels. Clearly, decreased testosterone levels will impact adaptive responses to training.
Low glycogen levels cause the body to try to get energy elsewhere, namely from fat and muscle. As glycogen levels drop, an enzyme is produced that breaks down branched chain amino acids from muscles for use as energy.
With this in mind, a low-carb diet will constantly keep you in a state of catabolism, where the body tries to use other fuels instead of the glucose that is normally stored and circulated.
Diet “9 table”: products and calorie content
The energy value of food and its calorie content are very important, so a diet for people with diabetes includes taking into account the calories and energy composition of the food items included.
Energy composition of the “9th table”:
- fats – from 70 to 80 g;
- proteins – from 100 g;
- carbohydrates – up to 400 g;
- table salt – up to 12 g;
- liquid – up to 2 l.
- For diabetes mellitus, the total energy value consumed per day should be no more than 2300 kcal.
- The weight of food products should not exceed 3 kg.
- At least 6 meals per day are required.
- All products are subjected to gentle processing (baking, boiling or steaming).
- It is recommended to distribute carbohydrates evenly throughout the day.
- The temperature of the prepared food should be room temperature.
- Light snacks and limited physical activity are a must.
Diet No. 9 is indispensable for people with excess body weight, as it helps to normalize carbohydrate metabolism and prevent the development of fat metabolism disorders. Properly structured nutrition makes it possible
prevent obesity
And
complication of diabetes
.
Acceptable and prohibited products:
| Can: | It is forbidden: |
| Inconvenient flour products and bread | Baking and puff pastry |
| Lean meats and poultry | Duck, goose, canned food, smoked meats, sausages |
| Low-fat types of fish, canned fish in tomato and own juice | Fatty fish, smoked and salted fish, caviar |
| Chicken egg, soft-boiled (no more than 1-1.5), white omelet | Yolks |
| Low-fat dairy products | Cream, sweet and salty cheeses |
| Butter (ghee and unsalted), vegetable oils | Cooking and meat fats |
| Cereals (oatmeal, buckwheat, pearl barley, millet), legumes | Semolina, rice, pasta |
| Vegetables, taking into account the permissible norm of carbohydrates (potatoes, carrots, cabbage, green peas, beets, pumpkin, zucchini, lettuce, tomatoes, cucumber, eggplant) | Pickled and salted vegetables |
| Fresh berries and fruits in any form (jelly, compotes, mousses, sweets with sugar substitute) | Bananas, grapes, raisins, dates, figs, sugar, ice cream, jam, honey. |
| Mustard, pepper and horseradish (limited) | Salty, spicy and fatty sauces |
| Appetizers (salads with fresh vegetables, vegetable caviar, soaked herring, jellied fish and meat, salads with seafood, unsalted cheese and low-fat jelly (beef)) | |
| Drinks (coffee and tea with added milk, juices from vegetables, low-sweet berries and fruits, rosehip decoction) | Lemonades with added sugar, grape juice |
Return to content
Low-carbohydrate diet - menu for the week: recipes for weight loss
Small amounts of carbohydrates are contained in zucchini 7 g, cauliflower 5 g, champignons 2 g, cherry tomatoes 6 g, celery 1 g, tofu 3 g. All products are in the public domain.
In some cases, doctors prescribe this type of nutrition to pregnant women and people with cardiac problems. Eating with a limited energy source has no side effects and is not accompanied by loss of strength or fainting. When following a diet, a person feels lightness and a surge of energy.
For snacks between heavy meals, you should leave not buns and sweets, but nuts and dried fruits. People who are predisposed to developing diabetes should be extremely careful when consuming foods with a high GI. Carbohydrates are substances consisting of molecules of oxygen, hydrogen and carbon.
In the process of metabolism in the body, they are converted into a source of energy - glucose. The body uses glucose for energy, but if it is not used during a sedentary lifestyle, the unused glucose is stored in the form of glycogen, a polysaccharide formed by glucose residues.
This substance is a reserve carbohydrate for the body and accumulates in the liver and muscle tissue in reserve or in the form of subcutaneous and intra-abdominal fat.
Possible harm and contraindications
The danger of easily digestible carbohydrates is increased body weight. When you lead a sedentary lifestyle, energy turns into fat. Other negative effects of substances on the human body include:
- Pancreas overload. The body is forced to produce an increased amount of insulin and wait for the next intake of carbohydrates. When working in this mode, the iron wears out, which can lead to the occurrence of malignant tumors.
- Disruption of the nervous system. Increasing blood sugar levels increases the production of serotonin, which ensures a good mood. After eating carbohydrates, a person feels uplifted, but over time a feeling of depression arises.
- Disturbance of intestinal microflora. Simple carbohydrates change the acid-base balance, creating conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. The functioning of the immune system is disrupted, and infectious diseases begin to occur frequently.
- Diabetes. The breakdown of disaccharides requires a large amount of insulin, the breakdown of fat slows down and the absorption of glucose is impaired.
- Hypoglycemia. A sharp refusal to eat easily digestible carbohydrate foods contributes to the appearance of weakness, decreased performance and the development of anemia. The person becomes irritable and suffers from dizziness and headaches.
- Carbohydrate addiction. Sweet tea and cookies relieve hunger for a short time. Eating a balanced meal at lunchtime does not contribute to satiety, because the body requires carbohydrates. Therefore, a person has a desire to eat candy.
- Cardiovascular diseases. Fat deposits narrow the lumens of the arteries, leading to the development of atherosclerosis.
- Caries. Eating sweet foods helps create an environment favorable for the growth of bacteria in the oral cavity.
Fast carbohydrates are not of particular value to the body, so their quantity can be limited.
Source