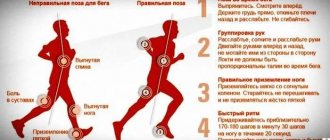
Recently, visiting fitness clubs, gyms and simply playing sports have become fashionable. It is considered prestigious to lead a healthy lifestyle, look good and be in excellent physical shape. However, most of those who take their first steps towards beauty and health are faced with the problem of fatigue after training. Not only experienced instructors, but also a certain diet, rest, and sometimes a person’s psychological state will help you not to deviate from the chosen course and not lose interest in sports.
Why do I get a headache after exercise?
Most often, headaches after physical activity are the result of overexertion.
Sports can only be beneficial if the loads are dosed correctly. In addition, you should remember that in some cases, playing sports may be contraindicated, and before starting training you should undergo a medical examination. Most often, headaches caused by excessive physical activity go away after rest. With active muscle work, metabolic processes accelerate, the body needs more glucose and oxygen. If a person has certain diseases, then oxygen starvation is possible, resulting in headaches. Here are the main causes of headaches:
- Problems with the functioning of the heart muscle or blood vessels.
- Diseases of the bronchopulmonary system.
- Disorders of the hematopoietic system, for example, anemia.
- Obesity.
- High loads that do not correspond to the athlete’s level of training.
- Ailments of infectious and inflammatory nature.
- Osteochondrosis.
- Diseases of ENT organs.
- Traumatic brain injuries.
- Inflammation of the brain and its membranes.
If headaches occur frequently after physical activity, it may be due to the presence of chronic illnesses that the body does not tolerate oxygen starvation well. Quite often, beginner athletes have problems with well-being after training. It must be remembered that the loads should increase gradually. If you ignore this wish, then more serious problems are possible. Now we’ll tell you in more detail why it becomes bad during physical activity, in particular, headaches occur.
The cardiovascular system
A state of hypoxia under the influence of physical activity can arise due to the body's oxygen needs not being met. Let us remember that red blood cells are the carriers of oxygen in tissues. When the heart muscle is not able to transport a sufficient amount of this substance, pain may appear in different parts of the body.
Blood vessels are also important in this matter, because they regulate the flow of oxidizing agents into the tissues of the whole body. If the vessels are in poor condition, this negatively affects cellular metabolism. The body's resistance to physical activity may decrease as a result of the presence of certain illnesses, for example, hypertension or heart failure. Due to problems with blood vessels, blood flow is disrupted, which can also cause headaches.
Respiratory system
Chronic lung diseases or acute pneumonia can cause spasms of blood vessels. Pneumosclerosis is the process of replacing lung tissue with connective tissue. This leads to a decrease in lung contractility, a decrease in oxygen absorption, and lung saturation.
Blood saturation is the saturation of hemoglobin with the oxidizing agent. A decrease in the ability to consume oxygen can be caused by asthma, acute obstructive bronchitis, and pulmonary emphysema. The latter disease increases the airiness of the lung tissue, which in turn reduces blood oxygenation. Another cause of headaches after exercise can be pneumonia. This is an inflammatory disease in which substances are synthesized in the body that cause narrowing of blood vessels.
Endocrine system diseases and anemia
Anemia is a decrease in the number of red blood cells or hemoglobin in the blood. As a result, oxygen deficiency occurs, and the brain is extremely sensitive to this phenomenon. Various diseases of the hormonal system can also cause the development of headaches after physical activity. This primarily applies to diabetes and hyperthyroidism.
If many people know about diabetes, then it’s worth talking about hyperthyroidism in a little more detail. This disease is characterized by an increase in the rate of thyroid hormones, which leads to a sharp increase in their concentration. This negatively affects the heart rate and increases blood pressure. Under the influence of physical activity, metabolic processes accelerate sharply and headaches appear due to increased blood pressure.
In diabetes, the body synthesizes a large number of ketone bodies, an excessive concentration of which can cause acidosis. With this disease, the condition of the capillaries sharply worsens. With excessive physical activity, the risk of headaches in this situation increases sharply. Also speaking about why it becomes bad during physical activity, it is necessary to remember about hormones such as cortisol and aldosterone. They are produced by the adrenal glands, whose overactivity may cause pain in the head area.
Inflammatory diseases in acute and chronic forms
Any acute respiratory disease in itself can cause headaches, as well as an increase in body temperature. Due to high physical activity, these symptoms may intensify. If inflammatory processes occur in the sinuses of the head, then physical activity can cause fluid fluctuations in the cavities. As a result, the ternary and other nerves are irritated.
Osteochondrosis and craniocerebral injuries
With various head injuries, pain may occur, and physical activity contributes to its intensification. Damage to the cervical vertebrae is also dangerous. Concluding the conversation about the causes of headaches after physical activity, I would like to note that they cannot appear out of nowhere. When this condition occurs frequently, it is worth undergoing a medical examination.
Method 5. Visit a sauna or steam bath
In addition to cool baths, on the way to recovery after intense training, you can turn to a sauna or bathhouse. These establishments are a great place to relax and maintain health. Don't forget about hot wraps, they also have a beneficial effect on the muscles and also improve the condition of the skin - moisturize, nourish and tighten.
Remember!
Hot wraps have a number of contraindications. They are not recommended for oncology, diseases of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems, varicose veins, thrombophlebitis, lymphovascular diseases, pregnancy, gynecological diseases, as well as in the presence of cuts, wounds and other injuries on the skin.
Symptoms during exercise that should not be ignored
Almost every athlete listens very sensitively to pain in joints or muscles. However, there is a high risk of missing more serious warning signals sent by our body. Now we will talk about symptoms that should never be ignored. If you want to know why you feel bad during physical activity, you should remember them.
Cough during cardio exercise
Most often, athletes in such a situation think that their throat is simply dry and they need to drink water. However, everything can be much more complicated, and a cough that appears indicates the possible development of asthma. Many people are sure that this disease is associated with suffocation, but another sign of the development of the disease is coughing.
If you often have a cough during cardio sessions, then it is worth determining at what point in the session this occurs. If by this time you have already been training for about 20 minutes or your heart rate has reached 160 beats per minute, then it is definitely worth visiting a doctor. Try to conduct classes in the fresh air or in a well-ventilated area. For various ailments of the respiratory system, the best place for training will be a warm room with high humidity, such as a swimming pool.
Headaches during strength training
We have already examined the main reasons for this phenomenon. Many athletes are sure that it’s all about normal overexertion and that after rest the problems will disappear. However, overwork is the least of your problems. If the cause of headaches is associated with increased blood pressure, then the situation is much worse than you think.
Sudden changes in pressure can cause various serious ailments, for example, dissection of blood vessels. If an athlete has osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebrae, pain in the head can be caused by spasms of the neck muscles. To eliminate this problem, it is necessary to cure osteochondrosis.
If you feel headaches during the training, then interrupt your activity and measure your heart rate and blood pressure. When the pulse is 40 percent higher than the maximum permissible value, and the upper pressure is higher than 130, it is better to complete the training.
When performing power movements, you need to monitor your breathing and not hold it. Also, avoid using weights that force you to overextend yourself. If you are in a state of severe stress or nervous excitability, then a strength training session should be preferred to a half-hour cardio session carried out at a medium pace. If problems with blood pressure occur frequently, and the desire to engage in bodybuilding is high, we recommend contacting a specialist who will help in drawing up an individual training program.
Pain in the chest area
Most often, athletes in such a situation are confident in their heart muscle, and the pain is attributed to the high intensity of the training. However, things can be much more complicated. During clinical examinations of patients, so-called stress tests are often performed using exercise bikes or a treadmill. With their help, you can identify hidden problems in the functioning of the heart muscle.
If you feel pain in the chest area while cycling or jogging, do not ignore the symptom. Perhaps the problem is not in your heart, but, for example, in intercostal neuralgia, but it is better to make sure of this. Note that the latter condition often occurs in novice athletes who use excessive loads.
The thing is that during exhalation and inhalation, the muscles contract very actively and this can lead to pinching of nerve endings. If you notice this symptom, then you should interrupt the activity, but there is no need to panic. The first step is to determine the nature of the pain. If the pain appears with light pressure, movement, or you are able to feel its source, then perhaps it is all due to muscle spasm. However, you should not refuse a visit to a specialist.
Pain in the right side while running
Many athletes experience this phenomenon, and during prolonged cardio exercise it is considered normal. Pain occurs in the liver area. Due to the acceleration of blood flow, the organ increases in size and puts pressure on the nerve endings. However, the problems may be related to the gallbladder. If after rest the pain goes away, then everything is fine. But when they do not disappear for a long time after completing the training, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Everyone is familiar with muscle pain after heavy physical exertion, especially if the person has not exercised for a long time before. This pain occurs 4-6 hours after exercise, and intensifies on the second day. This is why this happens.
During intense work, the muscle works in the so-called anaerobic mode, that is, in a mode when it lacks oxygen and uses stored energy. The end product of anaerobic processes is lactic acid. If the load is moderate, then lactic acid is safely removed from the muscles by the blood. But if the load is intense, then lactic acid does not have time to be removed from the muscles and begins to irritate the nerve endings. This is how pain arises.
This is the first type of pain caused by heavy muscle strain. It occurs during physical exercise and intensifies as it continues, but gradually goes away after the exercise stops. After physical activity, blood flow to the muscles increases, their tone increases, and the muscles increase in volume.
But there is a second type of muscle pain from exercise - delayed muscle pain. It occurs the next day after exercise and can increase over 2-3 days. Its reason is different - the occurrence of micro-tears in muscle fibers. Delayed muscle pain is accompanied by muscle inflammation. With training, delayed muscle pain syndrome weakens.
How to avoid muscle pain after exercise?
Firstly
, you need to do physical exercise regularly. Muscle pain occurs among beginners who, after a long period of idleness, decided to quickly get into shape.
During the training process, the body gets used to the load, and it no longer causes muscle pain. This does not mean that lactic acid stops being produced. It’s just that our body, with regular training, learns to cope with the usual load and not respond to it with sharp muscle pain.
Secondly
, no need to overexert yourself from the first lesson. The increase in load should be gradual. There is a misconception that muscle pain after the first exercise session is a normal side effect of exercise, a sign that the muscles have worked well. Nothing like this! Pain is a signal from the body that something is wrong. In this case, the body tells us through pain that the muscles have become overloaded.
Third
, before classes you should always do a warm-up to “warm up” the muscles.
What to do if pain has already appeared?
Firstly
, do not stop exercising under any circumstances, as physical exercise helps speed up your metabolism. You just need to reduce the intensity of your workouts.
Secondly
, for muscle pain it is good to massage. After exercise, the muscles are in a compressed state, and massage helps to relax.
Third
, if the pain is very severe, a warm shower is useful, because it also increases the metabolic rate and promotes relaxation.
Fourth
, drinking plenty of fluids is beneficial, since water participates in all metabolic processes of the body and helps remove metabolic products from the body.
By the way…
Muscle pain after exercise can result from a muscle tear. This is much more serious than the pain of an untrained muscle! It is not difficult to distinguish between these two types of pain: if the pain is the result of overload, then the muscles simply ache slightly when walking and other movements. When muscles are torn, any movement causes acute pain that prevents movement. The first type of pain goes away on its own, the second requires seeing a doctor!
Intense physical activity after a sedentary lifestyle causes discomfort. A reasonable question arises: why do muscles hurt after physical activity? We will try to find an answer to this question. The onset of pain occurs after 4-6 hours, and its intensification on the second day.
Basic practical conclusions: massage, shapewear, cool water
Pressure drops
Hypotonic people are familiar with the feeling of exhaustion after training. Symptoms appear quickly:
- Sweating increases;
- Your head starts to feel dizzy;
- “Shortness of breath” appears;
- Visual perception changes, the eyes may become dark
Doctors recommend monitoring your blood pressure on a training day, and postponing exercise if there is a problem. You need to get specific recommendations on creating a training plan, nutrition, and medications from a therapist and sports doctor.
Malaise
Women feel it in the last third of the menstrual cycle. And this is completely natural. Nausea may be a reaction to an enlarged uterus. General unwellness can be caused by lack of sleep, an onset of a cold or a headache. In this case, it is better to skip amateur training, and professionals should reduce the load within reasonable limits.
A drop in sugar levels is a problem for those losing weight on a low-carb diet. They should take BCA to support their body during a tough workout. Anyone looking to lose weight should eat a balanced diet and consume complex carbohydrates before exercise. If this is not possible, fruit is allowed half an hour before the start of class, but it is better to avoid juices. They sharply increase blood sugar levels and just as quickly “collapse” them.
Constant nausea and a feeling of lightheadedness can be symptoms of anemia. After training, the discomfort gets worse. If the problem is recurring, you should take a biochemical blood test and follow the doctor’s recommendations. Iron capsules are usually prescribed. The condition is not a contraindication to moderate physical exercise.
A heavy meal can cause nausea. The food does not have time to be digested, remains in the stomach, and prevents you from exercising at full capacity. Nausea can be avoided by taking enzymes with a solid meal, or by planning your diet so that you don't eat right before your workout. Is the problem recurring and every healthy meal seems “too heavy”?
Sodium deficiency
Sodium is a microelement for maintaining water-salt balance. There are not enough of its ions, a person may feel sick. The body “hints” that it would be nice to drink mineral water or eat salty food. Sodium is excreted through sweat and during active physical activity - this is a natural process.
Sodium can be taken either additionally, in tablets, or in the form of regular table iodized salt. Don't go on a salt-free diet unless medically necessary, and you won't experience nausea.
Heatstroke
Overheating is a common reaction to exercising in poorly ventilated gyms, taking thermogenics, and trying to lose weight by doing exercises in thermal suits. With heatstroke, nausea is accompanied by vomiting, the person feels very bad, his consciousness is confused, his speech is incoherent, and he may “pass out.” In this case, it is necessary to position the patient so that he does not choke on vomit, loosen clothing, ensure air flow and call an ambulance.
This is a common problem among security forces. If you use weightlifting belts that are too tight and do not unfasten the belt after an approach, blood circulation may be impaired. And as long as there is a certain amount of food in the stomach, the body will try to get rid of the unnecessary in a natural way - vomit. That is why wearing hard belts in fitness is not recommended, as well as exercises that require straining on the belt.
Poor circulation is a common problem among lovers of corsets for weight loss and waist reduction. Perhaps such equipment disables the oblique abdominal muscles from working, but it will almost inevitably make you sick from using it. For the sake of health, you should just learn to do the exercises correctly, and not waste time choosing belts.
An allergen can be anything from the perfume of your beautiful neighbor on the treadmill to the phenolic compounds emitted by some unscrupulous water bottle manufacturers. Dizziness and nausea with vomiting, loss of consciousness and swelling are serious symptoms for which the victim must receive immediate help. Allergy sufferers should carry a nebulizer with them and warn the gym staff about possible health problems.
Dehydration
Water deficiency can be either accompanied by cramps or “limited” by nausea. When dehydration is combined with alcohol intoxication the day before, the athlete vomits bile and has a metallic taste in the mouth. If dehydration is caused by an improperly organized diet for weight loss (a desalted diet in the hot season), you should immediately give electrolytes, for example, Rehydron or Gatorade drink. In case of poisoning, you must call a doctor. If muscle cramps begin, even minimal ones, the training is stopped and the athlete is shown to a doctor.
Normally, a person should have some amount of glucose in the blood. Hypoglycemia plagues those on a low-carb diet. Not only can such a diet be dangerous to the health of a non-professional athlete, but it also contributes to nausea during training. The best advice here is to adjust your diet so that your diet creates a slight calorie deficit, and allows you to lose weight, but does not force you to suffer from nausea every workout.
Those who have had their gallbladder removed or have suffered from pancreatitis can also feel sick during and after exercise. In this case, you need to see a doctor for the underlying disease.
Important: if nausea occurs during high-intensity training, due to overtraining and fatigue, you should seek help immediately. It is known that overloads of this kind can cause rhabdomyolysis, that is, a disease in which catabolic processes literally destroy the body and the excretory system.
After a hard workout, it can be helpful to schedule a massage. It is superior to all other treatments in relieving long-term muscle soreness, fatigue, and even helps combat muscle damage and inflammation up to 72 hours after exercise. In all the described cases, the athlete went for a massage straight from the gym, but how effective this remedy will be the next day is unknown.
Despite all the advantages, massage has 2 undoubted disadvantages: it requires time and money.
If one of these resources is lacking, choose shapewear. MASS reported a meta-analysis on this clothing, although it did not compare its effects to other restorative techniques. According to French researchers, shapewear ranks second in its ability to alleviate muscle pain and third in relieving fatigue, behind only massage and immersion.
The strong recovery has fallen short of expectations. Although it turned out to be one of the most effective methods of counteracting muscle pain, at the same time it increased fatigue after exercise. On average, this increase is small, but its value varies widely across studies.
Stretching also failed to take a prize place on the efficiency podium. Although many people practice stretching and claim that it reduces post-workout soreness, scientific research has not confirmed its effect on either strength or fatigue.
And finally, cold water immersion: A few years ago, Australian scientists showed that immersing yourself in a cold bath after strength training slows down muscle growth and strengthening. Athletes in that study sat waist-deep in water at a temperature of about 10°C for 10 minutes.
However, the results of the meta-analysis suggest that immersion in water at any temperature below body temperature promotes recovery. Of course, you shouldn’t jump into an ice hole, but you can recover without damaging your muscles by plunging into cool or lukewarm water.
Treatments as varied as massage, shapewear, and water immersion have one thing in common—they all compress tissue to varying degrees, affecting blood flow to muscles and other parts of the body. The authors of the meta-analysis suggest that compression prevents swelling in the muscles and facilitates the elimination of waste and metabolic byproducts after exercise.
According to MASS article author Greg Nukkolls, it would be interesting to study the long-term effects of these recovery methods on muscle growth and strength gains. If cold water immersion weakens muscles due to the act of immersion rather than the cold, then, theoretically, all 3 strategies could promote recovery but reduce adaptation to training.
If restricting muscle blood flow is preventing muscle growth, massage will help with recovery, but shapewear is unlikely to do so. If muscle growth is hampered by the accelerated elimination of metabolic products, then massage in the long term is more likely to harm than help. Nukkols himself believes that muscle growth is affected by rapid cooling when an athlete is immersed in water, but this assumption needs to be tested.
Mechanisms of muscle pain
Intense muscle work is accompanied by a lack of oxygen, as a result of which the stored energy is used. Due to oxygen deficiency, lactic acid is produced. With moderate exercise, it is removed from the muscles along with the blood. A strong load prevents the removal of acid from muscle tissue, which leads to irritation of nerve endings and pain.
The pain that occurs during physical activity increases as it continues and begins to gradually subside when the activity stops. Physical activity promotes increased blood flow to the muscles, increasing their tone and increasing their volume.
There is delayed type muscle pain. As a rule, a person does not experience muscle pain immediately, but on the second day after exercise. Moreover, pain may increase in increasing amplitude over 2-3 days. The main cause of such pain is micro-tears of muscle fibers. Delayed pain syndrome is accompanied by muscle inflammation.
Replenish fluid loss
Physical activity involves active loss of fluid. And, naturally, it needs to be replenished. This same action increases the body's recovery rate after exercise because it supports nutrient delivery and improves metabolism. You should drink especially plenty of fluids after training in hot weather.
It is advisable to drink acidified drinks, for example, still mineral water with lemon or lime juice and the addition of stevia powder (a natural sweetener). You can also resort to isotonic drinks. These are fluids that provide a person with water and electrolytes, which leave the body through sweat.
Important!
Isotonic drinks are presented on the market in two forms - dry concentrate in cans and liquid concentrate in bottles. The taste can be very diverse - from forest cherry to exotic passion fruit
The main thing is to pay attention to the composition when choosing; it should not contain acesulfate and saccharin. These are cheap sweeteners that do not make the composition balanced, moreover, they are dangerous to health
It is better to opt for drinks that contain salts, glucose polymers, dietary supplements and vitamins.
Ways to prevent muscle discomfort
1. The occurrence of muscle pain is observed in beginners who expose themselves to intense exercise on the first day. Therefore, in order to prevent the occurrence of pain, it is necessary to do physical activity regularly.
2. There is a misconception that muscle pain after physical activity is normal. In fact, it is the result of an overload that the body is trying to tell us about. Therefore, you should not overload the body during the first lesson. It is necessary to increase the load gradually so that the muscles can adapt to new conditions.
Method 10. Plan your workouts
For training to be successful, it is necessary to clearly define the goal and, accordingly, develop a rational action plan that will allow you to achieve the desired results faster. It is quite difficult to draw up a training plan on your own, especially for a beginner, so at the first stage you should contact a specialist with a specialized education who has extensive experience in sports. Only regular and systematic training will make your dream come true, but never overwork and lack of a plan!
How to eliminate discomfort?
To reduce pain, it is necessary to reduce the level of activity, but you should not suddenly stop exercising. The best option is walking or light jogging and exercise. Since physical activity causes muscles to become tight, it is necessary to perform a relaxing massage to eliminate pain.
For severe pain, it is recommended to take a warm shower or a warm bath, which helps speed up metabolic processes and relaxation. To quickly remove metabolic products from the body, you need to drink plenty of fluids. Following these simple rules will help prevent muscle pain.
Painful sensations in the muscles the next day or two after intense training is a phenomenon familiar to everyone: both experienced athletes who have moved to a new, higher level of load, and beginners who have recently started training to improve their body, know firsthand about muscle soreness.
How to treat delayed onset muscle pain syndrome - as possible negative consequences for the body or as evidence of positive dynamics in the development of muscle mass? You can answer this question by understanding the causes of muscle soreness.
Working on the athleticism of your figure is unthinkable without stress and pain. But is muscle pain (appearing during exercise or 24 hours after it) a sign of improved fitness?
Serious physical stress that muscles experience during strength exercises or cardio training cannot but affect their condition. The appearance of pain and a burning sensation during exercise is due to insufficient flow of oxygen-enriched blood to the muscle fibers to replenish the required amount of energy. At this time, the human body launches a “backup” mechanism that compensates for the lack of oxygen by producing lactate (lactic acid). It is its accumulation in the cells of the loaded muscles that causes unpleasant pain.
Should you stop training if unpleasant signs of burning appear in those muscle groups that are subject to intense stress? In most cases, it is better to endure and continue with the previously planned training program. If the pain becomes unbearable, you should not torture yourself to the point of exhaustion. Within a short time after the end of the lesson, the blood vessels will again be enriched with oxygen, and the accumulations of lactic acid in the muscle tissue will gradually dissolve in the blood, the pain will disappear without negative consequences for the body.
So, the pain caused by the action of lactate has ceased to bother me, and the aspiring athlete, inspired by today’s successes, is ready to continue training tomorrow with renewed energy. But the next morning, getting out of bed, he realizes that there is no talk of any training - his muscles hurt so much that it’s time to learn to walk again, slowly moving his legs, and his hands can only hold a piece of paper, but not a barbell or dumbbells .
Unusual weakness, severe pain and a feeling of “bloated” muscles - these constant companions of delayed muscle pain syndrome are known to everyone who has had or is involved in constant physical activity. The cause of muscle soreness, which occurs 1-2 days after intense training, is microtrauma of the fibers. These injuries, only a few hundredths of a millimeter in size, should not be confused with sprains, when muscle fibers are injured over an area ranging from a few millimeters to several centimeters. Due to the fact that the body begins to fight microtraumas by sending immune cells to the damaged area, an inflammatory process occurs, which, as is known, is always accompanied by pain. Usually, during an exercise, an athlete receives not one, but many microtraumas, so it feels like the whole body hurts.
Typically, delayed onset muscle pain syndrome goes away in 2-3 days, sometimes it takes a week to recover and continue training. If recovery takes much longer, or the pain does not decrease, you should consult a doctor - perhaps it is not a sore throat, but a sprain or something more serious.
The more developed the muscles, the less likely it is that signs of soreness will appear. This is why beginners with an untrained muscular system are more “lucky” - at the beginning of their journey to a perfect figure, they will have to face this phenomenon more than once. Krepatura in experienced athletes can manifest itself when changing the training program, intensity of loads, adding new exercises, etc.
The goal is to be in good shape
In this case, we are not interested in constantly increasing the load, and therefore the question should not arise after how many workouts the muscles will stop hurting. Pain, if it is present, will only be at the beginning of training. Gradually, when the muscles get used to certain loads, they will stop hurting and will maintain their current state without development. If you don’t have a goal to change your body or adjust your shape, then such loads are quite enough to maintain tone and good mood.
A good option for exercise in this case would be Pilates, yoga and aerobics. These exercises develop all muscle groups well without overloading them or causing pain.
Krepatura - good or bad?
Delayed muscle pain syndrome should not be considered a reason to stop training. On the contrary, if signs of muscle soreness appear tomorrow or the day after tomorrow, you can be sure that the body responded to unusual loads correctly and is trying to recover in all possible ways. After proper rest and bringing your condition back to normal, it is recommended to continue exercising in the gym, because the muscles have become more resilient and stronger, which means the body is ready for new achievements.
If muscle pain has not manifested itself for a long time, you should think about increasing the loads and training time, changing the program: the muscles have adapted to the same exercises, and building them up requires more tangible efforts. Performance will be higher if the training program is adjusted or changed every 2-3 months.
Types of training
To answer the question why an athlete feels bad after training, you need to plunge into the training process itself. Not all workouts are created equal.
Among them, there are those that improve your health, and there are those that improve your athletic performance. In the second case, health may suffer.
- Health training.
As a rule, this is a set of light exercises that tone muscles and improve overall well-being. This can be light cardio or moderate strength training that does not stress the body. You won't feel sick after a workout if you exercise at a low intensity. - Warm-up workout.
This is training before the competition. It is characterized by a high speed of performing exercises with a low intensity of the load itself. During such training, hypoxia often develops, and after. - Workout training.
This is a workout using sports equipment that involves working with your own weight. It can overload your body, especially if you don't keep a workout log and push yourself to do more than you're capable of. - Aerobic training.
This is serious cardio. How well you will feel depends on the intensity and timing. Aerobic training is often accompanied by dehydration and all the ensuing consequences. - Strength anaerobic training.
This is a tough workout with heavy weights in the gym. If the body is not prepared for such stress, you will experience a full range of side effects, starting with and ending with loss of consciousness. - Drying workout.
This is a relatively easy workout that can be done both. However, keep in mind that during the drying itself, your body is already in a stressful situation and, as a result, cannot fully recover.
So, some types of exercise will definitely make you feel bad, while others will only make you feel better. However, first of all, how you feel after training is determined not by the load, but by your readiness for this load.
Prevention of muscle pain
There are no ways to completely prevent muscle pain after training, since their occurrence is a natural reaction of the body. However, there are several tips to reduce the duration and severity of the pain.
Secondly, you should follow the drinking regime. With dehydration, which accompanies any workout, the blood thickens, as a result of which a sufficient amount of oxygen and, accordingly, energy does not reach the muscles.
Thirdly, proper use of exercise equipment and equipment helps reduce pain after training. If a person exercises without a system, makes mistakes, overloading or incorrectly influencing muscle groups, then subsequently severe pain cannot be avoided. It is better if the trainer tells you how to create an effective training program or perform this or that exercise safely.
Fourthly, we must not forget about a good warm-up before training. Loading a huge number of repetitions with weights on unheated muscles will only harm your body.
Fifthly, the principle of “from light to heavy” will help prevent the appearance of pain: starting training with lighter weights but more repetitions, you can avoid too intense symptoms of soreness the next day.
Why do muscles hurt?
Obviously those that your exercises were aimed at. That is, if, when lifting the barbell, your biceps and triceps hurt, then the exercise can be considered completed successfully, you have achieved the desired result. If, during the same exercise, a burning sensation occurs in the back area, you should immediately stop doing it.
This means that the execution technique was not followed. Although sometimes a situation arises that a trainee, due to inexperience or lack of understanding, harms his health, much more often the cause of injury is negligence and neglect of safety precautions, which trainers tirelessly repeat in the gym.
During training, the familiar burning sensation is the result of the formation of lactic acid in the muscles. It is a product (metabolite) of the oxygen-free breakdown of glucose in muscles. They need to somehow obtain energy when a sufficient amount of oxygen does not pass through them.
After training, there is no longer a burning sensation, the muscles are moderately sore. For several hours, the muscles experience pleasant fatigue from a lack of nutritional material and energy. When reserves are restored, fatigue goes away. It may take 4-6 hours until this point. The strength is felt again in the muscles, but now it becomes painful.
Anabolic pain is a sign of a good workout. Its presence means that you have given your muscles the load that will lead to progress. This pain goes away up to 7 days. And this period depends on the level of training of the student. If you've tried a new program or are new to the program, you will experience delayed muscle soreness that lasts longer than normal post-workout anabolic soreness.
Bad pain occurs immediately after exercise, or within a few hours. While the body is hot, you may not feel the full force of this pain. Then, when you have rested, been in a sedentary state for some time (two hours at the computer), then you will feel post-traumatic pain in all its glory. Especially after a sudden habitual movement.
How to relieve muscle pain after exercise
Typically, delayed muscle pain syndrome, subject to proper rest and sleep, goes away without negative consequences within 2-3 days. But sometimes the pain is so unbearable that you have to use additional means to reduce its manifestation. There are several ways to relieve muscle pain:
- Any water procedures - swimming in the pool, a warm bath, a contrast shower - help relax stressed muscles and reduce pain.
- A sauna is another great way to let your body relax. At the same time, we must not forget about drinking plenty of fluids.
- Massage procedures not only warm up muscles and increase blood flow to areas of pain, but also have a positive psychological effect.
Delayed onset muscle pain syndrome is a common phenomenon, and it is impossible for either a professional athlete or an ordinary gym client to avoid it. It is important to continue training so that the muscles that have adapted to the load remain toned and the body is athletic and toned.
Why do you experience constant fatigue and fatigue?
Weakness and fatigue appear against the background of depression. One of the reasons is carbohydrate metabolism. To perform functions, the body needs glucose, which is stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles. In order for it to be transformed into energy of the required quality, you need to move after eating. In a sitting position, the necessary biochemical processes do not occur.
This happens due to the tension present when the sympathetic part of the central nervous system is stimulated. It is responsible for metabolic processes and the feeling of hunger. The patient is concerned about:
- dyspeptic symptoms;
- discomfort in the right hypochondrium;
- hiccups;
- gagging;
- weight loss;
- chills and weakness;
- fatigue.
With VSD, loss of appetite occurs. Due to destabilization of the gastrointestinal tract, sometimes the illusion of a full stomach occurs. Some people develop a fear of sudden vomiting immediately after eating. People often turn to their doctor with a request to improve their diet. A psychologist works with an internal problem. Autonomic gastrointestinal disorders in VSD are provoked by dysfunction of the nervous system and a depressed psychological state. VSD and weakness, sweating, fatigue are treated with movement and mental balance.
Eat Enough Food Before Starting Powerlifting
In addition to consuming some sugar to boost energy as part of her workouts, Karina Baymiller also pays close attention to her pre-workout food intake. “In order to have the energy to perform high volumes of exercise during my intense powerlifting sessions, I always make sure to eat enough before training,” says Baymiller. “At this time, I consume about 25 percent of my total daily carbohydrate intake.”
In addition to the high dose of carbohydrates, Baymiller takes in about 25-35 grams of lean protein; at the same time, it necessarily provides the body with enough time to digest food before going to the gym. The digestive system of each person has a number of individual characteristics. But a general good rule for all athletes is to consume less fiber immediately before training and remember that after large meals you need at least 60-90 minutes for adequate digestion.
System overload and symptoms
First of all, do not forget that feeling unwell is just a symptom, which means an overload of certain systems in the body. Such overload can easily be treated symptomatically, but does not eliminate the root cause of the condition. For an athlete, this is a clear sign: it is necessary to change the training process, nutrition, or give the body more time to rest.
| System | Symptom | Cupping |
| Overload of the cardiovascular system | Chest pain, headaches, nausea, weakness, drop in blood pressure. | Reduce caffeine consumption. Reducing the intensity of the training process. Use of sedatives. |
| Overload of the gastrointestinal system | Nausea, vomiting, indigestion, or diarrhea. Immunity to certain nutrients. | Taking digestive enzymes. Rest until complete recovery. Chamomile tea. |
| Overload of the central nervous system | Insomnia, nervousness, mood swings, headache, muscle tremors. | Sedatives and vitamins based on magnesium and vitamin B6. |
| Hormonal overload | Weakness, poor health, fever, sudden drop in mood. | Complete rest from stress, it is possible to take testosterone stimulants such as tribulus or zinc. |
| Traumatic overload | Pain in muscles, ligaments, joints. | Complete rest, restorative warm-up. |