The exercise, hanging bent leg raises (knees), pumps the lower abs, as well as the rectus femoris muscle. Develops strength and tightens the lower abs. Basic exercise.
Hanging knee raises are excellent for strengthening both the abs and the hip flexor muscles, which are responsible for keeping the pelvis in a stable position, which directly affects your posture. Thus, by training these muscles, you increase the strength of the entire lumbar region as a whole, which is very important for sports such as football, acrobatics, gymnastics, karate, pole vaulting and steeplechase.
Hanging Knee Raises - Abdominal Exercise
Two reasons why you can't do pull-ups
- Reason #1. You're too big. Maybe you're overweight, or maybe you're a heavyweight powerlifting champion. The physics is simple. In pull-ups, body weight is an additional burden for the muscles that are involved in the pull-up. And the greater the weight, the stronger they need to be to lift your body to the bar. Work on your diet, lose those extra pounds, and maybe you can do your first pull-ups without additional training.
- Reason #2. You're too weak. In this case, you will not get a centimeter closer to the cherished bar of the horizontal bar. You need a workout program for pull-ups. You must become stronger in the accessory exercises, increase the mass and strength of the working muscles before climbing the bar. Likewise, if you want to deadlift a 500kg barbell, it makes no sense to set that weight and try to lift it off the floor. You need to ease the exercises up to your current capabilities and train to improve those capabilities.
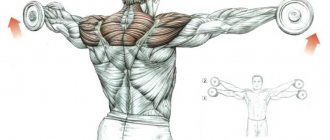
Abdominal Anatomy
The abdominal press is a set of muscles of the abdominal wall that belong to the stabilizer muscles. It consists of internal oblique, external oblique, transverse and rectus muscles.
The abdominal muscles start from the chest and end at the pelvic bones.
Functions of the abdominal muscles:
- stabilizing (fixing the position of parts of the skeleton relative to each other);
- motor (turns, pelvic movements, etc.);
- formation of posture and stabilization of the body.
Rectus muscle - pumping it up at home
The rectus muscle runs across the entire abdomen and is the strongest flexor of the spine. On the outside, it is crossed horizontally by bridges of tendons, and vertically by connective tissue, which creates the appearance of “cubes” on the abs. It is worth understanding that with any movement the rectus muscle tenses along its entire length, the difference lies only in the degree of tension - only from this point of view is it correct to distinguish exercises for the “upper” and “lower” abs.
Functions of the rectus muscle:
- twisting the body, moving the chest towards the pelvis;
- with a stationary chest - raising the pelvis;
- increased intrauterine pressure;
- movement of the ribs, participation in breathing.
External oblique muscles
The external oblique abdominal muscle is located on the front and side surfaces of the abdomen and part of the chest.
Functions of the external oblique muscles:
- turn the body to the sides;
- pulls the ribs down, bends the torso;
- help in lifting and carrying heavy objects.
Internal oblique muscles
The internal oblique muscle lies directly under the external oblique, constituting the second powerful muscle layer of the abdominal wall.
Functions of the internal oblique muscles:
- rotate the body;
- pull the chest down;
- bend the body to the sides;
- squeeze your stomach.
Transverse muscles
The transversus muscle is the third and deepest layer of muscle that encircles the entire abdomen.
Functions of the transverse muscles:
- support internal organs, shapes the waist;
- tighten the ribs and participate in breathing;
- bend the body to the sides and forward;
- turn the body.
1
What muscles are involved in pull-ups?
Pull-ups are a multi-joint exercise that involves the entire group of muscles in the shoulder girdle. You must know them in order to understand what to train and which exercises are best to use.
Core muscles
- Latissimus
- Biceps
- Teres muscle
- Brachialis
- Brachioradialis
Accessory muscles
- Deltoid
- Triceps
- Chest
- Diamond-shaped
- Trapezoidal
Muscles when pulling up
Losing weight in the abdominal area: simple and effective exercises with a chair that quickly eliminate fat
To make your stomach flat and elastic, you don’t have to go for hours of morning jogging and do squats fifty times when you return home. It is enough to adopt just a few simple but effective exercises and perform them daily while sitting on a chair. This is the opinion of people who have brought the parameters of their bodies closer to the ideal.
How is the effect of the exercises suggested below expressed? Consecutive execution of each of them involves the use of different groups of abdominal and back muscles.
A person who leads a sedentary lifestyle or an office employee who is forced to constantly sit at the workplace is familiar with the problem of obesity. The only way to maintain health and prevent premature aging of the body is sports. sport is hard work, but the results are worth it. A sports person always feels better than his non-physical colleagues.
All necessary exercises are presented below.
How to increase your pull-ups or do your first pull-ups. Exercises
As I wrote above, there is no point in twitching on the horizontal bar if you do not yet have the strength to do at least one pull-up. You need to temper your ego, go down a notch and work on the muscles involved in pull-ups. Below I have prepared a list of three basic exercises that you should focus on if you don’t know how to do pull-ups.
Exercise No. 1. Horizontal bar row or low pull-ups
Absolutely anyone can do this exercise, because the difficulty of the exercise is easy to adjust to your strengths. Maximum intensity in horizontal rows is achieved when the body is positioned horizontally to the floor. The most prepared athletes can perform “deficit” pull-ups, that is, when the legs are elevated, above shoulder level.
Low pull-ups
Your task is to gradually come to this low position. But it’s worth starting from a more vertical starting position. Perform 4-5 sets of 12-15 reps per workout, getting into a position where you can fail the set without breaking it. Rest between sets 1.5-2 minutes. From workout to workout, move your feet a couple of centimeters forward. This will be your progression of loads to become stronger.
Exercise No. 2. Negative pull-ups with reverse grip
Reverse grip pull-ups are easier than classic pull-ups. Therefore, at first it is logical to concentrate on this technique.
Reverse pull-ups
Negative reps are a training technique that takes advantage of one of the properties of muscle contractions. Our muscles find it easier to lower (the eccentric phase of the movement) than to lift up (the concentric phase) in pull-ups. You can use this trick as follows.
Use a platform or step to get into the top position of a pull-up. Then lower yourself down as slowly as possible, resisting the gravity of your body weight. Aim for 3-5 seconds of lowering. Then repeat the sequence again. Do 5-7 sets of 3-5 negative reps. Count the total time under load in seconds and try to increase it.
Exercise No. 3. Lightweight pull-ups
In this exercise you have the opportunity to do your first strict pull-ups. The technique for light pull-ups is identical to the technique for strict pull-ups, with one exception. Your feet are on the floor and you “unload” your body weight, which needs to be pulled to the bar. Perform 4-5 sets of this exercise to failure each workout. Strive to increase the sum of all repetitions. When you can do 10-12 reps per set, you're ready for your first pull-up!
Lightweight pull-ups
Treatment of injury
If one of the peritoneal muscles is stretched, then treatment will directly depend on how pronounced the symptoms of the disease are and the degree of injury suffered. Thus, the degree of stretching of the abdominal wall muscles will determine the duration of therapy.
The key point for such patients is complete rest for the abdominal muscles and the absence of even the slightest stress. At home, the patient should avoid heavy lifting and sudden movements, which increase muscle tone. This is especially important during the first two days after the injury.
If the patient has suffered moderate to severe sprains, then in this case experts recommend applying cold to the injury, which must be done in sessions lasting 15-20 minutes. After they expire, you should take a break. In order to apply cold to the injury, you can use ice cubes wrapped in cellophane and a towel. It is not recommended to apply them directly to a bare area of the body. In order to relieve unbearable pain, the attending physician may prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics in the form of tablets, injections or ointments. This will significantly alleviate the patient’s condition and improve his well-being.
In order to get back into shape after an injury, the patient will have to make some efforts. Do not forget that if sharp painful sensations occur as a result of lifting heavy objects or performing sports exercises, you must immediately stop the load on the body. Physical activity should be limited or completely suspended. This will depend on the severity of the injury.
At the same time, during the period of treatment and restoration of health, it is recommended to rest regularly, apply cold compresses for 1-2 days after the injury, do not refuse to take painkillers, and gradually stretch the abdominal muscles when the pain begins to recede.
Correct pull-up technique
Strict pull-ups have certain standards. Remember: technique was not created to complicate the movement. Specific accents help to optimally use muscle strength and at the same time fulfill all the control points inherent in this technique. Mistakes can lead to injury. And cheating will make it easier to perform the movements, but in this case your pull-ups cannot be called “clean”.
A. Deep grip
Deep grip
In the case of pull-ups, the bar is the fulcrum for applying force. If you hang on your fingers, the contact with the support is weak. It's like squatting on your toes or confidently resting your entire foot on the floor. Practice a deep grip while hanging on the bar for a while. Make sure your finger bones are pointing toward the ceiling.
B. “Active” shoulders
Active shoulders
Each repetition should be started from the correct starting position. Retract your shoulder blades and lower them down. Pull your chest back a little. You are now ready for the dynamic pull-up phase.
C. Socks pulled up, body tense
Socks pulled up
By bending your legs, you “switch off” your core muscles from working. Try to stretch your legs, bring them together and tense. Tighten your abs and buttocks. A stiff body is easier to lift than a relaxed one. Stabilizing muscles play an important role in pulling up. We will talk about this below.
D. Chin down
Chin down
There is no need to lift your chin to cross the line of the bar. Strive to touch the horizontal bar with your upper chest. This will be the purest execution of a pull-up.
E. Full extension of the elbow joint
Straightening the elbow joint
The repetition ends when you fully straighten your elbow joint, but don't forget about the "active" shoulders. You must return to this position to begin the next repetition.
F. Smooth movement without jerking or kipping
A strict pull-up is strict because we are doing a power movement without twitching the legs. And the keeping style is best used in CrossFit complexes, when you are already doing more than five repetitions. Your primary goal is to become stronger, the kipping technique is designed to develop endurance in CrossFit.
You can find out what kipping pull-ups are and when it’s best to use them in my video:
https://youtu.be/odXnw1LtXxw
Hamstring stretch
This exercise is considered one of the most effective in the fight against sore lower back. There are even several ways to do stretching. Daily repetition will improve the muscles of the thighs and relieve pain in the lumbosacral region.
You need to sit on the edge of a chair and then straighten one leg forward. The heel remains pressed to the floor, and the stomach moves towards the hips due to body pressure. In a maximally bent position, you need to wait 30 seconds, and then do the same with the other leg. A total of 6 repetitions is enough.
How often to train pull-ups. Pull-up training every day
Your result in the set of exercises from this article is based on the principle of hypertrophy.
Muscle hypertrophy is an increase in the size of muscle fibers from strength training. Obviously, the larger the muscle, the stronger it is. Training causes fatigue and stress, changing the biochemical balance within the muscle. This state triggers the regeneration process after the end of the workout. For its optimal course, rest of the working muscle is required.
Remember, growth does not happen during the training itself, otherwise the one who trains more would always win. In fact, if you interfere with the recovery process, you can end up in a state of overtraining and not achieving your goal.
The recovery process takes from 48 hours to 10 days. That is, after at least 48 hours, the loaded muscle is ready to receive a new portion of stress in order to continue growing. Typically, the less muscle and stress, the faster the recovery will be, and vice versa.
Hence the conclusion that if you train hard and do a volumetric strength program of pull-ups, you need to repeat it no more than three times a week. On rest days, you can work on other muscles, do active recreation, run or cycle.
Prolapse of internal organs: How to treat
The disease primarily affects narrow-shouldered and thin-boned asthenics with overly extensible connective tissue. Their insides can sink due to constant physical strain and chronic fatigue, when neuromuscular tone decreases. Prolapse of the stomach, kidneys, transverse colon, and pelvic organs is most often observed.
Depending on which organ is omitted, certain features of the clinical picture of the disease are revealed. But any form of prolapse is characterized by complaints of constipation, decreased appetite, decreased performance, and sleep disturbances.
The pain appears over time, gradually and intensifies towards the end of the working day, while at the same time it is weaker in a horizontal position. As muscle strength decreases, the ligamentous apparatus weakens, the balance created by the pressure of the internal organs on each other is disturbed, and the lower abdomen protrudes.
Abdominal adipose tissue plays a certain role in maintaining the normal position of organs. With significant weight loss, the layer of adipose tissue decreases and the entire burden of the internal organs falls on the muscles.
Intermittent aching and nagging pain in the abdomen may indicate prolapse of the stomach and intestines. Unpleasant sensations usually occur in an upright position and subside when you lie down.
When the kidneys prolapse, pain in the lumbar region bothers you.
If it is accompanied by a nagging pain in the lower abdomen and sacrum, episodes of urinary incontinence appear when coughing, sneezing, laughing, or physical exertion; prolapse of the uterus and vagina is possible, which sometimes ends with their loss.
IF THE OPERATION COULD NOT BE AVOIDED...
Today, the usual solution is surgery, however, as practice shows, there is a possibility of relapse, depending on many reasons, and it is impossible to take into account and prevent all factors.
If, unfortunately, you had to undergo surgery, then after some time it will still be necessary to perform exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, because the body is even more weakened by surgical intervention, which means it requires constant attention and systematic strengthening so that there is no need for repeated operations.
Don't rely on a bandage - it will only make the problem worse.
After a temporary improvement, which can last 1–2 years, the symptoms of the disease begin to bother you with triple strength: pain increases, constipation and nausea that cannot be treated appear.
General weakness, increased fatigue and irritability occur, and sleep is disturbed. It is already very difficult to help: the muscles, accustomed to inactivity under the bandage, have completely atrophied and are not able to provide the slightest support to the sagging organs.
Train your core to learn how to do pull-ups faster
Core training should be a mandatory part of your pull-up program. By strengthening your midline muscles and learning to control them, you will gain more control over your body. A tight, collected body makes it easier to work the lats and biceps in pull-ups.
To do this, add just two exercises to your workout and gradually progress in them.
Core exercises #1. Raising your knees to your chest
This is a dynamic exercise that will simultaneously strengthen your grip and pump up your abs. When performing lifts, pay attention to your technique: deep grip, active shoulders, pointed toes. Avoid swinging your body, lower your legs slowly and under control.
Raising your knees to your chest