Exercises for osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine are a set of exercises for systematic implementation in order to normalize the condition of the cartilaginous part of the vertebrae. At the initial stage, when pathological changes are still reversible, exercise therapy helps restore the natural state of an important part of the musculoskeletal system. Physical impact on the thoracic spine is recognized as a necessary part of the treatment of patients, since it effectively complements conservative therapy, and sometimes completely replaces it. Training helps restore health to the patient, avoid long-term disability or disability, and all associated pain.
Intended Benefit
It is important to know! Doctors are shocked: “An effective and affordable remedy for joint pain exists. " Read more.
Pain in the thoracic region, swelling, weakness and increased fatigue - all these signs can be eliminated by proper exercise therapy. The complex is formed by a specialist, taking into account the stage of vertebral degeneration, the patient’s weight, height, lifestyle, and the presence of concomitant pathologies.
Exercise for thoracic osteochondrosis solves several problems at once:
The thoracic spine suffers less than the cervical or lumbar spine, which bear the main load. For a speedy recovery, you need to know the reasons for the development of pathology. It is useless to undergo a physical therapy program if the negative impact on the spine continues.
Dr. Sperling comments:
Sequestrated spinal hernia and its treatment
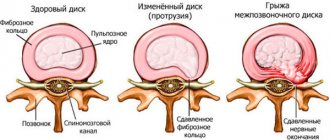
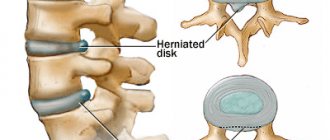
A herniated disc is a spinal disorder that occurs as a result of disc injuries. It is divided into a number of types, the most dangerous of which is sequestered hernia of the spine.
The protrusion of the hernia in this case is directed into the spinal canal. In this case, rupture of the fibrous ring and prolapse of the nucleus pulposus may occur. As a result, the spinal cord and nerves are compressed, which can ultimately lead to complete paralysis.
Hernias are divided by location - most often they form in the cervical or lumbar region, less often in the thoracic region.
The lumbar region is the most vulnerable, since it is the one that experiences large overloads, regardless of body position. There are 5 large vertebrae in the lower back. Treatment of lumbar disease is only surgical and involves the longest rehabilitation period.
During the process of sequestration of an intervertebral hernia, the fibrous ring of the disc ruptures, and part of the nucleus pulposus is “squeezed out” outside the spinal column
Herniated discs of the sacral and lumbar regions account for 75% of all sequestered diseases. This type is dangerous because it compresses the bundle of nerves responsible for the proper functioning of the pelvic organs. That is, with this course of the disease, the functions of the pelvic organs may be impaired.
Cervical spine disease is less common, but has serious consequences. So, vision may deteriorate and headaches may appear. Some patients complain of worsening mental status. The peculiarity of this department is that it is responsible for the sensitivity of the entire body, and if the hernia is not treated, then paralysis of the areas located below the site of the lesion, that is, almost the entire body, can occur.
Thus, regardless of which department the hernia is detected, it means that a disc protrusion has occurred in this place, which means that the person needs urgent treatment.
The main cause of the disease is mature and old age. The following reasons are also identified:
- hard physical labor;
- Weightlifting;
- protrusions, osteochondrosis, scoliosis;
- excess body weight;
- metabolic disorders and bad habits;
- heredity;
- injuries.
There are some professions that can provoke a hernia: loaders, athletes, builders, etc.
Symptoms of the disease
Since a sequestered hernia of the spine affects the spinal nerves, the symptoms of such a disease are much more obvious than with other herniated diseases of the spine. So, those patients who already suffer from other types of hernias or disc protrusion should be especially careful.
The first symptom of the disease is acute, persistent pain at the site of the hernia. Pain is triggered by stress, heavy lifting, heavy exertion and even hypothermia. Most often, the pain is localized in the lower back and then moves to the lower extremities. Along with this comes a feeling of weakness and numbness. Eventually the reflexes in the legs disappear.
If you do not take timely measures and do not receive qualified treatment, then paralysis of the limbs and complete limitation of mobility are possible. This sequestered appearance differs from the usual intervertebral disc herniation. The usual type of disease never leads to paralysis.
Along with paralysis, a serious complication of the disease is an autoimmune reaction that occurs when fragments of the collapsed nucleus fly out of the disc and enter the spinal canal, causing inflammation.
In non-acute cases of the disease, conservative treatment methods are used. With drug treatment, lifestyle changes and physical therapy, more than 70% of patients achieve lasting positive results.
We list the basic principles of non-surgical treatment:
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to relieve swelling and inflammation;
- corticosteroids are prescribed to prevent autoimmune reactions;
- drugs to reduce muscle spasms;
- analgesics for severe pain.
After the external symptoms of the disease have been removed and the acute period has passed, physical therapy and gymnastics are prescribed and emphasis is placed on strengthening the muscle corset with the help of specially selected exercises.
If conservative treatment is ineffective and the patient complains of a deterioration in general condition, then surgery is used to eliminate the hernia.
Such operations belong to the class of neurosurgical and are performed using microscopes, video cameras and other high-precision modern equipment. They have the lowest percentage of hernia recurrences.
Since sequestered hernia of the spine is a serious disease affecting the spinal nerves, rehabilitation after surgery is quite complex.
At the first stage, the patient is provided with complete rest and is prohibited from moving. During the first month, the operated patient can only lie down. If there is no pain or numbness, then you are allowed to sit down. In the first two to three months, it is prohibited to sit for long periods of time, engage in heavy labor, and drive a car for more than 1.5 hours a day.
The load on the hands is increased gradually. So, in the first month it is forbidden to lift weights of more than 1.5 kg, and later the load is increased to 3 kg for each hand separately. This distribution allows the spine to gradually recover and strengthen.
To keep the spine in the right condition, it is recommended to wear a postoperative bandage. The bandage is selected exclusively by a specialist, depending on the affected area, and is worn for several hours a day. Gradually, the periods of wearing it are reduced.
Doctors recommend gentle physical therapy during the rehabilitation period, as well as free swimming and massage.
Thus, treatment of sequestered spinal hernia is a rather lengthy process. When the first symptoms of disc protrusion appear, you should immediately consult a doctor in order to avoid complications such as paralysis. It is worth remembering that a hernia is not a death sentence. In 70% of cases, the doctor will suggest conservative treatment based on medications and exercise. Surgery is prescribed in extreme cases.
Sequestration loss, as a rule, occurs after high physical activity or sudden incorrect movement as a result of severe muscle spasm. In rare cases there may be no apparent cause, but this is the exception.
Sequestration is accompanied by sharp pain in the damaged part of the spine. Depending on the location of the pain, there are several types of hernia:
- cervical region. The result of rupture of the fibrous ring and prolapse of the nucleus between the 6th and 7th vertebrae (18-19% of cases);
- lumbar region. Located between the lumbar and sacral regions. People call it “cauda equina syndrome” (up to 80% of cases);
- thoracic region. The cause is constant stress in 1-2% of patients.
In addition to the location of the hernia, it is important to determine the direction of the original focus.
Circular. The maximum protrusion is directed to the dorsal or foraminal zone - the entire disc is uniformly affected, but the greatest protrusion is located in its posterior part.
Dorsal. The protrusion occurs on the back surface of the spine, in the spinal canal.
Foraminal. Damage to the area where the spinal nerves exit.
Training exercises
At stages 1 and 2 of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, exercises help:
When performing training, it is important to exclude risky positions: half-bending without support and turning the body, which can aggravate the course of the disease by damaging the bony base of the spine.
Even “advanced” joint problems can be cured at home! Just remember to apply this once a day.
Patients should not forget that exercises for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region will only be beneficial if done in doses and not excessively. Increased, and therefore harmful, load on the muscular system leads to weakness and even decreased immunity; serves as a favorable condition for wear of intervertebral discs.
Deterioration of health (dizziness, nausea, lack of coordination of movements) is the basis for stopping the exercises and visiting a specialist again.
How to consolidate the result
The positive effect obtained as a result of charging will be even more pronounced if it is fixed. The techniques discussed in the table help eliminate residual tension and prevent the replacement of muscle fibers with connective or fatty tissue.
| A technique that promotes positive dynamics and recovery | Purpose of the technique | Features, important recommendations |
| Massage | By compressing the densified fiber area:
| Only a massage therapist or chiropractor can carry out the procedure correctly. Carrying out the action in question by a non-professional is dangerous due to multiple complications |
| Hardening the body | Prevention of expanding the spectrum of pathology. By improving the tone of blood vessels, patients are less susceptible to body hypothermia, a factor that contributes to the exacerbation of inflammatory processes. | You need to harden gradually, avoiding hypothermia and aggravating phenomena |
| Acupuncture | Effectively reduces muscle tension, helps reduce pain, and increase the volume of physical activity | Only a doctor who has certificates to carry out the relevant activities can carry out the procedure safely. |
| Static stretch | The protein complex of the metabolic environment located inside the disc is normalized, which helps prevent the destruction of the cartilaginous part of the vertebrae and prevents their drying out | The stretching procedure requires gradual implementation. Trying to restore the condition of the vertebrae in one procedure is impractical and dangerous |
For older patients, it is important to consider age as the muscles may be shortened or atrophied. The best adviser in this matter is a chiropractor, who will determine what exercises are needed to treat a particular patient and whether, in principle, exercises for the spine will help him with osteochondrosis.
Treatment methods
Treatment of a sequestered hernia largely depends on its location and severity of symptoms. In most cases, surgery will be required. In some cases, it is possible to prescribe drug therapy, but it does not cure the disease completely, it only temporarily relieves discomfort and relieves pain.
Today, surgery uses two methods to remove a sequestered hernia:
- minimally invasive (laser vaporization)
- radical (laminectomy, discectomy)
The most popular method today. During the operation, a laser light guide is inserted into the cartilage fibers and heats the core of the disc, as a result of which the amount of fluid in the core decreases and its size becomes smaller.
This type of operation is the least traumatic and has a minimal rehabilitation period. The use of laser has a low level of structural changes that are typical for surgical intervention.
The disadvantages of laser vaporization include insufficiently studied side effects that appear in the postoperative period. Swelling or inflammation may appear at the intervention site, requiring additional treatment. In addition, it should be noted that this method does not completely restore the motor activity of the vertebra.
These radical methods involve removing the diseased disc and installing a titanium prosthesis to preserve the motor activity of the spine.
A microdiscectomy uses a microscope and removes the damaged disc through a small incision. With this method, nearby tissues are not injured. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. This method is highly effective, the risk of relapse is minimal - no more than 10%. After the operation, function in the affected area is completely restored.
Disadvantages include the presence of adhesions, possible inflammatory processes in the membrane of the spinal cord and a long recovery period.
Additional recommendations
In severe stages of the disease, in addition to exercise, the following rules of conduct in everyday situations are recommended:
- Try to bend over as little as possible during the day - while cleaning the house or lifting various objects from the floor. If these movements cannot be excluded, be sure to keep your back straight when bending.
- It is important for women to purchase a bra that matches their body parameters and does not tighten the chest area. Incorrect selection of underwear is a favorable condition for deformation of the thoracic vertebrae.
- Reduce daily rotations and twisting of the body to facilitate the functioning of the intervertebral discs, reducing the load on them.
- Avoid prolonged stays in uncomfortable, fixed positions.
It is advisable to use a special bandage (corrector). The device is especially useful if osteochondrosis of the thoracic region has developed in response to a systematic violation of posture.
Benefit
Exercise for osteochondrosis solves the following problems:
- Eliminates problems with blood circulation. Osteochondrosis is a degenerative pathology, and training allows you to establish nutrition for the nerves and musculoskeletal structures that make up the spine.
- Strengthens the muscle corset. Weakened muscles located near the spine cannot withstand the load, and at the same time the bone base is damaged, and it is not capable of independent regeneration.
- Stops spasm. Back pain occurs as a result of muscle strain. By relaxing the muscles, the patient gets rid of pain, and his condition improves significantly.
It is imperative to identify and eliminate the causes of the development of pathology, since all exercises will be useless if the negative impact on the spine continues.
If exercises are carried out regularly, then after 2-3 weeks the patient will feel improvements:
- the feeling of tightness in the spine will disappear;
- pain and fatigue will pass;
- the inflammatory process in tissues will decrease;
- the general condition of the body will become significantly better - vigor will appear, immunity will improve;
- the effectiveness of medications taken will increase;
- the muscles will be stronger and more mobile.
Features of massage and other procedures
Typically, physical therapy is prescribed 2 weeks after surgery, that is, already in the late postoperative period. One of these procedures is massage. It should be done in the first days, when the spinal cord nerve roots are restored. It should be as gentle as possible.
A properly selected massage technique reduces the likelihood of numbness, improves nerve conduction and prevents limb weakness.
Acupuncture is prescribed even later - about a month after surgery. It cannot be recommended to absolutely all patients. The procedure is performed only by qualified specialists and only as prescribed by a doctor.
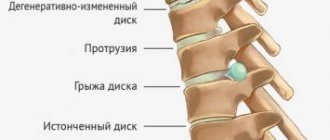
Cartilaginous discs running between the vertebrae allow movement. When there are problems and injuries to the discs, which often occurs with osteochondrosis, they burst and the central part goes beyond the intervertebral space. In this case, a hernia forms, which compresses the nerve endings and provokes severe pain and impaired movement.
If the changes that occur are quite pronounced and do not respond to conservative therapy, then surgical intervention is performed. A spinal hernia is removed using modern, low-traumatic techniques, without significant incisions or damage to soft tissue. In particular, the following is carried out:
- endoscopic excision;
- laser vaporization;
- plastic surgery to strengthen the vertebrae.
Laser therapy is considered the most preferred method, since it provides the most effective and gentle effect that helps eliminate the hernia. In addition, such surgical intervention has much less negative consequences. It is also possible to quickly restore damaged cartilage.
Rules
It is best to perform the exercises under the supervision of a physical therapy instructor, at least for the first time. In the future, you can practice at home on your own.
To get the most out of charging, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- Exercises must be performed daily, otherwise there will be no result.
- Clothing for classes should be comfortable.
- Before charging, you can take a warm shower to warm up your muscles.
- The first exercises should be aimed at stretching.
- The load should increase gradually as the muscles strengthen.
- Sudden movements are prohibited - all exercises are performed only smoothly.
- It is recommended to charge for 20 minutes, but 10 minutes is enough to get started.
- The number of approaches is 2-3.
- If pain occurs while performing exercises, you should stop immediately and seek advice from a specialist.
- There should be short rest periods while charging.
- When performing exercises, you need to drink a lot of water, then the cartilage tissue will recover faster.
- Be sure to correct your posture, otherwise all your efforts will come to nothing.
General recommendations
Therapeutic and preventive exercises for osteochondrosis, regardless of the method of implementation and points of influence, are carried out according to certain rules:
- movements are performed evenly, smoothly, without sudden jerks;
- in any position - sitting, standing, when walking, watch your posture - shoulders turned, head, back - straight;
- exercises for osteochondrosis are carried out in a room with good ventilation;
- It is advisable to “remove” extraneous irritants during exercise – loud music, screams, intense light;
- don't forget about clothes! It should be spacious, made of natural material;
- As soon as pain appears during charging, stop immediately.
Read also: How to cure osteochondrosis at home
Set of exercises
Here are a few exercises that are recommended to be performed for osteochondrosis of thoracic calving:
You can learn more about the benefits of exercises for thoracic osteochondrosis, as well as see instructions for different types of complexes here.
In the morning you need to do a warm-up, the duration of the warm-up is no more than 5-7 minutes, in addition, it is very easy to do:
- stretch while lying on your back - stretching the spine;
- moving your shoulders in a circle while lying on your back;
- while sitting or lying down, rotate your arms in the elbow area;
- while standing, make several smooth bends forward, to the sides, as well as circular movements of the body;
- standing, raise your knees bent forward.
Rhythmic exercises are carried out at a fast pace; they allow you to strengthen the muscles of the back and abdomen in order to prevent the development of thoracic osteochondrosis and develop correct posture. To perform these exercises you will need dumbbells, a tourniquet and a wooden pole (mop or shovel handle).
- Standing, hold the pole with both hands, so that the distance between your palms is slightly wider than your shoulders. Raise the pole to chest level, arms extended at the elbows, then inhale and press the pole to the chest, elbows move back, shoulder blades move closer to each other. Repeat 10-15 times.
- The starting position is the same. As you exhale, lift the pole up; as you inhale, the pole returns to your chest.
- Your feet should be placed wider than your shoulders, and the pole should be held in your hands behind your back at shoulder level. Squat, tilting your head and torso forward, and stretching your arms with the pole in front of you. Return to starting position. Repeat 5-10 times.
- Hold the tourniquet by both ends with your hands, extend your arms in front of you. As you inhale, the arms are straightened, as you exhale, they are pulled towards the chest, while the tourniquet is stretched as much as possible (the arms move to the sides). Repeat 10-15 times.
- Hands with a tourniquet are raised above your head, while exhaling, bring them back and stretch the tourniquet at the level of the shoulder blades. Return your hands to the starting position. Repeat 10-15 times.
- Get down on one knee, as if doing a lunge. Bend the other leg at a right angle, keeping your back straight. Take a small dumbbell in your hand from the side resting on your knee and, while inhaling, lift it up and to the side. Repeat 5 times, then change knees and work the other side of your back.
- Lying face down, place one hand behind your head, straighten the other at the elbow and turn your palm out, lift it 10 cm from the floor. Repeat 10 times, then do the same on the other hand.
What to do at home?
A set of exercises performed at home should be selected by a doctor on an individual basis. Below are the main ones.
- Lying on your back, stretch well and inhale, straighten your arms above your head. As you exhale, return your arms along your body.
- Lying on your back with your palms clasped at the back of your head, tighten your abdominal muscles and raise your head and shoulders.
- Lying on your stomach with your arms extended forward, lift each shoulder and arm up in turn.
- While sitting on a chair, rest your upper third of your back against the back of the chair, bend back, and throw your head back. Hold for 5 seconds, return to the starting position.
- Sitting on the floor or on a chair, clasp your hands at the back of your head and twist your body in both directions, so that the twist is felt in the thoracic area.
- Standing on all fours, arch your back, keep your head straight. Hold the pose for 10 seconds, then relax.
- Standing straight, bring your hands clenched into fists back and place them below your shoulder blades. Pulling your shoulders back, arch your back and press your fists into your back. Then unclench your fists and smoothly lean forward, relaxing your back.
- Hanging on the bar. If it is not possible to perform a full hang, you can perform a partial hang, but the effectiveness of such a hang is lower.
- It's good to stretch your spine while in the water. In a large circle, go into the water to a depth of more than 2 meters, so that your feet do not touch the bottom, and hang afloat for 20 minutes.
- Lying on your stomach, lift your chest off the floor, stretch your arms perpendicular to your back. Bring your shoulder blades together, your arms are relaxed, but also slightly moved back. Hold the pose for 10-60 seconds.
For proper breathing
- Sitting on a chair with a straight back, wrap the lower part of your chest with thick fabric. Holding the ends of the fabric with your hands, you need to slowly pull it, while taking a deep breath. Holding your breath at maximum, loosen the tension of the tissue and exhale.
- While standing, slowly bend towards the floor, in the middle of the tilt, take a breath through the nose, which ends with the tilt of the body. Straighten up and exhale.
- Breathe sharply according to a certain pattern - 4 inhalations through the nose, 4 exhalations through the mouth. After inhalations there should be a pause of 3-5 seconds. The shoulders and stomach do not take part in breathing.
Indications for exercise therapy
Important arteries pass through the neck, supplying food to the brain.
Therefore, neck mobility must be maintained until old age. In exercise therapy for osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebra, it is prescribed for various reasons, mainly recommendations for treatment take place when certain functions of the spine are impaired, resulting from injury, heavy physical work, or sports associated with lifting weights. There are proprietary methods developed specifically to eliminate cervical osteochondrosis, for example, Dikul isometric gymnastics. It helps restore mobility to the vertebrae, relieves pain, and helps prevent intervertebral hernias. All sets of exercises for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine can be dynamic and static (isometric) in nature.
Before starting classes, you should definitely consult with a specialist. With the right approach through consultations and sessions with your doctor or trainer, even the first physical exercises can have a beneficial effect on the patient and his recovery.
Dynamic exercises
A set of exercises for the cervical spine consists of tilting the head back and in different directions, repeated several times. Simple but regular exercise helps eliminate symptoms that cause pain and helps relax the muscles of the cervical spine. Most exercises are performed while sitting on a chair or standing.
Static exercises
When performing static exercises, the whole body is tensed and held in a certain position for several seconds, and then the original state is returned. At the same time, flexibility of the spine develops and blood circulation improves. The amplitude of vibrations when performing isometric (static) exercises should be minimal. This exercise is aimed at strengthening the cervical and lateral muscle tissues. Such exercises are indispensable for those who lead a sedentary lifestyle.
Additional recommendations
If the stage of the disease is severe, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules in everyday life:
- Bend over as little as possible when cleaning or lifting objects. If it is possible to avoid bending, they should be performed with a straight back.
- Women should wear a bra that does not tighten the chest area - incorrect selection of underwear can contribute to deformation of the thoracic vertebrae.
- Rotate the body less to reduce the load on the vertebrae.
- Avoid prolonged stays in uncomfortable and static body positions.
- It is recommended to wear a special corrector – a bandage.
It is categorically undesirable to delay treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis; it can lead to irreversible consequences. Regular exercise significantly reduces the transition of the disease to a chronic form and minimizes the likelihood of surgical treatment of osteochondrosis.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic segment of the spine occurs less frequently than damage to the cervical and lumbar spine. Its peculiarity is that symptoms usually occur with significant wear of the intervertebral discs. An important sign of pathology is periodic sharp pain between the shoulder blades, especially in a sitting and inclined position.
The main cause of the disease is a passive lifestyle and working at a computer, which causes congestion in the vertebrae and disruption of their blood supply. To help the patient in such a situation, special exercises for thoracic osteochondrosis are intended - an obligatory component of therapy.
Charging - how does it work for osteochondrosis?
Exercise refers to a set of exercises aimed at relaxing the desired muscle groups. Of course, exercise performed daily by a healthy person will be very different from exercise with back problems. The basis of physical therapy is natural body movements, which completely eliminate injury and aggravation of the human condition. After exercise, there should be no overstretching of the muscles, severe fatigue, or increased pain.
Exercises are carried out at home, include only simple exercises and can be easily performed even without physical training. Exercise therapy is considered the most effective way to prevent thoracic osteochondrosis. If the disease already exists, then the results from doing the exercises will also be noticeable:
- Reducing pain due to the growth of intervertebral spaces and reducing pressure on blood vessels and nerves;
- Relieving muscle spasm, pinching, swelling;
- Strengthening the muscles of the back and chest;
- Creating a sufficiently strong muscle corset - good support for the spine;
- Improving the quality of blood supply to the vertebrae and cartilage;
- Increased elasticity of ligaments, which will reduce the load on the spinal column;
- Acceleration of cellular metabolism, tissue regeneration processes;
- Reducing the stiffness of the patient’s movements, increasing the range of motion of the spine;
- Improved posture, which will optimize the distribution of load on the spine;
- Restoring normal ventilation.
Exercise for osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine will affect the cause of the pathology - changes in the discs and vertebrae due to impaired blood supply. In this way, exercise therapy is fundamentally different from ointments and some tablets, which are exclusively symptomatic.
Physiotherapy
The selection of exercises for patients with sequestered hernia should be done exclusively by the attending physician. He knows exactly what physical activity on what muscle groups will be optimal in each specific case. Self-selected exercises may not only be useless for the patient, but also cause harm to the body or lead to exacerbation.
A sequestered hernia is a disease that can lead to disability. Its treatment takes a long period and surgical intervention is required for complete recovery. Additional treatments provide short-term pain relief and temporary improvement. A timely visit to a doctor will help you quickly return to your normal lifestyle and minimize possible complications.
Even if no negative consequences are observed after the hernia excision operation, and the recovery period is actively underway, exercise therapy can be performed no earlier than 2 months later. The set of exercises must be selected by the doctor, taking into account all available indications and contraindications.
Basically, during this period, many exercises to strengthen the back muscles are performed while lying on the floor, so you first need to prepare a fairly soft mat. Classes must be done daily, as this is the only way to achieve good results.
Who shouldn't do exercises?
Exercises can be harmful if performed without taking into account the recommendations of a specialist. It is important to take the entire range of diagnostic measures and make a correct diagnosis before starting exercise therapy. The causes of pain may be other than the development of osteochondrosis (intercostal neuralgia, diseases of internal organs, tumors), and uncontrolled exercise will cause damage to the body.
Special gymnastics is also needed for vertebral instability, scoliosis, kyphosis, and only a doctor can develop it!
The main contraindication to exercise concerns the acute phase of osteochondrosis. When the pain is severe, the inflammation is more pronounced, overloading the back is strictly prohibited. Physical activity can increase pinched nerves and force a person to go to the hospital. Exercises for flexion and extension of the back are especially poorly tolerated: the pain from such actions will definitely increase, as will inflammation. During an exacerbation, spinal traction has worked well, but it is performed under the supervision of a doctor.
Other contraindications to charging:
- Acute infections;
- Spinal injuries;
- The presence of a herniated disc;
- Oncopathology;
- Autoimmune lesions of the spine;
- Exacerbation of diseases of internal organs;
- Serious diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
How is the disease diagnosed?
The main standard for diagnosing a sequestered hernia is a comprehensive examination by a neurologist. During the initial examination, he checks the sensitivity and presence of tendon reflexes in the patient, determines the degree of development of the disease. If necessary, prescribes treatment and additional examination.
The most complete information about the presence of an intervertebral hernia and its condition, as well as the degree of compression of nerve endings, is provided by the method of magnetic resonance therapy. This method allows you to establish sequestration, accurately determine the localization site and plan the course of the operation.
If MRI is not possible, CT scan images will be sufficiently informative. But CT images are not clear enough and can only be used as a last resort.
Recently, experts have abandoned the use of radiography, considering this method uninformative and outdated. It does not give a complete picture of the location of the hernia.
Before the operation is scheduled, general clinical laboratory tests are prescribed, which are of auxiliary value, but they are not important for diagnosis.
Charging rules
The ideal option is to carry out the first classes together with a physical therapy instructor. Further, warm-up and training of the thoracic region can be done at home, on your own. You need to start exercising after relieving pain with the help of massage and medications. For elderly patients and in advanced stages of pathology, the loads are the most gentle.
Exercise for thoracic osteochondrosis involves following the following recommendations:
- Exercises must be done regularly (daily), otherwise positive effects will not be achieved.
- For exercise, it is better to wear loose, comfortable clothes, and immediately before exercise, take a warm shower to warm up your muscles.
- The first exercises should always be aimed at stretching tendons, ligaments, and muscles.
- A gradual increase in loads is practiced as the muscles strengthen.
- Jerky movements are strictly prohibited; all movements must be smooth.
- The maximum duration of classes is 20 minutes, the number of approaches per day is 2-3. At the initial stage, it is enough to exercise for 10 minutes once a day.
- Be sure to remember to take short rest periods while charging.
- If pain or other discomfort occurs, you should immediately stop exercising and consult a specialist.
- From the beginning of the exercises, you should drink more water so that cartilage restoration occurs at a more intense pace.
- At the same time, it is necessary to correct your posture, otherwise the positive dynamics will come to naught.
Morning exercises and activities outside the home
Morning warm-up will help you get used to daily exercise: this is where you should start training. Charging duration is 5-7 minutes, it is very simple to perform. The exercises are:
- Stretch, trying to stretch the spine (lying down);
- Move your shoulders in a circle, pull them up (lying down);
- Rotate your arms in the elbow area (lying or sitting);
- Perform smooth bends forward, to the sides, and body turns (while standing);
- Raise your bent legs forward (while standing).
With thoracic osteochondrosis, exercises can be done even at the workplace. To do this, while sitting on a chair, you need to bend your back forward, inhaling and exhaling deeply while relaxing. You can also clasp your hands above your head and bend to the sides. In the car, you can also stretch your stiff back: stretch your shoulders forward, then move them back so that the shoulder blades come closer together. Rotate your shoulders. Repeat the lesson 5-10 times.
Exercises against thoracic osteochondrosis at home
Exercising for thoracic osteochondrosis at home can include many different exercises, but the entire complex is selected individually by the doctor. Before charging, it is advisable to walk around, raising and lowering your arms, moving your shoulders. This will help prepare your joints and ligaments for training.
The set of exercises is as follows:
- Lie on your back and stretch well. Take a breath. Straighten your arms above your head, and as you exhale, straighten them along your body.
- On your back, fold your hands behind your head, then strain your abdominal muscles, while raising your head and shoulders.
- On your stomach, place your palms under your shoulders on the floor, slowly raise your upper body, while arching your back in the thoracic region. At the very top, more precisely, you need to linger for a few seconds, then lower yourself to the floor.
- Stretch your arms out in front of you on your stomach, place your head parallel to the floor. Lift each shoulder in turn from the floor, while raising your arm up.
- Get on all fours, arch your back, hold. Keep your head straight. After 10 seconds, relax.
- Make a thick tourniquet from a sheet, throw it in the thoracic area. Inhale deeply while tightening the tourniquet in front. When exhaling, you need to fight the resistance of the tourniquet.
- Stand straight, hands in fists, place them on your back below the shoulder blades. Pull your shoulders back, bend your back, pressing on it with your fists. Slowly tilt your head back. Then unclench your fists, smoothly lean forward, hunching your back, and return your head to its original position.
All exercises are also suitable for the prevention of osteochondrosis, so they will be useful for every person.
Physical education for cervical osteochondrosis of the spine: basic exercises
If you are faced with constant pain in your head and neck, dizziness, weakness in your arms, or a burning sensation between your shoulder blades, you should immediately consult a specialist and undergo an examination. These may be symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis. If the disease is diagnosed, comprehensive treatment should begin, a mandatory part of which is physical therapy. It is recommended to do the following exercises:
- Turn the head in both directions. It is very important to perform them carefully, with a small amplitude - this will not cause harm to the vertebrae.
- Bend forward. They will gradually strengthen the neck muscles and help normalize blood circulation.
- Stretching the neck to the left and up, to the right and up. Strengthens the muscle corset, eliminates compression of the vertebrae.
The ideal starting position for all exercises is standing with your arms at your sides. If this is not possible, you can practice while sitting. It is advisable to do similar exercises near an open window in order to simultaneously saturate the muscles and tissues with oxygen.
It is gradually possible to complicate the training by adding other basic exercises to it:
- Include static loads in exercise therapy. Clasp your hands, place them on your forehead, then, straining your neck muscles, try to move your head back. Freeze in a pressing position for 10-20 seconds, relax.
- The exercise is similar to the previous one, but the hands are placed in a lock at the back of the head. Using the force of your neck muscles, you should try to move your head back, fighting the resistance of your hands. Stay in the pressing position for 10-20 seconds, then relax. Such exercises effectively stretch the muscles and help relieve the painful manifestations of osteochondrosis.
- Place your hand on your ear. Bend to the right or left, exerting slight resistance with your hand. Stay in the inclined position, relax, and then repeat the exercises in the other direction.
Read also: Treat osteochondrosis at home
The same complex can be used to prevent disease. The main thing is to gradually increase the load, avoid overwork and pain, try to exercise not for the sake of “showing off”, but to regain your health. After a couple of months, you will notice improvements - the spinal column will gain greater flexibility, the pain will subside, and the muscles will become more elastic.