As a result of overexertion or injury to the spine, lumbosacral or gluteal region, hypothermia or unsuccessful injection, the so-called piriformis syndrome occurs. Its manifestations are pain in the buttock, which radiates to the upper thigh, lower leg and groin, accompanied by numbness (manifestations of sciatica).
The following methods are used for treatment:
- drug therapy;
- special exercises;
- relaxation massage;
- physiotherapy.
Butt stretch
Lying on your back, legs bent at the knees. Place your right ankle on your left knee. Grab your left thigh and pull it towards your chest. You will feel a stretch along your buttock and outer thigh. Hold the achieved position for 15-30 seconds. Then repeat the exercise with the other leg. 3 reps on each leg.
Relaxing massage
This is another effective treatment for muscle spasms, including the piriformis muscle. It begins with kneading the paravertebral and lumbosacral areas, then massaging the sore buttock and finally the back surface of the leg.
The session lasts about 15-20 minutes, 12 to 20 procedures are required per course of treatment. To consolidate, repeat after a month. Acupressure is also used for this purpose.
Leg abduction with expander
Stand by the door, with your healthy side facing it. Attach the end of the resistance band to the ankle of the affected leg, and the other end to a door or other stationary object at ankle level. Move your straight leg to the side, then return to the starting position. 2 sets of 15 reps. To enhance the effectiveness of the exercise, gradually move further away from the door.
Treatment methods
After making a final diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment. As a rule, it is complex and consists of several components:
- Drug therapy.
- Massage.
- Manual therapy.
- Physiotherapeutic treatment.
- Reflexology.
- Physiotherapy.
- Corrective treatment (insoles, buttock pads, etc.).
Drug treatment:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. The basis of drug therapy is drugs from the group of anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs. The most effective drugs based on diclofenac have proven themselves - Voltaren, Dikloberl, Diklo-F, Meloxicam, Ketanov, etc. Depending on the degree of development of the disease, they are prescribed orally or intramuscularly. The course of treatment is at least 10 days, 2 injections of the drug are given daily with a period of 6 hours.
- If the patient is in pain, painkillers and antispasmodics are prescribed. They relieve muscle spasms well, reduce pressure on the sciatic nerve and surrounding vessels. Suitable painkillers include: Baralgin, Tempalgin, Sedalgin, etc. The most commonly used antispasmodics are No-Shpa, which is administered intramuscularly along with anti-inflammatory drugs.
- If the inflammatory process is complicated by bone deformation, then antispasmodics cannot fully relieve the painful spasm. In this case, muscle relaxants are prescribed. They effectively relieve tone from inflamed muscles, freeing pinched nerves and blood vessels. Most often, doctors prescribe Mydocalm.
- Drug therapy may include drug blockades. When inflamed, the piriformis muscle becomes painfully stretched and compressed, and the roots of the sacral region are involved in the process. The task of the novocaine blockade is to remove spasm and tension from these pelvic structures. The doctor marks the points of the ischial tuberosity, ilium and greater trochanter, connects these marks and determines the area of drug administration. Then he inserts the syringe needle to a depth of 6-8 cm and slowly releases novocaine into the space between the muscle body and the sacral root. The adult dose for blockade is 10 ml.
Pathologies of the piriformis muscle are quite difficult and lengthy to treat. Therefore, the drug course is repeated at least 2 times a year during seasonal exacerbations.
Plank
Lying on your stomach, lean on your elbows at shoulder level. Lift your hips off the floor, balancing on your forearms. It is important that your hips and shoulders are in line. Try to hold this position for 15 seconds. Then slowly lower yourself to the floor and relax. In the first stages, you can simplify the exercise by resting on the floor with your knees instead of your toes. Gradually increase the time you hold the plank to 1 minute.
Causes of piriformis syndrome on the left and right
The piriformis muscle is located in the pelvic area, is subject to large static loads and can be injured during active movement.
The following reasons for the development of piriformis syndrome on the left or right side are also identified:
- prolonged sitting or any position that involves flexion of the hip joint;
Due to a passive lifestyle and excess weight, the piriformis muscle often becomes inflamed. - fast walking that started with a sudden movement;
- long distance running;
- hypothermia of tissues located in the pelvic area;
- intervertebral hernia or other spinal diseases;
- riding a bicycle with an uncomfortable or very narrow seat.
In medical practice, there are cases when a spasm of the muscle fibers of the pelvic area occurs after a person falls from a great height, gets hit, or receives other mechanical injuries. Eliminating the cause of the pathology is a prerequisite for successful treatment.
Side plank
Lying on your side. Shins, hips and shoulders are on the same line. Rest on your elbow directly under your shoulder. Lift your hips off the floor while balancing on your elbow. Try to hold this position for 15 seconds. Then slowly lower your hips to the floor. Switch sides and repeat the exercise. In the first stages, the exercise can be simplified by bending your knees and hips towards your chest.
Characteristic symptoms
Signs of piriformis syndrome are manifested by dysfunction of the sciatic nerve, as well as the following symptoms:
- sharp or aching pain in the buttock area on the side where the muscle fibers spasmed;
- numbness of the lower limb;
- impaired mobility of the hip and knee joints;
- involuntary contraction and twitching of the muscles located on the inside of the thigh.
Almost all symptoms of the disease are neurological in nature, since spasm of the piriformis muscle disrupts the functioning of the sciatic nerve. In addition to the above signs of pathology, a person loses the ability to fully move and complains of acute pain that appears when trying to sit down.
What to do if you pulled a muscle
How to tell if you have a sprain
First, let's figure out how to understand that you have pulled a muscle. A sprain may appear during training - at one point you will feel a sharp pain. The severity of the pain will directly depend on the severity of the injury. Minor sprains may not interfere with your ability to work. Severe injuries will cause hellish pain, through which you will not be able to get over without pain relief.
https://youtu.be/jQJ5Hgu0Wlw
In some cases, pain occurs after sprains. For example, today you were playing table tennis and slipped, almost doing the splits (despite the fact that you cannot sit on it). As long as you continue playing, there is no pain. At home, after you have not moved for a while, you will feel a sharp pain somewhere in the back or outer part of your thigh. This is delayed pain.
A few hours after the pain, when examining the injury site, swelling and redness can be detected. The next day, a small bruise (blue-yellow) may form in that area. If these signs appear, you definitely have a sprain.
Don't confuse sprains with tears and fractures. For example, when your foot suddenly falls into a small hole while walking, you put your foot on one side. The muscles do not have time to fix the position of the leg, as a result of which the entire load is transferred to the ligaments. Naturally, they can tear. In this case, the leg in the ankle area will swell on both sides. In a day or two, a large bruise will appear. In this case, there may be either a rupture or a crack in the bone.
Therapeutic recommendations
When a pathology is diagnosed, drug therapy is prescribed, which depends on the root cause of the disease. They help eliminate spasms and help return to your normal lifestyle. A specialist may also prescribe physical therapy.
A mandatory component of treatment is:
- massage,
- compresses.
- physiotherapeutic procedures.
In parallel with medications, traditional medicine recipes are also used.
Physiotherapeutic procedures help eliminate muscle spasms and pain.
The following types are used:
- heating via UHF;
- ultrasonic influence;
- electrophoresis with hydrocartisone;
- applying applications with paraffin;
- massage using vacuum;
- dynamic currents;
- phonophoresis;
- amplipulse
The combination of physiotherapeutic procedures with muscle relaxants, deep massage of the affected area, and a complex of therapeutic exercises, as a rule, brings results.
Diagnostics
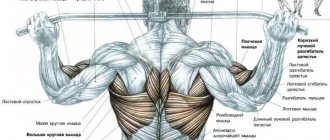
Pain syndrome with damage to the gluteal muscle is pronounced. However, similar symptoms may be accompanied by pathologies of the hip joint or lumbar region. The main method for identifying violations is palpation of the painful area and adjacent areas.
During the examination, the doctor palpates:
- the inner side of the femur;
- sacroiliac joint;
- sacrospinous junction;
- hip joint;
- piriformis muscle.
To clarify the diagnosis, transrectal palpation is sometimes prescribed. In case of traumatic injuries, they are additionally sent for an X-ray, computed tomography or MRI. After research, an accurate diagnosis is made with a code according to ICD-10, the international classification of diseases.
The dangers of continuing to work through pain
If you hope that the pain will go away during training and continue to work, you can get a complication. The tendon will become inflamed and fluid will accumulate around it. This will lead to the fact that while moving you will hear a characteristic dull crunch in the sore spot.
Over time, the acute pain will pass, but the inflammation will remain. You will be able to do daily procedures (pick up a kettle, walk), but with stronger loads it will hurt. And this pain will not go away.
If you have pushed the situation to this stage, it’s time to contact a traumatologist. After the MRI, he will refer you for physical therapy.
The main one is electrophoresis, which allows you to deliver medicine (usually iodine, dimexide and painkillers) through the skin to the desired location using an electric field. Usually 10 procedures are prescribed. And everything ends with recovery - now you need to start rehabilitation.
If electrophoresis does not help enough, another 10 sessions of magnetic treatment are prescribed. As a rule, this is where it all ends. If this does not help, a permanent cast may be applied for 2 weeks. So think about whether it’s worth exercising through pain.
Painful sensations can last for months, six months or more. If left untreated, the tendon will lose elasticity and you will not be able to fully train. So get treatment on time.