General information
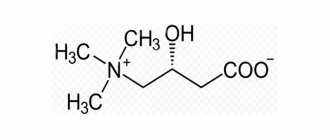
Vitamin B5 is a water-soluble compound that, when it enters the human body, is converted into pantethine, a substance that is part of the acetylation coenzyme (A), which plays a key role in all types of metabolism: protein, lipid and carbohydrate.
Vitamin B5 exists in two forms:
- pantothenic acid (from the Greek pantothen, which means “everywhere”, as it is widespread in nature);
- calcium pantothenate (a medicinal form of pantothenic acid, which is its calcium salt).
Pantothenic acid was discovered by American biochemist Roger Williams in 1933. While studying natural substances that stimulate the growth of yeast, he discovered an acidic, heat-labile substance, which, as it turned out later, is found in small quantities in most organisms of both plant and animal origin.
In 1940, a group of scientists led by Professor Williams managed to decipher the chemical structure of a substance consisting of residues of the amino acid β-alanine and pantoic acid, which was called pantothenic acid, and also synthesized this compound in a highly purified state from liver extracts, which was in crystalline form. calcium salt.
Parallel studies have revealed that liver extract freed from thiamine, riboflavin and pyridoxine cures nutritional dermatitis in chickens. The antidermatitis factor was called vitamin G, but upon further study of the compound, scientists discovered that it is identical in structure and function to pantothenic acid.
After the discovery of the vital coenzyme A in 1947, scientists proved the vitamin nature of pantothenic acid and renamed it vitamin B5. Despite the serial number 5, this vitamin was discovered fourth among the B vitamins, but after the discovery of vitamin B6.
Pantothenic acid deficiency
Since pantothenic acid is found in almost all foods, deficiency is very rare, mainly in severe cases of malnutrition. The effects of vitamin B5 deficiency are difficult to isolate because it is often accompanied by deficiencies in many other nutrients. The few reliably known individuals who were deficient in pantothenic acid either ate foods that contained virtually no pantothenic acid or took drugs that were antagonists of pantothenic acid metabolism.
Experiences from World War II prisoners of war and studies of diets deficient in vitamin B5 and combined with pantothenic acid metabolism antagonists show that pantothenic acid deficiency is associated with numbness and burning of the hands and feet, headaches, fatigue, irritability, anxiety, sleep disturbances and nutrition.
At-risk groups
People with Hallervorden-Spatz disease
Pantothenate kinase is an enzyme required for the production of CoA. Mutations in the PANK2 gene, responsible for its synthesis, cause a rare inherited disease - Hallervorden-Spatz disease, or neurodegeneration with iron deposition in the brain type 1. It can manifest as dystonia (spasms of opposing muscle groups), spasticity (abnormally high muscle contractility) and pigmentary retinopathy (coating of the retina with melanin pigment). The disease develops quickly and leads to disability; treatment is primarily aimed at reducing symptoms.
Excess panthethic acid
There are no known cases of panthetic acid poisoning. When taking ultra-high doses of vitamin B5 (about 10 g/day), some patients may experience mild diarrhea and gastrointestinal disturbances, the causes of which are not yet known.
Importance for the body
Pantothenic acid is involved in many biochemical reactions:
- stimulates the synthesis of steroid and glucocorticoid hormones, alleviating the manifestations of allergic reactions, providing a desensitizing effect, reducing pain and local swelling of tissues in inflammatory diseases of the joints, intestines and heart;
— participates in the processes of glucose formation from non-carbohydrate compounds, thanks to which its level in the blood is maintained during fasting, a sharp decrease in the intake of carbohydrates from food, and during the recovery period after intense and prolonged physical activity;
- regulates lipid metabolism, promoting the oxidation of fatty acids and having an inhibitory effect on the formation of low and very low density lipoproteins, thereby providing an antiatherogenic effect;
- participates in protein synthesis more than any other vitamin, helping to increase muscle mass and physical strength;
— takes part in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, reducing the severity of anxiety and depressive disorders, normalizing sleep;
— increases the bioavailability of vitamin E and folic acid;
— increases the absorption of potassium in the intestines, which has a beneficial effect on the strength of muscle contractions, including the myocardium of the heart;
- facilitates the functioning of the liver, accelerating the removal of toxic substances from the body, including those formed from alcohol and radioactive radiation;
- participates in the formation of immunity, promoting the production of antibodies;
- stimulates intestinal peristalsis, as a result of which it is used for intestinal atony after surgical operations on the abdominal organs;
— quickly restores mucous membranes;
- used to treat acne.
Natural Sources of Vitamin B5
The list of foods containing pantothenate in varying concentrations is endlessly long. The widespread distribution of vitamin B5 makes it easy to provide the body with the minimum necessary for the normal course of physiological processes.
| Product name | B5 content in mg per 100 grams of product |
| Green peas (peeled) | 15,0 |
| Baker's yeast | 11,0 |
| Soybeans | 6,8 |
| Apples | 3,5 |
| Rice bran | 3,0 |
| Porcini | 2,7 |
| Buckwheat | 2,6 |
| Oats, dried peas | 2,5 |
| Rice | 2,0 |
| White wheat bread | 1,8 |
| Champignon | 1,7 ̶ 2,5 |
| Peanut | 1,7 |
| Cocoa powder | 1,5 |
| Avocado, asparagus | 1,4 |
| Rye, wheat, beans, cashews | 1,2 |
| Pistachios, barley | 1,0 |
| Flax seeds | 0,99 |
| Cauliflower | 0,98 |
| Rye bread | 0,9 |
| Dates | 0,78 |
| Garlic, broccoli | 0,6 |
| Corn | 0,6 |
| Dried apricots | 0,52 |
| Pumpkin | 0,5 |
| Figs | 0,4 |
| Potato | 0,32 – 0,65 |
| Carrots, grapefruit, eggplant, bell pepper, lemon, cranberry, wheat flour | 0,3 |
| Strawberries | 0,26 |
| Banana, orange | 0,25 |
| Pineapple, beets, watermelon, kiwi, spinach, beans, fennel | 0,2 |
| Onion | 0,13 |
| Tomatoes | 0,1 ̶ 0,37 |
| Strawberry, plum, raspberry, raisin, mustard, leek | 0,1 |
When compiling a daily diet based on the data in the table, it is important to understand that the figures given represent a reference value and may vary depending on the region of growth and the variety of the product itself. In addition, it is necessary to take into account the losses that occur during storage and preparation of food: during heat treatment and canning, about 50% of the total amount of pantothenic acid breaks down, and during freezing - about 30%.
You should also take into account the peculiarities of your own diet, since a high-carbohydrate menu significantly reduces the absorption of pantothenate by the body. Proteins and lipids have a positive effect on the metabolism of vitamin B5, however, if the nutritional formula for some reason is shifted towards carbohydrates, you should either review the menu or increase the dosage of pantothenic acid (if the high carbohydrate content in the menu is explained by medical indications and is temporary nature).
With a properly formed diet, the symptoms of hypovitaminosis will not disturb your body. Natural sources are easily digestible and do not cause any adverse reactions, and therefore are recommended as vitamin therapy for everyone who seeks to maintain their health.
Medicines
Calcium pantothenate (Russia).
It is used in complex therapy of the following diseases and conditions: polyneuritis and neuralgia; bronchitis, bronchial asthma; intestinal atony; eczema; trophic ulcers; burns; allergic reactions; toxicosis of pregnant women; circulatory failure; withdrawal syndrome.
Dexpanthenol (Türkiye).
Gel for external use. Indications: dry skin, violation of the integrity of the skin caused by mechanical, chemical, temperature factors: burns, scratches, abrasions, bullous dermatitis, abscess, boil, trophic ulcers of the lower extremities, bedsores, cracks, aseptic postoperative wounds, poorly taking root skin grafts, erosion cervix, cracks and inflammation of the nipples of the mammary gland in nursing mothers, prevention and treatment of diaper rash, prevention and treatment of diaper dermatitis in young children. Corneal erosion, eye burns, keratitis of various etiologies, dystrophic diseases of the cornea, prevention of corneal damage when wearing contact lenses.
Supradin (Switzerland).
A multivitamin complex that helps prevent general vitamin deficiencies and allows for their treatment, as well as preventing diseases and maintaining the mental and physical condition of the patient. It is used during poor and unbalanced nutrition, increased physical and mental stress, recovery from long-term and/or severe illnesses, including infectious diseases, complex therapy of chronic alcoholism, prescription of antibiotics and chemotherapy.
Price of drugs
The price of pantothenic acid in pharmacies depends on the type of drug and its release form. “Calcium pantothenate” produced by Akrikhin KhFK costs 250-270 rubles. The medicine “Pantothenic acid” from foreign pharmaceutical companies can have a price from 800 to 1000 rubles. “Dexpanthenol” in ampoules costs 120-150 rubles.
The price of pantothenic acid in the form of topical products (ointments, creams) is from 150 to 500 rubles, and vitamin-mineral complexes (Vitrum, Duovit) are from 250 to 500 rubles. The nootropic drug “Pantogam” costs from 560 to 930 rubles.
Notes
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/newsweek/Listing_of_vitamins.htm "PANTOTHENIC ACID (vitamin B5)"
- Small medical encyclopedia. Volume 1. 1991. pp. 330-337
- ↑ 12
And again the repartees... - N.B. Gubergrits, S.V. Nalyotov, P.G. Fomenko. Modern gastroenterology No. 1 (69), 2013. pp. 157-165. - 4.2.2.1.1.8. Pantothenic acid | Norms of physiological needs for energy and nutrients for various groups of the population of the Russian Federation | Office of Rospotrebnadzor for the Kaliningrad region. 39.rospotrebnadzor.ru (December 18, 2008). Retrieved September 20, 2020.
- Shrimton DH (2008) Micronutrients and their interactions. Russian medical journal. T. 16., No. 7.
Precautions and contraindications
There are no restrictions on taking vitamin B5 supplements as such. They are well tolerated by the body.
Sofia Sokolova
Pharmacist. Author of articles on the site
Ask a Question
Possible contraindications include hypervitaminosis and hemophilia. It has been noted that pantothenic acid can increase the period of blood clotting. Such changes pose a serious danger in this disease.
During pregnancy and lactation, taking supplements is not prohibited. However, you should still consult a doctor before using them.