Nature is smart and generous, providing us with cures for many diseases, we just have to take a closer look. This is definitely true for inositol.
Never heard of him? You are not alone. Despite the fact that inositol preparations are quite common, they are often forgotten about. However, you will definitely be interested in knowing what inositol is for, especially if you are facing infertility or other fertility problems.
In the article we will look at what inositol is, its instructions for use and preparations, how inositol is useful.
History of the discovery of vitamin B8
Johann Joseph Scherer
The first mention of this chemical compound dates back to the middle of the 19th century. According to some sources, the discoverer was the German chemist Justus von Liebig (1848), but more often they say that the compound was discovered by the German chemist and physician Johann Joseph Scherer (1850). A new substance was discovered in muscle fibers. That is why it was given the name “inositol”, which comes from the Greek “inos” - “fiber”.
Since the chemical structure of inositol is extremely similar to carbohydrates, at first the name “muscle sugar” was assigned to the compound. Only at the beginning of the 20th century the substance was given the status of vitamin B8.
However, already at the end of the 20th century it became known that the human body is capable of producing inositol in the required quantities. This was the reason why vitamin B8 was transferred to the category of vitamin-like substances. Due to its performance of a number of important functions for humans, vitamin B8 is today classified as a conditionally essential nutrient .
Synonymous names for vitamin B8:
- Inositol.
- Inositol.
- Cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol (chemical name).
- Vitamin of youth.
Physicochemical properties of vitamin B8
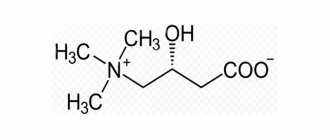
The chemical formula of inositol is C6H12O6. In its pure form it is a white powdery crystalline substance. It is odorless and has a sweetish taste. Inositol is highly soluble in water and has low solubility in alcohols. Organic compounds are not able to dissolve inositol.
Vitamin B8 is well preserved at non-extreme temperatures and is not destroyed by exposure to air or direct sunlight. Non-hygroscopic.
In nature, inositol is represented by nine stereoisomers (spatial configurations), which are isolated from various vegetables, fruits, organs and animal tissues. The most common is mesoinositol or myoinositol . It is this form of vitamin B8 that is biologically active and provides all the beneficial properties of inositol. Mesoinositol is rarely found in free form; it is usually associated with phosphoric acid.
Vitamin B8 can be synthesized in the body from glucose. The heart, liver and kidneys actively produce inositol, which is subsequently transported to all cells and tissues. Human blood contains at least 4.5 mcg/ml vitamin B8. The tissues of the nervous system, the lens, the back wall of the eye and the tear fluid are especially rich in inositol.
What foods contain vitamin B8?
According to scientific research, inositol can be found in almost any food. Cantaloupe melon, oranges and other citrus fruits are especially rich in it. High levels of vitamin B8 are found in whole grains and cereals, legumes, nuts, yeast and liver, brown rice, soy flour and green leafy vegetables. Myoinositol is found in large quantities in the liver, internal organs and meat of animals, as well as in milk.
Foods rich in vitamin B8
It is noteworthy that vitamin B8 is found in the milk of mammals. For example, in the milk of nursing mothers, the concentration of inositol is in the range of 12-48 mg/100 ml, and in cow's milk it contains 4-11 mg/100 ml. Therefore, even newborns receive this vital compound in the required quantity.
Daily requirement for vitamin B8
Standard intake of vitamin B8 for children and adults
Inositol deficiency has never been demonstrated in humans. It is believed that the average human diet contains 300-1000 mg of vitamin B8. At the same time, the body itself is capable of producing 2-4 grams of inositol per day. Taking high doses of vitamin B8 orally can cause diarrhea.
The recommended daily dosage should be increased for diabetes, alcohol abuse and coffee lovers.
Daily norm
Any vitamin has its own daily requirement. Although vitamin compounds are beneficial for the body, if the dosage is exceeded, any beneficial substance turns into harmful and can cause intoxication and other adverse consequences. Vitamin B8 cannot be classified as a particularly toxic substance, however, it also has its own daily requirements.
Table 1. Daily intake of vitamin B8
| Patient category | Daily value of B8, mg/d |
| Children 0-12 months | 30-40 |
| 1-3 years | 50-60 |
| 4-6 year old children | 80-100 |
| At 7-18 years old | 200-500 |
| Adults | 500 |
Vitamin B8 is synthesized in the body, therefore, with the right diet, a person has enough of it. Increased dosages of inositol (up to 8 g/d) are required for people in the following cases:
- in a state of depression, stressful experiences or psychological overstrain;
- in sports, if intensive training is expected for athletes;
- with increased mental stress;
- to improve memory, especially during sessions and exams for students;
- for diabetes;
- in the presence of pathologies of blood vessels, liver or intestines;
- with frequent abuse of alcohol or fast food;
- pregnant and lactating women;
- when taking hormonal drugs and other drug therapy.
Also, dosages need to be increased if visual stress increases, with dislocations, fractures or severe bruises, or when drinking large amounts of water. In case of severe deficiency, which is extremely rare, you can resort to the help of inositol preparations, taking them according to the instructions.
Vitamin B8 - why the body needs it
Although vitamin B8 is not as widely advertised as other members of the B group, inositol is an organic component of every cell membrane. It functions similarly to choline and is involved in a wide range of bioactive processes.
In experiments on laboratory rats and gerbils, it was shown that vitamin B8 deficiency leads to the development of lipodystrophy, hypolipidemia and fatty liver. This is due to the fact that inositol regulates the processes of transport and utilization of fats, primarily cholesterol. In addition, vitamin B8 acts as a catalyst for a large number of metabolic reactions in all tissues of our body. And when inositol phosphate is broken down, the energy needed by the body is formed. This, by the way, also distinguishes inositol from other vitamins, the energy value of which is zero.
Beneficial properties of vitamin B8:
- It is a structural component of all cell membranes and ensures the integrity and normal functioning of cells.
- Maintains the potential (ionic charge) of the cell membrane.
- Provides the transport function of membranes of all cells.
- Takes part in the processes of formation of new cells (in particular in the process of gene expression).
- Participates in the intracellular control of the concentration of calcium ions (Ca2+).
- Regulates lipid transport and fat catabolism. Protects the liver from excessive accumulation of fat in it. Reduces cholesterol levels.
- Strengthens the walls of blood vessels.
- Participates in the exchange of copper and zinc.
- Supports peristalsis of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Increases the activity of neurotransmitters: serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, acetylcholine, GABA. Ensures normal impulse transmission between nerve cells. Improves concentration, memory and attention, stimulates the cognitive activity of the nervous system. Has antidepressant properties and improves mood.
- Necessary for the normal functioning of the hormone insulin.
- Maintains healthy skin and hair.
- Prevents the development of dystrophy and reduces the risk of malignant tumors.
What is myo-inositol
Myo-inositol is the most common form of inositol, found in almost all plants and animals ().
What is inositol for? All cells require myo-inositol to survive. Cells convert myo-inositol into phosphatidylinositol, an essential component of membranes. It affects the very structure of cells, metabolism in brain cells, fat burning and storage, energy consumption and stress response
Myo-inositol also helps regulate hormone activity (). It is used by the ovaries to produce hormones that affect fertility and ovulation (such as FSH) ().
The second most common inositol after myo-inositol is D-chiro-inositol. It acts as an antioxidant and helps improve PCOS symptoms and hormonal imbalances in women ().
Related articles:
- How to lose weight with polycystic disease
- How to replace metformin: natural alternatives
Myo-inositol levels are especially high in the brain. It has been proven that the brain can produce large amounts of myo-inositol from glucose breakdown products. Myo-inositol levels in brain cells are a measure of the cells' "energy charge". The more inositol in brain cells, the better they are protected and the greater the total energy in the brain ().
Myo-inositol is also increased from any type of brain injury as a way of compensating for injury and healing. But this increase is also associated with the formation of brain scar tissue and cognitive problems ().
A balanced level of inositol in the body is a key factor in homeostasis. Low levels are associated with infertility, anxiety, and metabolic and hormonal problems. But extremely high levels are associated with brain damage and mania.
Vitamin B8 during pregnancy
During pregnancy, inositol ensures the formation of full-fledged cells in the new organism. In combination with other B vitamins, inositol ensures the normal formation and development of fetal nervous tissue. With further intrauterine development, vitamin B8 is included in the development of the cardiovascular and digestive systems, ensuring the health of the child’s skin and hair.
Despite the significant role of inositol for a pregnant woman and her baby, vitamin B8 is usually not included in vitamin and mineral complexes for pregnant women and women planning pregnancy. The expectant mother obtains the required amount of this compound from endogenous synthesis and food consumed.
Use of vitamin B8 in medicine
Inositol is extremely rarely used as monotherapy (as the only treatment). However, very often they complement treatment, and such therapy demonstrates excellent results.
Indications for use of vitamin B8:
- Diabetes mellitus (including pain and decreased tissue sensitivity to insulin).
- Asthenia.
- Increased mental and physical stress.
- Mental disorders, including panic attacks, depression, schizophrenia, anxiety, bipolar disorder, bulimia, obsessive-compulsive disorder.
- Insomnia (usually in combination with green tea extract, L-theanine or hydroxytryptophan 5-HTTP).
- Visual impairment associated with reduced retinal nutrition.
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children.
- Alzheimer's disease.
- Autism.
- High blood cholesterol levels.
- Liver diseases and cholelithiasis.
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (including reduced peristalsis and constipation).
- Hypertension and circulatory disorders.
- Dermatological diseases (including eczema and psoriasis).
- For the prevention of cancer and other malignant neoplasms. Recovery after radiation or chemotherapy.
- Alopecia (baldness) and other hair problems.
- Disorders of the sex glands, infertility.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (take 2 times a day, 2 grams).
- Overweight and obesity.
In a Russian pharmacy it is quite difficult to find pure vitamin B8 in ampoules or tablets. Pure inositol is usually available in capsules. It is also part of multicomponent preparations.
Vitamin B8 preparations:
- Inofert (30 sachets, inositol 1000 mg + folic acid 0.1 mg, manufacturer - Humana Pharma International, Italy).
- Fertina (30 sachets, inositol 1000 mg + folic acid 0.1 mg, manufacturer - Fine Foods & Pharmaceuticals, Finland).
- Myo-inositol for women (120 capsules, 500 mg each, manufacturer: Fairhaven Health, USA).
- Inositol (100 capsules, 500 mg, manufacturer: Now Foods, USA).
- Inositol (100 capsules of 750 mg, manufacturer - Jarrow Formulas, USA).
- Inositol (100 capsules of 500 mg, manufacturer - Nature's Way, USA).
- Inositol (100 capsules of 500 mg, manufacturer - Solgar, USA).
- Inositol Powder (powder 227 or 454 grams, manufacturer - Healthy Origins, USA).
- Inositol Powder Cellular Health (powder 113, 227 or 454 grams, manufacturer - Now Foods, USA).
- Pure Inositol Powder (powder 226.8 grams, manufacturer - Source Naturals).
Vitamin B8 preparations
Domestic preparations based on vitamin B8 (inositol) are unknown.
Tips for choosing supplements
The vitamin can be purchased in powder form or in tablet (capsule) form. The capsule is much more convenient to take; it already contains the required dosage for an adult. But the powder is convenient for those whose whole family (i.e. people of different ages) takes the supplement.
You can buy dietary supplements in ampoules, but they are usually used in cases of emergency recovery, for example, after sports injuries, and contain additional painkillers and anti-inflammatory components.
https://youtu.be/kPd0M8xHAjo
Inositol supplements may contain additional vitamins and microelements, whose effect is enhanced when taken together.
Lack of vitamin B8 in the body
Vitamin B8 deficiency has only been reproduced in laboratory animal studies. No clinically significant inositol deficiency has been identified in humans.
Based on experimental data, it was found out what a lack of vitamin B8 :
- Male sterility and arrest of sperm production.
- Dermatitis, eczema, psoriasis and other skin problems.
- Weakness, dullness and hair loss.
- Eye diseases and visual impairments.
- Excess copper in the body, which leads to insomnia, anxiety, depression and increased irritability.
- Cognitive disorders: decreased memory and attention, impaired thinking and speech.
- Neurological complications in patients with diabetes mellitus.
- Constipation due to weakness of the muscle layer of the intestines.
- Reduced fertility in women, infertility.
- Increased blood cholesterol levels.
Interaction of vitamin B8 with other substances
- Caffeine, tea, alcohol and antibiotics inhibit the body's production and reduce the absorption of inositol from food. Therefore, if you are exposed to one or more of these substances, you should take additional doses of vitamin B8.
- A combination of vitamin B8 with choline, vitamin E or any vegetable oil is recommended. This combination accelerates the transition of inositol to its active form, and the complex of vitamins B8 + B4 forms lecithin, which is beneficial for the body.
- In combination with melatonin, it helps normalize sleep and circadian rhythms (sleep/wake).
- In combination with phytic acid (a derivative of inositol), an increase in the anti-cancer properties of vitamin B8 is observed.
- Reduces the side effects of lithium.
- Estrogen drugs sharply reduce the production and absorption of vitamin B8.
Vitamin B8 is a “fighter of the invisible front.” We talk about it little, but this does not prevent inositol from performing a huge list of important functions. The health of the nervous, digestive, cardiovascular and reproductive systems, skin and hair, protection against cancer and maintenance of normal cholesterol levels is largely due to vitamin B8.
Learn more about the authors of this article.
4.7 / 5 ( 8 votes)
Contraindications and overdose
No side effects or significant contraindications were found for Inositol, but the drug should not be taken if:
- Individual intolerance;
- pregnancy.
You should be careful, as an overdose of this drug can lead to dizziness, nausea, sleep and digestive disorders.
Women during pregnancy and breastfeeding should definitely refrain from taking any medications that are not prescribed by their doctor.
No negative effects of vitamin B8 when interacting with other medications have also been identified. It was noted that Inositol significantly improves the absorption of B vitamins and vitamin E. It also becomes the basis for the formation of lecithin in combination with choline.
Note!
It is worth noting another important point - all B vitamins are very water soluble and are excreted from the body in urine. This is good in the sense that it is almost impossible to overdo it with inositol and get an overdose. On the other hand, it is necessary to introduce this substance into your diet daily.
It is also worth remembering that before you start taking any vitamins, dietary supplements or drugs that you buy at the pharmacy, you should definitely consult with your doctor!