A little about the knee
The knee joint has very limited mobility. It allows you to bend your leg in one projection and rotate it a little. And most importantly, anatomically from birth, protection is provided against bending the knee backwards. Otherwise we would not be able to stand on straight legs.
All mobility is provided by a complex of ligaments of the knee joint and cap. The main materials that make up the knee are cartilage and elastic fibers.
Let us also note about the pathological tuberosity of the tibia in children; later you will understand why we said this. Therefore, they may complain that their knee hurts when squatting.
It is known that friction occurs between moving parts within the knee. It is minimized by joint fluid. The joint itself is located in the articular capsule.
Most often, knees hurt when squatting and standing up. Less often - only after a squat. Improperly performed leg presses, squats, and lunges can cause knee injuries.
Knee pain can accompany both barbell and empty bar squats. And sometimes without it. Or you may feel pain even without exercising while sitting at home. Why? Perhaps you are overweight, or have a very sedentary lifestyle and a thousand and two other reasons for inflammation of the knee joint.
The knee joint is a joint that connects the patella, femur and tibia (roughly speaking, thigh, tibia and kneecap). It consists of cartilages, menixes, collateral ligaments, etc. The structure is really very complex.
This entire “mechanism” is placed in an articular capsule (also called a joint capsule), inside which a special fluid is produced. This fluid nourishes and moisturizes the joint, minimizes friction and protects the entire cartilage complex from mechanical damage.
If any of the above fails, a person will have difficulty squatting, let alone doing squats in the gym.
Treatment
Once a diagnosis has been made, and the pain in the knee area is the result of an illness or serious injury, there is no way to get by with general measures. How to treat knees if they hurt when squatting and standing up? In addition to the main treatment prescribed by a specialized specialist, he can recommend the following auxiliary measures to the patient:
- Knees creak when bending and straightening
- If an injury is detected, the knee joint should not be strained. All sports and any intense movements are prohibited. This is necessary to prevent consequences and complications.
- If arthritis has been diagnosed, non-steroidal drugs are prescribed as an analgesic and anti-inflammatory drug.
- If you have gout, it is recommended to review your diet and exclude from it those foods that have a fairly high content of purine bases.
- In the absence of deformations and degradation of cartilage tissue, as well as neoplasms in the joint area, exercise therapy is recommended.
All of these measures cannot be prescribed independently, since some of the measures aimed at improving the condition may have the opposite effect.
Important! After performing physical therapy exercises, rest is required. In the event that pain occurs in the affected area when performing an exercise, you should abandon it completely.
When is pain normal?
Knee pain due to sports activities is not a rare phenomenon. Its occurrence may be associated with changes in the muscle-tendon complexes and osteoarticular elements of the knee area. As a variant of the norm, the following should be considered:
- Mild, relatively short-term soreness of the whole group or only certain muscles of the leg and thigh. Most often, it is a natural phenomenon against the background of stress and is caused by the accumulation of lactic acid in the tissues. The likelihood of such pain occurring and its duration (up to a maximum of 3-4 days) are determined by muscle fitness. The more adapted they are to stress, the less muscle pain.
- Brief aching pain of uncertain localization in the knee area. Athletes feel it after training as a slight compression of the entire knee joint. There should not be one painful point.
Important to remember! Normal pain in the knee area after training is always short-lived, not intense, and decreases or disappears completely after rest. Unprepared muscles and joints always hurt after physical activity!
Cracks in the skin of the elbows, causes
A disease of the thyroid gland can be the cause of flaky, cracked skin on the elbows.
The cause of rough, dry, flaky skin on the elbows, with cracks, can be hypothyroidism - a disease of the thyroid gland.
In addition to dry, flaky skin on the elbows, knees and feet, there are other main signs of hypothyroidism:
- General weakness and fatigue
- Chills, skin cold to the touch and pale
- Hair becomes dry and brittle and begins to fall out
- Anemia
- The voice became rougher
- Hearing loss
- Muscle pain and cramps
- Shortness of breath and heart pain
- Bradycardia is a disorder of the heart, expressed as a pulse rate less than 55 beats per minute.
- Frequent cases of bronchitis and pneumonia that do not cure for a long time
- Flatulence, constipation, loss of appetite and nausea often occur
- Lethargy and apathy towards the outside world
Why do my knees hurt when squatting?
Problems can arise due to meniscus injury, inflammation, cartilage damage, lack of joint (synovial) fluid, etc. Below we will look at the main causes of pain.
Arthrosis is a complex name for diseases associated with joint damage. The concepts of arthrosis and arthritis are often confused due to almost identical symptoms. For general development, let’s make a distinction: arthritis involves an inflammatory process throughout the body, and arthrosis refers directly to the composition.
Symptoms of arthrosis:
- Knees crunch when squatting. Don't get confused! Every person sometimes has a crunch in their joints, but with arthrosis it is rough and dry. It is difficult to confuse it with ordinary clicking.
- Decreased mobility in the knee. If you used to be able to sit with your legs tucked under you, but now you can’t, that’s not good.
- Deformation. Rarely appears in the initial stages, unless the cause is a knee injury.
- Pain when bending. It can appear before and after squats. It can be: aching, sharp, sharp, persistent, etc. In the initial stages, it does not occur at rest.
Arthrosis is getting younger and is difficult to diagnose. It can begin to form in adolescence, but young guys do not attach importance to the occasional tingling sensation. As a result, the disease is diagnosed by the age of 20 in a progressive stage. Why is this happening?
A teenager’s knee joints are not ready for serious physical activity. The muscles may be ready, but the joints are not. There is also no indicator, no “litmus test” that would tell a teenager that it’s time to slow down. The disease can develop without pain.
People who have flat feet are 31% more likely to develop osteoarthritis. It is not known how closely this fact is related to physical activity, but severe flat feet are a 100% contraindication to barbell squats. The defect simply makes the exercise technically incorrect. This can lead to increased stress on the knee joint. Replace the exercise with a leg press.
Sprains are a common injury during sports. Did you make a sudden awkward movement? Did you take on too much weight? Started training without warming up? Keep the sprain.
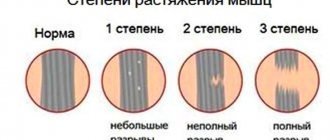
There are 3 degrees of sprain severity:
- I-degree – accompanied by acute pain, which goes away on its own within 1-3 weeks maximum. She won't bother you anymore, but you still need to get checked.
- II-degree - the tissue structure is severely damaged, the joint can no longer maintain its integrity. Medical intervention is required.
- III – degree – torn ligaments. The pain is so severe that the person goes into shock. Previously, such an injury meant the exclusion of any physical activity. Now you can correct the situation surgically.
Knee dislocation
Another cause of pain when bending. In the first minutes after an injury, many people confuse a knee dislocation with a severe sprain. The symptoms are similar: sharp pain, impaired mobility, swelling, etc. It is easy to distinguish one from the other. With dislocation, deformation is almost always visually noticeable; with stretching, this effect is absent.
Menix damage
The last cause of pain that we will look at today is damage to the menix. It can be diagnosed in older people (40-50 years old) or occur due to injury. For example, a menix rupture is detected in more than half of the fractures.
The damage is accompanied by an increase in temperature in the joint (the area “burns”), pain, clicking when bending, and an increase in the volume of the knee joint.
Preventive measures and prophylaxis
To prevent any damage to the joints of the lower extremities, as well as to reduce the likelihood of inflammation, common sense should be used. This is required not only in everyday life, but also when playing sports. If you have non-recurrent pain, you can try to get rid of it by following these instructions:
- Before any physical exercise, a warm-up is required.
- After performing exercises, your knees need rest and relaxation.
- When performing squats, the technique of their execution must be ideal.
- If pain occurs, you need to reduce the intensity of the exercise - this will prevent injury and deformation of the joint.
- Avoid hypothermia of joints.
- Treat all diseases in a timely manner.
- Eat a balanced diet and keep your weight under control.
Such measures will help to avoid unwanted processes in the joints in youth and reduce their likelihood in old age.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Pain associated with running
If jogging is a rare occurrence in a person’s life, then he cannot avoid the occurrence of muscle or joint pain in the knee area. But in cases where pain is a constant companion of an athlete when running, it should always be a concern. Behind it may be hidden:
- Traumatic injuries of the menisci. A typical mechanism for their occurrence is improper distribution of the load on the knee joint when running due to unsuccessful rotation of the tibia relative to the thigh. At the moment of injury, a sharp but short-lived pain appears. As a rule, after a run or after a workout it intensifies, more so when walking, which causes a limp. Later, local swelling and palpation tenderness appear along the lower inner edge of the knee.
- Dislocation of the patella (kneecap). May occur during a fall or blow to the knee. Manifested by sharp pain and swelling. After such a leg injury, it is impossible to continue running. Within a few days the pain goes away. If the athlete does not seek medical help, this will cause the formation of a habitual dislocation.
- Chondromalacia. Represents the destruction of the cartilaginous mass of the patella. It manifests itself as unpleasant aching pain during running and after training. Accompanied by limited mobility of the knee joint.
- Traumatic ligament injuries. Represented by their stretching and tearing. The damaged area is very painful at the time of injury. It is impossible to continue jogging. After training, pain persists, swelling appears, and mobility of the knee joint decreases. Walking becomes very difficult, touching the affected area of the knee is accompanied by pain.
Lack of adequate warm-up before training is one of the reasons for damage to the knee joints
Pain after squats
Related article: Why do my knee joints hurt?
- Tendinitis and tendovaginitis. Inflammation of the tendon sheaths can be caused by chronic overstrain, stretching or tearing. Depending on the degree of damage, pain characteristics are formed. Sharp, burning pain that occurs at the height of the load indicates serious damage. Periodic aching pain localized along the posterior-inner or posterior-outer surface of the knee indicates a chronic problem and requires mandatory correction of the load regimen.
- Bursitis. Around all the large tendons of the knee joint there are bags that facilitate their gliding and movement. In people involved in cycling, these bags are often affected by a chronic inflammatory process. After falling from a bicycle onto your knee, the most unpleasant type of bursitis occurs - prepatellar. Its occurrence makes movement in the knee joint impossible due to severe inflammation, prone to suppuration.
- Damage to ligaments and tendons. Cyclists often experience sprains and micro-tears of the colateral and cruciate ligaments, the iliotibial ligaments, and the tendon parts of the internal and external muscles of the back of the thigh.
The use of compression hosiery is a powerful means of preventing sports injuries
Performing squats with a barbell is associated with an increase in the load on the osteo-articular elements of the leg. The knee joints become their epicenter. This is the main mechanism for causing knee pain during or after squats. Persistent pain syndrome may indicate the following diseases:
- Arthrosis-arthritis. In such patients, the pain is accompanied by a crunching sensation in the knees when they are maximally flexed and extended.
- Old traumatic injuries of the menisci and cruciate ligaments. In this case, the pain is predominantly localized along the inner surface of the anterior-lower part of the knee joint. Knee instability or locking may occur at any time during a squat (usually during extension).
- Osgood-Schlatter disease and other types of damage to the tibia.
- Traumatic and inflammatory damage to the tendons that carry out movements in the knees when squatting.
The main rule for a person involved in sports is to reduce stress in the presence of pathological pain in the knee joints. You should definitely consult a specialist who will help you determine the cause of the pain, select the optimal loads and tell you how to treat this or that disease. You can learn in detail about the differentiated approach to the treatment of diseases manifested by knee pain in this article.
You need to try to determine the cause of the pain. Until it is installed, any physical activity should be avoided. If the cause is a slight sprain or minor bruise, you can limit yourself to self-medication and reducing the load. For “causeless” pain, self-medication is not recommended.
Decide on the nature of the pain before going to the doctor. Above we have already described the characteristic symptoms of diseases of the knee joint. Check your body for their presence. The doctor will definitely ask about this before the examination.
To accurately determine the diagnosis and prescribe treatment, the doctor first palpates your knee. Later he sends the patient for instrumental and laboratory diagnostics. They do to you:
- X-ray.
- Ultrasound.
- Biochemical and general blood test.
- Collection and analysis of joint fluid.
- MRI of the knee joint.
In most cases, the diagnosis is reliably known after MRI.
First aid for bruises, dislocations and sprains is different. If you are injured, proceed as follows:
- Apply a cold compress to the damaged area for 15-20 minutes.
- Apply the bandage tightly enough to prevent bleeding. Place the cold on top of the bandage again and leave it there for one and a half to two hours. Be careful not to overfreeze the area.
- After a few hours, take a warm bath to speed up the resorption of the spilled blood.
When stretched:
- Apply a cold compress and apply a bandage (or an elastic bandage).
- Do not load the ligament for two days. It is advisable to stay in bed at all.
- To prevent this from happening again, do therapeutic exercises and practice self-massage.
In case of dislocation:
- Call an ambulance.
- In any available way, fix the knee in the position it took after the injury, cool the area.
- Take a horizontal position, place the fixed leg so that it is higher than the rest of the body. This can only be done with outside help. If there is no one nearby, just don't move.
Since most of the causes of knee pain are associated with injuries, treatment should be aimed at eliminating them. For example, when a ligament is sprained or torn, when sharp pain occurs, it is necessary to apply a cold compress to the injury site. It will help reduce pain and swelling, and also prevent the formation of intra-articular hemorrhages.
Be sure to apply a tight bandage to the affected joint. The most dangerous and requiring long-term treatment is a rupture or sprain of the cruciate anterior ligament.
If pain occurs during squats with a barbell, it is necessary to bandage the knee joints with elastic bandages before starting the exercises. When pain becomes too severe, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, and after relieving acute pain, in many cases physiotherapy is used.
If the pain goes away immediately after stopping the exercises, then squats can be continued, but the initial load must be reduced, especially for training with a barbell.
Knee pain can be caused by arthritis; anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to relieve the attack. But you need to take into account that such diseases should be treated by a specialist.
For arthrosis, it is necessary to do special exercises, in most cases the so-called scissors and a bicycle are used, the latter involves performing circular rotations of the legs bent at the knees. “Scissors” refers to measured swings of the legs, while they must be fully straightened.
Nutrition
If the cause of pain is salt deposits, you should limit your consumption of salty and spicy foods. Try to adhere to healthy eating rules and include more fruits, vegetables and fish dishes in your daily diet.
If knee pain after squats appears due to excess weight, then in this case it is necessary not only to switch to a diet, but also to limit salt intake. In addition, it is recommended to drink only filtered water, since the chlorine and lime contained in tap water negatively affect the functioning of the joints.
If you experience unpleasant sensations in your knee while doing squats, you should definitely consult a doctor to find out the cause of their occurrence; this is the only way to determine what to do in each specific case. In addition to the methods of traditional medicine, there are various methods offered by traditional medicine.
One of these methods is to apply a compress of milk and bran in a 1:1 ratio. It is applied to the knee joint and held for half an hour; the procedure should be performed daily. Warm baths with decoctions of medicinal herbs or essential oils give a good effect.
Causes of dry elbows in women
Initially, women have much thinner skin than women, which means that the skin will deteriorate faster. That is why the fair half of humanity needs special and more thorough care for the epidermis.
Basically, the cause of pathology is physiological reasons, namely:
- Anemia. If the body lacks iron, metabolism is disrupted, causing the skin to become flabby and age quickly. Accordingly, the epidermis on the elbows changes its structure.
- Problems with hormonal levels. During growing up, during pregnancy, during menstruation - almost throughout life, the level of hormones in the blood of women changes. All these conditions cannot but affect the condition of the epidermis.
- Substance abuse. Every woman loves to soak in a warm bath with aromatic foam - it relaxes and soothes. But do not forget that gels and bubble baths can significantly dry out the skin - it is necessary to add essential oils to the bath. Dishwashing and cleaning detergents are extremely aggressive to the skin of not only the elbows, but also the hands. During cleaning, be sure to use protective gloves.
During menopause in women, a significant decrease in the functions of the skin can also be noted; it becomes much drier and loses elasticity. The overall level of all hormones begins to change, and this primarily affects the condition of the skin, nails, and hair. In such cases, problems with the epidermis are far from the only symptom of problems with hormonal levels. A woman may also experience the following symptoms:
- severe hot flashes;
- decreased performance;
- drowsiness;
- mood changes, tearfulness.
After giving birth to a child, a woman’s hormonal levels also change, which can cause increased dry skin. The same applies to pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is important to provide the mother with a nutritious diet - as soon as the hormonal levels return to normal, the condition of the skin will also normalize.
Pain when walking
The occurrence of pain in the knee at certain moments of walking, more often when bending the limb at the joint, may be associated with:
- Various types of knee injuries. This may include damage to the ligaments, menisci and synovium. It must be remembered that pain can be a consequence of both fresh injuries and old injuries. In the first case, determining the cause of pain is not difficult, in the second, diagnosis is problematic.
- Osgood's disease (Osgood-Schlatter). Occurs mainly in adolescence in boys. It is a nonspecific lesion of the tibia below the knee. The main manifestation of the pathology is point pain under the patella while walking.
- Osteochondritis dissecans is a disorder of the blood supply to the knee end of the femur, manifested by detachment of a section of articular cartilage with its complete destruction.
- Arthrosis. In the initial stages of development, the disease manifests itself as periodic pain inside the knee while walking.
Methods of pain relief
If after squatting you feel discomfort in your knee, the first thing you need to do is relieve the pain and provide rest to the joint. It is advisable to secure it with an elastic bandage. Before the doctor arrives, you can use pain-relieving ointments such as Diclofenac and Indomethacin.
Compresses using medicinal herbs, which have analgesic and warming properties, will help relieve pain and speed up the recovery process. There are special patches made from medicinal plants. They relieve swelling and pain in the knee joint that occurs when squatting. For severe pain, use dry cold - an ice compress.
What is suitable for your case - cold or heat, can only be determined by a doctor after diagnosis.
How to treat knee pain?
Knee joint diseases are an age-related problem. It is present in 30% of people aged 50-60 years. Athletes (especially runners, football players and bodybuilders) develop the disease earlier. Are you at risk? Read how to prevent the disease and cure it.
Make sure that your diet contains vitamins C, E, B6, B5 and A. Together they will have a positive effect on cartilage tissue cells: they neutralize substances that cause cartilage destruction and promote the restoration and growth of cartilage tissue.
Healthy skin on the elbows: what vitamins are needed?
Since vitamin deficiency is a fairly common cause of problems with the skin, let’s consider which vitamins need to be given special attention in order for the epidermis to recover:
- Vitamin C. Takes an active part in tissue metabolism - if there is not enough of it in the body, the skin may begin to crack and peel.
- Retinol. With its deficiency, the skin regenerates much more slowly, which means that a person will be bothered not only by dryness, but also by cracks that will take a long time to heal.
- Vitamin E. The strongest antioxidant that is vital for every person. Prevents the aging of tissues and skin, helps accelerate the exfoliation of dead epidermal cells.
Important! All of the above vitamins can be easily purchased at the pharmacy. But you need to drink them according to the instructions and the characteristics of the body, otherwise hypervitaminosis may develop. Therefore, before starting to use such medications, it is advisable to consult with your doctor.
How to exercise when you have pain?
No way. No responsible trainer will let you into the gym if you complain of sudden sharp pain when doing squats. With injuries, the situation is a little simpler.
If the pain is caused by a minor bruise or injury, modify your workout to rest the knee joint for a while. Eliminate squats, reduce the load. How to replace exercises? Do seated dumbbell presses, pump up your upper abs, etc.
A visit to the doctor will not always reveal the cause of the pain. It often happens that the doctor will throw up his hands and say that you are healthy. This happens because MRI does not show signs of arthrosis in the early stages. In the early stages, a crunch in your knee may give you away. Although some live with this all their lives without progression, not knowing about any arthrosis.
If you haven't been diagnosed, try this:
- Determine at what point during the squat your knees hurt. If you can do a partial squat without pain, do it.
- Do the leg press in the same way. Pain is your compass.
- Wrap your knees with elastic bandages. You can’t wrap it too tightly, so that you can walk around with bandages throughout the entire exercise. This often helps. Work first with an empty bar, not with a heavy barbell.
- Warm up well - preferably on an exercise bike. It will provide maximum safe warming up for your knee system.
- You can use warming ointments. But remember, if your skin is sensitive, you will only get harmed. Your skin will burn, and if you wrap it in bandages, you won’t be able to exercise at all.
- Increase weights gradually and slowly. You are a pain researcher and must clearly understand when pain begins and what you can do without it. Pain is your guide and the red traffic light.
- Take additional chondroitin and glucosamine, vitamins and unsaturated fatty acids in the form of dietary supplements or in their natural form.
The most important thing is to be careful about your health. Remember that acute pain and discomfort in the knee joint are contraindications to weight training. It is better to postpone training until you consult a doctor. This way you will not cause additional harm to the sore joint and will most likely prevent a more serious problem.
Trainer Tip: Sleep at least eight hours a night. It is better to sacrifice an evening of watching TV than your health and metabolism.