Why does hyperlordosis occur and what is dangerous?
Normally, the human spine has 4 curves. 2 have the form of backward-facing arcs. They are called kyphosis and are present in the thoracic and sacral regions. And 2 arcs are facing forward (neck and lumbar region). They are called lordosis. Without natural curves, walking will be difficult. Lordosis ensures disc mobility. In this natural position, the balance of the body is ensured, the shock-absorbing pressure on the intervertebral discs is reduced, which allows a person to move freely.
For high-quality movement, the bending angle should not exceed the established values. When the indicator fluctuates within the normal range, this indicates physiological lordosis.
Sometimes these curves have too much or not enough curvature. This indicates the development of pathology. Such changes greatly affect the spine and posture. In an advanced stage, this leads to pain and deterioration in the functioning of internal organs.
Hyperlordosis of the lumbar region can occur under the influence of unfavorable factors. Improper arching in the lower back causes damage to the vertebrae or back muscles, as well as the hip joints. The pathology causes discomfort and provokes damage to internal organs. The causes of hyperlordosis can be different. It all depends on the age of the patient and his individual characteristics.
There are several provoking factors that lead to the disease:
- leg and back injuries;
- rickets;
- the presence of congenital anomalies (for example, an extra vertebra in the lumbar region);
- pathologies accompanied by muscle paralysis;
- osteochondrosis;
- spinal spondylosis;
- neoplasms in the spine and nearby organs;
- infectious diseases;
- lack of vitamins.
In addition, the reason may be rapid growth during adolescence, when muscle tissue cannot fully form a corset. As a result, the wrong load appears, and the posture deteriorates.
Hyperlordosis of the lower back is accompanied by the presence of pain of varying severity. Discomfort is localized mainly in the lumbar and sacrum areas. The pain gets worse after sitting for a long time or being immobile.
Hyperlordosis most often develops in the presence of several provoking factors. It is a dangerous disease that can lead to complete loss of mobility. Deformation and displacement of the vertebrae with lumbar hyperlordosis threatens pinched nerve roots, intervertebral hernias, inflammation of the muscles surrounding the spine, and other complications.
Diagnostics
Before correcting a severe deflection in the lumbar area, the patient must undergo a thorough examination. To check yourself, a person can stand with his back to the wall, press his buttocks and head against it and try to move his hand into the lumbar curve. If this is successful, there is a possibility of developing hyperlordosis. But, if even a palm does not fit into the hole, the bend is too straight, which also requires treatment.
At the first suspicion of the development of a pathological process, a person should immediately contact a traumatologist. The initial examination will allow you to draw superficial conclusions and determine the required diagnostic methods. They are as follows:
- X-ray. It clearly shows the location of the vertebrae, which helps to establish the correct diagnosis, but the reasons for the deviation may remain unknown;
- MRI. The study is prescribed if there is a suspicion of soft tissue damage, the presence of malignant neoplasms and neurological causes of the development of pathology;
- CT scan. Allows you to obtain information about the condition of bone tissue.
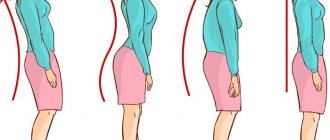
Another name for increased lordosis is hyperlordosis. In this case, the patient's lower back is bent inward too much at a large angle. Flattened lordosis is hypolordosis; it means that the bend is much less than normal or completely absent.
How to tell if you have excessive arching in your lower back
A concave back may hurt, especially when walking and other physical activities, or if you sleep on your stomach. Severe forms of lumbar hyperlordosis are diagnosed using an X-ray machine. If the lower back does not hurt, there is no restriction of mobility, but there is a suspicion of problems with posture (the buttocks bend back, the spine protrudes), then there are several tests to check.
Pelvic bone test
To carry out the test you will need:
- chalk or pencil;
- vertical plane;
- ruler;
- protractor.
The test is carried out as follows:
- Stand up straight and feel the protruding pelvic bones in front and behind - the anterior and posterior superior iliac spine.
- On the plane, mark the level of the anterior superior spine.
- Mark the level of the posterior spine.
- Draw 2 parallel lines.
- Connect the marks and measure the angle.
The norm is the pelvic tilt angle from 7° to 15°.
Two palm test
This test is simpler because... it does not require any measurements. You need to place the edge of one palm on the diaphragm and the other on the lower abdomen. It is correct when one palm is placed above the other. If the upper arm protrudes forward relative to the lower arm, then there is excessive deflection in the lumbar region.
Bent-over one-arm dumbbell row
Starting position: the left leg (supporting leg) stands on the floor, the right leg rests on the chair with a bent knee. The dumbbell is in the left hand (the hand that holds the dumbbell and the supporting leg coincide), the right hand rests on the chair (make sure that the palm is under the shoulder joint).
Technique: pull the dumbbell straight up in the same plane with the body until maximum contraction of the muscle (keep your back parallel to the floor with an arched lower back). We return to the starting position.
Starting position: step on the expander or securely fasten it at the bottom (so that you can freely pull it up and down). Take a standing position in an inclined position, your feet are shoulder-width apart, and you hold the handles of the expander firmly in your hands. Swap the handles of the expander (cross them).
Execution technique: spread your slightly bent arms to the sides, and at the top point (at shoulder height) take a short pause. Return to the starting position.
Important: make sure that during the exercise your arms are perpendicular to your torso throughout the entire range of motion.
How to Correct Hyperlordosis with Exercises
To have a straight spine without bends, you need to tone weak muscles and at the same time relieve tension from hard ones. Exercises for lumbar hyperlordosis can eliminate the pathology, but they must be selected strictly individually, depending on the degree of damage and the course of the pathology.
You should start a set of exercises with a minimum load, gradually increasing the complexity of the movements. There should be no pain or discomfort during exercise. If you experience dizziness or increased heart rate, you should stop exercising. To prepare your joints you need to warm up. After finishing classes you should feel slightly tired. To get results, training must be done regularly.
If you know how to bend in the lumbar region, your buttocks will be visually larger and your waist will be slimmer. This will not only make your figure more beautiful and aesthetically pleasing, but will eliminate the risk of developing a vertebral hernia and injuries when lifting heavy objects.
Stretching exercises
You need to start by relaxing the tight muscles. Since the tight muscles are located deep, it is impossible to roll them out on massage rollers or balls. Therefore, they should be relaxed by stretching the lumbar region. The cause of posterior pelvic tilt is tightness of the external oblique and rectus abdominis muscles, buttocks and hamstrings. The posture resembles a tug-of-war between the glutes, calves, and hamstrings.
Most people believe that the cause is in the hips and that they need to do some quality stretching. However, lack of flexibility in the back of the thigh is a consequence. The hip flexors, iliacus, rectus femoris and spinal erectors need strengthening.
When muscles are stretched, tissue nutrition improves, blood circulation increases, and even strength increases. The result of regular stretching, even without other exercises, is a strong back. Stretching not only improves metabolic processes, but also increases endurance.
Cat-cow
This exercise warms up and stretches the back extensor muscles well.
Starting position: stand on all fours. Arch your back upward, starting from the lower back. While performing the exercise, you should try to feel that your back is rising vertebra by vertebra. Now you need to bend your back down gradually, vertebra by vertebra, starting from the thoracic region. Do 5-8 repetitions.
Tilt towards the legs with stretching
This exercise stretches the quadratus lumborum and spinal extensor muscles. You can use a stopwatch or do counting inclines.
Starting position: sit on the floor, straight legs stretched forward. Bend over without bending your knees and stretch forward, counting to 10, while rounding your back. Then, tensing your back extensor muscles, bend in the other direction, holding the position for 10 seconds. Bend forward again and stretch your legs for another 40 seconds. Perform 3-5 such cycles. You can deepen the pose to give the deep muscles a good stretch.
Quadratus lumborum stretch
Sit on the floor, stretch your right leg forward and bring your left leg back. The angle at the knees should be 90°. Tilt your body to the right, place your right hand on the floor, stretch your left hand to the side and forward, stretching your left side.
While stretching, you should try to pull your left thigh down and back. You need to hold the pose for half a minute, then repeat everything in the other direction.
Iliopsoas stretch
Get down on one knee. There should be right angles between the thigh and the lower leg, the body and the thigh. It is necessary to tense your buttocks, twisting your pelvis. Lower your shoulders, squeeze your shoulder blades together and tighten your abs as much as possible. It is necessary to maintain tension until the end of the exercise.
From this position you need to sway a little back and forth for a minute, then change your leg and repeat.
In this exercise you need to keep your buttocks tense and your pelvis twisted. If you do everything correctly, you will feel tension in the groin of the supporting leg.
iliopsoas stretch on the floor
Lie on your stomach, bend your right knee, raise your shin and grab your ankle with your right hand. Rotate your pelvis and lift your body up. Only the chest should rise, look down, and neck straight. Stay in this position for a second, then lower yourself onto your stomach and change legs. You need to do 5 repetitions on each limb.
These 5 exercises will take no more than a quarter of an hour, but they will relieve the feeling of fatigue and your back will become more flexible.
Strength exercises
Stretching alone is not enough to correct your posture. It is also necessary to perform strength exercises that will increase the tone of weak muscles. Abdominal exercises help to correct hyperlordosis.
Slow crunches
Lie on your back, stretch your arms above your head. Slowly twist your back, first lifting your arms and neck, then the thoracic spine, then the lumbar spine. At the extreme point, the angle between the lower limbs and the body should be 90°, arms raised.
Start slowly lowering yourself to the starting position. Perform the exercise 10 times. Each rise and fall should be completed no faster than 20 seconds.
You need to try to spend more time in difficult poses, and not linger at the extreme points. After contact with the floor, you must immediately lift your body up.
Classic and side planks
Stand in a classic plank position on your hands for half a minute. Turn to the side and lift your hand off the floor, moving into a side plank. Hold this position for 30 seconds.
Return to the straight plank for half a minute, then go to the side plank for the same amount of time. Do as many repetitions as possible.
Exercise “Vacuum”
This exercise will increase the tone of the transverse abdominis muscle, which supports the internal organs.
You need to lie on your back, bend your knees, place your feet on the floor. Place your hand on your stomach to control your movements. Inhale so that your stomach inflates and the hand that lies on it rises. Exhale, imagining that your navel needs to reach the floor or spine. At the same time, the stomach will be strongly drawn in. Stay in this position for 3-5 seconds. Perform 10 repetitions.
Exercises for hips and buttocks
To strengthen the gluteus maximus and hamstring muscles, perform the following exercises:
- Squats with dumbbells, barbell, expander.
- Lunges on one or two legs.
- Deadlift with a barbell or dumbbells on one or two legs.
4 exercises are enough: 2 for the buttocks, 2 for the hamstrings.
Hyperextension
Exercise improves posture. Aimed at strengthening the extensor muscles of the back, buttocks and hamstrings.
- Finding Him: 5 Reasons Why You Haven't Met the Love of Your Life Yet
Starting position: lying face down on the floor.
Technique: smoothly lift your chest and legs off the floor, while contracting your back muscles. Then smoothly return to the starting position. Immediately (without stopping), begin to lift your arms and legs off the floor again. Perform the required number of repetitions in this way.
Required number of repetitions: 20 repetitions (4 sets).
Breathing: when lifting your body and legs, inhale, when lowering, exhale.
How often should you exercise?
The entire workout will take no more than half an hour. If muscle pain appears after the first lesson, then strength exercises can be performed every other day, and stretching - daily.
When the body gets used to it, the whole complex is performed daily. This will be useful for people who lead a sedentary lifestyle.
Sedentary work, decreased physical activity and other unfavorable factors lead to various back pathologies. Hyperlordosis, a forward bend of the spine, is especially often diagnosed.
Why does hyperlordosis occur and what is dangerous?
Normally, the human spine has 4 curves. 2 have the form of backward-facing arcs. They are called kyphosis and are present in the thoracic and sacral regions. And 2 arcs are facing forward (neck and lumbar region). They are called lordosis. Without natural curves, walking will be difficult. Lordosis ensures disc mobility. In this natural position, the balance of the body is ensured, the shock-absorbing pressure on the intervertebral discs is reduced, which allows a person to move freely.
For high-quality movement, the bending angle should not exceed the established values. When the indicator fluctuates within the normal range, this indicates physiological lordosis.
Sometimes these curves have too much or not enough curvature. This indicates the development of pathology. Such changes greatly affect the spine and posture. In an advanced stage, this leads to pain and deterioration in the functioning of internal organs.
Hyperlordosis of the lumbar region can occur under the influence of unfavorable factors. Improper arching in the lower back causes damage to the vertebrae or back muscles, as well as the hip joints. The pathology causes discomfort and provokes damage to internal organs. The causes of hyperlordosis can be different. It all depends on the age of the patient and his individual characteristics.
There are several provoking factors that lead to the disease:
- leg and back injuries;
- rickets;
- the presence of congenital anomalies (for example, an extra vertebra in the lumbar region);
- pathologies accompanied by muscle paralysis;
- osteochondrosis;
- spinal spondylosis;
- neoplasms in the spine and nearby organs;
- infectious diseases;
- lack of vitamins.
In addition, the reason may be rapid growth during adolescence, when muscle tissue cannot fully form a corset. As a result, the wrong load appears, and the posture deteriorates.
Hyperlordosis of the lower back is accompanied by the presence of pain of varying severity. Discomfort is localized mainly in the lumbar and sacrum areas. The pain gets worse after sitting for a long time or being immobile.
Hyperlordosis most often develops in the presence of several provoking factors. It is a dangerous disease that can lead to complete loss of mobility. Deformation and displacement of the vertebrae with lumbar hyperlordosis threatens pinched nerve roots, intervertebral hernias, inflammation of the muscles surrounding the spine, and other complications.
Causes
Since the pathological phenomenon can be defined as congenital or acquired, the causes of its occurrence are numerous and varied. It is worth dividing them into two large groups. The first includes the causes of congenital lordosis, the second - acquired.
Congenital pathology - causes:
- one of the parents suffered from the disease;
- during the gestation of the fetus in the womb, the mother violated the diet, resulting in a deficiency of certain elements;
- the woman (mother) had injuries during pregnancy;
- The child was injured during childbirth.
Acquired pathology – causes:
- during pregnancy, due to the deepening of the lumbar deflection to compensate for the increased load, lordosis becomes pathological, but after childbirth it returns to normal;
How to tell if you have excessive arching in your lower back
A concave back may hurt, especially when walking and other physical activities, or if you sleep on your stomach. Severe forms of lumbar hyperlordosis are diagnosed using an X-ray machine. If the lower back does not hurt, there is no restriction of mobility, but there is a suspicion of problems with posture (the buttocks bend back, the spine protrudes), then there are several tests to check.
Pelvic bone test
To carry out the test you will need:
- chalk or pencil;
- vertical plane;
- ruler;
- protractor.
The test is carried out as follows:
- Stand up straight and feel the protruding pelvic bones in front and behind - the anterior and posterior superior iliac spine.
- On the plane, mark the level of the anterior superior spine.
- Mark the level of the posterior spine.
- Draw 2 parallel lines.
- Connect the marks and measure the angle.
The norm is the pelvic tilt angle from 7° to 15°.
Two palm test
This test is simpler because... it does not require any measurements. You need to place the edge of one palm on the diaphragm and the other on the lower abdomen. It is correct when one palm is placed above the other. If the upper arm protrudes forward relative to the lower arm, then there is excessive deflection in the lumbar region.
Treatment
People with crooked backs should start working on their posture.
It is important to follow the following recommendations:
- You can't sleep on soft things. It is not recommended to sit a small child on pillows.
- When working sedentarily, you need to control your posture.
- Regular training and exercises are needed for a curved back.
- A child should not be led by the hands until he begins to walk on his own.
For prevention, you need to engage in different sports from childhood. You should eat healthy food. It is necessary to promptly treat diseases associated with metabolic processes and the functioning of the musculoskeletal system. It is necessary to monitor correct posture even at school age, since prolonged sitting at a computer or desk causes problems with posture.
Swimming
Swimming is an effective method for correcting posture. Children perceive this technique not as treatment, but as a game. During swimming, the load on the spine decreases.
Such training strengthens the muscle corset and also trains muscles and ligaments. In children who swim, the conditions for normal development of the vertebrae are restored. Exercising in the pool is also useful for preventing flat feet. Swimming also has a hardening effect.
Massage
For crooked posture, massages and physiotherapy are recommended. The massage technique helps improve blood flow and helps stimulate metabolic processes. When performing a massage, the specialist takes into account the type of curvature and selects the optimal effect. This allows you to relieve hypertonicity from the muscles.
The course includes several stages:
- First there is an increase in muscle tone.
- At the second stage, the deformity of the spinal column is corrected.
- The results are being consolidated.
With the help of massage, metabolic processes are improved, pain is reduced and passive correction of the spinal column is carried out. There are three types of massage. General massage is performed 1-2 times a week and lasts up to 30-40 minutes. Local massage is used for joints and muscles. Preliminary prepares the muscles for exercise. Different types of massage are used - stroking, rubbing, kneading and vibration.
How to Correct Hyperlordosis with Exercises
To have a straight spine without bends, you need to tone weak muscles and at the same time relieve tension from hard ones. Exercises for lumbar hyperlordosis can eliminate the pathology, but they must be selected strictly individually, depending on the degree of damage and the course of the pathology.
You should start a set of exercises with a minimum load, gradually increasing the complexity of the movements. There should be no pain or discomfort during exercise. If you experience dizziness or increased heart rate, you should stop exercising. To prepare your joints you need to warm up. After finishing classes you should feel slightly tired. To get results, training must be done regularly.
If you know how to bend in the lumbar region, your buttocks will be visually larger and your waist will be slimmer. This will not only make your figure more beautiful and aesthetically pleasing, but will eliminate the risk of developing a vertebral hernia and injuries when lifting heavy objects.
Stretching exercises
You need to start by relaxing the tight muscles. Since the tight muscles are located deep, it is impossible to roll them out on massage rollers or balls. Therefore, they should be relaxed by stretching the lumbar region. The cause of posterior pelvic tilt is tightness of the external oblique and rectus abdominis muscles, buttocks and hamstrings. The posture resembles a tug-of-war between the glutes, calves, and hamstrings.
Most people believe that the cause is in the hips and that they need to do some quality stretching. However, lack of flexibility in the back of the thigh is a consequence. The hip flexors, iliacus, rectus femoris and spinal erectors need strengthening.
When muscles are stretched, tissue nutrition improves, blood circulation increases, and even strength increases. The result of regular stretching, even without other exercises, is a strong back. Stretching not only improves metabolic processes, but also increases endurance.
Cat-cow
This exercise warms up and stretches the back extensor muscles well.
Starting position: stand on all fours. Arch your back upward, starting from the lower back. While performing the exercise, you should try to feel that your back is rising vertebra by vertebra. Now you need to bend your back down gradually, vertebra by vertebra, starting from the thoracic region. Do 5-8 repetitions.
Tilt towards the legs with stretching
This exercise stretches the quadratus lumborum and spinal extensor muscles. You can use a stopwatch or do counting inclines.
Starting position: sit on the floor, straight legs stretched forward. Bend over without bending your knees and stretch forward, counting to 10, while rounding your back. Then, tensing your back extensor muscles, bend in the other direction, holding the position for 10 seconds. Bend forward again and stretch your legs for another 40 seconds. Perform 3-5 such cycles. You can deepen the pose to give the deep muscles a good stretch.
Quadratus lumborum stretch
Sit on the floor, stretch your right leg forward and bring your left leg back. The angle at the knees should be 90°. Tilt your body to the right, place your right hand on the floor, stretch your left hand to the side and forward, stretching your left side.
While stretching, you should try to pull your left thigh down and back. You need to hold the pose for half a minute, then repeat everything in the other direction.
Iliopsoas stretch
Get down on one knee. There should be right angles between the thigh and the lower leg, the body and the thigh. It is necessary to tense your buttocks, twisting your pelvis. Lower your shoulders, squeeze your shoulder blades together and tighten your abs as much as possible. It is necessary to maintain tension until the end of the exercise.
From this position you need to sway a little back and forth for a minute, then change your leg and repeat.
In this exercise you need to keep your buttocks tense and your pelvis twisted. If you do everything correctly, you will feel tension in the groin of the supporting leg.
iliopsoas stretch on the floor
Lie on your stomach, bend your right knee, raise your shin and grab your ankle with your right hand. Rotate your pelvis and lift your body up. Only the chest should rise, look down, and neck straight. Stay in this position for a second, then lower yourself onto your stomach and change legs. You need to do 5 repetitions on each limb.
These 5 exercises will take no more than a quarter of an hour, but they will relieve the feeling of fatigue and your back will become more flexible.
Strength exercises
Stretching alone is not enough to correct your posture. It is also necessary to perform strength exercises that will increase the tone of weak muscles. Abdominal exercises help to correct hyperlordosis.
Slow crunches
Lie on your back, stretch your arms above your head. Slowly twist your back, first lifting your arms and neck, then the thoracic spine, then the lumbar spine. At the extreme point, the angle between the lower limbs and the body should be 90°, arms raised.
Start slowly lowering yourself to the starting position. Perform the exercise 10 times. Each rise and fall should be completed no faster than 20 seconds.
You need to try to spend more time in difficult poses, and not linger at the extreme points. After contact with the floor, you must immediately lift your body up.
Classic and side planks
Stand in a classic plank position on your hands for half a minute. Turn to the side and lift your hand off the floor, moving into a side plank. Hold this position for 30 seconds.
Return to the straight plank for half a minute, then go to the side plank for the same amount of time. Do as many repetitions as possible.
Exercise “Vacuum”
This exercise will increase the tone of the transverse abdominis muscle, which supports the internal organs.
You need to lie on your back, bend your knees, place your feet on the floor. Place your hand on your stomach to control your movements. Inhale so that your stomach inflates and the hand that lies on it rises. Exhale, imagining that your navel needs to reach the floor or spine. At the same time, the stomach will be strongly drawn in. Stay in this position for 3-5 seconds. Perform 10 repetitions.
Exercises for hips and buttocks
To strengthen the gluteus maximus and hamstring muscles, perform the following exercises:
- Squats with dumbbells, barbell, expander.
- Lunges on one or two legs.
- Deadlift with a barbell or dumbbells on one or two legs.
4 exercises are enough: 2 for the buttocks, 2 for the hamstrings.
Treatment program
Treatment of pathological lordosis is a long process. After a detailed medical examination, a treatment complex is prescribed, which includes:
- medication treatment;
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- exercises.
Physiotherapy
For symptoms of primary or congenital lordosis, surgical treatment is indicated, followed by rehabilitation.
For other types of disease, medications are used to effectively relieve pain, relax back muscles, and reduce inflammation. Only a doctor can prescribe drug treatment, based on the data of MRI and other examinations. The patient should be explained that all tablet forms of drugs have a wide range of contraindications and side effects, so you should not select medications on your own.
Treatment with physiotherapeutic procedures is prescribed in courses. They use acupuncture, therapeutic massage and other procedures according to indications.
Acupuncture session
Special mention should be made about therapeutic exercises. She should become a companion of a patient with pathological lordosis for life. Exercises for the lumbar region have their own characteristics - during any exercise it is necessary to adhere to the principle of “exercise without pain.” In order to prevent hyperlordosis, pregnant women are recommended to wear a bandage and also do special exercises that they are taught at the antenatal clinic.
If you correctly combine medication, physiotherapeutic treatment and physical exercise, the pathological bend will certainly be corrected, but the patient will need a lot of patience and time. We offer you a small set of exercises, which is included in the comprehensive treatment of lordosis.
Simple and effective
Even the simplest exercises must be performed while monitoring your breathing. During exercise, you should breathe through your nose so as not to put a strain on the respiratory system.
- Lying on your back, spread your arms to the sides. Without changing your body position, lift your straight legs up and try to throw them behind your head. It’s very good if you can touch the floor behind your head with your socks. You may not be able to do this at the beginning of classes, but with systematic exercises you will definitely achieve results. By the way, this exercise has a healing effect not only on the lumbar spine, but also on the functions of the pelvic organs.
- Lean forward, trying not to bend your legs. Try to touch the floor with your fingertips.
- Stand against the wall more often, leaning against it with the back of your head, shoulder blades, and buttocks. In this position, try to let your lower back touch the wall. At first, this is very difficult for patients with lordosis.
We reviewed the main types and symptoms of various lordoses, treatment and gymnastics for this disease. If you are familiar with this diagnosis firsthand, try to protect your children from spinal pathologies, monitor their posture, and instill in them healthy habits.
Hello! A beautiful back and correct posture are the dream of both girls and guys. To work out the muscles of this part of the body, it is not necessary to visit the gym. In this article you will learn how to pump up your back at home.