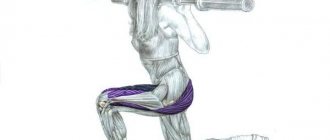
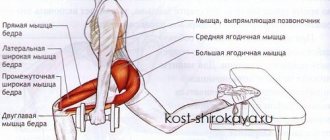
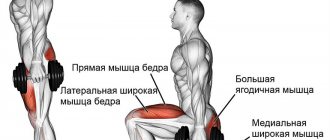
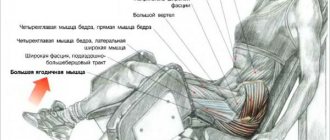
What muscles are trained by curtsey lunges?
Like any lunge, first of all, the gluteal muscles and quadriceps of the thigh are subjected to greater load In addition to the external muscles (gluteus maximus and gluteus medius), the exercise works the gluteus minimus muscles, since the muscle is internal, it will add additional roundness and volume to the buttocks, which cannot be obtained by training only the external group. The shape of the buttocks becomes more “raised” at the top. Additionally, the work includes the hamstrings and adductor muscles of the thigh. To stabilize the spine, the abdominal and lower back muscles are also involved.
Training program for pumped buttocks
If you set out to get round and firm buttocks, then it is better to play it safe and use a specially designed program for this. So, three days every other day is the optimal complex, but you can increase your training frequency - every other day. One approach is one of the listed exercises, which you can choose at your discretion.
| Day/Approaches | 1 approach | 2nd approach | 3 approach | 4 approach | Total |
| 1) Monday | 16 | 16 | 11 | 11 | 54 |
| 2) Tuesday | 17 | 16 | 14 | 12 | 59 |
| 3) Wednesday | 18 | 16 | 16 | 14 | 64 |
| 4) Thursday (Closed) | — | — | — | — | — |
| 5) Friday | 21 | 21 | 16 | 16 | 74 |
| 6) Saturday | 22 | 21 | 19 | 17 | 79 |
| 7) Sunday | 23 | 21 | 21 | 19 | 84 |
| Monday (Closed) | — | — | — | — | — |
| 9) Tuesday | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 104 |
| 10) Wednesday | 29 | 27 | 27 | 26 | 109 |
| 11) Thursday | 31 | 29 | 28 | 26 | 114 |
| 12) Friday (Closed) | — | — | — | — | — |
| 13) Saturday | 36 | 34 | 33 | 31 | 134 |
| 14) Sunday | 38 | 36 | 34 | 31 | 139 |
| 15) Monday | 41 | 36 | 36 | 31 | 144 |
| 16) Tuesday (Closed) | — | — | — | — | — |
| 17) Wednesday | 44 | 38 | 38 | 34 | 154 |
| 18) Thursday | 46 | 39 | 39 | 35 | 159 |
| 19) Friday | 47 | 41 | 39 | 37 | 164 |
| 20) Saturday (Closed) | — | — | — | — | — |
| 21) Sunday | 51 | 46 | 45 | 42 | 184 |
| 22) Monday | 53 | 48 | 45 | 43 | 189 |
| 23) Tuesday | 56 | 49 | 46 | 43 | 194 |
| 24) Wednesday (Closed) | — | — | — | — | — |
| 25) Thursday | 66 | 56 | 53 | 49 | 224 |
| 26) Friday | 66 | 58 | 54 | 46 | 229 |
| 27) Saturday | 66 | 61 | 55 | 47 | 234 |
| 28) Sunday (Closed) | — | — | — | — | — |
| 29) Monday (Final) | 71 | 63 | 56 | 49 | 244 |
Read more: What are the benefits of running on a treadmill for the body?
The main thing is, if you want to quickly achieve results, do not postpone the training to “Monday”.
| Day/Approaches | 1 approach | 2nd approach | 3 approach | 4 approach | Total |
| 1) Monday | 16 | 16 | 11 | 11 | 54 |
| 2) Tuesday | 17 | 16 | 14 | 12 | 59 |
| 3) Wednesday | 18 | 16 | 16 | 14 | 64 |
| 4) Thursday (Closed) | — | — | — | — | — |
| 5) Friday | 21 | 21 | 16 | 16 | 74 |
| 6) Saturday | 22 | 21 | 19 | 17 | 79 |
| 7) Sunday | 23 | 21 | 21 | 19 | 84 |
| Monday (Closed) | — | — | — | — | — |
| 9) Tuesday | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 104 |
| 10) Wednesday | 29 | 27 | 27 | 26 | 109 |
| 11) Thursday | 31 | 29 | 28 | 26 | 114 |
| 12) Friday (Closed) | — | — | — | — | — |
| 13) Saturday | 36 | 34 | 33 | 31 | 134 |
| 14) Sunday | 38 | 36 | 34 | 31 | 139 |
| 15) Monday | 41 | 36 | 36 | 31 | 144 |
| 16) Tuesday (Closed) | — | — | — | — | — |
| 17) Wednesday | 44 | 38 | 38 | 34 | 154 |
| 18) Thursday | 46 | 39 | 39 | 35 | 159 |
| 19) Friday | 47 | 41 | 39 | 37 | 164 |
| 20) Saturday (Closed) | — | — | — | — | — |
| 21) Sunday | 51 | 46 | 45 | 42 | 184 |
| 22) Monday | 53 | 48 | 45 | 43 | 189 |
| 23) Tuesday | 56 | 49 | 46 | 43 | 194 |
| 24) Wednesday (Closed) | — | — | — | — | — |
| 25) Thursday | 66 | 56 | 53 | 49 | 224 |
| 26) Friday | 66 | 58 | 54 | 46 | 229 |
| 27) Saturday | 66 | 61 | 55 | 47 | 234 |
| 28) Sunday (Closed) | — | — | — | — | — |
| 29) Monday (Final) | 71 | 63 | 56 | 49 | 244 |
Features of the curtsy exercise
The peculiarity of the technique of performing cross lunges, performed like a dance “curtsey,” is the additional stretching of the gluteal group. The more a muscle is stretched, the better it grows, since in addition to its contraction, the stretching phase gives the muscle the opportunity to quickly restore its correct (physiological) shape. This is what happens in the lower phase of the lunge, when the supporting (front) leg experiences a greater stretch in the buttocks due to the oblique lunge (criss-cross).
Pros of exercise
- Forms the gluteus maximus muscles, works the deep muscles (gluteus minimus), making the shape feminine and round.
- In addition to contraction, it stretches the muscles, preventing them from becoming stronger in the future.
- Improves coordination of movements, activates stabilizer muscles.
- Tones the outer and adductor surfaces of the thighs, tightening the leg muscles and removes fat deposits of the “breeches” type.
- Fights fatty tissue throughout the body, removing volumes evenly.
- Removes excess fluid, relieving swelling in the legs, improves skin texture.
Disadvantages of curtsey squats
- The technique requires good coordination and stability of the pelvis during a cross lunge, and is difficult for beginners.
- Any problems with the hip, knee, or ankle joints are a contraindication to performing the exercise, since during a cross lunge the joints are displaced, which can cause pain.
- The technique is recommended to be performed only by healthy and flexible people, without disrupting the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Nuances when performing the exercise
The first thing to remember when performing the exercise is the right angle of the working leg. Squatting deeper is dangerous, as you can damage your knee if the angle is more than 90 degrees.
It is worth noting that in order to perform this exercise correctly and without causing injury, the athlete must have great flexibility in almost all the muscles and joints located below the pelvis. If there is no flexibility and stretching, it is better not to perform such movements, they can greatly harm your health.
Technique for performing curtsy lunges
- Place your feet close to each other, palms on your waist.
- Leave your right leg in place, and while inhaling, lunge (step) your left leg back slightly diagonally onto your toes, thus crossing your legs.
- The knee of the back leg does not touch the floor, and the front knee remains at a right angle.
- Feel the stretch in your buttocks; if necessary, move your foot a little more diagonally.
- Exhale and push off with the heel of your supporting foot and return your left leg to the starting point. It is important to feel not only the quadriceps, but also the gluteal muscle when lifting.
- Repeat as many times as necessary on your right leg, then switch sides.
An important feature of the technique: the pelvis does not rotate in the direction of the lunge; keep it stable, without rotating the hip joint and body.
How to perform cross lunges?
Cross lunges are performed at a non-standard amplitude, requiring good joint flexibility. The knees and ankles are placed in an unnatural position, placing increased stress on the target muscle group. The main work falls on the gluteal muscles, leg flexors/extensors, membranosus and semitendinosus muscles.
Execution technique
To learn the correct cross lunges, strictly follow the instructions below. It will help to correctly distribute the load and protect the joints:
- Diagonal lunges begin with the correct position: stand shoulder-width apart, feet parallel to each other. Hands can be folded near the chest or placed on the belt.
- The weight is transferred to one leg. The second in diagonal amplitude is retracted back. Turn the abducted toe slightly inward (the knee points in the same direction).
- Squat down so that the thigh of your supporting leg is parallel to the floor. The knee joint does not extend beyond the toe, the weight rests firmly on the heel. As you lower, pull your knee towards the floor, but do not reach it. In the peak phase, maximum stretching of the gluteal muscles is felt.
- Rise back up, straightening your legs to the starting phase.
- Perform diagonal lunges alternately on both legs, or first on one leg, then on the other.
At the initial stage, carefully focus on the range of motion. Here it is important to feel the work of the muscles, feel the tension and prevent pain in the joints.
What muscles work?
During the work, the main emphasis falls on the gluteus maximus/minimus muscles, as well as the quadriceps muscles of the lower extremities. Additional load is placed on the adductor muscles of the thighs and quadriceps. Curtsy promotes the development of spinal stabilizers, lumbar muscles and abs.
Cross lunges are a favorite exercise among girls who dream of pumping up beautiful rounded buttocks and working on slender legs. Men perform this exercise less often, using it in situational leg training. Curtsy lunges are optimal for working with your own weight, which is important for people working out at home.
Although in general, diagonal lunges are a universal exercise that is suitable for men and women. You can load your legs using this method even during a simple morning warm-up.
Be sure to check out:
- Ready-made training plan for 3 days for girls
- Ready-made 10-minute exercises for posture
What should you pay attention to?
When performing diagonal lunges, control your own technique by performing the exercise in front of a mirror. Pay special attention to the following aspects:
- Do not lift the heel of the supporting leg. Only the leg laid back is on the toe.
- Vary the load, listening to the body. The growth of physical indicators will allow you to work with weights. Beginners are advised to focus on bodyweight exercises.
- Take your foot a little more than a standard step. You don't need to put it too far away. At the bottom point, the shin of the supporting leg remains exactly perpendicular to the floor - use this position as a guide.
- If you find it difficult to maintain balance, it is permissible to turn the toe of your supporting leg slightly inward.
- The optimal number of repetitions is 15 times for 3-4 approaches.
Cross lunges are easy to master. The main thing is to slowly repeat the instructions on the technique, and also remember a number of common mistakes.
Top 30 exercises for slender legs
Basic errors during execution
Every mistake when performing diagonal lunges can negatively affect the health of the knee joints. Please note the errors that need to be excluded:
- Do not rotate your knee joint. Fix its direction in the same direction where the sock is pointing. This way you can avoid pain or injury.
- Don't turn your pelvis to the side. The pelvis looks straight forward, focus on the pelvic bones. Otherwise, the load on the buttocks will be insufficient.
- Avoid lifting weights at first. While studying the specifics of the exercise, bring the movement to automaticity without weights. Only then take the weight, gradually increasing the weight of the dumbbells.
- Do not hurry. Diagonal lunges are performed at a medium pace; you should feel the tension in every working muscle.
- Don't do exercises like the diagonal lunge without warming up. Start your session with a good warm-up of your legs by performing warm-up exercises (basic squats, leg raises, knee rotations).
Ready pre-workout warm-up
Avoid this position of the supporting leg in front:
High load level
Option No. 1: with a platform
Perform lunges while standing on a platform, lowering your feet to the floor diagonally. The platform will increase stretching of the gluteal muscles.
Option #2: Cross Lunges with Dumbbells
- Take light dumbbells in your hands.
- Lower them straight along the body.
- Perform cross lunges without bending your elbows, holding dumbbells in one position along your thighs.
Option No. 3: with a barbell
- Place a small barbell or empty bar on the top of the trapezius muscle.
- Keep your back straight without bending forward.
- Stabilize your position and tighten your back and abdominal muscles.
- Perform lunges on one leg, then change to the other.
- After this, lift the barbell above your head, lower it slowly to your chest, and straightening your elbows, lower it to the floor.
Important! When working with heavy weights, perform the exercise in a special power rack, removing the barbell from the racks and returning it back immediately after completing the exercise.
Option #4: Smith machine
- Level the bar in the machine by placing it at shoulder level.
- Place the bar on the trapeze, grasp it with your hands wider than shoulder-width apart.
- Lift the bar from the racks, turning the hands, remove the locks.
- Standing in the center, perform lunges on one side, then on the other. Do not rotate your body and pelvis.
- After completing the approach, rotate and secure the bar to the racks.
Types of Back Lunges
There are many different variations of back lunges that specifically load individual muscle groups in the legs. Most often, athletes resort to methods of performing with their own weight, barbell or dumbbells.
The type of exercise you choose depends on your training and personal preferences. Be open to experimentation. This is the only way you can create the most effective workout to achieve your goals.
10-minute static exercises for the abs
Reverse lunges with dumbbells
Taking the shells in your hands, stand with your back straight. Shoulders are straightened, there is a natural arch in the lower back. Place your feet shoulder-width apart, then take a step back. In the lower phase, the back leg stands on its toe, barely touching the floor with its knee. The lower leg of the working leg is fixed perpendicular to the floor. The bend angle of the knee joint is 90 degrees.
The main work falls on the gluteus maximus, as well as the quadriceps muscles of the thighs. The calf and soleus muscles are additionally strengthened. The option with dumbbells is optimal for beginner athletes. At first, work with light weights to establish the technique.
Reverse lunges with barbell
Accept the barbell on the trapeze. Don't slouch or roll your shoulders forward to avoid injury! Place your feet shoulder-width apart. Now take a step back, placing your supporting foot on your toes and your working foot on your full foot. In the lower phase, maintain a right angle when bending your working leg. Push off forcefully and return to the starting position.
Back lunges with a barbell are optimal for experienced athletes due to the high load on the back. The exercise requires good physical fitness. In addition to the leg muscles, it develops body stabilizers, strengthens the muscles of the lumbar region and paravertebral columns.
Back lunges with pulse 1-2-3
Reverse pulse lunges are performed with a 1-2-3 rocking motion at the bottom. Excellent for working out the relief of the quadriceps and shaping the gluteal muscle group.
Squat + Back Lunge
Do a classic squat. Then, without fully straightening, lunge back, taking a wide step back. The training element develops the overall strength of the legs, allowing you to improve the relief, increase muscle volume and burn excess fat.
Back Lunge + Knee Raise
Intense reverse lunges with knee raises are great for a fat-burning workout. They actively work the lower part of the abs, allowing you to remove fat from the waist area.
Back lunge + forward leg swing
A more advanced variation of the swinging backward lunge is often included in fat-burning workouts. The idea is this: rising from the bottom phase, kick forward, raising your leg parallel to the floor.
Back Lunge + Forward Lunge
Lunges to increase strength and volume of leg muscles. Lunge back, rise to the starting phase and immediately lunge forward. Your glutes and quads will literally start to burn!
Lunge with leg abduction
Lunge and instead of returning to the starting position, lift your straight leg back and up, then lower back into the lunge. This complicated variation of the lunge helps to specifically work the buttocks and back of the thigh, which means it will especially appeal to girls.
2 workouts for the hamstrings
Half Squat Back Lunges
Sit in a deep squat position with your arms clasped together in front of your chest for balance. From this position, lunge backwards. The training element is aimed at burning fat and developing static strength, which helps adapt the muscles to high loads.
Jumping lunges
After making a reverse lunge, forcefully return to the initial phase so that you get a jump at the peak. In the same jump, lunge backwards. This is an indispensable exercise for home cardio training.
Comparison of different types of lunges
Back lunges have many variations. Beginning athletes often think about their features, since some methods have a lot of similarities. Let's look at a number of exercises that are relatively similar to each other:
- Reverse lunges with a barbell or lunges with dumbbells. The barbell is more suitable for experienced athletes. In addition to the load on the legs, the back and lower back work here. Maintaining balance becomes more difficult, but the efficiency of the exercise is higher. The option with shells in each hand is easier to learn, helping to actively load the hips and legs. Lunges for women with dumbbells are more preferable. Lunges for men, in turn, are best mastered with a barbell.
- Forward lunges or backward lunges. The difference lies in the direction, which affects the load distribution. The reverse variation is better suited for beginners due to less stress on the knee (since the supporting leg remains stationary).
- Standing lunges and reverse lunges. By performing repetitions on the spot, you improve the relief of the quadriceps, and also actively pump up the gluteal muscle. Reverse lunges are more basic. They help increase the physical fitness of the muscles of the lower extremities. Also, lunges on the spot constantly load the knee joint, which is why they are traumatic.
Leg and butt workout for beginners