Types of long distance running
Running distances between 800 and 3000 meters are called middle distance running. Anything over three kilometers is a long distance.
This type of physical activity has an alternative name – stayer running. Stayer from the English “stayer” - hardy.
There are professional and amateur varieties of this sport. Let's look at the main types of long-distance running.
Olympic distance
Olympic distance – 5000 and 10000 meters race. This is an athletics classic. Competitions are held at the stadium. Athletes start from a high start and run in a circle. The length of the Olympic circle is 400 meters.
Marathon
The classic marathon is included in the Olympic program. The race takes place on the highway. Distance – 42 kilometers 195 meters. There are different types of marathon.
The half marathon is also an Olympic discipline. The length of the route is 21 kilometers 97.5 meters.
An ultramarathon is a race over any distance beyond the marathon. This sport is popular in many countries, but is not included in the Olympic program. The World Championships are held under the auspices of the International Ultramarathon Association. The standard distance is 50 and 100 kilometers.
Timed running is another type of long distance running. The runner's task is to run as far as possible in a certain period of time.
There is no set distance for this type of run. The organizers set only a time limit: from one hour to one day. The latest world record for 24-hour running belongs to Australian runner Yanis Kouros. In 24 hours he ran 303.506 km.
Cross
Cross – long distance running over rough terrain. Until 1924, this type of athletics was part of the Olympic Games program. Now cross-country is a health jog.
The race is held among amateurs. The conditions of the competition do not have strict international regulation. The route runs through a forested area and open spaces, outside the stadium. Length from 4 to 12 kilometers.
Cross-country is the best type of running for health. Rough terrain puts stress on your muscles. The sun's rays provide vitamin D. Fresh air enriches the body with oxygen. Aerobic metabolism starts in the body, and calorie consumption increases. The extra pounds are gone. The mood is lifted.
Jogging
Jogging is a good way to avoid a heart attack. Essentially the same cross, with one global difference. No competitive activity. This is a pure form of amateur running.
In the USA, jogging has another name - jogging. From the English “Jogging” - shuffling.
A characteristic feature of jogging is a special running step. The “flight” phase is very short. The relaxed foot “slaps” on the ground. The runner shuffles his feet. The impact load on the joints is minimized.
The beauty of jogging is its ease. The technique is based on natural, relaxed body movements. This allows you to go on long runs. Typically, training time is 40–60 minutes. Running speed 7–9 km/h.
Jogging (cross), like other types of long-distance running, causes a condition called runner's euphoria. Running gives us such a positive psychological state. And this is not the only bonus.
Finishing technique
Finishing is the most emotional and important stage in long-distance running. The finishing technique is aimed at trying to preserve the maximum strength and speed of the athlete for the final throw.
At the finish line, running speed usually increases. The average length of the distance to increase speed is 200-300 meters, it all depends on the specific capabilities of the individual.
At the final stage of the distance, the athlete’s torso tilt increases and the activity of the arms increases. When finishing, the running gradually slows down, and the athlete gradually takes a step and stops.
The benefits of long distance running
The peculiarity of long-distance running is prolonged aerobic exercise. The body triggers many biochemical reactions. The essence of all processes can be expressed in one word – benefit.
What does long-distance running develop?
1. Endurance. Easy long-distance running is an ideal training regimen for developing endurance. At this pace, the heart rate is 60–70% of MHR . This rhythm will strengthen the heart muscle and increase lung capacity.
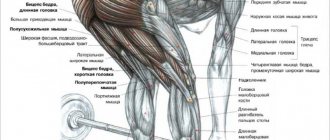
2. Musculoskeletal system and internal organs. The uniqueness of stayer running is in its biomechanics. A long distance means a short running stride. This technique softens the shock load. Running training triggers aerobic processes . Every cell of the body breathes and gets rid of toxins.
The benefits of running for internal organs
Long distance running increases lung capacity. The lungs draw in air and force the heart muscle to work.
The heart “drives” blood through the vessels. The blood supplies the internal organs with nutrients and takes away waste through the walls of the vessels.
The vessels become elastic. Their capacity is increasing. Cholesterol content decreases.
The liver receives greater blood flow, which accelerates the processes of regeneration and cell renewal.
Prolonged exercise burns glycogen in the liver and uses up fat deposits.
Calories “burn” and heat the body. The temperature is rising. Harmful microbes die. ARVI and flu are running away.
The sweat glands open up. Toxins are removed along with sweat. The condition of the glands is improving. The skin becomes more elastic.
Running exercise helps the digestive organs and eliminates toxins. Muscles are in constant motion. The intestines receive a kind of massage. This tone relieves diarrhea and constipation.
The benefits of running for the skeleton and muscles
Long-distance running develops the musculoskeletal system and strengthens the skeleton. Good blood circulation improves phosphorus-calcium metabolism. The mineral content in bone tissue increases. The benefits are obvious. Cross compacts bones and strengthens ligaments.
Stayer running involves working the whole body. The lower limbs receive the maximum load. Regular exercises develop leg muscles, tighten the buttocks, dry out the abs, and strengthen the back.
The benefits of running for the psyche
Regular long-distance running strengthens mental toughness. This type of physical activity causes a special condition.
The runner feels a surge of adrenaline and elation. Increases resistance to pain and fatigue. Scientific theory calls this phenomenon runner's high .
Athletes compare it to mild intoxication. In this state it is easier to overcome difficulties. As a reward, the athlete receives good health and increases self-esteem.
Runner's euphoria is the nervous system's response to physical activity. The muscles are actively working, the brain rewards the body with hormones of happiness.
Running a long distance will relieve depression and relieve nervous tension.
Training program for long sprints and middle distance running[edit | edit code]
The most important physical quality of long-distance runners is high aerobic capacity, which is necessary to maintain a steady and fast pace during a long race. The sources of energy used during the race are glycogen and free fatty acid. An example of a periodization model is given in the table.
- ergogenesis: distance 10,000 meters – 3% lactate system, 97% aerobic system; marathon – 100% aerobic system;
- main sources of energy: glycogen, free fatty acid;
- limiting factor: long-term muscular endurance;
- training goals: long-term muscular endurance (all distances), strength endurance (distance 10,000 meters).
Periodization Model for Long Distance Running and Marathon
| Periodization | Oct. | Nov. | Dec. | Jan. | Feb. | March | Apr. | May | June | July | Aug. | Sep. | ||
| Prep. | Compet. | P | ||||||||||||
| Force | 8 /L | 6 MS, M | 6 SMV, MS, SV | 8 Conv. in the DMV | 14 Subject: DMV, MS, SV | Comp. | ||||||||
| Energy systems | Aerobic performance | Aerobic performance, Aerobic M | Aerobic performance, Aerobic M, lactate performance | Other activities | ||||||||||
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Exercises for the gluteal muscles - how to pump up the gluteal muscles?
Effective training of the gluteal muscles. Exercises for the buttocks at home and in the gym Maximum strength less than 80% of the repeated maximum. Legend: AA - anatomical adaptation, slave. – performance, competition. – competitive stage, comp. – compensation, conv. – conversion, sub. – support, DMV – long-term muscular endurance, SMV – medium-term muscular endurance, MC – maximum strength, M – power, SV – strength endurance, prep. – preparatory stage and P – transitional stage.
How to learn to run long distances
If you want to learn to run for health, and not for rewards, then do not think about speed and distance. Focus on the duration of the run.
If you've never run before, start with short runs. The first run should not take more than 15 minutes. Gradually increase the distance. Increase your running duration to 40–60 minutes. When such a load begins to pick up, switch to interval running .
Common mistakes in technology
Improving middle-distance running technique is impossible without examining common mistakes.
- At the start, the pushing leg should not be too close to the zero line. Shoulders cannot be carried beyond the starting line. The legs should not be bent to a half-squat; it is only correct to bend them slightly at the knees;
- During acceleration, the legs, bent at the knees, are not thrown very upward, and the foot in the air always remains parallel to the floor (do not lift up);
- While running, the chin is pressed to the chest, they do not look around, the gaze is concentrated on the treadmill;
- The arms are not thrown up at the finish, especially during the chest jerk, they are even pulled back slightly.
- Pay attention to the position of the foot when running at medium distances - the toes are slightly turned inward.
Main distance
The main distance is covered with a sweeping step, length from 1.6 to 2.2 m, with a frequency of 3 to 4 steps per second.
— When running, it is best to start placing your foot on the support starting from the front of the foot, and only after that lower it completely to the surface. Thanks to this approach, the braking effect is reduced and running becomes much smoother.
— Long and medium distance running technique
, instructs athletes to push off from the surface in such a way that the supporting leg straightens in the projection of all joints. Then, bend at the knee joint, with the heel slightly above the knee.
— Bringing the leg forward while running is best done through the movement of the leading hip. The thigh of the leg does not rise to the horizontal level, but slightly lower.
— The optimal tilt of the runner’s torso is 4-5 degrees forward, which increases during the athlete’s push-off and decreases for landing.
— While running, your arms should be bent and move in unison with your legs, your shoulders should be relaxed and lowered. When the arm moves forward, the shoulder should also move forward along with it, due to which the work of the opposite leg, hip, and arm is compensated.
— Regarding breathing during running, the clarity of its rhythm and active, correct exhalation are very important. If an athlete exhales correctly, the inhalation will be deeper and fuller.
The main principle of overcoming a medium or long distance is the desire for smoothness and conservation of energy. Athletes with good technique know how to rest their muscles while running, when strenuous leg work is not required.
Equipment selection
Much of long-distance running technique depends on elements such as shoes and clothing.
- Sneakers . Long-distance running shoes are called “marathon” shoes. They are created using special modern technologies that ensure comfort for your feet throughout the entire race. They are made from lightweight materials with the thinnest soles. These sneakers are flexible, they have almost no drop between the heel and toes. But when choosing a model, you need to take into account not only these factors, but also the weight of the runner and the biomechanics of the leg. Never skimp on running shoes for long runs, otherwise both your technique and your limbs may suffer greatly.
- Cloth . It is recommended to run long distances in T-shirts and shorts made of synthetic materials, since natural ones will get wet and become heavy. Products designed with DRI FIT KNIT technology are popular. They are made from super-thin materials that provide cooling and maximum elasticity.
- Socks . Professionals typically use compression socks. In addition to comfort, they improve blood circulation and keep leg muscles toned.
It is also worth noting such a moment as nutrition. The athlete's body must receive the required amount of proteins and carbohydrates, which will replenish energy resources. An important nuance is the liquid. Violation of water-salt balance is a common problem during long runs, since a lot of water and salts are excreted through the skin through sweat. It is recommended to drink 50-100 ml of fluid every 15 minutes of running. Moreover, to maintain balance, it is better to drink not just water, but isotonic sports drinks, which are close in composition to blood plasma.
Long-distance running is a special discipline in athletics. Those who want to learn how to run long distances, cover long distances and win competitions will have to train a lot, understand their capabilities, calculate their strength and conduct thorough preparation for the race.
How to train?
Training for middle distance running requires a consistent approach.
- To begin with, it is important to study the technique in theory - for this, athletes watch videos, analyze tactics in diagrams;
- Next, they practice the technique of movements of each part of the body - arms, legs, head, body, feet;
- Beginners begin to run in a straight line, practicing alternating speeds. Interval running and hill running are considered excellent exercises;
- A tow race is often practiced, in which a strong athlete leads a weaker one on a leash (literally, on a rope). Harsh methods are not used everywhere and can lead to injury;
- Separately, exercises for running over medium distances are practiced to increase endurance - long and medium sprints, running up stairs, shuttle running, with obstacles.
- Athletes also learn to competently enter a turn without losing speed;
- Particular attention is paid to studying correct starting and finishing techniques.
Types of long running
Depending on your goals and specialization, a long run may contain different execution scenarios. Its content, volume and intensity will differ in relevance for different periods of preparation in the annual cycle:
- Long running at a constant pace to develop general or specific endurance (for example, 32 km at 4:45/km).
- Long run with an approach to the finish line (for example, 20 km easy + 4 km at half marathon pace).
- Long progressive run (eg 28 km from 5.30/km to 4:20/km).
- Long variable running (for example, 30 km = 5 series * (2 km easy + 4 km at marathon pace).
- Long run with accelerations inside (for example, 32 km = 20 km at 5:00/km + 8*500 m fast/500 m easy + 4 km easy).
And also as a specific remedy:
- Long tempo run on a depleted glycogen (eg 20 km at 4:00/km with a preliminary carbohydrate fast of 18 hours).
- A special block that combines long and tempo running (for example, 30 km = 20 km moderately depleting glycogen + 10 km at half marathon pace).
Execution technique
Middle distance running
- Be able to take starting positions.
- When running, keep your torso straight, move your pelvis forward, bend slightly at the lumbar part (shoulders free, arms bent at the elbows).
- Lower the swing leg onto the support using a raking motion on the forefoot.
- Take off with full extension of the leg and active movement of the bent swing leg forward and upward.
- Actively perform counter movements of the hips in the unsupported period.
The technique and tactics of middle-distance running are based on sequentially overcoming 4 phases: start, acceleration, running and finish. Athletes learn to competently enter each stage and successfully combine them into a single whole. All efforts are aimed at the ability to properly spend energy, maintaining maximum speed. Let's look at all the phases of middle distance running individually.
- They start moving from a high start. Starting position – pushing leg in front, swing leg behind, the distance between the feet is 20-35 cm. Legs are half bent at the knees, the weight of the body is transferred to the front, the head is lowered, the gaze is looking down. The arms are bent at the elbows, relaxed, the hands are gathered into weak fists;
- According to the rules of middle-distance running, there is no “Attention” command here; immediately after “To the start” comes “March”. As soon as the last one sounds, the athlete makes a powerful push forward.
Overclocking
- You should accelerate immediately to maximum from the first seconds of the race. Later the speed will decrease slightly for efficient energy consumption;
- The starting speed is always higher than the distance speed, because it is psychologically important for the athlete to get ahead at the very beginning of the distance;
- Closer to 70-100 meters, it is necessary to gradually reach the desired speed limit, at which the athlete will successfully complete the route without losing position;
- The step length should be about 2 meters, the athlete takes 3-5 steps per second;
- The body is slightly tilted forward, literally 5°.
- The arms are bent at the elbows and move in opposite directions with the legs, and the intensity of their movements greatly affects the speed of movement. The more actively the athlete works with his upper limbs, the faster he covers the route;
- The upper body is as relaxed as possible.
- This stage begins another 300 m before the end of the middle distance;
- The athlete increases the frequency of steps;
- The torso leans forward more to take advantage of inertia;
- An octopus or finishing acceleration is practiced, in which the athlete gathers his remaining strength and performs a powerful acceleration;
- It is allowed to use the final jerk to the finish line - a lunge with the chest or shoulder.