Running speed gives a person many benefits that can be applied in everyday life and sports. Running is a cyclic exercise in which there is a single-support position, which turns into a flight phase. Running while standing on two legs is impossible.
It is worth paying attention to the flight phase. To increase running speed, you need to reduce this phase to a minimum. Since running is the pushing of the supporting leg from the surface, the flight phase is only the result of a cycle. That is, flying while running is a side effect. If you shorten the flight phase, then over the same distance you can make more push-offs, but in less time.
Maximum, average and record running speed
A fast step is considered to be moving at a speed of 5–8 km/h. Running starts at 9 km/h. In theory, the maximum running speed of a trained person can reach 64 km/h, but so far no one has been able to come close to this figure . Usain Bolt's world record, listed in the Guinness Book of Records in 2009, is 19.28 km/h less than this figure.
In practice, a person’s running speed depends on the body’s endurance, weight, height, goal and, especially, the distance covered. Each running distance in athletics has its own name and best indicators:
- Sprint is short distance running from 100 to 400 meters. In the fastest form of running, athletes do not need to distribute their forces. In order to run quickly in extreme conditions with a lack of oxygen, they have to train using a special anaerobic technique with holding their breath for a certain segment of the distance. The best sprinters run 100 meters in 10–11 seconds. The world record is held by Jamaican athlete Usain Bolt, who ran the 100 meters in 9.58 seconds and the 200 meters in 19.19 seconds. The 400-meter record holder is Weide van Niekerk with a result of 43.03 seconds. However, endurance champions demonstrate such indicators in competitions, and during regular training they run 10–30% slower.
- Stayer - average distances ranging from 800–3,000 meters. Stayer running is not much different from marathon running. Athletes have to use different running techniques: run smoothly for most of the distance, saving strength for acceleration at the finish line. The average speed of an adult with training experience is 18–23 km/h.
- Marathon - long distances of more than five kilometers. Over long distances, athletes reach their maximum possible speed in the last section. But because marathon runners have to distribute energy over long distances, they cannot accelerate like sprinters. Beginners complete marathons at an average speed of 9–12 km/h, while trained athletes run 16–18 km in an hour. Wilson Kipsang showed the fastest speed at a distance of 42.2 km. He accelerated so much in the last seven kilometers that the average was 20.5 km/h.
The sporting achievements of the fair sex are 8–14% less than those of men. My running results are worse for several reasons:
- increased muscle elasticity;
- the proportion of adipose tissue is approximately 10% higher compared to men;
- the proportion of muscle mass is 15–25% lower;
- the volume of the lungs and heart is 10–15% less;
- hemoglobin is 15% lower than in men, which causes the body’s lower ability to transport oxygen;
- 20% less energy-generating mitochondria;
- the level of testosterone, which regulates the functioning of the musculoskeletal and endocrine systems, is 10–15 times lower than in men.
If there are less than 3 weeks left before passing the standard or competition
In this case, it will not be possible to have time to train the body well. Therefore, it is necessary first of all to teach him to run. To do this, perform speed runs. For example, 10 times 30 meters. Or 7 times 60 meters. Run at ¾ strength, and for the last time in the series, try to run at your maximum. It is best if the time of all runs is the same, and the last one is the fastest. Don't try to do everything 10 times to the maximum.
At the beginning or end of each workout, perform 3 sets of squats, steps, or some type of jumping. Just don’t overdo it, 3-4 exercises per workout will be enough. 4 days before the start, stop all strength and jumping training and focus only on speed running. 2 days before the start, leave only the warm-up and light accelerations, no more than 3-4 times.
Biological capabilities and running characteristics
The biological limit of maximum speed is determined by:
- injuries and illnesses;
- leg length;
- body weight;
- the ability to resist fatigue during oxygen deficiency;
- metabolic rate and muscle recovery;
- endurance;
- anaerobic threshold - the extreme intensity at which lactate accumulates in the muscles and blood faster than the body can remove it.
The following factors influence the speed indicator:
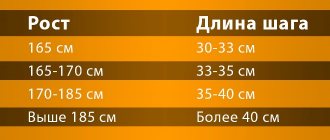
- stride length;
- coordination of movements;
- flight phase;
- the force of the foot hitting the running surface;
- the period of time during which the foot is in contact with the support;
- torso tilt.
Athletes regularly perform gymnastic stretching and basic leg exercises to increase running speed and endurance: squats, lunges, jumping rope, and hopping. The set of exercises is so simple that you can work on explosive leg strength both at home and in the gym. To increase functional strength, professionals conduct sprint training with resistance and weights: a parachute, a weighted harness, a loaded vest.
Development of speed, means for this
Speed is not an innate quality; it can be developed. The means include general strengthening and special sets of exercises. The latter are divided into three types:
- Cyclic (performed repeatedly, with increasing frequency). Example: working on an exercise bike.
- Acyclic exercises (using higher speed) - boxing punches.
- Mixed - football, basketball.
A general requirement for performing exercises is to use maximum speed. In this regard, tasks should be simple.
How fast can an average person achieve in running?
Children (before puberty) run a hundred meters in physical education lessons in 14–17 seconds. The average young person who has no contraindications to running, excess weight or bad habits can run a little slower. Over a month of training, non-professionals can improve their results by 1–2 seconds. With regular exercise, progress will gradually slow down.
An average person who regularly exercises for health runs a hundred meters in 13–15 seconds. Women are 1–1.5 seconds behind men. As for the average running speed at other distances, for trained men this value is within the range of 15–20 km/h, and for women – 12–15 km/h. High speed is needed for records, not for health. The simplest and most accessible type of activity for an untrained person is jogging. Speed is not important in this type of running. Beginners should focus only on internal comfort and periodically record their heart rate and pressure. If the indicators are normal, you can increase the pace.
Motor reaction time
In another way, the motor reaction time can be called the latent period. That is, it is a pause, with a different time period, between the perception of the stimulus before the start of making a decision regarding it.
The speed of the reaction, in turn, is determined by the time that passes from the moment of action of the external stimulus to the body’s reaction to it.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Dumplings with potatoes, calorie content, benefits and dietary properties. Diet on dumplings and dumplings
There may be several or one irritant. In the first option, they can occur synchronously or in stages. But in various situations, new reactions, easy and difficult, will be born in a person’s head.
An example of the first would be starting a run, shooting at targets for a while, throwing a ball on a whistle. Using the example of a runner, the shorter the time period from the moment the signal for action is given to the point at which it begins, the higher the level of speed of his simple reaction will be.
Moreover, athletes have a shorter latent time for a simple reaction than people who do not have special training. When working with it, a person uses a complex of innate analyzers - this is perception using vision, hearing and other senses.
An example is the game of a hockey player who, having seen a moving puck, must analyze its speed, trajectory, mentally work out the tactics according to which he will act, and be able to translate it into reality.
Health running
Beginners who have tried to run aimlessly or torment themselves with super speeds often come to the conclusion: “Running is not my thing!” But you shouldn’t chase other people’s achievements and try to surpass athletes who brag about their success in motivational videos. You need to choose a time, duration, normal pace and place that is convenient for training. For example, many people prefer mountain cross-country to road running. Working out on a treadmill is not comparable to running outdoors.
When choosing running shoes, take into account the nature of pronation of the foot. To determine your arch type at home, you need to do a “wet test”: wet your bare feet and stand on a sheet of thick paper. Having left the sheet, you need to circle the prints with a pencil. With overpronation (flat feet), the foot is completely imprinted - there is practically no bending on the inside. Too much curvature indicates underpronation. And if the print description is between these two cases, then you have a neutral (correct) arch.
The first stage of preparation for health running is brisk walking, which develops joints and prepares the body for further stress. After several weeks of walking (the duration of training depends on age and health), you can move on to jogging. It is better to start with interval running, the technique of which is to alternate jogging with walking. Optimal speed for recreational running:
- jogging - from 6 to 9 km/h;
- light elastic running “footing” - from 10 to 12 km/h.
Healthy running should be regular and begin with a 10-minute warm-up and end with muscle stretching. It is advisable to exercise at least three times a week, create a training program and choose a pace taking into account the maximum heart rate. To calculate your maximum heart rate, you need to subtract your age from 220.
Heart rate characteristics when running:
- 80–100% of maximum heart rate—speed development;
- 70–80% of the indicator (optimal heart rate when running) - improved form, heart training, increased muscle tone;
- 50–60% - improved overall health, increased endurance, accelerated recovery processes in the body.
Pulse monitors, special watches and other gadgets that signal when a given threshold is exceeded will help you monitor your heart rate while jogging. You can independently calculate the frequency of impacts in 15 seconds and multiply the indicator by 4.
Strive to enjoy running and set realistically achievable goals. A great mood and a positive attitude will help you go through a fascinating journey from the couch to a 10-kilometer run and set your own record!
About agility
Dexterity is an ability that allows you to instantly rearrange the functioning of the motor system, according to a changing situation. This is a most complex quality, manifested in the constant mastery of complex coordinated movements. Moreover, the task at hand must be dealt with economically and resourcefully, instantly and with precision.
Dexterity directly depends on a complex of developed physical qualities - strength, endurance and speed. Because a constantly changing environment requires high speed of information processing and programming of response decisions.
As a result of increased mobility of nervous processes, muscles are quickly involved in work, thereby ensuring rapid transitions from contraction to relaxation.
Speed and agility are qualities that can only be developed through intensive training, and they are formed throughout the rest of life. The most favorable period for the perception and assimilation of new motor actions is considered to be the age of 10–11 years.
It is necessary to develop agility systematically, that is, training cannot be skipped. And the better developed the motor system, strength and muscle structure, the greater the speed.