Exercises for Tibial Syndrome
Muscle pain syndrome is caused by spasm.
To determine the cause of the pain, you need to analyze your previous day. The reasons may be the following:
- Trauma and overexertion. Pain occurs when the integrity of muscle fibers is damaged and there is increased tone.
- Poor posture. Sitting at a table for a long time in the wrong position, wearing uncomfortable shoes, skewing the body to one side - all these factors contribute to the appearance of pain.
- Emotional stress. Especially typical for children. Stress often causes muscle tone.
- Myalgia. A disease accompanied by insomnia. It is characterized by muscle pain on all sides.
- Excessive physical activity. Typical for men involved in heavy sports or in the gym.
- Myositis. The inflammatory process in muscle fibers develops after infections or injuries. The pain intensifies with movement.
During active exercise in the gym, lactic acid accumulates in the muscles, and microcracks may appear in the fibers. Before each approach, it is recommended to shake the limb to disperse the fluid that puts pressure on the nerve endings.
Pain after training can be natural or pathological. Natural ones occur in the following cases:
- after the first workout, since the body is not yet accustomed to the stress;
- after a long break;
- when adding new exercises to the program;
- with increased intensity of exercise.
To relieve pain of this nature, it is enough to stretch and take a warm shower after finishing the workout.
Pathological pain is characterized by severity and duration. Occurs in cases:
- incorrect execution of exercises;
- classes without warming up and stretching;
- poor nutrition;
- excessive physical activity.
Additional symptoms may appear - hematomas, swelling. If such pain occurs, you must stop training and immediately consult a doctor. In the future, it is important to give the muscles proper rest between workouts so that they have time to recover.
Lack of sleep, daily grueling workouts, poor nutrition - all these factors have a detrimental effect on the condition of the muscles.
Types of calf muscles
If you experience pain in your tibialis anterior muscle, it is likely due to a condition called anterior tibial syndrome, or shin splints. There are several factors causing this condition:
- Flattened arch of the foot (flat feet). Causes a divergence of the bones between the shin and the metatarsus, this increases the load on the tendons of the front of the shin and provokes pain in the lower third.
- Tendinitis. Inflammation can affect all tendons of the leg. It occurs mainly due to running on unsuitable surfaces, which causes one foot to regularly roll inward. A one-time increased pronation (dislocation) can also cause tendinosis.
- Tenosynovitis. Another type of inflammatory process. Localized in the tissues of the tendon sheath.
- Syndrome of the anterior fascial bed of the leg. Injuries that cause swelling of muscle tissue (bruises) create pressure in the area where the deep peroneal nerve and anterior tibial vessels - artery and vein - are located.
- Stress fractures. This bone damage is the result of increased physical activity. It occurs most often in sprinters and marathon runners. The manifestation of tibial syndrome in this case is preceded by inflammation of the periosteum.
- Insufficient recovery from previous injury. Enough time must pass for the ligaments to recover, otherwise the risk of relapse is high.
- A sharp increase in physical activity. The workout should begin with a warm-up, and its intensity should correspond to the person’s level of training.
With the development of tibial syndrome, pain in the lower leg is noted, which is especially severe in the morning. In advanced cases, pain is felt when moving, discomfort during palpation and swelling. If neuralgia occurs, that is, damage to the nerve, the patient’s gait changes, it becomes awkward, with emphasis on the toes.
As soon as you feel that the tibialis anterior muscle hurts when walking or begins to cramp, you must urgently reduce the load and consult a doctor.
Cold compress to neutralize inflammation in the knee area
Treatment for the syndrome does not require you to stop training completely. However, it is necessary to regularly provide rest to the injured limb.
If your tibialis anterior muscle hurts when running, you may want to increase your cadence by 10%.
It is also necessary to apply cold to the injured limb to neutralize inflammation. The main rule is to wrap the ice in a towel to prevent direct contact with the skin. As part of anti-inflammatory therapy, you can also use ointments, lotions, and shock wave therapy.
Massage will help relieve tension, restore blood supply to the limb and tone the muscles.
It is important to exercise your legs regularly. Strengthening and stretching the muscles will make them more elastic and also protect the tibia from cracks and fractures. This has a beneficial effect on both the condition of tendon tissue and strength qualities. In addition, all the proposed measures will help restore the ability of the tibial nerve to innervate the surface of the leg.
After conducting an examination, the doctor will be able to tell why the pain does not go away. Modern diagnostic methods identify many diseases, such as transposition of the posterior tibial muscle, tear and rupture of ligaments and tendons.
Light exercises to relieve symptoms
When the tibialis anterior muscle hurts, exercise will help not only relieve symptoms, but also prevent re-injury to the tissue. To strengthen the muscles of the lower leg, the most effective exercise is to stretch the ankle joint. It is equally important to strengthen the longitudinal arch of the foot.
For training you will need a towel. Algorithm of actions:
- starting position - sitting, clasp your foot with a towel, holding both ends in your hands;
- alternately change the neutral position of the foot to supination and pronation.
The following gymnastics will be no less effective:
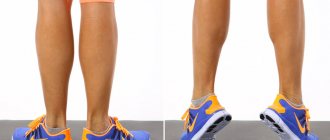
- Raising and lowering the heels. The ideal place for this workout is on a ladder, but any support can be used. Stand on the step with your heels hanging down. Rise and fall on your toes, gradually increasing the range of motion. This exercise will also help pump up your calf muscles.
- Self-massage on a roller. You need to take a sitting position on the floor, press one ankle to the floor, and place a hard cushion under the other. Move your leg back and forth on the roller so that your entire shin is massaged. Pay special attention to the sore area. Repeat the same with the other leg.
- Jumping on straight legs. This exercise can be done either independently or with a jump rope. Stand on your toes, without bending your knees, slightly jump up. Adjust the number of repetitions according to how you feel.
Exercises that put a lot of stress on the ankle muscles, such as squats, should be postponed for now. There is an increased risk of tendon rupture.
The human legs are a supporting organ that bears a tremendous load every day. Without physical training, it is very easy to stretch or even tear muscles and tendons. The tibialis anterior muscle plays an important role in the process of locomotion.
https://youtu.be/u-qlcS6Gz4I
Causes and consequences of weakening the BMS
As a result of loss of tone, tendinopathy of the posterior tibialis muscle develops - the tendon of the posterior tibial muscle undergoes pathological changes. The main symptom of this disease is an unpleasant sensation, especially after walking or running, in the area of muscle attachment, ligament and localization of the ligament.
Inflammation in the muscles, vessels, veins and arteries of the leg is also very likely.
It becomes difficult for them to supply the muscle with blood in the required volume, as a result it partially loses its functions.
Weakness of the backbone not only causes flat feet, but also inhibits the development of the gluteal muscle. In this case, it will be possible to pump up the buttocks only after the functions of the hip joint have been restored.
Tibialis anterior - bodyweight exercises
To practice jumping onto a hill, you will need to find a fairly stable and low podium, the role of which can be played by either an ordinary box or a suitable step. The main thing is that the hill is durable and has a height sufficient for training jumps (a ledge of 15-20 cm is suitable).
Standing at a distance of about 40 cm from a hill, you need to jump onto it, intensively using the leg muscles. When doing such jumps, it is important to keep your hands still. There is no need to jump back, just go down. The exercise should be repeated at least 10 times in one approach. It would be best to start with four approaches, and then increase them as you train.
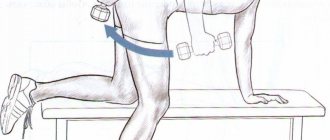
Wide lunges help pump up your legs and also work your glutes. To perform the exercise, you need to stand up, straighten up and place your feet parallel, slightly wider than your hips. It is better to keep your knees slightly bent and cross your arms over your chest. Looking straight ahead and inhaling, take as wide a step forward as possible, while trying to keep your torso straight.
Shifting your center of gravity to the leg you just extended, do a squat on it, keeping your knee at a right angle and not touching the floor with the knee of your remaining leg. Exhaling and maintaining the position of the torso, return to the starting position. Repeat the same with the other leg. Perform at least 10 lunges in one approach.
Strength exercises using your own weight are a good opportunity to demonstrate and prove by your own example the effectiveness of home training. There are many other exercises for training the muscles of the legs and lower legs, including the folding jump, calf raises, squats on the toes, climbing stairs, etc.
Exercises for the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles
Pavel Spasibukhov
Expert in training and bodybuilding / Published
Share this page
The problem of a lagging shin is painfully familiar to many of us. Yes, there are athletes who don’t train the lower half of their body at all, hiding its lag behind wide pants, so they don’t care what happens to their calves. But in this article we will talk about athletes striving for symmetrical and proportional development of all regions of their body.
How to pump up your calves?
Not every gym goer can boast of good calves.
Some blame genetics, while others simply do not pay attention to this muscle group. However, strong calf muscles will help you with basic exercises like squats and deadlifts. Therefore, pumped calves are needed not only to get a proportionally developed body, but also for better results in the main bodybuilding exercises. Possible causes of poor calf development:
- you don't do enough calf exercises;
- you do too many calf exercises;
- wrong exercises.
Those who are lucky with their genetics may not need separate calf exercises. They are involved in all leg exercises and this load can be enough. Everyone else will need to do additional exercises to pump up their calves at the end of their leg workout.
There is an opinion that calves need to be pumped up with high-repetition training and as often as possible. But in practice, this approach can overwork the calves.
A little anatomy
First, let's get acquainted with the structure of the lower leg. The lion's share of it is occupied by the gastrocnemius muscle, consisting of two heads - medial and lateral. It is their development that gives the main volume of the lower leg. Below the gastrocnemius is the soleus muscle - it is flat but wide, so its development can add width, both in side view and in frontal positions.
An important difference between the gastrocnemius and the soleus is that the former crosses the knee joint and is attached to the femur, while the soleus does not cross the knee joint and is inserted within the tibia. This means that the calf muscle is maximally activated in a standing position, but is virtually inactive when the leg is bent at a 90-degree angle. At these moments, the soleus muscle takes over the baton.
From this anatomical structure of the lower leg follow the specifics of training the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles - the gastrocnemius is trained in a standing position, and the soleus in a sitting position, but more on that later.
In addition to the triceps surae, the extensor digitorum, peroneus longus, and tibialis anterior muscles are also present on the anterior surface. To directly train them, you need a special simulator, which is so rare in gyms that you can forget about it. If you have such a machine in your training room, I strongly recommend using it more often.
Exercises for the soleus muscle
To load these muscles, you need to bend your leg at the knee joint 90 degrees and rise on your toes. A special simulator is used for these purposes, but if it is not available, then the same Smith simulator will do. If you don't have one, you can use free weights, but you may need a safety partner. It is necessary to load the barbell with weights in advance, sit on the edge of the bench, place your toes on the stand and place the barbell on top of your thighs, closer to your knees. Most likely, heavy weight will cause discomfort in the hips, so I recommend placing a towel or weightlifting belt under the barbell. You can do it easier - place a dumbbell on the upper thigh, butt down. You can work both legs at the same time, or alternately.
Exercises to pump up your calves
Seated calf raises
Seated calf raises work best on the soleus muscle.
- secure your knees with the pads of the exercise machine (not your hips!);
- rest your toes on the platform below (feet shoulder-width apart);
- rise on your toes, without spreading your knees;
- Raise your knees as high as possible, squeezing your calves as much as possible at the top.
If the gym does not have a special machine for seated calf raises, then use free weights and a footrest (step). Sit on a bench and place the barbell on your knees, supporting the weight with your hands on top. To avoid pain from the barbell, you can wrap it in a towel and then place it on your knees.
Standing calf raises
Standing calf raises work the calf muscles better
- stand with your toes on the lower block of the simulator, feet shoulder-width apart;
- rest your shoulders against the upper cushions of the machine;
- rise on your toes as high as possible, feel the compression of your calves at the top point;
- when lowering down, the heel drops below the toes, the calf muscles are fully stretched;
- do not perform the exercise by inertia, rise up and fall down under control;
If your gym doesn't have the required machine, you can use a Smith/free weight and a footrest.
Toe press
The exercise is performed in a leg press machine.
- lie down on the machine, rest your toes on the bottom edge of the platform, feet shoulder-width apart;
- the angle at the hips should be 90 degrees;
- squeeze the simulator platform with your toes up;
- try to maximize the range of motion (squeeze the platform as high as possible); if that doesn’t work, reduce the working weight.
Donkey calf raises
- stand on the stand with your toes;
- lean forward and place your hands on the bar/simulator;
- your partner should sit on your back;
- rise on your toes as high as possible.
Single leg calf raises
Very often, exercises performed alternately on each leg can give better results than exercises on both legs.
- start the exercise with the “weak” leg (for right-handers – the left);
- stand with the toe of your working foot on the stand;
- to make it more difficult, take a dumbbell in your hand (in your left hand if your working leg is left) - but for beginners it is better to do the exercise without additional weight;
- with your right hand, grab the support;
- go up and down, after completing the required number of repetitions, change your leg and do the same number of repetitions for the other.
Heel raises
Quite often this exercise is ignored because it primarily targets the front of the lower leg. But if pumping up your calves is a sore point for you, then heel raises should definitely be added to your training program. This exercise is also often used by runners.
- stand with your heels on the stand, toes hanging down;
- lower your toes down and lift them up in a smooth motion without sudden jerks.
The exercise is best performed in a Smith Machine.
Features of lower leg training
On the Internet you can find information that supposedly the calf muscles are very durable, consist of “slow” fibers and they need to be trained exclusively with many repetitions with light weight, and large weights are useless here. Actually this is not true. The lower leg is both a resilient and strong muscle group.
Yes, most people's calves are made up primarily of slow-twitch fibers, but that doesn't mean they should only be trained in a high-rep style. If the shin is sharpened for many repetitions in everyday life, then why load it in the same style in the gym? Why can’t you use the opposite type of stress – heavy weights? Of course, this can and should be done.
When using heavy weights, you need to remember that the spine, ankle and Achilles tendon will experience a much greater load than when working with small weights, especially when standing. With heavy weights, it is not recommended to lower yourself too much at the bottom of the exercise, as this can lead to injury.
Seated calf raises avoid excessive stress on the spine, but you still need to be careful with the ankle. In seated lifts, you can work with heavier weights more often, the main thing is that the movements are smooth and controlled.
You can load the lower leg relatively more often than other muscle groups, although in this case everything depends on the volume of the load. It is perfectly acceptable to work your lower legs three times a week if you only used one exercise in each workout. For example, if on Monday it was standing calf raises, then on Wednesday you can perform seated calf raises, and on Friday calf presses. All 4-5 approaches, the number of repetitions can also be varied. For example, calf raises can be done for 8 reps, and standing raises and calf presses can be done for 12-15 reps.
If the shin lags behind, then there is nothing left but eternal specialization on them. This means that at the beginning of your workout you should hit your calves for 4-5 sets of 1-2 exercises, and only then move on to the main workout. Here you will have to choose - either load them powerfully and harshly, or moderately, but more often. I recommend the second option as a basic one. If you really want hardcore, then you can use drop sets. After a good warm-up, you load a machine or barbell with a heavy weight that can be lifted 8-10 times, perform a set to failure, quickly drop the weight by 25% of the original, do another set for the maximum number of repetitions, then drop the weight again by 25% and again do as many reps as you can. This all adds up to one approach. I recommend doing no more than 3-4 such approaches during a workout.
Exercises to pump up your calves
Seated calf raises
Seated calf raises work best on the soleus muscle.
- secure your knees with the pads of the exercise machine (not your hips!);
- rest your toes on the platform below (feet shoulder-width apart);
- rise on your toes, without spreading your knees;
- Raise your knees as high as possible, squeezing your calves as much as possible at the top.
If the gym does not have a special machine for seated calf raises, then use free weights and a footrest (step). Sit on a bench and place the barbell on your knees, supporting the weight with your hands on top. To avoid pain from the barbell, you can wrap it in a towel and then place it on your knees.
Standing calf raises
Standing calf raises work the calf muscles better
- stand with your toes on the lower block of the simulator, feet shoulder-width apart;
- rest your shoulders against the upper cushions of the machine;
- rise on your toes as high as possible, feel the compression of your calves at the top point;
- when lowering down, the heel drops below the toes, the calf muscles are fully stretched;
- do not perform the exercise by inertia, rise up and fall down under control;
If your gym doesn't have the required machine, you can use a Smith/free weight and a footrest.
Toe press
The exercise is performed in a leg press machine.
- lie down on the machine, rest your toes on the bottom edge of the platform, feet shoulder-width apart;
- the angle at the hips should be 90 degrees;
- squeeze the simulator platform with your toes up;
- try to maximize the range of motion (squeeze the platform as high as possible); if that doesn’t work, reduce the working weight.
Donkey calf raises
- stand on the stand with your toes;
- lean forward and place your hands on the bar/simulator;
- your partner should sit on your back;
- rise on your toes as high as possible.
Single leg calf raises
Very often, exercises performed alternately on each leg can give better results than exercises on both legs.
- start the exercise with the “weak” leg (for right-handers – the left);
- stand with the toe of your working foot on the stand;
- to make it more difficult, take a dumbbell in your hand (in your left hand if your working leg is left) - but for beginners it is better to do the exercise without additional weight;
- with your right hand, grab the support;
- go up and down, after completing the required number of repetitions, change your leg and do the same number of repetitions for the other.
Interesting trick
There is another interesting training technique that will help you “break through” a stubborn shin. This is a rest-pause. Personally, I use this technique as the last set of the calf exercise. After completing 4 sets of 10 reps, I step off the stand, rest for 15 seconds, then get back on the stand and do a few reps, usually about seven. Then I rest again for 15 seconds and repeat everything again until the number of repetitions drops to three. Since the lower leg is a very durable muscle group, the number of such approaches will be quite large. I need 6-7 sets to get the number of reps down from seven to three. After such an execution, the shin feels pleasantly sore for several days.
How to pump up your calves?
Not every gym goer can boast of good calves. Some blame genetics, while others simply do not pay attention to this muscle group. However, strong calf muscles will help you with basic exercises like squats and deadlifts. Therefore, pumped calves are needed not only to get a proportionally developed body, but also for better results in the main bodybuilding exercises.
Possible causes of poor calf development:
- you don't do enough calf exercises;
- you do too many calf exercises;
- wrong exercises.
Those who are lucky with their genetics may not need separate calf exercises. They are involved in all leg exercises and this load can be enough. Everyone else will need to do additional exercises to pump up their calves at the end of their leg workout.
There is an opinion that calves need to be pumped up with high-repetition training and as often as possible. But in practice, this approach can overwork the calves.
Tibialis posterior [ edit | edit code ]
Beginning [edit | edit code ]
- Proximal two-thirds of the posterior surface of the tibia
- Proximal two-thirds of the medial surface of the fibula
- Interosseous membrane of the leg
Attachment[edit | edit code ]
- Tuberosity of the scaphoid
- Cuboid bone, medial, intermediate and lateral cuneiform bones
- Base of metatarsal bones II-IV
Innervation [edit | edit code ]
- Tibial nerve, L5-S1
Participation in sports [edit | edit code ]
The tibialis posterior muscle, flexor hallucis longus and flexor toes (not described in this book) belong to the medial postural muscles of the foot, because due to the small lever arm they do not develop much force during plantar flexion and supination of the foot. These muscles set the foot in a position that is optimal for developing maximum strength of the triceps surae muscle, and change it depending on the support. Thus, it plays a big role in all team sports, cross-country, artistic gymnastics and alpine skiing (edging). Together with the pronator muscles, it stabilizes the foot, for example, during a one-legged stand, which is used in figure skating, rhythmic gymnastics and many contact sports. In addition, this muscle, due to plantar flexion and supination, participates in movements when playing all types of sports indicated for the soleus muscle.
Team sports, cross-country, artistic gymnastics, alpine skiing (edging)
Placing the foot in the optimal position on the supporting surface in accordance with the unevenness of the support
Supination of the foot, together with the pronators
Dynamic concentric and static
Artistic gymnastics, figure skating, rhythmic gymnastics, contact sports
Stabilization of the ankle joint of the supporting leg, for example, one-legged stand on a balance beam
Supination of the foot, together with the pronators
Location and functions
The posterior tibial muscle (PTM) is located between the small and large tibia bones of the leg and is attached to the interosseous septum. She occupies the deepest position. Above it are the flexor muscles of the fingers, the flexor of the thumb and the muscles of the lower leg. Its base is located closer to the heads of the tibia.
- Forming the arch of the foot, lifting it up. This is an isolated movement.
- Stabilization of the fibula. If the fibula is not properly secured, it will become loose. Friction between the heads of the tibia and fibula causes knee instability. This gradually leads to arthrosis of the knee joint. Instability also occurs in the ankle joint, and the position of the talus changes. It moves slightly forward, which limits the flexion and extension of the foot. This is especially important for athletes, since the stride shortens during walking and running. If this phenomenon is observed in one leg, over time it leads to the formation of a difference in the volume and tone of the buttocks.
- Supports the arch of the foot and stabilizes the knee joint.
If the backbone is weak, other muscles cannot work correctly: neither the gluteal muscle nor the extensors of the fingers. They turn off during movement, during a step. This causes pain and discomfort, ultimately leading to decreased mobility of the lower leg.
A sign of weakness in the cervical spine is pain in the calf area.
Weakness of the tibialis posterior muscle provokes weakness of the ligamentous apparatus of the foot; all the small bones that form its arch diverge to the sides, this leads to flat feet.
The transverse and longitudinal arch of the foot forms the tone of this muscle. The effectiveness of all legs depends on it.
Exercises for the lower leg muscles
The lower leg muscles are quite developed, along with their auxiliary apparatus. This is explained by the regular load on them during upright walking and the musculoskeletal function of the lower limb. The calf muscles act on the foot joint, as well as the ankle and knee joints.
The lower leg is divided into lateral, anterior and posterior muscle groups. The anterior group includes the tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus, and extensor pollicis longus muscles. The posterior group includes the triceps surae muscle (it includes the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles), plantaris and popliteus, flexor digitorum longus, tibialis posterior and flexor hallucis longus. The lateral group includes the peroneus brevis and peroneus longus muscles. These muscles begin on the bones, intermuscular septa and fascia of the leg.
This section contains a wide selection of exercises. The proposed materials (video, description and correct exercise technique) will help you decide how to pump up your legs in the most convenient way for you. You can choose exercises that use weights or weights.
Also on our website you can learn about a sports nutrition complex for gaining muscle mass.
Using body weight
The calf muscles play an important role in creating an aesthetic body image, so you should not neglect their training. The development of the shins should be approximately equal to the biceps. However, while they have the ability to recover quickly and have phenomenal strength and performance, they are also the most difficult muscle group to develop. Although they respond to training like other muscles, the calf muscles need to be trained from different angles and with serious weights. The high level of development and endurance of these muscles allows you to exercise the lower leg muscles two to three times a week, even at the initial stage of training. In this case, it is possible to perform 5-6 approaches of two or three exercises, performed in a repeated interval of 15 to 50 movements per approach. At the intermediate stage, you can perform three to four calf exercises three to four times a week. The number of approaches and the range of repetitions in the approach can be left the same. But the most noticeable muscle development is possible only at a high level of training.
The main exercise for building muscle mass in the legs is calf raises from a standing position. This exercise makes it possible to develop the muscles of the lower leg, soleus muscles, as well as the short and long heads of the gastrocnemius muscle. It is also a good example of how to pump up your legs at home without using special exercise equipment. When performing calf raises, it is important to use additional weight. Seated calf raises only target the soleus muscles.
To obtain the desired result when working with the lower leg muscles, you need to choose a variety and number of exercises that can work all areas of this muscle group - upper, lower, internal and external parts. In addition, for the effective development of the legs, you can use various methods of shocking the muscles - to prevent the muscles from getting used to a monotonous specific training program - after all, it is stress and load that lead to muscle growth. In order to shock the muscles, you can vary the exercises, the angles of impact on the muscles, the number of repetitions and approaches, use forced repetitions, super sessions, etc. Shocking the lower leg with partial repetitions has a good effect. When performing half and quarter movements with heavy weights, a huge load is placed on the lower leg muscles, which leads to their high-quality development.
Also on our website there is a set of exercises for the gluteal muscles.