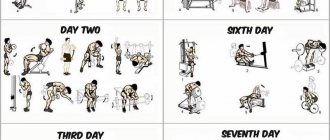
Features of the basic program
The basic program consists of several exercises that affect many muscle groups, using maximum working weight, the number of repetitions varies from 3 to 8.
The advantage of a basic training program for beginner athletes is that it ensures the growth of muscle fiber itself, and not sarcoplasm, which guarantees an increase in muscle density and elasticity.
Tips for compiling a database
Some expert advice:
- While performing basic training programs in the gym, pay more attention to rest and recovery. There is no point in training every day - your muscles and joint-ligamentous apparatus are simply not ready for this, sooner or later everything will end in injury or overtraining. The optimal option for such a complex is three times a week.
- Don't do squats and deadlifts on the same day. This is an excessive load on the lower back and spinal extensors.
- Take a day or two of complete rest before and after training your priority muscle group. This will contribute to speedy recovery and growth.
- Record your rest time between sets. Try to rest no more than 1.5-2 minutes; in squats and deadlifts, this time can be increased to 3-4 minutes.
- Focus on the technique of performing the exercise and the sensation of muscle contraction, rather than the working weight. Without technique, weight means nothing. But at the same time, try to systematically increase your strength indicators.
- Adapt your workouts to fit your schedule. For example, if Saturday is your day off, on which you can sleep longer and eat more, and therefore recover better, then it is better to do the hardest workout on Saturday.
- Don't forget to optimize your load. Monotonous training always leads to stagnation. If you feel that you have stopped growing and becoming stronger, make adjustments to your training process. Train hard one week, light the next, reducing the weights by 30-40%, increasing the number of repetitions and not reaching failure. This will give your muscles, joints and ligaments a break from heavy weights, which will lead to greater progress in the future.
Training frequency
The basic training program for bulking states that at least 72 hours must pass between each session.
Taking into account the fact, no more than 4 workouts should take place per week: three strength and one light (recovery).
If you do not follow this rule, you will soon experience a decline in functionality, and this will provoke a slowdown in the growth of muscle mass.
Decide on a goal
Before you create a training program, you must set yourself a goal. Everyone knows why they go to the gym, and you should be no exception. Each goal has its own landmark, and the direction of movement determines where you will arrive.
The goal determines everything: training schedule, set of exercises, duration of training, number of training days, nutrition, lifestyle and many other parameters that affect the result.
Decide what is important to you: developing strength, gaining mass, or increasing endurance. Based on your desires, you can build a training plan that will help you achieve your goal. To do this, we recommend keeping a training and nutrition diary.
Muscle mass
Theoretically, when gaining muscle mass, it is necessary to perform a large number of exercises: in this case, the workout will be varied and balanced. But, on the other hand, the number of exercises performed per muscle group depends on the type of training process.
You can train using a split program. This set of exercises is designed to work specific muscle groups on different days. If you have chosen this particular training plan, then perform 4 exercises for one muscle group, 2-3 approaches each.
You can also train two muscle groups in one training day, working on antagonist muscles. In this case, perform 3 exercises per muscle group, doing 3-4 approaches in each.
When working three muscle groups in one workout, perform 2 exercises per muscle with 4-6 approaches.
Force
If for muscle hypertrophy it is necessary to perform a large number of exercises and a relatively small number of approaches, then to develop strength, on the contrary, you need to do fewer exercises, but more approaches. This tactic will help improve nervous adaptation and provoke an increase in strength indicators.
Working on three muscle groups, perform 2 exercises for each muscle group, doing 4-6 approaches each.
When training four muscle groups per workout, perform 1-2 exercises per muscle for 4-6 sets. In this case, it is necessary to ensure that the total number of exercises does not exceed 6.
When working on six muscle groups, it is enough to perform 1 exercise for each group for 4–6 approaches.
We advise you to study a selection of training programs for strength and mass in the gym.
Endurance
Developing endurance requires special attention. If you're new to the gym, it's a good idea to work on your overall full-body development first. This is necessary so that the muscles get used to the loads, and the nervous system adapts to the new way of life. And then, with enough experience under your belt and a lot of sweat, you can safely move on to increasing endurance, if that is your goal.
A circular training program is excellent for developing endurance, consisting of 6-10 exercises per 1 training day.
Bench press
You need to lie down on the bench and take the equipment with a medium grip, after which it rises up. This is the original position.
As you inhale, you should gradually lower the equipment until the bar touches your chest.
After taking a short break and exhaling, the barbell should be returned to its original position.
The number of repetitions is 12, 3 approaches are done per workout.
Load adaptation level
The main goal of every training program for inexperienced athletes is the development of neuromuscular connections and a basic muscle corset for subsequent training. If your goal is to develop strength, then you should choose the optimal number of exercises (9-12) aimed at pumping up the main muscle groups. The duration of the training program should be 12 – 30 months. This period depends on the age of the athlete and the response of the muscles to this program.
If we go from the opposite, then the most important goal of training is to achieve maximum strength and maximum muscle mass. Therefore, such programs for such athletes should be determined by specific methods of muscle training, this is especially important during competitions.
In order for an athlete to quickly adapt to stress, it is recommended to additionally use supplements that restore energy balance in the body after intense training, as well as promote the growth of muscle mass and increase the overall tone of the body. Among the natural supplements for athletes, we can recommend the preparations “Elton P” and “Elton Forte” when engaging in aerobic sports, which accelerate the athlete’s adaptation to this kind of load, as well as natural supplements intended for athletes of power sports “Leveton P” and “Leveton Forte". In addition to increasing the energy balance in the body of athletes, the drugs “Leveton P” and “Leveton Forte” increase testosterone levels and are excellent adaptogens.
Vertical barbell pull
You need to lift the equipment, clasping it with your palms down. The grip is slightly less than shoulder width.
When inhaling, the device rises to chest level, the elbows should look up and to the sides. The bar must be kept as close to the body as possible.
While inhaling, the barbell lowers. The number of repetitions is 12, 3 approaches are performed.
Leg press
You need to sit down in a machine designed to perform bench presses.
The limbs are placed on the platform, and the feet are positioned shoulder-width apart.
After lowering the safety stops, the platform is pressed up, the legs are leveled.
During exhalation, the legs bend and the platform lowers. Number of repetitions – 12, number of approaches – 3.
Types of exercise
Every fitness enthusiast needs to understand the principle by which existing physical exercises are divided into basic and isolating. The first category includes exercises that work more than two joints and several muscle groups. Typical compound exercises are the squat, deadlift and bench press.
Isolating exercises are called exercises that help target a specific muscle group. For example, machine leg extensions target the development of the quadriceps and are therefore considered isolating, whereas basic squats place the load on the legs as a whole.
Crunches with legs suspended
You need to lie down, your lower back pressed to the floor. The arms are placed at the side of the body, palms down.
The legs are crossed at the ankles. Slightly bent at the knees, they rise until the thigh is perpendicular to the floor.
The shins are positioned parallel. Arms crossed over chest. This position is considered the starting position.
As you exhale, the upper body slowly rises and twists. When inhaling, the original position is returned.
The exercise is performed as many times as possible. Number of approaches – 3.
Training stage[edit | edit code]
Once the transition phase is complete, laying the foundation for future training should occur during the new annual plan. It is desirable that anatomical adaptations in a general strength training program occur early in the preparatory phase. In order for this program to include the maximum number of muscle groups, it is necessary to select a large number of exercises (from nine to twelve), regardless of the specifics of the sport.
As the program progresses, the number of exercises decreases, while during the competitive stage the athlete performs a minimum number of exercises - from two to four special exercises that are important for a particular sport. For example, American football, hockey, basketball or volleyball players will likely perform nine or ten exercises during the preparatory phase, but during the season the number of exercises will drop to four to six. By choosing the right exercises, coaches can increase the effectiveness of the training process and reduce the overall fatigue of the athlete.
Strength training is carried out in addition to technical and tactical training. In short, there is an inverse relationship between the load applied during training and the number of exercises performed per training session. A decrease in the number of exercises indicates that the athlete is performing specific training. As the number of exercises increases, the number of approaches in the exercise also increases. Thus, the majority of the load is placed on the prime mover muscles for a particular sport in order to achieve optimal muscle strength and power for the athlete to compete. Once the competition season begins, adaptation takes a backseat and fewer exercises are used and the number of sets is increased moderately in order to maintain the existing level of physiological adaptation.
Even though some sports (such as soccer, many athletics, and cycling) use the upper body to a limited extent, many strength training programs emphasize exercises that specifically target the upper body. In addition, many physical trainers who fall under the influence of bodybuilding offer their clients too many exercises. In reality, athletes who perform a large number of exercises reduce the number of approaches aimed at developing each of the main driving muscles. This approach leads to a low level of adaptation, resulting in a very weak training effect.
The desired result - a high level of adaptation and improved performance - is only possible if athletes perform a large number of approaches that involve the selected kinetic chain. The trainer can distribute all the sets of fundamental exercises required to perform them over several training sessions throughout the microcycle or group these approaches to reduce the number of training sessions. When using the first option, the athlete performs shorter training sessions, which contain a larger number of auxiliary exercises, while when using the second option, the duration of the training sessions increases, and the number of auxiliary exercises decreases.
Kettlebell raises
You need to take the equipment and stand straight, with your lower limbs shoulder-width apart.
The arms hang along the body. Elbows should be brought as close to the body as possible. This position is considered the starting position.
The body is held straight, while exhaling, the arms with weights are raised to the sides. Elbows are allowed to bend slightly.
The final position is that the weights are located slightly above shoulder level. The dumbbells are slowly lowered down. The number of repetitions is 10, three approaches are performed.
Kettlebell raises in a seated inclined position
The equipment is placed on the floor. You need to sit on the edge of the bench and take dumbbells. Keeping your body motionless, you need to bend your elbows slightly and raise your arms in different directions.
https://youtu.be/e2bFFQpQG7A
During the exercise, it is strictly forbidden to move your torso.
The weights are held at the top for a second, after which they slowly return to their original position. 10 repetitions are performed, the number of approaches is three.
Pull-up
This exercise is indispensable in the basic Workout training program, since it not only provides an increase in the width of the back in a short time, but also relieves tension in the spine.
To perform the exercise, you should grab the bar of the horizontal bar, your hands are located slightly wider than the shoulder line (if you want to get rid of the load in your hands, you should use gloves).
The legs bend at the knees and cross. Without performing any sudden movements, the body is pulled up.
The final position, the chin is located above the crossbar.
It is lowered to the starting position.
You can also use weights; a special belt is used for these purposes.
Perform 4 approaches as many times as possible.
Why is it important to perform a strictly prescribed number of repetitions/sets?
You should already understand that the main reason why a systematic, structured approach to your training is important is to obtain adequate training stress (undertraining is bad and too much physical activity is also bad).
One way to regulate training stress is to perform exercises for a given number of sets and repetitions with a certain amount of rest time between sets.
Athletes experimentally tested, and then scientists have proven, that different numbers of repetitions and approaches have different effects on increasing muscle mass, strength and endurance.
So, for example, in the industry of bodybuilding, powerlifting , and indeed in other strength sports, it is generally accepted that the number of repetitions performed is:
- 1-5 – for strength development
- 6-12 – volume of muscle mass
- 8-15 – muscle relief
- 12-20 – muscle endurance
The importance of performing a strictly designated number of repetitions in the approaches
In addition, these data are almost completely confirmed experimentally: scientific studies on various groups of people with different levels of training, one of them: Campos GE, Luecke TJ, Wendeln HK, Toma K, Hagerman FC, Murray TF, Ragg KE, Ratamess NA, Kraemer WJ, Staron RS. Muscular adaptations in response to three different resistance-training regimens: specificity of repetition maximum training zones. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2002;88:50-60.
Bent-over dumbbell row
Dumbbells are placed on both sides of the horizontal bench. The right leg, bent at the knee, is placed on the bench and tilted forward until the body is parallel to the floor.
With your right hand you should grab the edge of the bench. Take a dumbbell with your left hand, keep your back straight, palm facing inward. This position is considered the starting position.
While exhaling, the dumbbell is gradually raised, the elbow is held next to the body, the body is motionless. At this moment, special attention should be paid to the work of the back muscles.
It is important that it is the back muscles that work, not the arms.
While inhaling, the dumbbell is slowly lowered to its original position. The exercise is performed three times, the number of repetitions is 10 times.
Lunges with dumbbells
You need to stand up straight and take dumbbells in both hands. The right leg takes a step forward, the second leg does not move. As you exhale, you should squat down without bending at the waist and keeping your back straight.
The knee of the right leg should not go forward. It should be placed parallel to the foot. The shin of the front leg is perpendicular to the floor.
After pushing your feet off the floor and exhaling, you need to rise and return to your original position.
Perform 3 approaches, the number of times equal to 10 repetitions.
Squat with barbell held
Initially, you need to adjust your stance so that the bar is located above your shoulders. The barbell is loaded with a suitable weight. You need to stand under the bar and place it on the back half of your shoulders.
The lower limbs are positioned shoulder-width apart, with the toes turned outward. The head looks straight, and the back is arched in the lumbar region. This is considered the original position.
After inhaling, you should slowly sit down and move your pelvis back.
The squat continues until the top of the thigh reaches the level of the knee joint. Perform 4 sets of 10 times.
Creating a training program for 3 days from these basic exercises will not be difficult.
https://youtu.be/6uw7QzS8GWw
How many exercises and approaches to do per muscle group?
How many exercises and approaches per muscle group to perform in one workout in order to grow or, conversely, lose weight. How many exercises should a beginner and a professional athlete do?
“Soviet Sport” was looking for answers to questions that bother bodybuilders at all times.
How many exercises and approaches per muscle group to do for weight?
In bodybuilding, two schools traditionally argue. And the question of how many exercises and approaches to perform in one workout in order for the mass to grow remains open - there is no single point of view yet.
A set (or set) is the number of repetitions an athlete performs without rest. Proponents of abbreviated training believe that only 2-3 approaches and 1-2 exercises per muscle group per workout are enough. Two conditions. The exercises should be basic (that is, each exercise involves several muscle groups at once), and the weights should be increased with each workout (so that the muscles receive the stress necessary to grow).
An important question: should you perform strength exercises to failure?
Stuart McRobert, author of Think. Bodybuilding without steroids” and one of the main promoters of shortened training, believed: a weight program for beginners should consist of an average of two workouts per week (less often, three).
Workout 1 includes 2-3 working sets of heavy squats (warm-up sets do not count), 2-3 working sets of bench press, 3-4 sets of pull-ups (to failure), 2-3 sets of barbell curls, and 3-4 sets of on the press
Workout 2 consists of deadlifts (2-3 working sets), bent-over rows (2-3 sets), dips (2-3 sets), standing military press (2-3 sets), and 3-4 sets on the press
McRobert believed that more sets and exercises would reduce mass growth to zero. The athlete’s body will spend too many resources and will recover worse.
https://youtu.be/KdDCciSgXXA
Proponents of high-volume training believe that to gain mass, you need to do an average of three to four exercises per muscle group with a total number of approaches from 8 to 12 (sometimes higher). It is this range of exercises and approaches that allows you to “explode” the muscle and create its greatest hypertrophy, they believe.
In this program, training is carried out more often - 3-5 times a week. Basic exercises are divided into isolation exercises (which emphasize the load on the target muscle), and different muscle groups are trained on different days. For example, day 1 – back, biceps, abs, day 2 – legs, shoulders, abs, day 3 – chest, triceps.
Shortened training can work to increase mass for beginners, but very quickly it exhausts itself. The body adapts to the shortened training and stops responding to it with growth. Muscles need more load and additional exercises, according to proponents of high-volume training, including, for example, 4-time Mr. Olympia title holder Jay Cutler.
How many exercises and approaches per muscle group to do for relief?
If on the issue of the number of exercises and approaches for the mass, opinions differ radically, then on the issues of the relief program - everyone one way or another comes to a common denominator.
For a relief program, you need to increase the number of exercises, approaches and repetitions - this is the generally accepted opinion. Even Stuart McRobert, a proponent of shortened training, advises from time to time to abandon the “base” and train 3-5 days a week, introducing isolation exercises into the program, a number of approaches from 7-8 per muscle group and running.
The challenge is thrown – 5 fitness challenges from “Soviet Sport”
The goal of the relief program is to increase energy expenditure: the body must burn more energy than it consumes). Therefore, in relief programs, training usually takes 5-6 days a week. For each muscle group, do 3-5 exercises in the range of 9-12 approaches. Moreover, one muscle is often trained twice a week. The entire program is divided according to the “split” method. Isolation exercises begin to take up most of the training. At the same time, the weights in the basic ones are often reduced.
In recent years, circuit training and interval training have gained popularity. In the first, exercises are done without rest, one after another, in the second, segments of strength work are alternated with short pauses (10-20 seconds). Research from the Journal of Sport Medicine shows that these workout regimens are the best for fat loss—but they change the traditional number of sets and exercises.
Circuit training is usually organized on a full-body basis. They can include both basic strength training and cardio, and often involve performing as many repetitions as possible in a given amount of time.
Each human body is unique. Search, experiment and find what works best for you.
Attention! Before starting exercise, consult your doctor.